Adrenergic Agonists
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
The primary neurotransmitter in the sympathetic nervous system is __________.
norepinephrine
The two main enzymes that terminate NE signaling are __________ and __________.
MAO, COMT
The key mechanism of NE signal termination is __________ into the presynaptic neuron.
reuptake
In contrast to adrenergic signaling, cholinergic signaling is terminated by __________.
acetylcholinesterase
MAO-A preferentially metabolizes __________, __________, and __________.
norepinephrine, epinephrine, serotonin
MAO-B selectively metabolizes __________ and is targeted in __________ disease.
dopamine, Parkinson’s
The selective MAO-B inhibitor used in Parkinson’s disease is __________.
selegiline
MAO-A inhibition requires dietary restrictions to avoid __________ crisis.
hypertensive
The dietary amine degraded by MAO-A is __________.
tyramine
Foods rich in tyramine include __________, __________, and __________.
aged cheeses, cured meats, fermented products
Combining tyramine-rich foods with MAO-A inhibitors can cause excessive __________ release.
norepinephrine
The recommended washout period between MAOIs and SSRIs is approximately __________.
two weeks
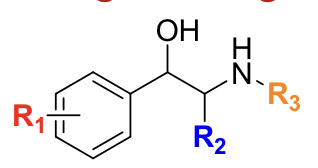
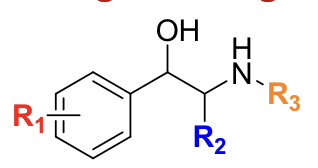
Direct agonists bind directly to __________ receptors.
alpha or beta adrenergic
Indirect agonists promote the release or block the reuptake of __________.
norepinephrine
Examples of direct agonists include __________, __________, and __________.
epinephrine, norepinephrine, phenylephrine
Examples of indirect agonists include __________, __________, and __________.
amphetamine, cocaine, tyramine
Direct agonists generally contain a __________ group, making them more polar.
catechol
Indirect agonists lack phenolic OH groups, increasing their __________ and CNS penetration.
lipophilicity
Amphetamine lacks both β-OH and N-methyl groups, making it a potent __________ stimulant.
CNS
Methamphetamine differs from amphetamine by having a __________ group on the nitrogen, enhancing CNS activity.
methyl
Adding bulky groups to the amine (R3) increases __________ receptor selectivity.
beta-2
Removing OH groups increases lipophilicity but reduces binding to __________ receptors.
adrenergic
Substitution at the α-carbon (R2) decreases receptor binding but increases resistance to __________ metabolism.
MAO
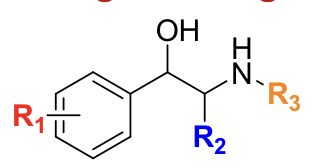
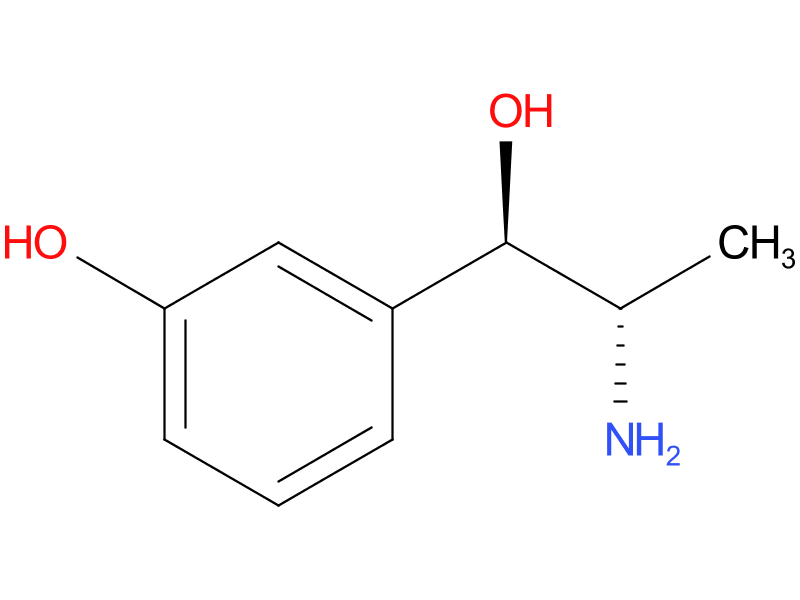
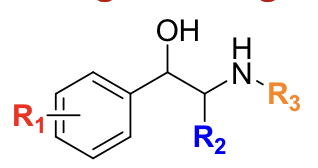
The parent structure of all direct adrenergic agonists is __________.
phenethylamine
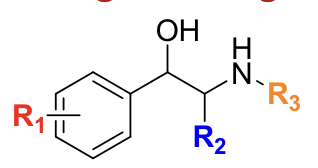
__________ has 3,4-diOH, no bulky amine, and targets α + β1.
norepinephrine
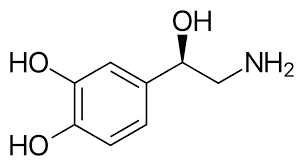
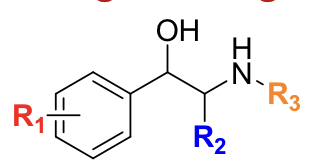
__________ has 3,4-diOH and a methyl on the amine, activating α, β1, and β2.
epinephrine
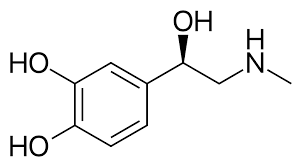
__________ has only a 3-OH group and is α-selective.
phenylephrine
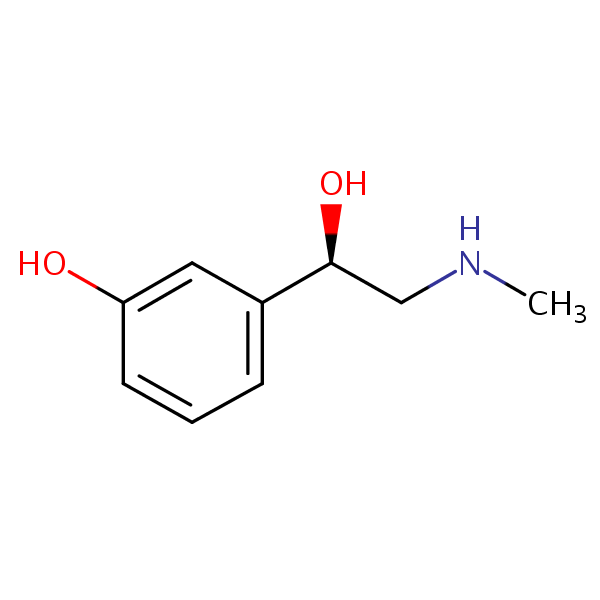
__________ has a 3-OH group and a CH₃ at the α-carbon, favoring α selectivity.
Metaraminol
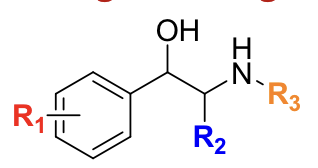
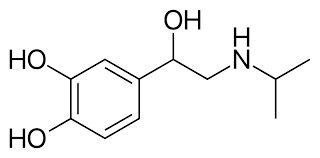
__________ has 3,4-diOH and an i-Pr group, making it β1 + β2 selective.
isoproterenol
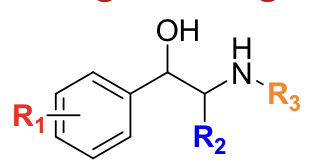
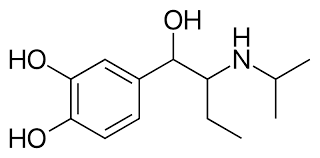
__________ has Et at R2 and i-Pr at R3; it is β-selective.
isoetherine
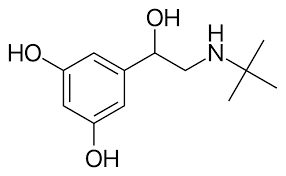
__________ has 3,5-diOH and a t-butyl group, giving it β2 selectivity.
terbutaline
Removing OH groups from catechols reduces __________ and increases __________.
polarity, CNS penetration
Amphetamine and methamphetamine are both basic and are formulated as __________.
salts
Drugs with bulky amines have decreased MAO metabolism and increased __________.
oral availability
Selegiline is metabolized into __________ and __________, which may cause false positives on drug screens.
amphetamine, methamphetamine
Methamphetamine is more __________ than amphetamine, allowing faster CNS entry.
lipophilic
Increased lipophilicity leads to greater __________ potential due to rapid CNS stimulation.
abuse
Methamphetamine has a longer half-life due to resistance to __________ metabolism.
MAO
A general rule: the fewer the __________ groups, the more lipophilic the compound.
hydroxyl (OH)
MAO inhibitors bind irreversibly to the enzyme’s __________ cofactor.
FAD
Once MAO is inhibited, the enzyme must be __________ to restore activity.
resynthesized
The pharmacodynamic effects of MAO inhibitors persist after drug clearance due to __________ inhibition.
irreversible
Drugs like __________ (a PPI) and __________ (a COX inhibitor) are other examples of irreversible inhibitors.
omeprazole; aspirin
COMT inhibitors are used in Parkinson’s disease to prolong the action of __________.
L-DOPA
The COMT inhibitor __________ prevents breakdown of L-DOPA by blocking methylation.
entacapone
Entacapone contains both catechol and __________ groups that make it an electron-withdrawing COMT blocker.
nitro
Lack of a catechol group increases __________ by preventing COMT metabolism.
half-life
When ranking drugs for CNS stimulation, consider lipophilicity. Rank these from most to least CNS penetration:
methamphetamine > amphetamine > pseudoephedrine
In “CAT-BAM,” C stands for __________, which leads to COMT metabolism and short half-life.
catechol
In “CAT-BAM,” A stands for alpha selectivity from a __________ group.
3-OH only
In “CAT-BAM,” T stands for __________ substitution at the amine, favoring β2 activity.
tert-butyl
In “CAT-BAM,” B stands for __________ R2 groups that block MAO metabolism.
bulky
In “CAT-BAM,” M stands for __________, which irreversibly inhibit enzymes and require washout.
MAOIs