Global economic history lecture 9 (Business and the global economy)
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What are multinationals?
Multinational are typically defined as companies operating from a home country that own assets in one or more countries abroad. These countries abroad in which multinational invest are typically called host countries
What is foreign direct investment?
Foreign direct investment (FDI) occurs when a company or individual from one country makes an investment in a business located in another country, usually by acquiring a lasting interest or significant degree of influence.
What are portfolio investments?
Portfolio investment involves the acquisition of foreign securities by individuals or institutions without any control over the management of the foreign entity. This kind of investment does not fall under multinational operations (Although multinational can as part of their activities do portfolio investment).
What is the hymer thesis?
The Hymer Thesis posits that multinational corporations are created and operate due to the existence of imperfections in the market for goods and services, leading firms to seek foreign markets to exert control over resources.
What are the three reasons for foreign direct investment?
Ownership/competitive advantages: Multinationals must have competitive advantages to overcome the liability of forgiveness and succeeded in host markets disadvantages include superior products, and know how
Vocational factors: Trade barriers, Labour costs, Market size, Resource endowment
Transaction costs theory: Transaction costs and markets push firms to internal operations rather than rely on external markets. Internalisation minimizes inefficiencies particularly in sectors like know how where information symmetry and weak patent enforcement exists
What is John Dunnings OLI model?
The OLI model, developed by John Dunning, outlines three key factors that influence a multinational corporation's decision to engage in foreign direct investment. - **Ownership Advantages**: These include specific assets or capabilities that give a firm a competitive edge over local firms in the host country, such as technology, brand reputation, and managerial skills. - **Location Advantages**: These refer to the benefits of a particular geographic location, which may include access to natural resources, favorable economic conditions, strategic trade advantages, and a skilled workforce. - **Internalization Advantages**: This aspect highlights the benefits of retaining control over resources and operations within the firm rather than outsourcing them. Internalization minimizes transaction costs and improves the firm's ability to leverage its ownership and location advantages effectively.
What are the three motives for foreign direct investments?
Resource seekers: Firms invest abroad to acquire location bound resources (minerals, low labor costs) Or specific skills (European pharmaceutical companies setting up R&D in the US)
Market seekers: Firms invest in foreign markets to supply goods/services locally bypassing barriers like tariffs or high transport costs or because local market justify production. This can also be a strategic move to follow competitors.
Efficiency seekers: Large diversified MNE invest To rationalise production leverage in economies of scale and scope they concentrate production in select locations to supply multiple markets exploiting differences in factor endowment demand patterns and market structures
What are the key benefits of multinational is to host countries?
Knowledge and technology transfers, capital inflows employment creation trade balance improvements and enhance competition
What are potential downside of multinationals?
Dominate markets, rely on domestic borrowing, or focus on resource extraction without creating local spillovers or additional processes.
What was the Union Miniere du Haut Katanga (UMHK)? And how do they fit into the OLI model?
It was a resource seeking FDI in the first global economy established by Belgian capital in Congo during the colonial rule it’s primarily goal was to exploit Katanga copper wealth driven by the high demand during the second Industrial Revolution.
OLI model:
Ownership: UMHK had no pre-existing ownership advantages but relied on capital from Belgium and foreign markets unavailable in Congo
Locational: Operated under supportive colonial rule with access to coerced labour ensuring undisturbed operations
Internalisation: Practice vertical integration by investing in smelting and refining facilities in Belgium and France to stabilise copper markets
After World War II, what were the key shifts in FDI patterns?3
Developed-to-developed investments: Investment flows prioritise developed countries with declining shares for developing countries
Sectoral shift: resource seeking investments declined replaced by market seeking investments in manufacturing sectors
American dominance: US firms lead FDI due to ownership advantages in technology in innovation and management
What did Nkrumah say about neocolonialism?
Kwame Nkrumah described neocolonialism as the final phase of imperialism, where foreign powers maintain control over a country's economy even after it has gained political independence.
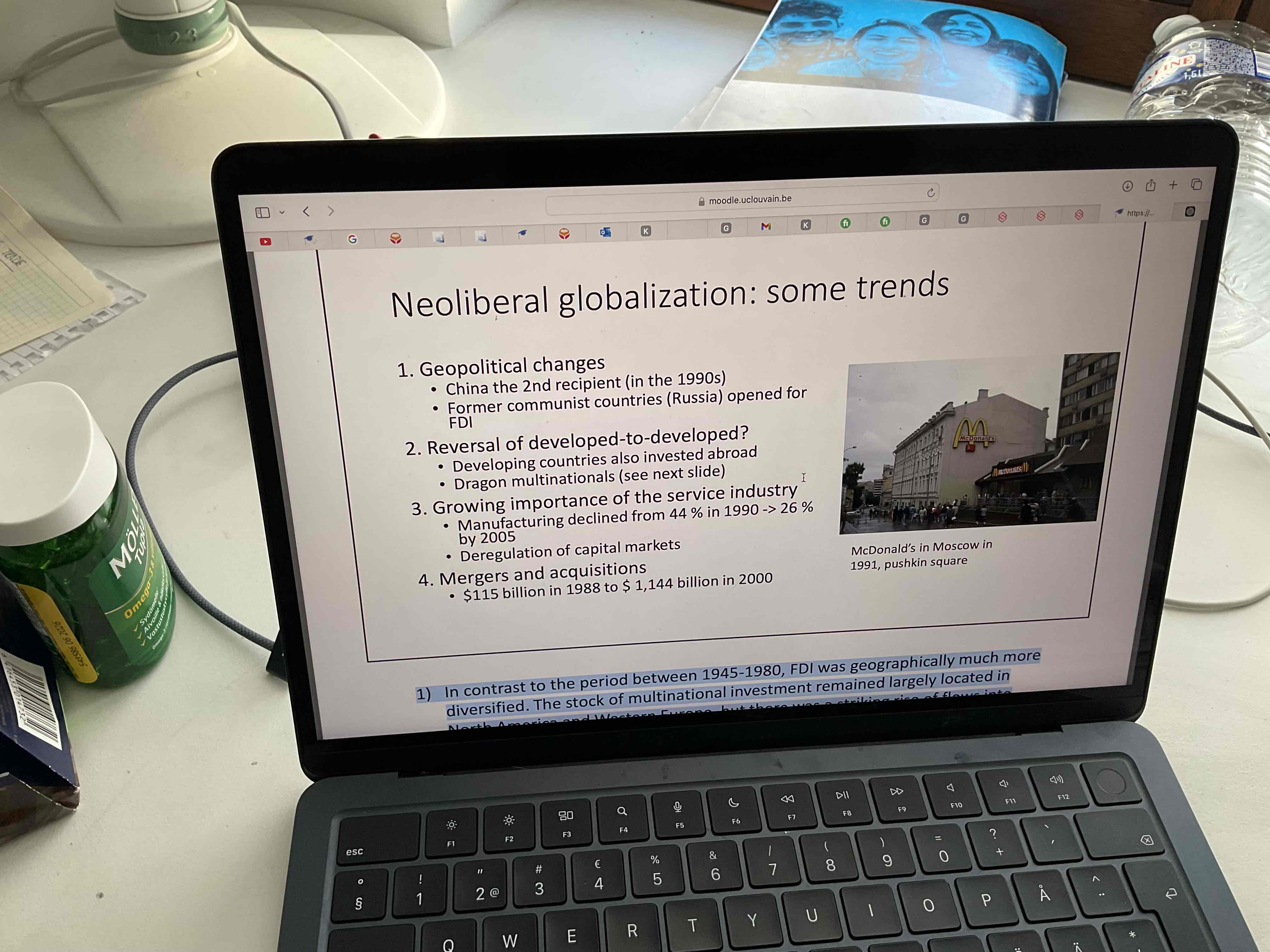
What were the four trends of neoliberal globalization?
What are dragon multinationals?
Dragon multinationals refer to companies from emerging markets, particularly in Asia, that have successfully expanded beyond their home countries and gained significant market share internationally. They are characterized by rapid growth, innovation, and a focus on competitiveness in the global marketplace.