Development Psychopathology
1/167
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
168 Terms
Definition of Developmental psychopathology?
Is a field of psychology that studies the origins and progression of psychological disorders by examining their relationship to atypical growth and maturation
In the developmental psychopathology field, what is used as a general approach to analyze development?
Lifespan perspective
Why is the lifespan perspective important?
Because it allows researchers and clinicians to understand how psychological disorders emerge, change, and persist (or not) across different stages of life
In this course, we will utilize a biopsychosocial approaches, meaning?
We will draw from fields of neuroscience, sociology, psychiatry, and more
Developmental psychopathology is about diagnosis of disorders and?
Analyzing mental health and development trajectories
What is meant by developmental trajectories?
Refers to the patterns of emotional, behavioral, or psychological development that unfold over time
What are the three primary domains of development?
The physical domain, the cognitive domain, and the social domain
What does the physical domain include?
Includes process of physical and biological changes in shape, size, and other bodily characteristics, and influence from the introduction of things to the body like substance use of teratogen exposure
What does the cognitive domain include?
Includes changes in thinking, problem-solving, memory, language, and other cognitive process
Example of something related to the cognitive domain?
Social differences in autism spectrum disorder
What does the social domain include?
Includes changes that involve the ability to develop and maintain relationships with others or the self
Example of something in the social domain?
Developing trust in others, individual personality differences, self-efficacy beliefs
What are the core assumptions of developmental psychopathology?
Normal and abnormal development are interconnected, development is dynamic, nonlinear, and influenced by context, disorders result from the interplay of multiple systems, and risk does not guarantee disorder; resilience is a complex mediating factor for risk (equifinality and multifinality)
What is meant by “Normal and abnormal development are interconnected”?
To understand what’s abnormal, we must first understand what’s normal and vice versa
Definition of Equifinality?
Many different paths can lead to the same outcome- anxiety can come from genetics, trauma, or parenting
Definition of Multifinality?
One risk factor can lead to multiple different outcomes- childhood abuse may result in PTSD, depression, or resilience
Types of continuity and discontinuity in development?
Homotypic continuity and heterotypic continuity
Definition of Homotypic continuity?
The same symptom persists over time
Definition of Heterotypic continuity?
Different symptoms emerge or develop from one source
What does biological risk consist of?
Genetics, prenatal exposures, temperament
What does psychological risk consist of?
Emotional regulation, attachment
What does environmental risk consist of?
Trauma, family/social conflict, poverty
Definition of cumulative risk?
When multiple risk factors interact, increasing vulnerability significantly
Definition of Resilience?
Positive adaptation in the face of adversity- it isn’t about be invulnerable; its about adapting well under pressure
Examples of why someone may have resilience?
Secure attachment, strong executive functioning, supportive adult relationships
Definition of differential susceptibility?
Some kids are more sensitive to both negative and positive environments
Definition of Normative Data approach?
Study a large group of people to figure out what’s normal at each age, and compare individuals to that to see if they’re on track
Definition of longitudinal study?
Type of research where the same people are studied over a long period of time- Case of Genie
Common methodologies and tools?
Longitudinal studies, behavioral genetics, neuroimaging, and ecological system models that explain how context matters
How is sexual orientation an example of behavioral genetics?
If identical twins both identify as gay more often than fraternal twins, that suggests a genetic component to sexual orientation.
How is “proteins activating genes called histones” an example of behavioral genetics?
Histones can help turn genes on or off in response to life experiences, which can exhibit different behaviors or mental health outcomes from two people with the same genes (DNA is not changed)
Definition of neuroimaging?
The relationship between the brain and behavior
What has been tied to the amygdala?
Patterns of aggression, fear, and helpfulness
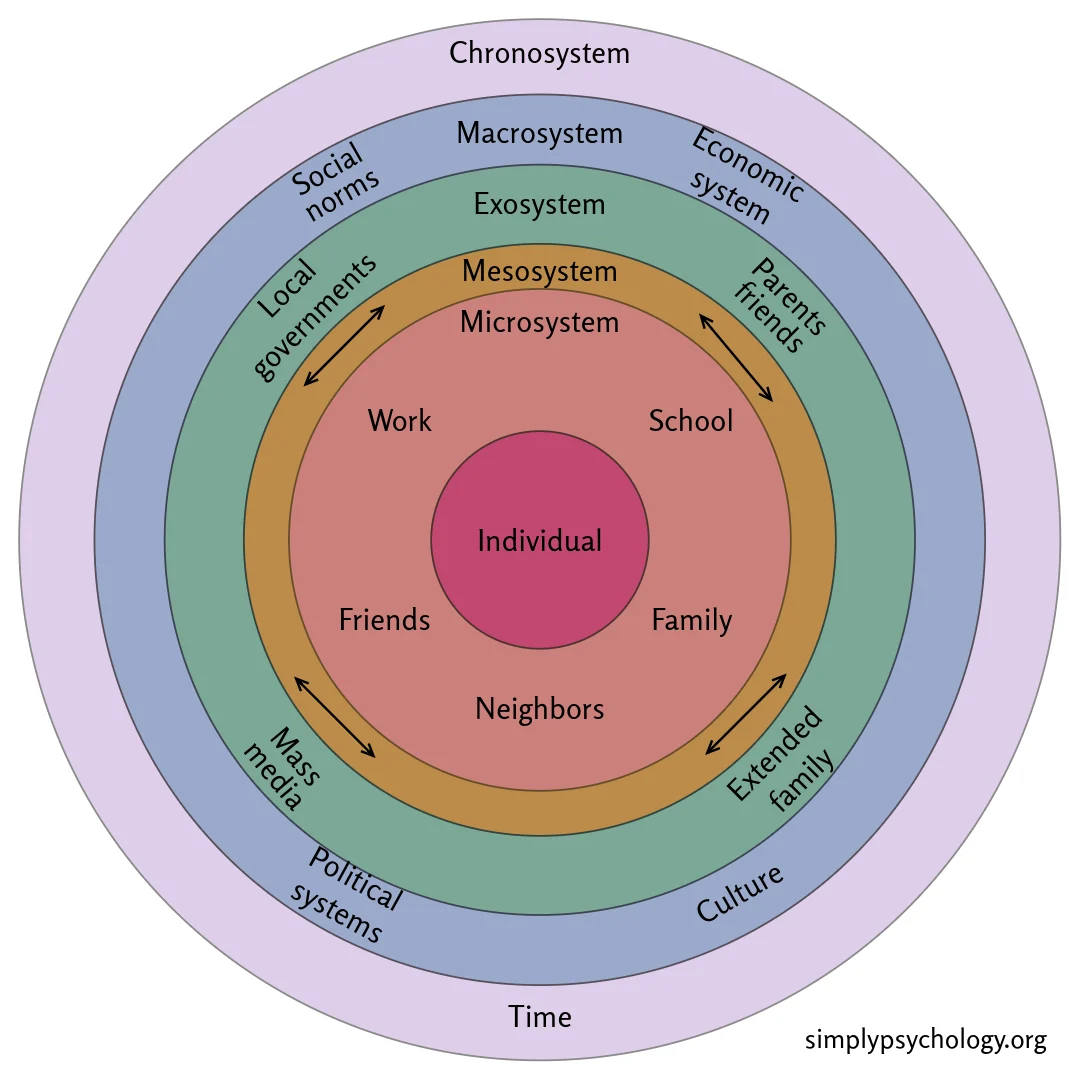
What is this model?
Bronfenbrenner’s ecological model
From the development psychopathologist’s perspective when should intervention occur?
Early intervention rather than later
Application of research may result in the creation of?
Early assessments, evaluations, or inventories for mental health problems that emerge in childhood, treatments that are developing sensitive, targeting risk and boosting protective factors
What is the Wakefield’s alternative, two-criteria approach?
Wakefield proposed a better way to define what counts as a mental disorder- The condition causes harm to the person or to others and something in the mind or brain isn’t working how it normally should
Example of Wakefield’s harm-dysfunction model paralleled in medical community?
Heart disease involves dysfunction of the body’s circulatory system and it causes pain/harm, just like depression, a mental disorder that is dysfunction in emotional regulation and cause impairment and harm to self in life avenues
Term for mental disorders divided into categories?
Categorical classification- also the older classification approach
Definition of Prototypical classification?
Mental disorders diagnosed by best-fit- by comparing someone’s symptom to a “best example” or ideal version of the disorder
Definition of Dimensional classification?
Mental disorders described by severity
Definition of Diagnostic specifier?
Extra information a mental health professional adds to a diagnosis to give more detail- Major Depressive Disorder, with seasonal pattern
How do psychologists diagnose mental health problems in children?
Presence of specific signs and symptoms, harmful dysfunction analyzed at the physiological, cognitive, and social domains
Diagnostic criteria for major depressive episode?
Has many small criteria for symptoms or signs that must be present for at least two weeks (on more days in the week than not)
Benefits of Diagnosis?
Can help to plan treatment, can aid in predication, aids in professional communication (name of disorders are self-descriptive), parsimony (one clear diagnosis can explain a lot of different symptoms in a simple way), can facilitate scientific discovery, can be helpful to caregivers, and can help in individuals obtain social or educational services
Limitations to diagnosis?
Arbitrary distinction of normality/abnormality (due to culture contexts), underlying cause often unknown, over focus or under focus on the nature of many childhood disorders, unclear boundaries of diagnostic categories (some researchers push for a trans diagnostic approach as a response/solution), medical approach to mental health problems, and role of social-culture surroundings and limited perspectives in mental healthcare providers
Definition of Prevalence?
Cases in a given population (challenging to determine)
Incidence definition?
New cases in a given period time
In the last month how many adolescents reported a mental health problems?
According to the National Comorbidity Survey Replication- Adolescent Supplement suggests more than 20% adolescents
How many children and adolescents with one disorder are diagnosed with two or more comorbid disorders?
40%
In the age group of children and adolescents, what is the highly comorbid?
Depression and anxiety
What is the annual total cost of child and adolescent mental health care in the US (2020)?
Around 247 billion dollars
In general who is most likely to experience disorders?
Adolescents over younger children
What are some examples of disorders that are common among younger children?
Autism and separation anxiety
In early childhood, disorders are seen more in who?
Boys
How likely are boys to be diagnosed with ASD?
4 times more
How likely are boys to be diagnosed with ADHD?
3 times more
Boys are more likely than girls to show, what kind of disorder?
Disruptive behavior problems, such as oppositional defiant disorder
What’s approximately equal in young boys and girls?
Prevalence of other disorders
In the adolescence stage, who is more likely to begin to have “more” problems?
Girls over boys
In the adolescence stage, boys are more likely to present with?
Externalized mental health issues like substance abuse
What can influence mood?
Perception of interpersonal stressors
Mental health reflects aspects of?
A child’s environment
Higher SES parents are less likely to?
Experience psychological problems themselves
Higher SES parents are also able to provide what for their children?
Environments that protect their children from psychological problems
Family composition is a related predictor, youths living with one biological parent are…
Twice as likely to develop an anxiety or mood disorder
Adolescents living in single-parent homes are…
6 times more likely to develop behavior or substance use disorder
How many children and adolescents develop a mental health problem at some point prior to adulthood?
NIMH suggests 20%
Among the children and adolescents that develop a mental health problem, how many receive treatment in medicinal or therapeutic form?
Only half receive treatment
The likelihood of treatment is based on a number of factors, what are some examples?
Children with ADHD mostly likely to receive treatment, while people with anxiety disorders are less likely to see treatment
Treatment can come in many forms, how many children report receiving primary treatment from/through their school?
24%
How many children report going to a mental health clinic or hospital?
23% and 10%
How many children receive social services through social agencies?
8%
How many children receive social services through the juvenile justice system?
5%
Unequal access to care based on?
SES, race, or other factors
Treatment is sometimes conducted by?
People who are specialists
What is meant by “Deviations vs Differences” ?
Deviation refers to something that strays from a norm, which might be something that needs attention (like a disorder or delay), and differences refers to things that aren’t the same, which might just reflect normal variation and not a “problem” (like different learning styles or personalities)
What is meant by “trajectories and change vs labels and static”?
Development over time and how mental health/behavior is not fixed vs being defined by their diagnosis/disorder and mental health/behavior is fixed
Definition of Adaptive behavior?
Develop social, emotional and behavioral competence (adjusting to change)
Definition of Maladaptive behavior?
Interference to adaptive behavior (coping in ways that hurt you or others)
Definition of the Diathesis-Stress model?
Suggests that a person’s predisposition to a disorder (diathesis) and the presence of environmental stressors interact to increase the likelihood of that disorder manifesting
Definition of the Gene-Environment correlation model (rGE)?
Suggests that genetic predisposition can influence the types of environments individuals are exposed to, and these environments, in turn, can affect the expression of those genes
Definition of Passive rGE?
Parents provide both genes and an environment that are correlated
Definition of Evocative rGE?
A person’s genetic traits evoke specific reactions from others (their environment)
Definition of Active rGE?
Individuals actively seek out environments that are compatible with their genetic predispositions
Definition of Epigenetics?
The study of how gene activity and expression can be changed without altering the DNA sequence itself- these changes can turn genes “on” or “off” and are influence by factors like environment, life experiences, and development stages
Epigenetic compounds can affect the expression of DNA in two ways which are?
DNA methylation and Histone modification
Definition of DNA methylation?
A process in which proteins attach chemical tags (called methyl groups) to certain positions of genes, turning them on or off
Definition of Histone modification?
A process in which DNA wraps either tightly or loosely around histones (tight means turns off, loosely means turned on)
Definition of a Neuron?
Narrow and long brain cell
Definition of a Neurotransmitter?
A chemical messenger- Dopamine
What are some learning theories?
Classical conditioning, Operant conditioning, and Social learning theory
Definition of learning theory?
Explains and predicts children’s overt actions
What is Bandura’s Social-Learning Theory?
Albert Bandura suggest that reinforcement or punishment isn’t necessary for children to learn new behaviors, instead he proposed that some behaviors are learned by observation and attempt at replication (1977)
What was Bandura’s experiment?
Bobo Doll experiment (1961)
Bandura’s Social-Learning Theory suggested that an observer needs a model and three other things for social-learning to take place, which are?
The ability to pay attention, the ability to remember, and the ability to physically replicate the task
Definition of Classical Conditioning?
Ivan Pavlov discovered that you can condition a response by pairing a neutral stimulus with a unconditional response, that was a response to an unconditional stimulus
Name the parts: the bell, salivate to food, food, and salivate to the sound of the bell
Neutral stimulus, unconditional response, unconditional stimulus, conditioned response
Definition of Skinner’s Operant Conditioning
B.F. Skinner (1938) proposed that using the law of consequences can shape the frequency or intensity of a behavior- a method of learning
Definition of Appetitive?
Describes a pleasant stimulus