PMCY 4510 -- Continuous Pharmaceutical Manufacturing (MS presentation -- for final)
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Define “advanced manufacturing”
a collective term for new or innovatively applied medical product manufacturing technologies that can improve drug quality, address shortages of medicines, and speed time-to-market

What are the primary modes of operation for a chemical manufacturing process?
batch
continuous
others are specific to certain equipment and processes (biologics)
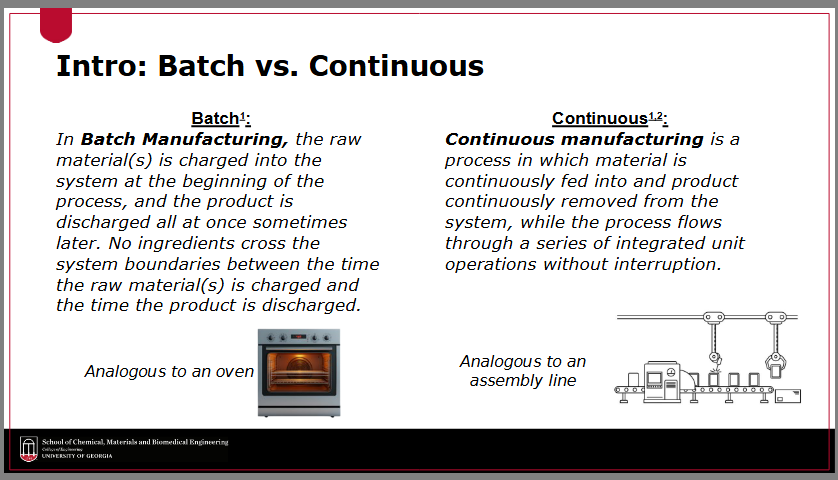
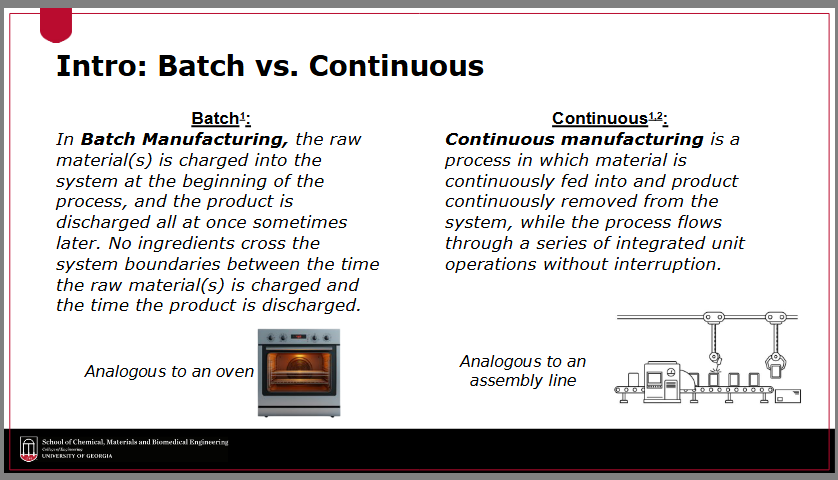
Define “batch manufacturing”
the raw material(s) is charged into the system at the beginning of the process, and the product is discharged all at once sometimes later
no ingredients cross the system boundaries between the time the raw material(s) is charged and the time the product is discharged
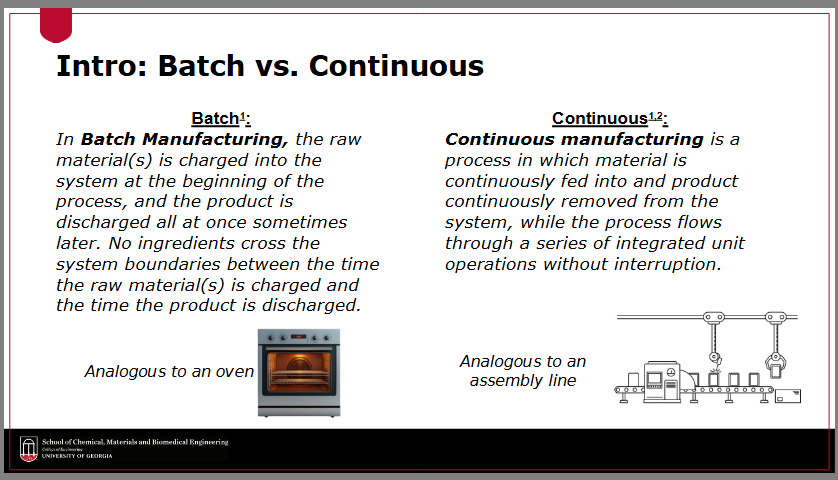
Define “continuous manufacturing”
a process in which material is continuously fed into and product continuously removed from the system, while the process flows through a series of integrated unit operations without interruption
Describe the core difference between batch and continuous manufacturing
The core difference is that batch manufacturing processes involve discrete charges of materials resulting in product discharge at intervals, while continuous manufacturing allows for uninterrupted flow of materials and products throughout the system.
batch manufacturing is like an oven when you’re baking a cake — you have to mix up each cake by itself and then put it in the oven, and then take out the first cake before you can bake the next one
continuous manufacturing is like a conveyer belt/assembly line — like parts moving along an assembly line where different actions are performed sequentially as the product progresses
What are the current limitations with the batch manufacturing process?
products have to be tested off-line instead of on-line (making PAT not as accurate as desired)
batch processes are relatively inefficient and less understood compared to other industries
not as fast as continuous manufacturing

What are the benefits of continuous manufacturing?
increased production flexibility
don’t need to shut down in between batches for cleaning
scale of batches are more easily modified (can respond to demand surges faster)
change run-time or duplicating lines instead of recalibrating each piece of equipment
more efficient production
don’t have to wait for one process to finish to start another
reduces energy needs and overall waste
real-time monitoring of product quality (PATs)
in-line measurement allows for feedback control and reduces risk of faulty batches (issues are caught earlier)
cost savings
reduces labor and operational costs
waste is reduced by preventing off-spec production
fewer cleaning and changeover steps
What are the challenges/drawbacks of continuous manufacturing?
upfront costs
necessary equipment and infrastructure can be expensive
requires skilled workforce familiar with continuous systems
adoption of new statistical tools and models to optimize processes can be expensive to acquire and train on
process complexity
integration of multiple unit operations requires robust design
real-time analytics adds to already strenuous technical demands
regulatory concerns
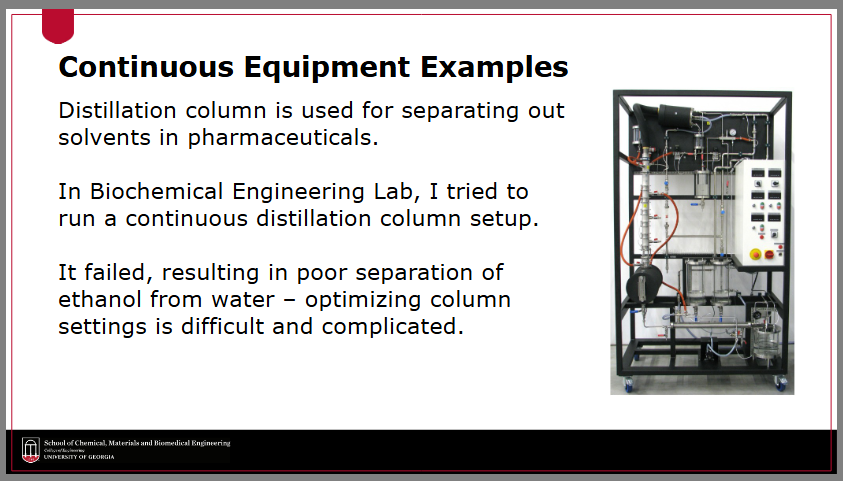
What are examples of equipment incorporated in a continuous manufacturing process?
spray dryer
roller compactor
tablet press
distillation column
(T/F) There are dedicated sections in the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) that exclusively govern continuous pharmacuetical manufacturing.
False
Which of the following is NOT a benefit of continuous pharmaceutical manufacturing?
A) reduced need for real-time monitoring
B) greater flexibility in production scale
C) faster response to demand changes
D) reduced cleaning and changeover steps
A — reduced need for real-time monitoring
What drug was the first to receive FDA approval for switching from batch to continuous manufacturing?
A) Lipitor
B) Orkambi
C) Prezista
D) Remdesivir
C — Prezista