Meningitis
5.0(1)Studied by 6 people
Card Sorting
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:38 PM on 3/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
1
New cards
Meningitis
Inflammation of the Pia mater and arachnoid, and infection of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that fills the subarachnoid space
2
New cards
Bacterial or Viral
Meningitis is typically due to ____ __or__ _____ infection in the CSF
(May also be due to tuberculosis, chemicals, or idiopathic)
(May also be due to tuberculosis, chemicals, or idiopathic)
3
New cards
Meningitis epidemic
Tend to occur in large group settings
\-Military
\-Daycare centers
\-College dorms (Especially with community dining)
\-Military
\-Daycare centers
\-College dorms (Especially with community dining)
4
New cards
Type of meningitis
Bacterial
Viral
Fungal
Parasitic
Non-infectious
Viral
Fungal
Parasitic
Non-infectious
5
New cards
Bacterial meningitis
Caused by bacteria
\-Neisseria meningitidis
\-Streptococcus pneumoniae
\-Staphylococcus aureus
\-Tuberculosis
\-Neisseria meningitidis
\-Streptococcus pneumoniae
\-Staphylococcus aureus
\-Tuberculosis
6
New cards
Viral Meningitis
Caused by viruses:
\-Arboviruses (transmitted by primary arthropod vector)
\-Enteroviruses (contamination through fecal matter or respiratory secretions from infected)
\-Herpes simplex
\-Mumps, measles
\-COVID-19 maybe
\-Arboviruses (transmitted by primary arthropod vector)
\-Enteroviruses (contamination through fecal matter or respiratory secretions from infected)
\-Herpes simplex
\-Mumps, measles
\-COVID-19 maybe
7
New cards
Fungal Meningitis
Caused by fungi:
\-Cryptococcus
\-Histoplasma
\-Cryptococcus
\-Histoplasma
8
New cards
Parasitic Meningitis
Angiostrongylus cantonensis (found in contaminated food, water and soil):
\-cryptococcus neoformans
\-Candida albicans
\-Aspergillus species and others
\-cryptococcus neoformans
\-Candida albicans
\-Aspergillus species and others
9
New cards
Non-infectious Meningitis
Caused by cancers:
AKA Neoplastic Mengingitis
\-Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and certain drugs
\-Head injury and brain surgery
AKA Neoplastic Mengingitis
\-Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and certain drugs
\-Head injury and brain surgery
10
New cards
Enteroviruses
Most common cause of viral meningitis
11
New cards
Can bacterial meningitis treated with antibiotics still result in death?
Yes
12
New cards
Are many fungal meningitis cases associated with immune deficiencies?
Yes
13
New cards
Risk factors fungal meningitis
* AIDS
* Immunosuppressant drugs
* Often prescribed after an organ transplant
* Immunosuppressant drugs
* Often prescribed after an organ transplant
14
New cards
African Belt
2012 outbreak related to contaminated steroid drug injections sickened \~750 and killed 64 across 20 states forming what is referred to as the _____ ________ on a map.
15
New cards
Tuberculous Meningitis (TBM)
Deposit of tuberculous granulations (**tuberculomas**) accompanied with meningeal inflammation
16
New cards
Tuberculous Meningitis
______ is hard to differentiate from bacterial meningitis
17
New cards
100 & 30
Untreated TMB fatality is ______ % and ______ % are fatal despite antituberculosis chemotherapy.
18
New cards
Hydrocephalus
TBM complication that results from the blockage of CSF abroprion and can also effect efferent CNs
19
New cards
Recent TB exposure
Evidence of TB in the body
HIV
Evidence of TB in the body
HIV
==Indicators of tuberculosis meningitis:==
20
New cards
0\.25 - 1 / 1000
2\.5 / 1000
2\.5 / 1000
==Neonatal bacterial meningitis incidence:==
Live births = ____ to _____
Premature births = __________
Live births = ____ to _____
Premature births = __________
21
New cards
5,000 to 7,000
Bacterial meningitis in adults occurs in \~ ____ to ___ in the US each year (Fluctuates!)
22
New cards
Spring to autumn
Meningitis is more common in ____ to ____ months.
23
New cards
meningococcal conjugate vaccination
\-All preteens and teens at 11 to 12 years old with a booster dose at 16 years old
\-Children and adults at increased risk for meningococcal disease
\-Children and adults at increased risk for meningococcal disease
24
New cards
People older than 10 at increased risk for meningococcal disease
According to the CDC who should receive the serogroup B meningococcal vaccination?
25
New cards
PATH and WHO
Meningitis Vaccine Project created by partnership between ___ and ___.
Mission = eliminating meningitis as a public health problem in sub-Saharan Africa through the development, testing, introduction, and widespread use of conjugate meningococcal vaccines (1 to 29-year-olds received a single dose of MenAfriVac)
Mission = eliminating meningitis as a public health problem in sub-Saharan Africa through the development, testing, introduction, and widespread use of conjugate meningococcal vaccines (1 to 29-year-olds received a single dose of MenAfriVac)
26
New cards
Risk factors
Infants, children, and elderly
Day care centers
Cancer patients:
\-Immunosuppressive chemotherapy
\-Indwelling ventricular devices
\-Indwelling vascular catheters
\-Neurosurgical procedures
Overcrowded conditions
Upper respiratory infection
Certain surgical procedures (cochlear implants)
Untreated conditions
Exposure to rodents and mice
Direct contact with someone with meningitis
Day care centers
Cancer patients:
\-Immunosuppressive chemotherapy
\-Indwelling ventricular devices
\-Indwelling vascular catheters
\-Neurosurgical procedures
Overcrowded conditions
Upper respiratory infection
Certain surgical procedures (cochlear implants)
Untreated conditions
Exposure to rodents and mice
Direct contact with someone with meningitis
27
New cards
Viral meningitis symptoms
\-Asymptomatic or less severe ==(viral only)==
\-High fever
\-Chills
\-Nausea and vomiting
\-Photophobia (Sensitivity to light)
\-High fever
\-Chills
\-Nausea and vomiting
\-Photophobia (Sensitivity to light)
28
New cards
Bacterial meningitis symptoms
\-High fever
\-Chills
\-Nausea and vomiting
\-Photophobia
\-Severe headaches
\-Stiff neck @@(meningismus)@@
\-Rapid breathing
\-Increased drowsiness
\-Agitation
\-Bulging fontanelles
\-Decreased consciousness
\-Poor feeding or irritability in children
\-Opisthotonos (Unusual posture, with the head and neck arched backwards)
\-Seizures
\-Stroke
\-Chills
\-Nausea and vomiting
\-Photophobia
\-Severe headaches
\-Stiff neck @@(meningismus)@@
\-Rapid breathing
\-Increased drowsiness
\-Agitation
\-Bulging fontanelles
\-Decreased consciousness
\-Poor feeding or irritability in children
\-Opisthotonos (Unusual posture, with the head and neck arched backwards)
\-Seizures
\-Stroke
29
New cards
Viral complications
\-Fatigue
\-Lightheadedness
\-Encephalitis (rare)
\-Lightheadedness
\-Encephalitis (rare)
30
New cards
Bacterial complications
\-Brain damage
\-Coma
\-Death ( \~10% fatal and > elderly)
\-Hearing loss (20%)
\-Paralysis
\-Seizures
\-Kidney damage
\-Learning disabilities
\-Coma
\-Death ( \~10% fatal and > elderly)
\-Hearing loss (20%)
\-Paralysis
\-Seizures
\-Kidney damage
\-Learning disabilities
31
New cards
Viral meningits Dx
Flat rash all over the body
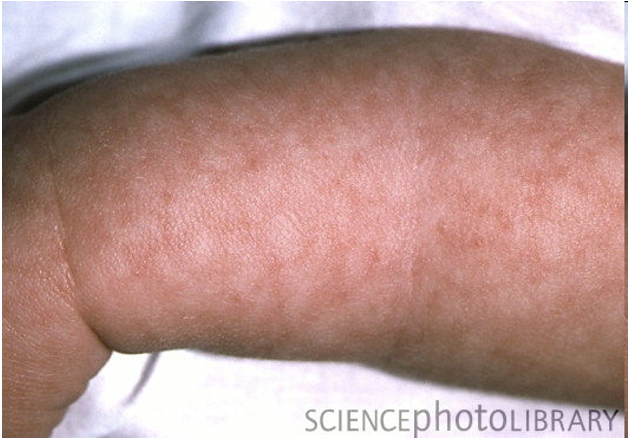
32
New cards
Bacterial meningitis Dx
\-Typical purpura ( blood vessels get inflamed, they can bleed into the skin, causing a reddish-purple rash)
\-Petechiae rash -- round spots that appear on the skin as a result of bleeding
\-Petechiae rash -- round spots that appear on the skin as a result of bleeding
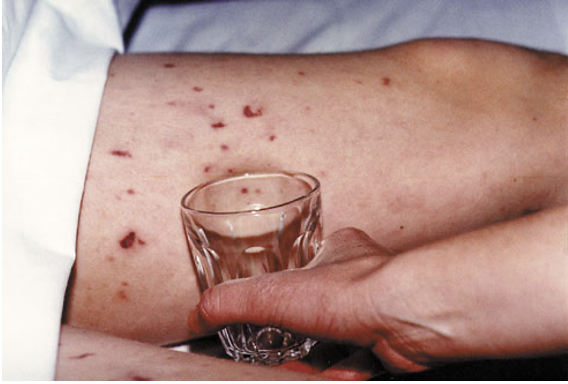
33
New cards
Petechiae
\-Small (1–3 mm)
\-Red
\-Non-blanching lesions caused by bleeding into the skin.
\-Red
\-Non-blanching lesions caused by bleeding into the skin.
34
New cards
Purpura
\-Larger (>3-1-mm)
\-Typically raised lesions resulting from bleeding within the skin
\-Do not blanch when applying pressure (Glass test)
\-Typically raised lesions resulting from bleeding within the skin
\-Do not blanch when applying pressure (Glass test)
35
New cards
Glass test
If rash does not change colors then medical referral should be given.
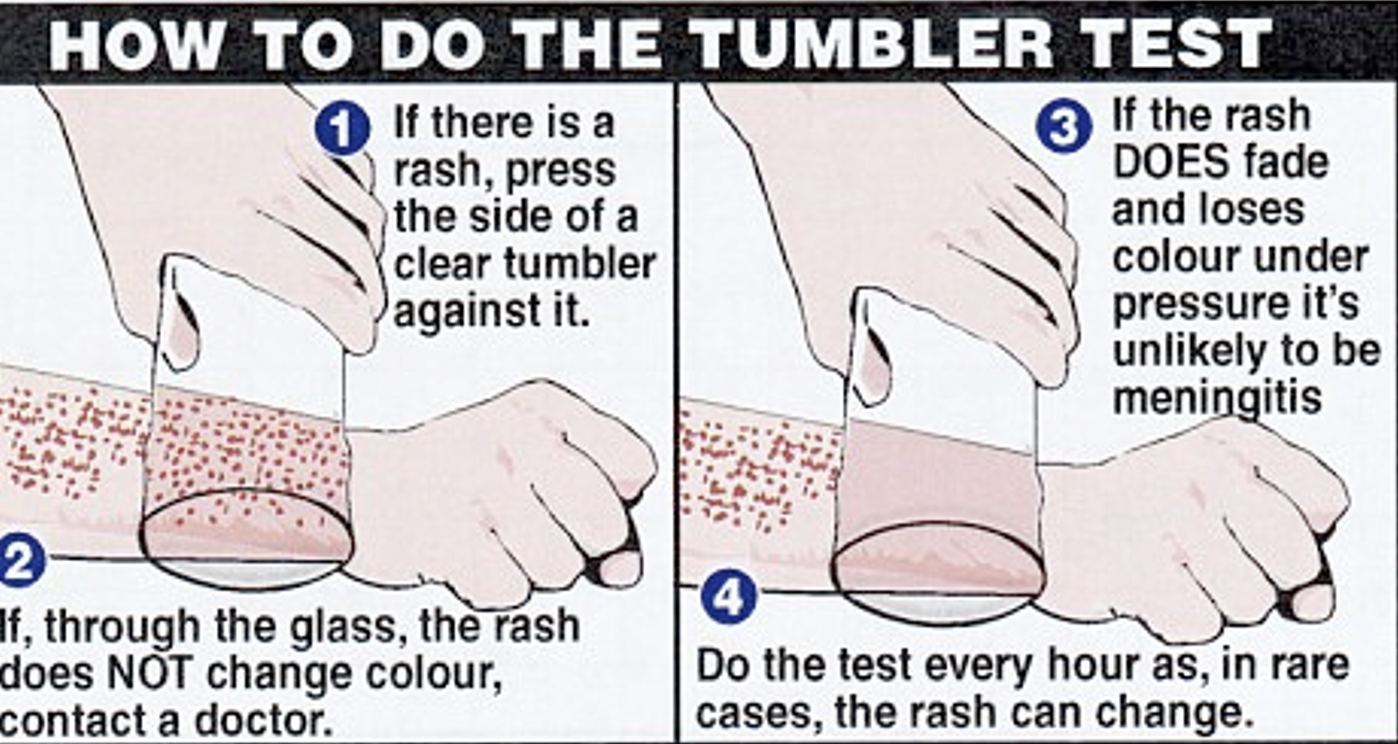
36
New cards
Brudzinski’s Sign
Checking for neck stiffness may include tilting the head is tilted forward and the knees will bend in result (AKA positive) indicative of:
\-Severe meningeal inflammation
\-Evidence of microbiological CSF infection
\-Severe meningeal inflammation
\-Evidence of microbiological CSF infection
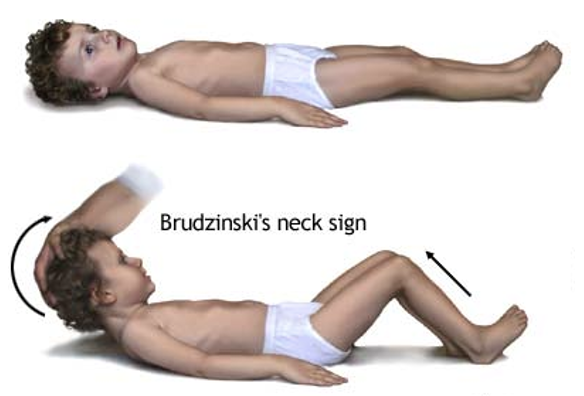
37
New cards
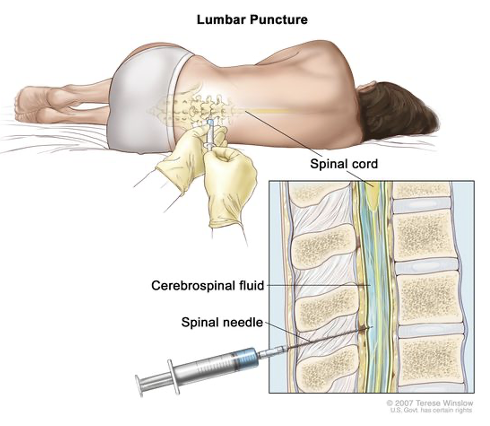
Lumbar puncture
==Culture of CSF to determine:==
\-Type of bacteria
\-Cell count
\-Glucose
\-Protein
\-Type of bacteria
\-Cell count
\-Glucose
\-Protein
38
New cards
Diagnosis
•X-rays
•Ultrasounds
•CT scans
•MRIg
•Ultrasounds
•CT scans
•MRIg
39
New cards
Septicaemia
________ blood poising caused by the same germs as meningitis.
\[Could occur with meningitis or on its own\]
\[Could occur with meningitis or on its own\]
40
New cards
2 weeks
How long does it typically take to completely recover from viral meningitis
41
New cards
Viral Meningitis Tx
Antibiotics are not helpful
Recommended:
\-Plenty of fluids
\-Rest
\-Medicine to relieve headache
Recommended:
\-Plenty of fluids
\-Rest
\-Medicine to relieve headache
42
New cards
Pharmacological AND prevention
==Bacterial Tx:==
___________:
•Hospitalization (life-threatening)
•Antibiotics (corticosteroid, intravenous)
(Some are ototoxic -- ask if they have been in the hospital)
AND
___________:
Some forms are contagious!
\-Stay away from direct contact with saliva
\-Get vaccinated
___________:
•Hospitalization (life-threatening)
•Antibiotics (corticosteroid, intravenous)
(Some are ototoxic -- ask if they have been in the hospital)
AND
___________:
Some forms are contagious!
\-Stay away from direct contact with saliva
\-Get vaccinated
43
New cards
antituberculous chemotherapy
==TBM tx:==
___________ ___________
•Choice of 4 drugs for two months
-Then a choice of 2 drugs for months nine to twelve after the infection
•Dexamethasone is given regardless of age or disease severity
-(only to HIV-negative patients)
___________ ___________
•Choice of 4 drugs for two months
-Then a choice of 2 drugs for months nine to twelve after the infection
•Dexamethasone is given regardless of age or disease severity
-(only to HIV-negative patients)
44
New cards
Otitis media
Viral meningitis is not typically associated with HL but a mild HL may be present if it occurs with ____ _____
45
New cards
rapid bilateral fever
==Sings of bacterial meningitis on case history:==
___________ onset of symptoms (HL or dizziness)
Most likely ___________ auditory symptoms
High ___________
Photophobia
___________ onset of symptoms (HL or dizziness)
Most likely ___________ auditory symptoms
High ___________
Photophobia
46
New cards
mild to profound
==Bacterial Meningitis Audiogram:==
______ to _______ SNHL
Progressive or fluctuating
______ to _______ SNHL
Progressive or fluctuating
47
New cards
7-36
5-30
4
5-30
4
==Bacterial meningitis HL incidence:==
* ____ - ____% of meningitis survivors
* ____ - ____% of bacterial meningitis and __% develop permanent bilateral HL
* ____ - ____% of meningitis survivors
* ____ - ____% of bacterial meningitis and __% develop permanent bilateral HL
48
New cards
Ossification
OHC
cochlear aqueduct
OHC
cochlear aqueduct
==Bacterial Meningitis Hearing Loss Pathophysiology:==
1. _________ of the cochlea tend to occur most at the basal turn of the S. Tympani.
2. ______ are thought to be damaged by the inflammatory by-products (oxidants), ischemia (poor blood supply), and disruption of the blood-labyrinth barrier (BLB)
3. The route of infection from the meninges to the membranous labyrinth of the inner ear is under debate:
1. ______ _____(most obvious)
2. Along the cochlear nerve,
3. Through blood
4. etc.
1. _________ of the cochlea tend to occur most at the basal turn of the S. Tympani.
2. ______ are thought to be damaged by the inflammatory by-products (oxidants), ischemia (poor blood supply), and disruption of the blood-labyrinth barrier (BLB)
3. The route of infection from the meninges to the membranous labyrinth of the inner ear is under debate:
1. ______ _____(most obvious)
2. Along the cochlear nerve,
3. Through blood
4. etc.
49
New cards
elevated absent
increased
WIII
increased
WIII
==Bacterial Meningitis test results:==
* Middle ear muscle reflex would be ____ or _____
* Decay testing is not possible if MEMR is elevated or absent
* ABR = poor morphology or absent response
* ________ interpeak latencies
* May have delayed ________
* ENG = nystagmus present
* Middle ear muscle reflex would be ____ or _____
* Decay testing is not possible if MEMR is elevated or absent
* ABR = poor morphology or absent response
* ________ interpeak latencies
* May have delayed ________
* ENG = nystagmus present
50
New cards
25-30 dB
35-40 dB
35-40 dB
==Bacterial Meningitis OAES:==
•Transient Evoked:
•Absent if > _________ HL
•Distortion Product:
•Absent if > ________ HL
•Transient Evoked:
•Absent if > _________ HL
•Distortion Product:
•Absent if > ________ HL
51
New cards
HA CI
==Bacterial Meningitis Habilitation/Rehabilitation:==
* ________
* ________
* Timely intervention is necessary to minimize the risk of cochlear ossification
* Bilateral simultaneous implantation is the treatment of choice for this special population
* Communication considerations:
•Auditory/Oral
•Manual
•Total communication
* ________
* ________
* Timely intervention is necessary to minimize the risk of cochlear ossification
* Bilateral simultaneous implantation is the treatment of choice for this special population
* Communication considerations:
•Auditory/Oral
•Manual
•Total communication
52
New cards
Referral needs
* Emergency room
* Untreated bacterial meningitis can cause death
* Otolaryngologist/otologist
* Audiologist
* Amplification
* Monitoring
* Untreated bacterial meningitis can cause death
* Otolaryngologist/otologist
* Audiologist
* Amplification
* Monitoring