Chap 15C - Arenes (Methylbenzene)
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Describe menthylbenzene
Prepared by Friedel-crafts alkylation of benzene
One methyl group bonded to benzene ring
Aka toluene
Structural formula: C6H5CH3
Describe effect of substituent groups on methylbenzene
Any substituent group attached to the benzene ring will affect the reactivity of the benzene ring and determine the orientation of the substitution
Describe ways electrons can be donated into or withdrawn from the benzene ring
Resonance effect
Donation or withdrawal of electrons through the overlap of p orbital on the substituent with a p orbital on the C atom of benzene ring
Inductive effect
Donation or withdrawal of electrons through a sigma bond due to electronegativity difference between the atom
Describe electron-donating substituent on methylbenzene + examples
Electron-donating group such as –NH2, –OH, –R (R = alkyl group) increases the electron density in the benzene ring
The monosubstituted benzene is more reactive towards electrophilic substitution (benzene ring is activated)
Reaction conditions used for electrophilic substitution are milder
–OH, –OR, –NH2, –NHR, –NR2, –NHCOR (resonance effect)
O and N atoms have a lone pair of electrons (usually in a p orbital) available for donation to the benzene ring
–alkyl (inductive effect)
Inductively donate electrons through the sigma bond linking the substituents to a benzene ring
Describe electron-withdrawing substituent on methylbenzene + examples
Such as –Cl, –CHO, –CO2H, decreases the electron density in the benzene ring
Monosubstituted benzene is less reactive towards electrophilic substitution (benzene ring is deactivated towards electrophilic substitution)
Reaction conditions used for electrophilic substitution are harsher
–CHO, –COR, –CO2H, –CO2R, –NH3+ ,–NO2, –CN (resonance effect)
More electronegative N and O atoms are able to withdraw electrons from the benzene ring
–Cl, –Br, –I (inductive effect)
Inductively withdraw electrons through the sigma bond linking the substituents to a benzene ring
State what determine position of incoming electrophile
The substituent group on the benzene ring determines the position of the incoming electrophile after the reaction (NOT the incoming group)
G is either 2,4-directing and directs the electrophile onto positions 2 and 4 or is 3-directing and directs the electrophile onto position 3
State what determine position of incoming group E
The position of the incoming group E, is determined by the nature of the group G, already bonded to the ring, and NOT by the nature of the incoming group E (given in the Data Booklet)
If multiple substituents are present, the more activating group will dominate the orientation of substitution
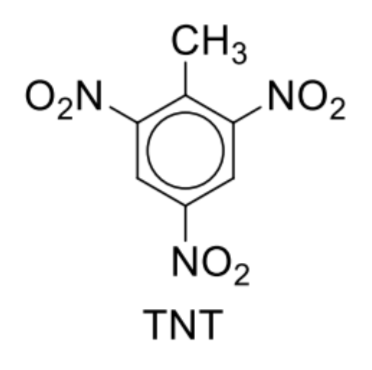
Describe nitrobenzene and methylbenzene and substituent groups
Nitrobenzene undergoes further substitution to form 1,3-dinitrobenzene and 1,3,5-trinitrobenzene at higher temperatures as –NO2 group is 3–directing and deactivating
Further alkylation of methylbenzene occurs more readily to give 1,2-dimethylbenzene and 1,4-dimethylbenzene as –CH3 group is 2,4–directing and activating
Major product: If 1.2-disubstituted and 1,4-disubstituted products are the major products, substituent G stabilises the 1,2-disubstituted and 1,4-disubstituted intermediate cations to a greater extent over the 1,3-disubstituted intermediate
Explain why halogens are electron-withdrawing but 2.4-directing
Halogen atoms are electronegative -> electron-withdrawing such that they deactivate the benzene ring towards electrophilic substitution.
BUT: the halogen atom directly bonded to the benzene ring also has a lone pair of electrons which enables them to stabilise the positively-charged intermediate formed during the electrophilic substitution reaction -> This makes halogen atoms electron-withdrawing but 2,4-directing
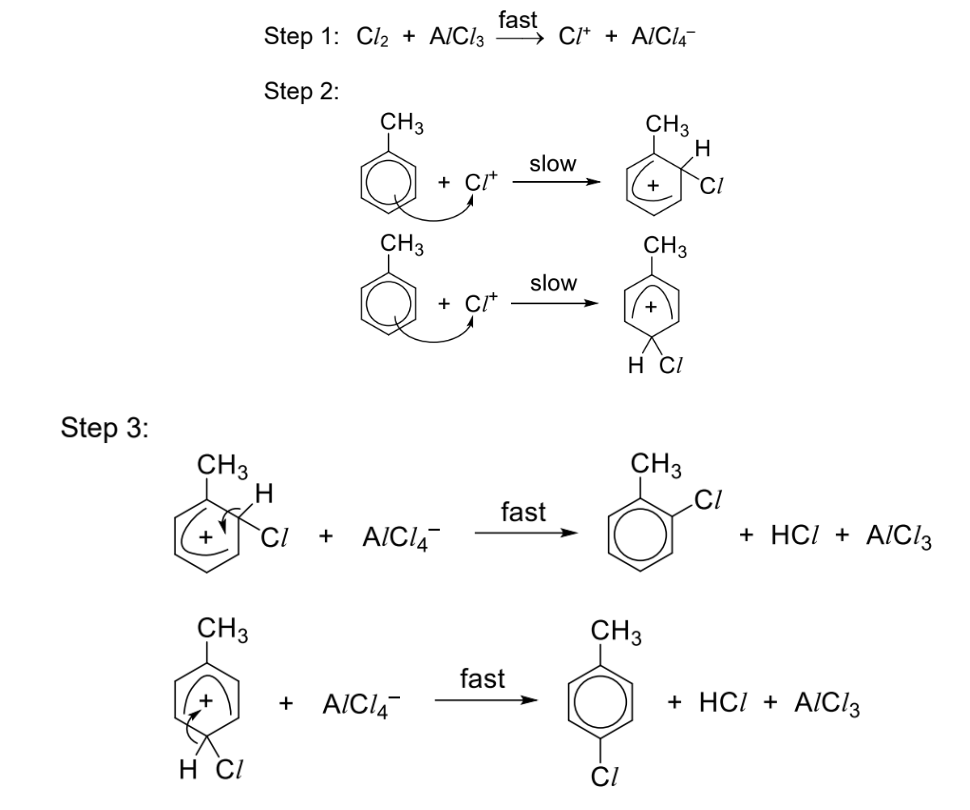
Describe halogenation + general reaction
Reagents and conditions: Cl2, anhydrous AlCl3 catalyst (or FeCl3 catalyst), excess methylbenzene
Observations: Similar to benzene
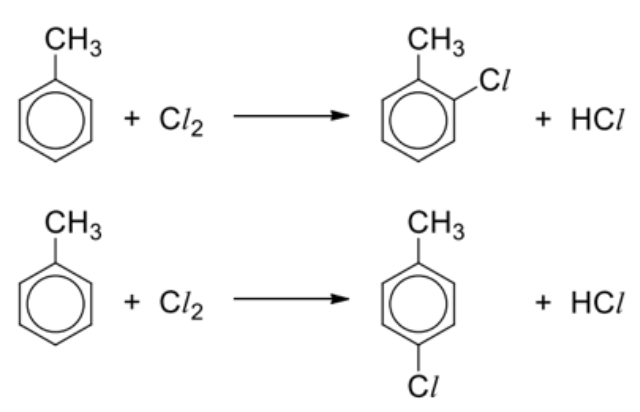
Draw halogenation mechanism
Describe nitration reagents and conditions
Reagents and conditions: concentrated HNO3, concentrated H2SO4 catalyst, 30C
The temperature of reaction is lower than that for benzene as –CH3 is activating
|
Describe general reaction of nitration
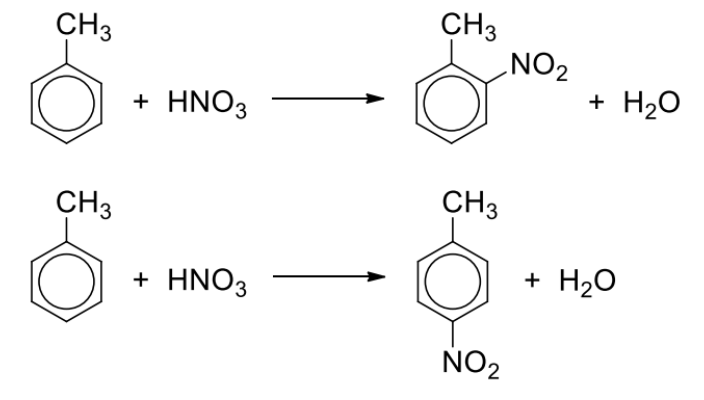
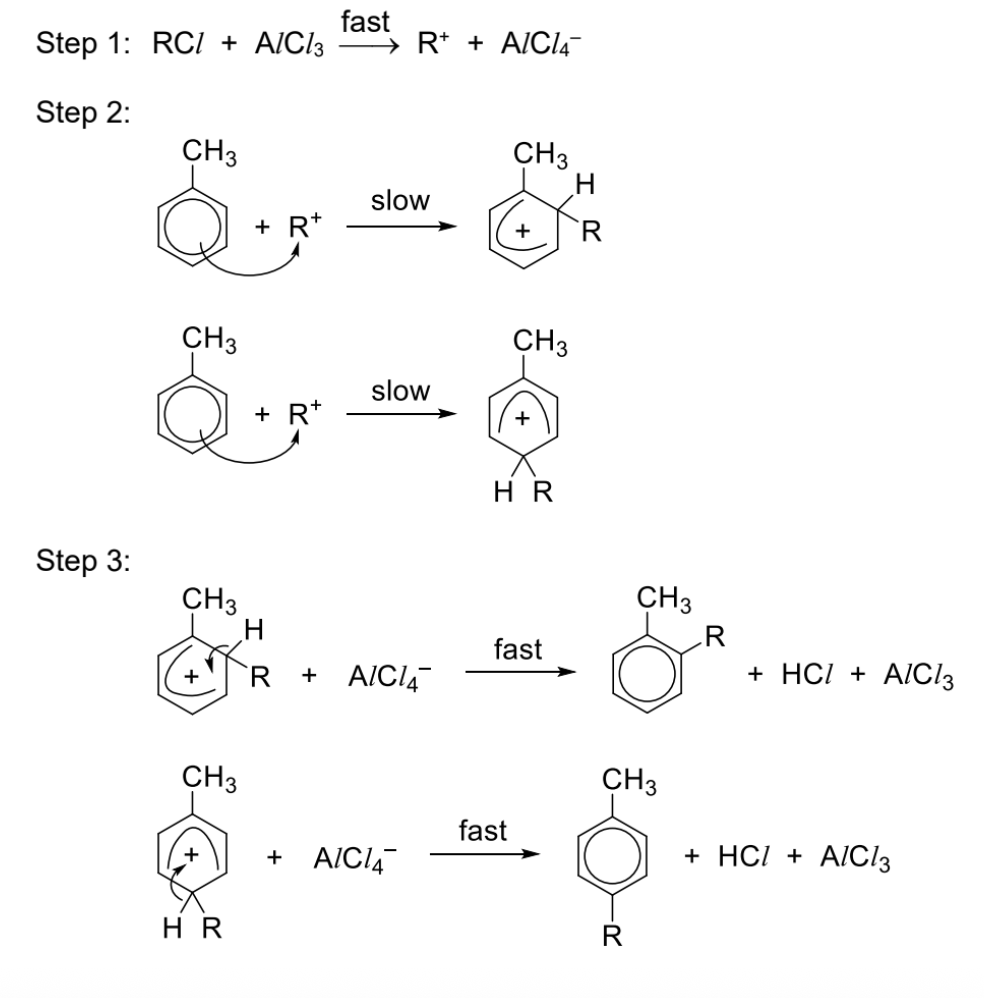
Describe friedel-crafts alkylation + general reaction
Reagents and conditions: RCl, anhydrous AlCl3 catalyst (or FeCl3 catalyst), excess methylbenzene
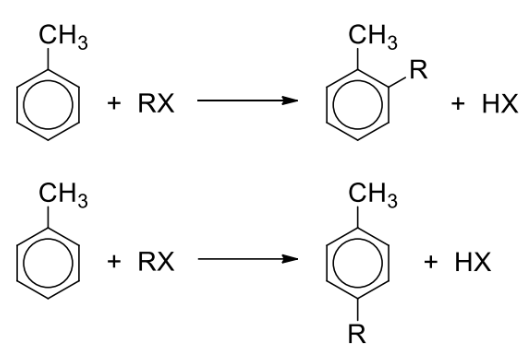
Draw mechanism for friedel crafts alkylation