Anterior Chamber Uveitis Intro
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Cells
a spillover of white blood cells into the anterior chamber from actively inflamed iris or ciliary body
<1
number of cells in a grade 0 cells reaction
1-5
number of cells in a grade 0.5+ cells reaction
6-15
number of cells in a grade 1+ cells reaction
16-25
number of cells in a grade 2+ cells reaction
26-50
number of cells in a grade 3+ cells reaction
>50
number of cells in a grade 4+ cells reaction
Flare
leakage of protein into the anterior chamber often accompanying cells, but can persist after cells resolve as well. An intense reaction may lead to the formation of a fibrin sheet.
1+
clinical grade of a flare reaction that is faint
2+
clinical grade of a flare reaction that is moderate with iris and lens details still clear
3+
clinical grade of a flare reaction that is marked with iris and lens details obscured
4+
clinical grade of a flare reaction that is intense with fibrin aqueous
Fibrinous exudate
coagulation of protein and inflammatory cells forming a sheet like substance in the anterior chamber. Is a severe, but rare, anterior chamber reaction. Is more common in darkly pigmented irises.
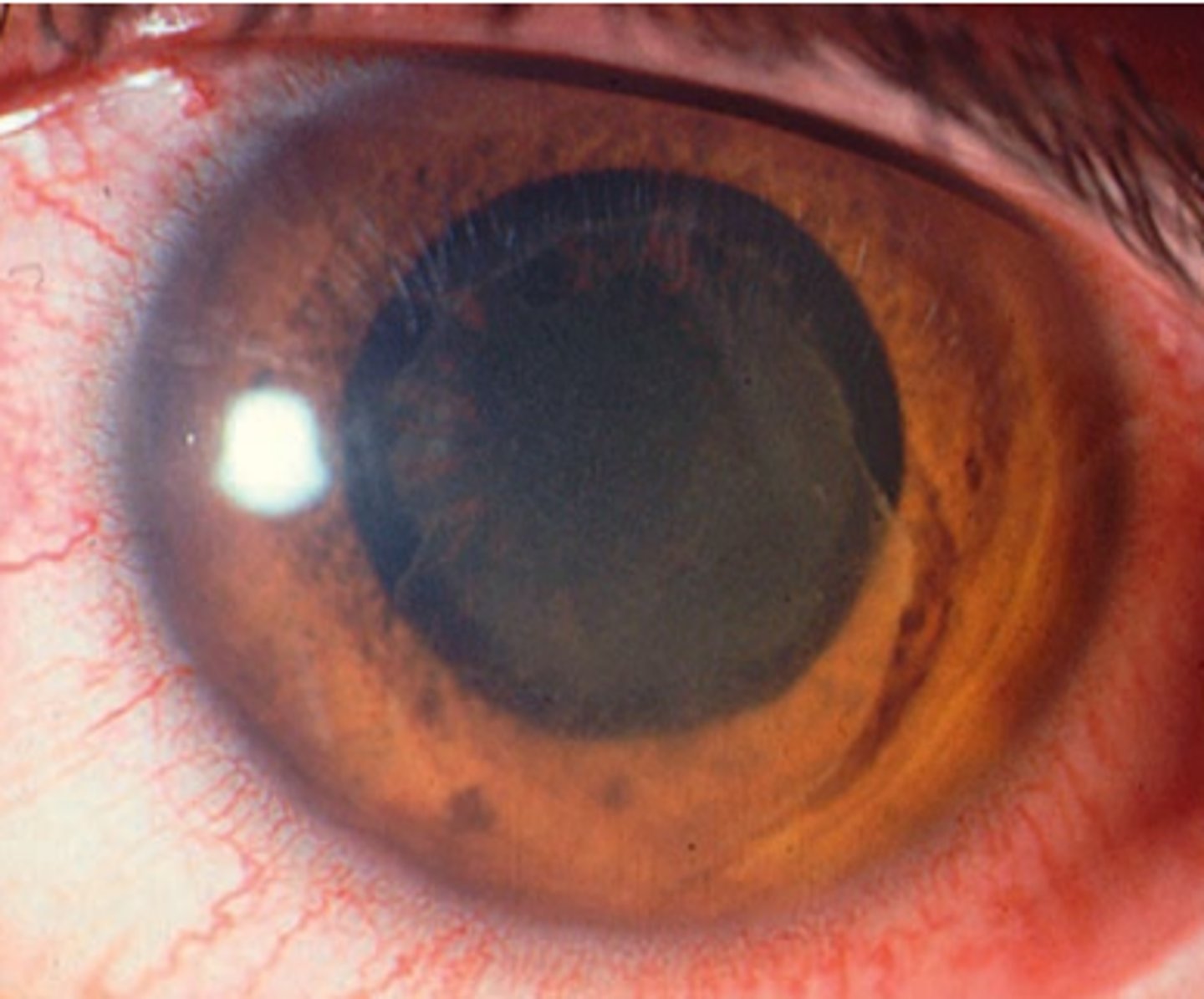
Keratic precipitates
inflammatory and white blood cells originating from the iris and ciliary body and adhering to the corneal endothelium.
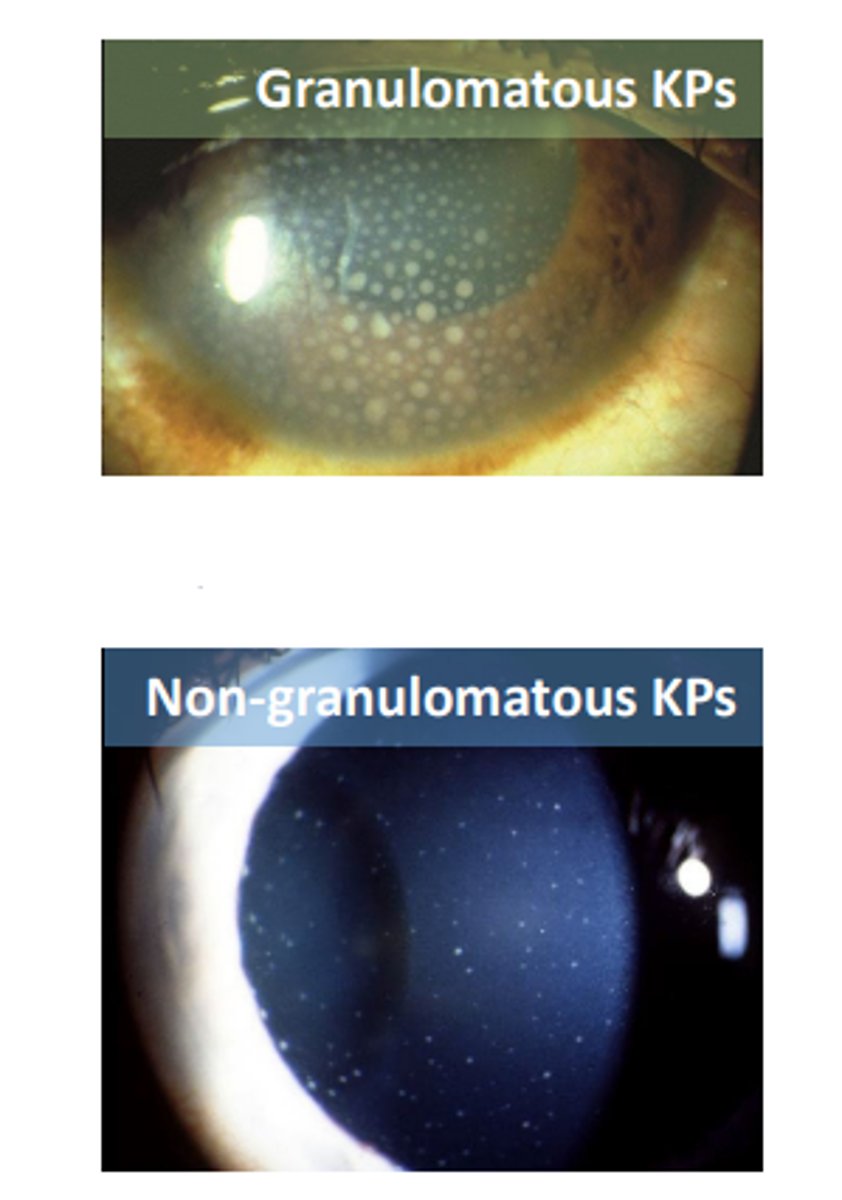
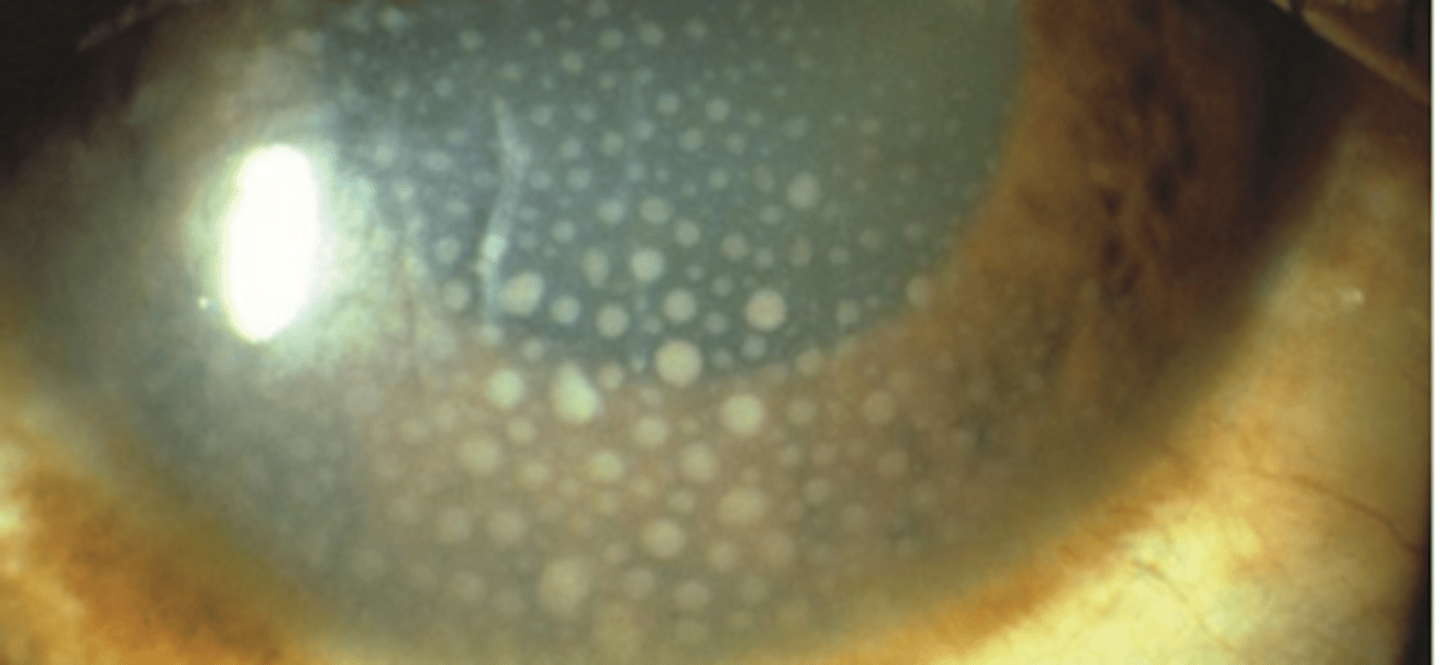
Granulomatous
keratic precipitates that are larger and composed of macrophages. Have a greasy appearance and can be diffuse or localized.
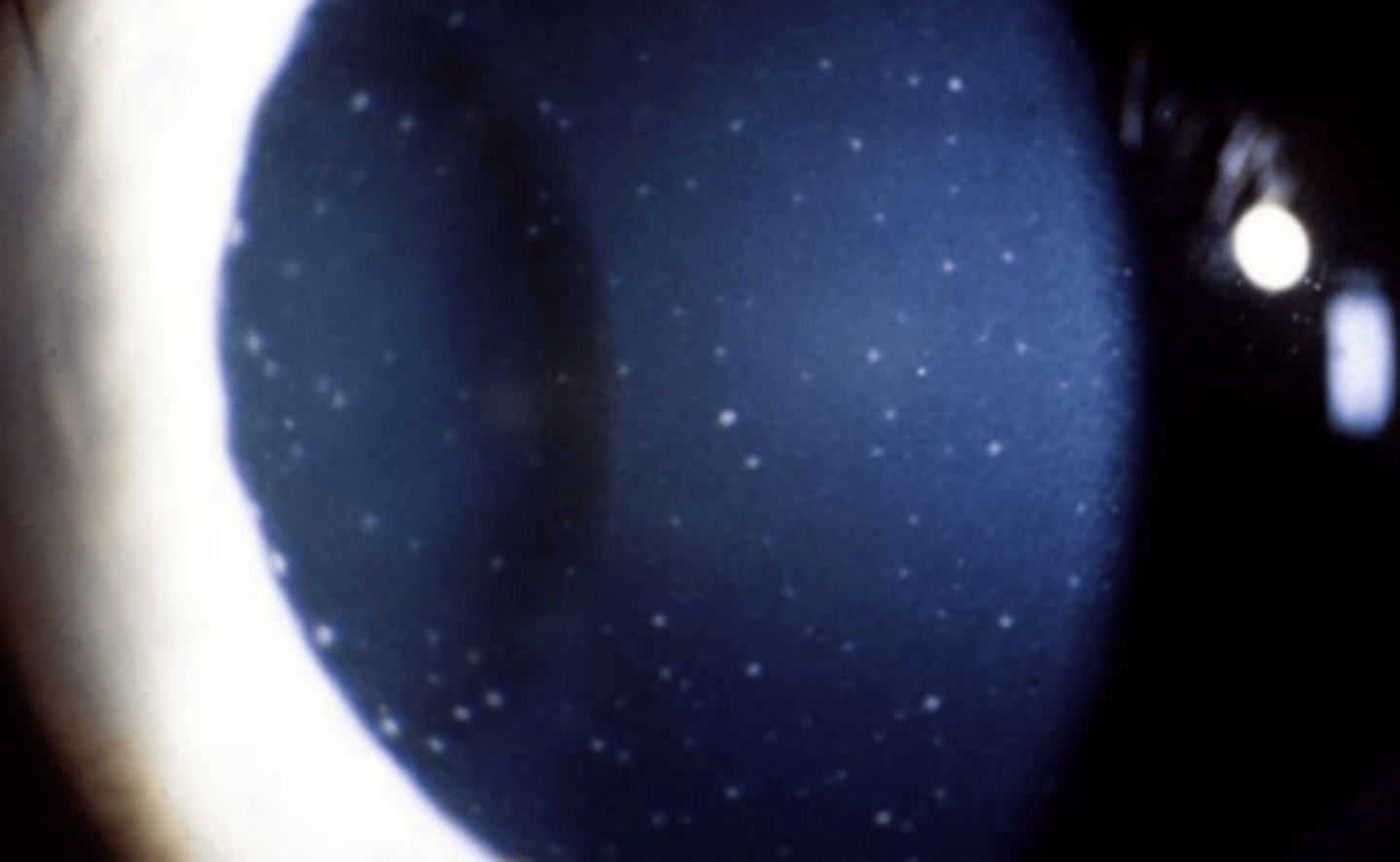
Non-granulomatous
keratic precipitates that are smaller and composed of lymphocytes. Have a dust like appearance being white to slightly pigmented in color.
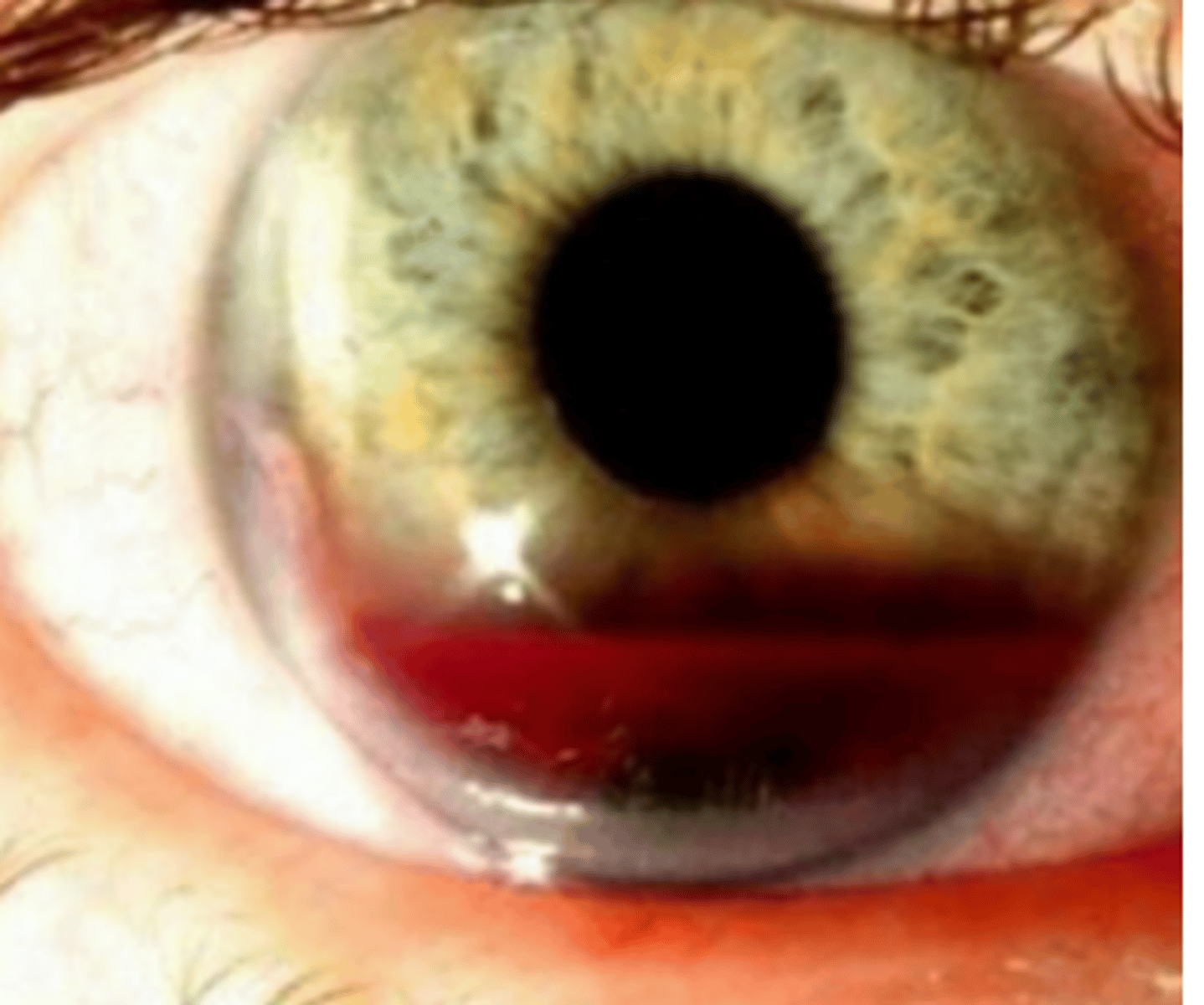
Hypopyon
sedimentation of white blood cells in the inferior aspect of the anterior chamber. Is graded by its height in mm, or by the percentage of anterior chamber involved. Can be caused by inflammation, infection, trauma, tumors. Is managed with anti-inflammatory and anti-infective agents.
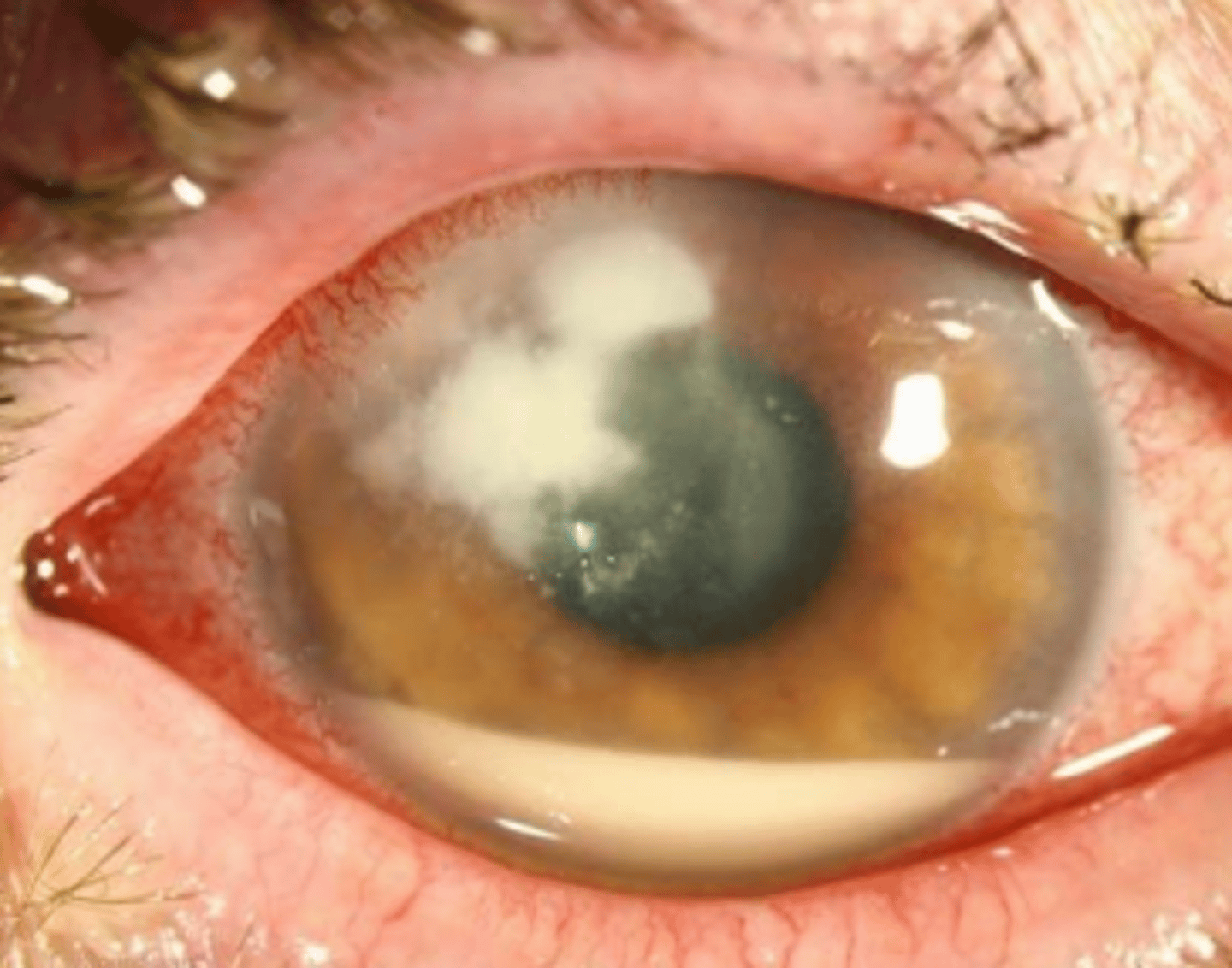
Pseudohypopyon
a blood stained hypopyon that does not contain a cell or flare reaction as it is most likely related to a cancerous growth. Is non-responsive to corticosteroid treatment. Is rare; is a manifestation of leukemia.
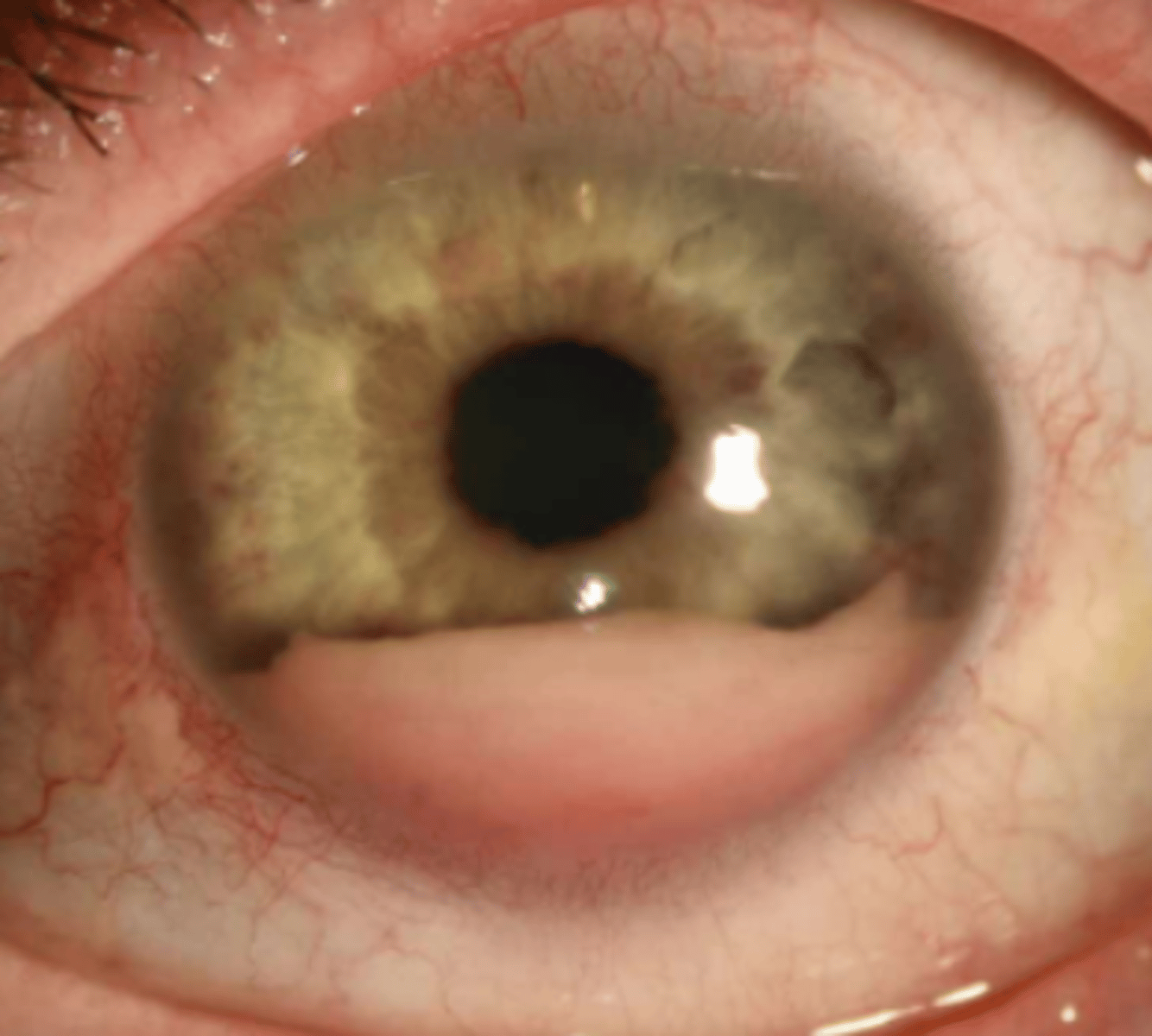
Hyphema
collection of red blood cells in the anterior chamber. Is graded by its height in mm, or by the percentage of anterior chamber involved. May be visible only on gonioscopy (micro). Can be caused by trauma** and uveitis. Is managed with bed rest (head at 45 degrees), minimal eye movement, and avoidance of NSAIDs.
Uveitis
inflammation of all or a portion of the uveal tract (iris, ciliary body, choroid). Has no demographic patterns, but is associated with certain diseases. Is potentially life threatening, with many cases leading to legal blindness annually. Presents as pain, photophobia, lacrimation, decreased vision, and floaters.
bilateral, reoccurring
Uveitis is not likely idiopathic, and is more likely to be related to an underlying disease when it is ___ or ____
ciliary muscle spasm, CN V1
Pain occurring in uveitis occurs due to ____, and occurs as referred pain along ____
CN V irritation
Photophobia occurring in uveitis occurs due to ___
discharge
Lacrimation occurring in uveitis almost always occurs without...
chronic
does clouding of the media occur in acute or chronic uveitis?
posterior
are floaters indicative of anterior or posterior uveitis?
posterior synechiae
A miotic or sluggish pupil seen in uveitis can be caused by...
herpetic disease
A dilated pupil in the absence of mydriatics seen in uveitis can be caused by...
posterior uveitis
An afferent pupillary defect seen in uveitis is more common in...
-Epithelial and stromal lesions
-keratic precipitates
-band keratopathy
three cornea findings of uveitis
-Cells
-flare
-hypopyon
-hyphema
four anterior chamber findings of uveitis
-Nodules
-abnormal vasculature
-posterior synechiae
-atrophy
-heterochromia
five iris findings of uveitis
Iris bombe
anterior bowing of the iris caused by increased posterior chamber pressure secondary to apposition of the iris to the anterior lens or vitreous. Poses a risk for glaucoma due to blocking of the trabecular meshwork.
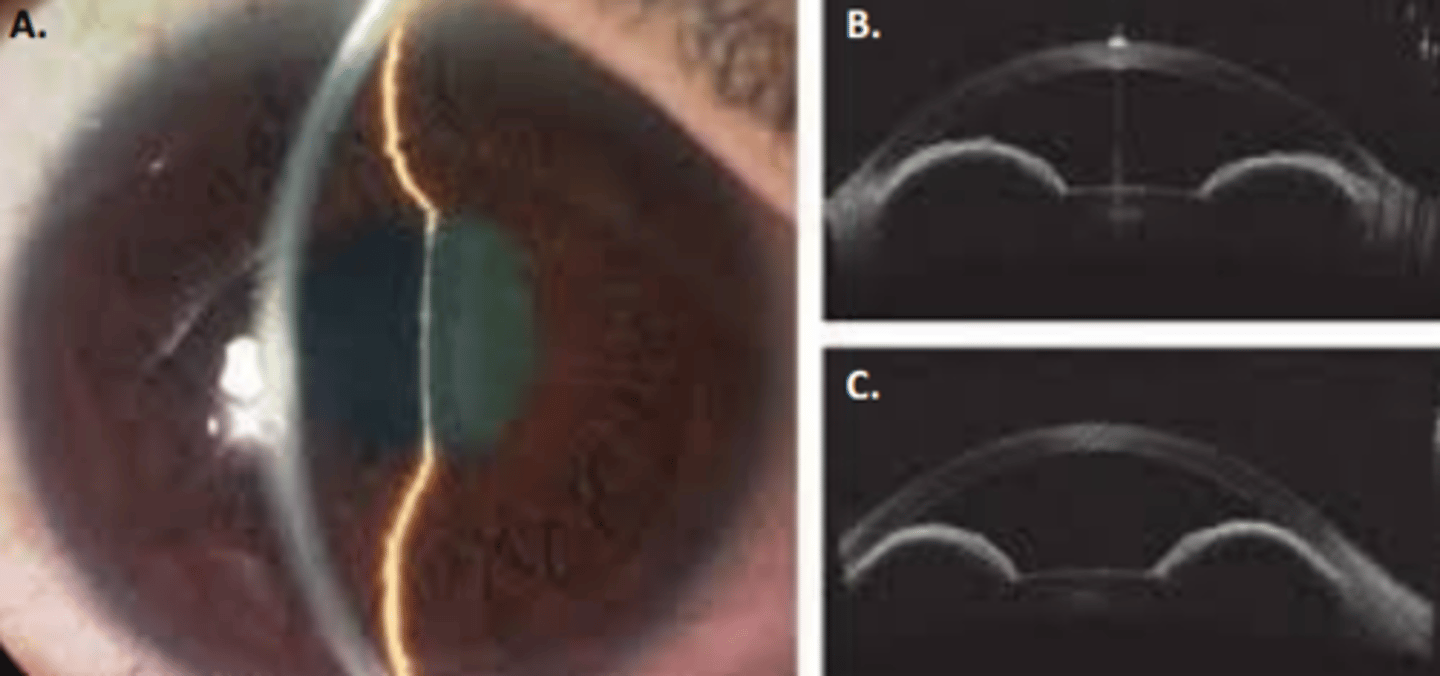
Vossius ring cataract
cataract formed due to pigment deposition on the lens. Seen in uveitis.
Posterior subcapsular cataract
cataract seen in uveitis caused by nutrient deprivation, toxic response to inflammation, and/or steroid use.
decreased
Acute uveitis usually results in a (increased or decreased) IOP in the affected eye. This is because the production of aqueous by the ciliary body is compromised due to its inflammation.
increased
An acute (increased or decreased) IOP may be seen in uveitis due to blockage of the trabecular meshwork, synechiae, iris bombe, neovasculariztion, etc. This is seen in early uveitis caused by herpetic disease, Posner-Schlossman syndrome, UGH syndrome, and syphilitic disease.
-herpes
-syphilis
-UGH syndrome
-Posner Schlossman syndrome
four conditions associated with an early, acute IOP elevation in uveitis. Otherwise, acute uveitis presents with an initial decrease in IOP.
prostaglandin analogs
If a patient experiences an IOP elevation secondary to steroids use in the treatment of uveitis, a drop used to decrease IOP should be added, but _____ should be avoided.
Anterior uveitis
uveitis involving the anterior chamber. Accounts for 50-90% of cases
Posterior uveitis
uveitis involving the retina or choroid. Accounts for 25% of cases
Panuveitis
uveitis involving the anterior chamber, vitreous, retina, and choroid. Accounts for 15% of cases
Intermediate uveitis
uveitis involving the vitreous. Accounts for 10% of cases
Acute
uveitis that has a sudden onset with limited duration
Recurrent
uveitis that has repeated episodes separated by periods without inflammation that are at least 3 months
Chronic
uveitis that has repeated episodes of inflammation separate by periods without inflammation that are less than 3 months
Unilateral alternating
uveitis where either eye is affected, but only one at a time. Attacks are episodic and recurrent
Bilateral asynchronus
uveitis where the onset does not occur in both eyes at the same time, but inflammation of the second eye occurs before the first eye is resolved. Disease course is typically chronic.