Cell theory
5.0(2)Studied by 16 people
Card Sorting
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Cell division, sexual vs. Asexual reproduction,
Last updated 6:09 PM on 1/29/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
1
New cards
Cell meaning
A cell is the simplest form of life that can live and function independently. Molecules and atoms do not show the 7 functions that living organisms do. Every living organism I made of one or more cells. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function. All cells arise from pre-existing cells.
2
New cards
Cell division meaning
process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells
3
New cards
Reasons cells divide
* Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in size
* Repair damaged tissue (nerve cells cannot be repaired)
* If cells get too big, it cannot get enough nutrients into the cell and wastes out of the cell
* Repair damaged tissue (nerve cells cannot be repaired)
* If cells get too big, it cannot get enough nutrients into the cell and wastes out of the cell
4
New cards
Differentiation meaning
the process by which cells, tissue, and organs acquire specialized features, especially during embryonic development.
5
New cards
Totipotent Cell meaning
Potential to be any type of cell. (blank slate)
6
New cards
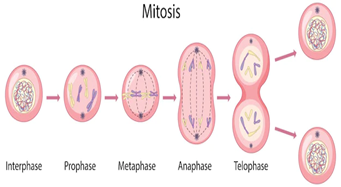
Mitosis stages
Interphase
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
7
New cards
Interphase (mitosis)
step 1: when the cell becomes bigger
8
New cards
Prophase (mitosis)
Step 2: the cell makes protein. DNA doubles
9
New cards
Metaphase (mitosis)
Step 3: DNA (chromosomes) line up in the equator (center)
10
New cards
Anaphase (mitosis)
step 4: spindle fibers pull & split chromosomes
11
New cards
Telophase (mitosis)
step 5: cytoplasm divides (Cytokinesis)
12
New cards
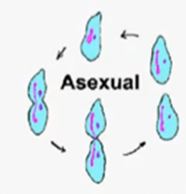
Asexual reproduction factors:
* Requires only 1 parent
* Offspring have 100% the same chromosomes as the parent
* Clones
* Most unicellular organisms reproduce this way
* Mitosis
* Offspring have 100% the same chromosomes as the parent
* Clones
* Most unicellular organisms reproduce this way
* Mitosis
13
New cards
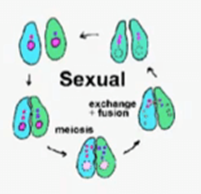
Sexual reproduction factors
* Requires 2 parents
* Not identical to the parents
* The offspring has chromosomes from both parents
* Most multicellular organisms reproduce this way
* Meiosis
* Not identical to the parents
* The offspring has chromosomes from both parents
* Most multicellular organisms reproduce this way
* Meiosis
14
New cards
All cells have:
* Ribosomes
* Cytoplasm
* DNA (chromosomes)
* Cytoskeleton
* Cell membrane
* Cytoplasm
* DNA (chromosomes)
* Cytoskeleton
* Cell membrane
15
New cards
Ribosomes
They make protein for use by the organism
16
New cards
Cytoplasm
It is a fluid material within the cell
17
New cards
DNA (chromosomes)
(Deoxyribonucleic acid)
Genetic material
Genetic material
18
New cards
Cytoskeleton
Internal framework of the cell
19
New cards
Cell membrane
Outer boundary, some things can cross the cell membrane
20
New cards
Living system characteristics
MRSGREN
Movement
Respiration
Senses
Growth
Reproduction
Excretion (Co2, urine, sweat)
Nutrition
Movement
Respiration
Senses
Growth
Reproduction
Excretion (Co2, urine, sweat)
Nutrition
21
New cards
Examples of unicellular organisms
Bacteria, fungi, yeast
22
New cards
The organizational hierarchy of organisms
Cells → tissue → organs → organ systems → orgnisms
23
New cards
Tissue
A group of cells in the body that perform the same function. i.e. bone marrow
24
New cards
Organs
Part of an organism with a specific function, made up of tissue. i.e. skin, heart, brain
25
New cards
Organ system
An organ system is composed of a group of organs that work together to accomplish one or multiple functions. i.e. digestive system, cardiovascular system, pulmonary system…
26
New cards
Organism (multicellular)
An organism is composed of multiple organs systems that work together to function as an individual entity.
27
New cards
Cellular membrane
The cellular membrane is the boundary that controls what enters or leaves the cell. It separates the inside from the outside. What goes in (O2, glucose), what comes out (CO2, waste). All cells have a cell membrane. It surrounds the cytoplasm.
Explore top notes
Personality 210 Psychology Notes (Part 3) Continuing Traits and Trait Traditions
Updated 1344d ago0.0(0)
Personality 210 Psychology Notes (Part 3) Continuing Traits and Trait Traditions
Updated 1344d ago0.0(0)