AP world unit 7 1900- present ish
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
key themes, takeaways, continuity and changes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms

The shifting of state power after 1900
decline of the ottoman empire and their reforms: secularization of schools and law codes, establishment of political elections, imposition of turkish language (Turks took over)
Russian empire (Russian Revolution: russian revolution overthrew the Romanov dynasty leading to the creation of the Soviet Union and the rise of communism (1917)
Qing Dynasty problems:
Taiping rebellion: put down by Qing authorities, cost of millions of lives, loss of opium wars, loss of sino-Japanese war (no match for industrialized Japan)
boxer rebellion
Mexican Revolution: a decade-long conflict that resulted in significant political, social, and land reforms. This then led to the establishment of a constitutional republic
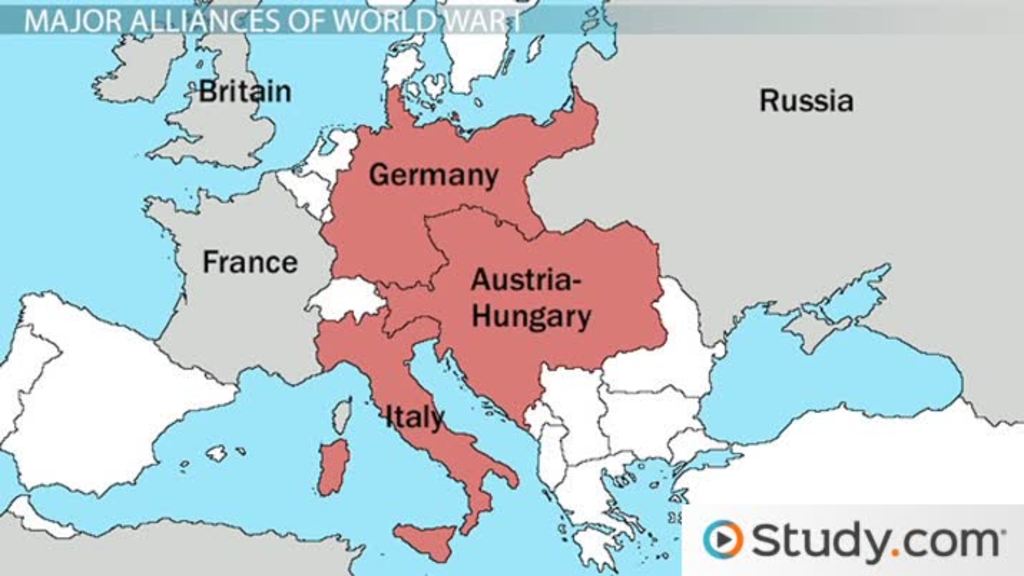
Main causes of WWI
militarism: the buildup of military forces and arms races creating an atmosphere of tension. (ex. Germany's powerful military)
the alliance systems 2 major alliances:
triple entente and the triple alliance
dragged other nations into regional conflict (the buddy system)
imperialism and its effects- competition for colonies and global dominance led to rivalries (specifically Germany and other European powers like Britain and France)
nationalism- intensified the desire for independence among various ethnic groups
assassination: the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria in 1914 acted as the immediate trigger for the war, leading to declarations of war among the major powers.
note: Nationalism caused the assassination and ensured the anger about it and because Serbia was aligned with Russia, Austria Hungary was aligned with Germany, Russia was aligned with Britain and France, and Germany was aligned with France this caused to alignment system "blowing up"

How WWI was fought (4 years long)
Total war
governments using propaganda to motivate people to fight in the war
new military technologies made WWI extremely deadly (machine guns, tanks, chemical gas)
Trench warfare: a combat method characterized by soldiers fighting from deep ditches, leading to stalemates and high casualties.
calling colonial states to fight in the war (they did it expecting to be free after the war)
The war ended because of the treaty of Versailles, which imposed harsh penalties and reparations on Germany.
poison gas

global economy during wars
Germany: due to war dept Germany printed excessive amounts of currency resulting in hyperinflation. (exchange was 1 usd = 4.2 trillion german marks)\
global debt cycle: U.S. lent money to Germany to pay reparations which were then used by Britain and France ot pay war debts back to the U.S., creating a fragile economic interdependence
Russia's new economic policy: made by Vladimir Lenin, instituted in 1923, introduced some limited free market principles
After Lenin's death Joseph Stalin took over, allowing him to create a 5 year plan
The Great Depression

The Great Depression (1929-1939)
Stock market crash led to a global economic downturn
global impact: countries worldwide experienced economic contraction, rising unemployment, and famine
decline in trade: nations adopted tariffs, and protectionist policies, leading t a decrease in international trade
causes:
stock market crash
bank failures and loss of savings
overproduction and declining demand
decline in international trade and agricultural collapse

unresolved tensions after WWI
European and the Japanese maintained their colonial holdings and the interwar period and in some cases gained colonial territory as a result of the war
republic of turkey was established after the war
Woodrow Wilson: "states have the right to govern themselves:
Mandate system:
class C: smallest population and least developed, treated as colonies, several islands in the Pacific took this position, Class B: larger populations but still under developed, most of Germany's colonies in africa fall under this class , Class A: large populations and had sufficient developments

Unresolved tensions after WWI pt.2
Japan expands: got an empire (invaded Manchuria)
colonial resistance:
indian national congress:
formed before the war to petition the British government for better portion of rule in India
formation of the African national congress - founded in South Africa by Western educated lawyers and journalists and dedicated itself to obtaining equal rights for colonial subjects in South Africa (influenced by pan africanism)

The causes of WWII
WWI Grievances:
Italy: Bitter because they did not receive promised land grants
Germany: required reparations payments ruined their economy, forced demilitarization (made them vulnerable), War guilt clause: Germany forced to accept entire blame for the war
continued expansions
economic crisis (Great Depression- famine , poverty)
rise in facisits (Italy, Germany)
Hitler's Invasions

Hitler polices
cancel reparations payments
remilitarize Germany rebuild military strength and expand territory
territorial expansion
get rid of all races (except "Ariaen Race"")

How WWII was fought
alliances:
Fascists (Italy, Germany, Japan)
Allied Powers (UK, USA, USSR, France)
Note: USSR was not involved in the war until Japan bombed Pearl Harbor
Mobilization
WWII propaganda: used to demonize enemies and get civilians to want to fight in the war
Ideologies of WWII:
Fascism vs. Democracy
Totalitarianism vs. Liberalism
communism
Repressions of basic freedoms
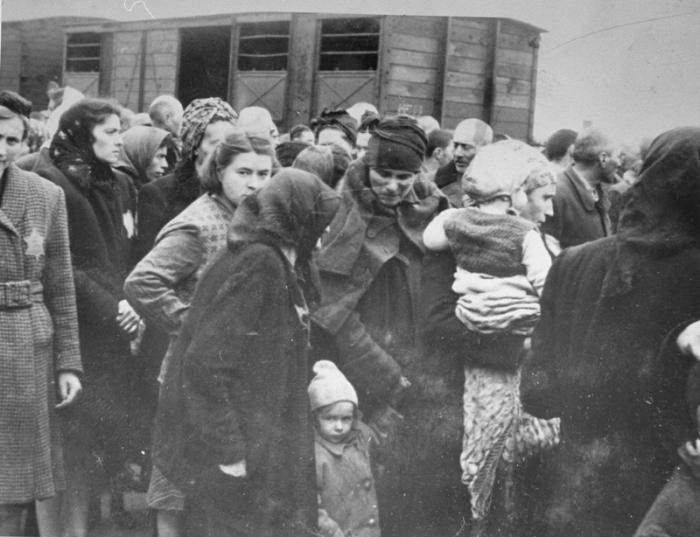

mass atrocities in the 20th century
causes:
two world wars
-about 120 million deaths
-50% were civilians
new tech (firebombing, atomic bombs)
racial genocide
the armenian genocide: systematic extermination of Armenians by the Ottoman Empire during World War I, resulting in the death of approximately 1.5 million people.
The holocaust:the genocide of six million Jews and millions of others, orchestrated by Nazi Germany during World War II.
the cambodian genocide:systematic killing of approximately 1.7 million people by the Khmer Rouge regime in Cambodia between 1975 and 1979.
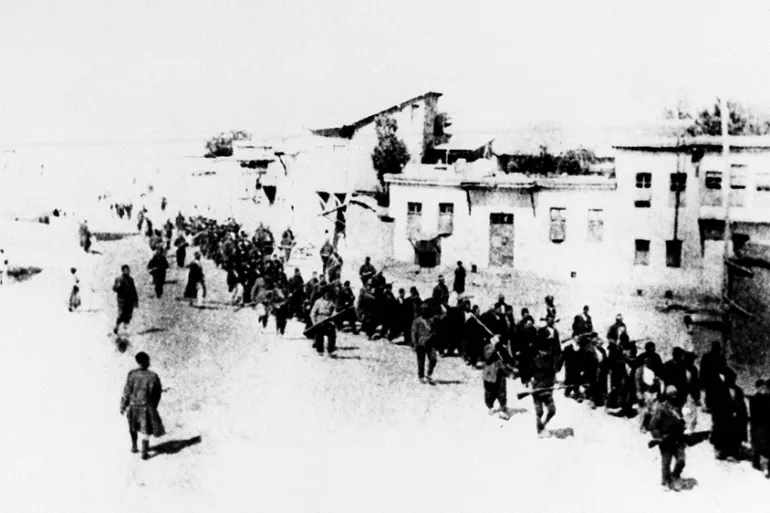

vocab
Total war: a war which requires the mobilization of a country's entire population both military and civilian to fight
War propaganda: often motivated people to fight in the war as well as demonizing the enemy
5 year plan: a government program in the Soviet Union designed to industrialize the economy and increase production through centralized planning.
holodomor: famine in Soviet Ukraine caused by the policies of the government, leading to the death of millions.
Mandate system: Middle Eastern territories would become mandates administered by the League of nations
Fascism: extreme nationalism authoritarian leadership , and militaristic means to achieve its goals
more vocab
fascism: the glorification of the state, the use of militaristic means, serves the interests of the states
communism: soviet economy , rapid industrialization through 5 year plans, brutal and unflinching demands
democracy: Propaganda dubbed it a "People's war", government promised expansion of welfare
continuity and change
change:
by the end of the century many of their maritime and land-based empires would fall apart and give rise to new states
the war continued the difficulties of industrialization which then led to the Russian Revolution (led by Vladimir Lenin leader of the political group called the Bolsheviks)
preparation for WWII similar to preparation for WWII difference is the casualties, death, and weapons