OB Exam Review
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
139 Terms
How is the estimated due date calculated?
Nageles Rule:
First day of LMP - 3 months + 7 days + 1 year
Know how to do GPA classifications
Gravida = # times pregnant
Para = # of births
Subcategories of para:
Full term
Premature
Abortions
Living children
How many para do twins count as?
One
Ex: first time pregnant mother gave birth to twins full term
G1 P1002 (2 for 2 kids)
At how many weeks is the fundal height palpable
8 weeks
At how many weeks does the fundus become an abdominal organ
12 weeks
At how many weeks is the fundus at the umbilicus
20 weeks
At how many weeks does the uterus decrease in fundal height
36-40 weeks (baby "drops")
At how many weeks is the fundus at the midpoint between pubic symphysis and umbilicus
16 weeks
At what weeks will the fundal height correlate with gestational age
26-34 weeks
When would you go with the ultrasound gestational age vs LMP?
US > 1 wk off than LMP in first trimester
US > 2 wks off than LMP in 2nd trimester
US > 3 wks off than LMP in 3rd trimester
What is Leopold's first maneuver used to determine?
Superior side:
- consistency
- shape
- mobility
What is leopolds second maneuver used to determine?
direction the back is facing
What is leopolds third maneuver used to determine?
What part of the fetus is at the inlet
What is leopolds 4th maneuver used to determine
Degree of fetal extension into pelvis
What screening is done to screen for chromosomal abnormalities? When is it done?
MaterniT21 btwn 10 and 20 weeks
T/F MaterniT21 can evaluate neural tube defects
FALSE
when is the Maternal Serum alpha fetoprotein test performed? What does it look for?
15-21 weeks
Looks for risks of neural tube defects
When is the simple glucose challenge test (GCT) done?
24-28 weeks
What should you do if the simple GCT is positive?
+ if >140 1 hr post 50 g of glucose
Do 3 hr hour GTT if +
When is group B strep screened for during pregnancy?
Vaginal swab @ 35-37 weeks
Tx w/ penicillin if +
What are the trimesters?
1st -> conception to 12 weeks
2nd -> 13 - 28 weeks
3rd -> 28 weeks to delivery
What vaccines should not be given during pregnancy?
LIVE:
- MMR
- Yellow fever
- BCG
- Varicella
- Oral polio
What vaccines SHOULD be given in pregnancy? When?
Flu: flu season
Tdap: 27-36 weeks
What vitamin should be started prenatally to avoid neural tube defects?
Folate
What samples are collected in integrated screening
2 blood samples: one from 1st trimester and one from 2nd
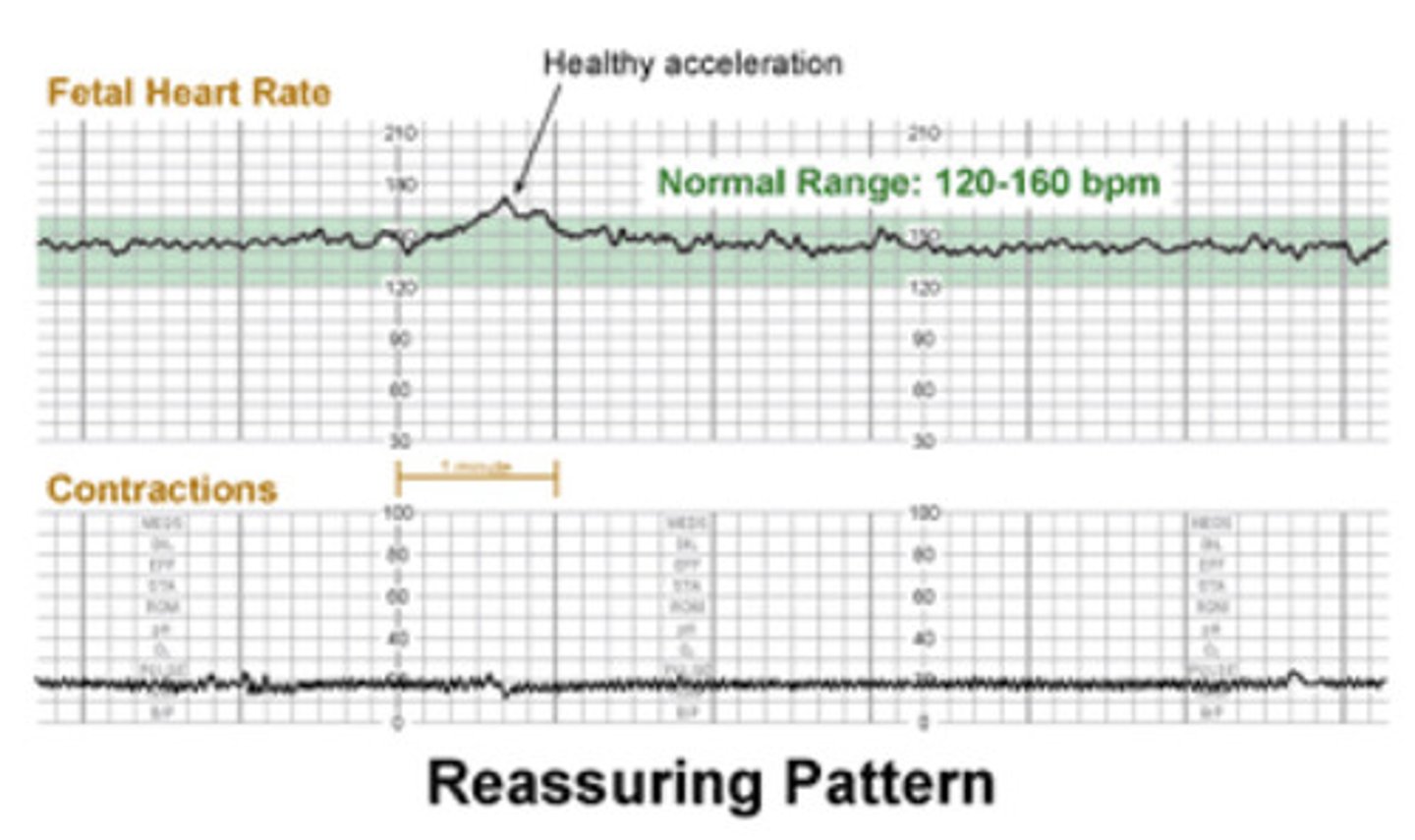
What is a normal fetal HR and what does it look like on a NST
120-160
Normal: small squiggles
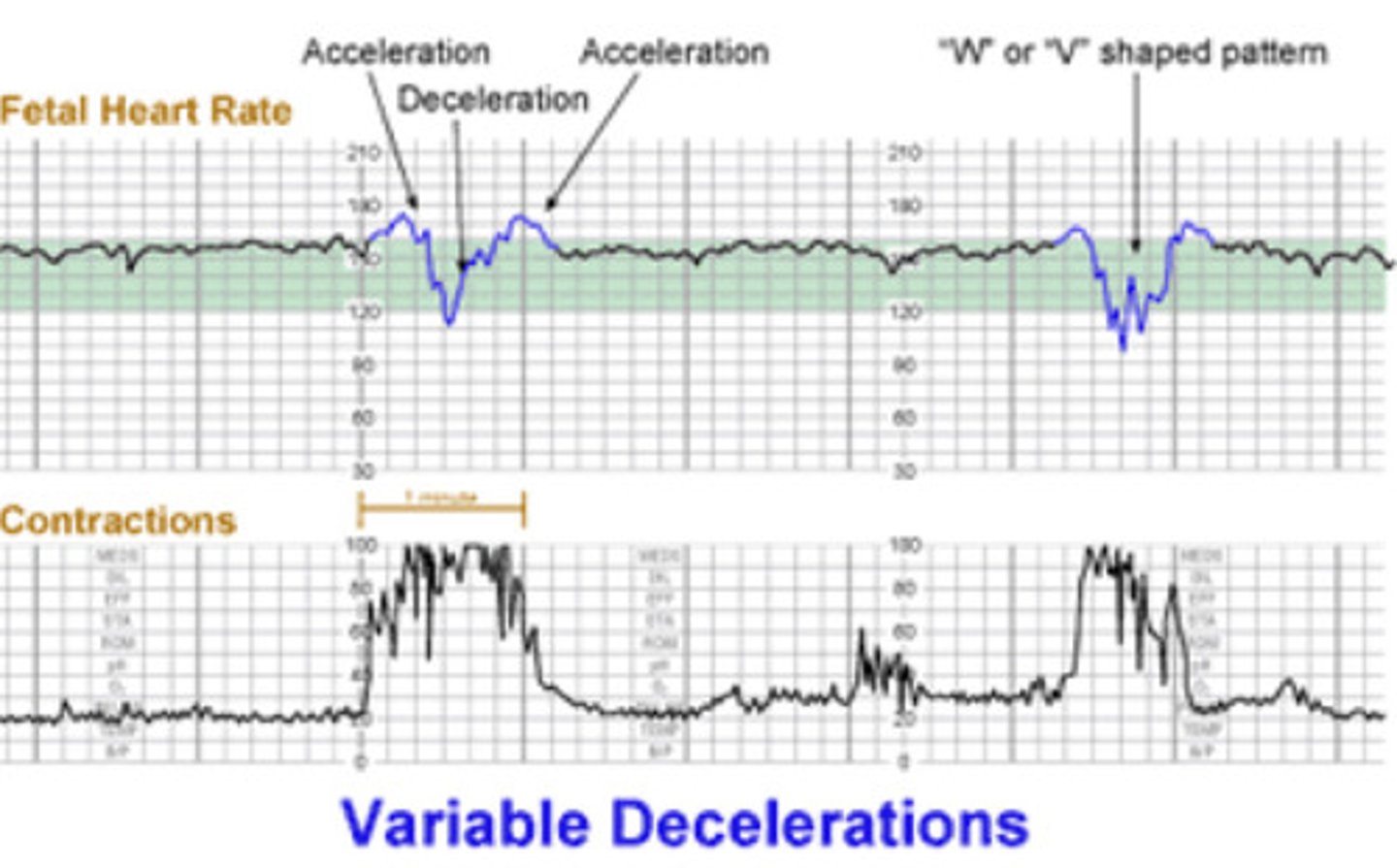
What do decelerations look like on NST?
Drops/ V or W pattern
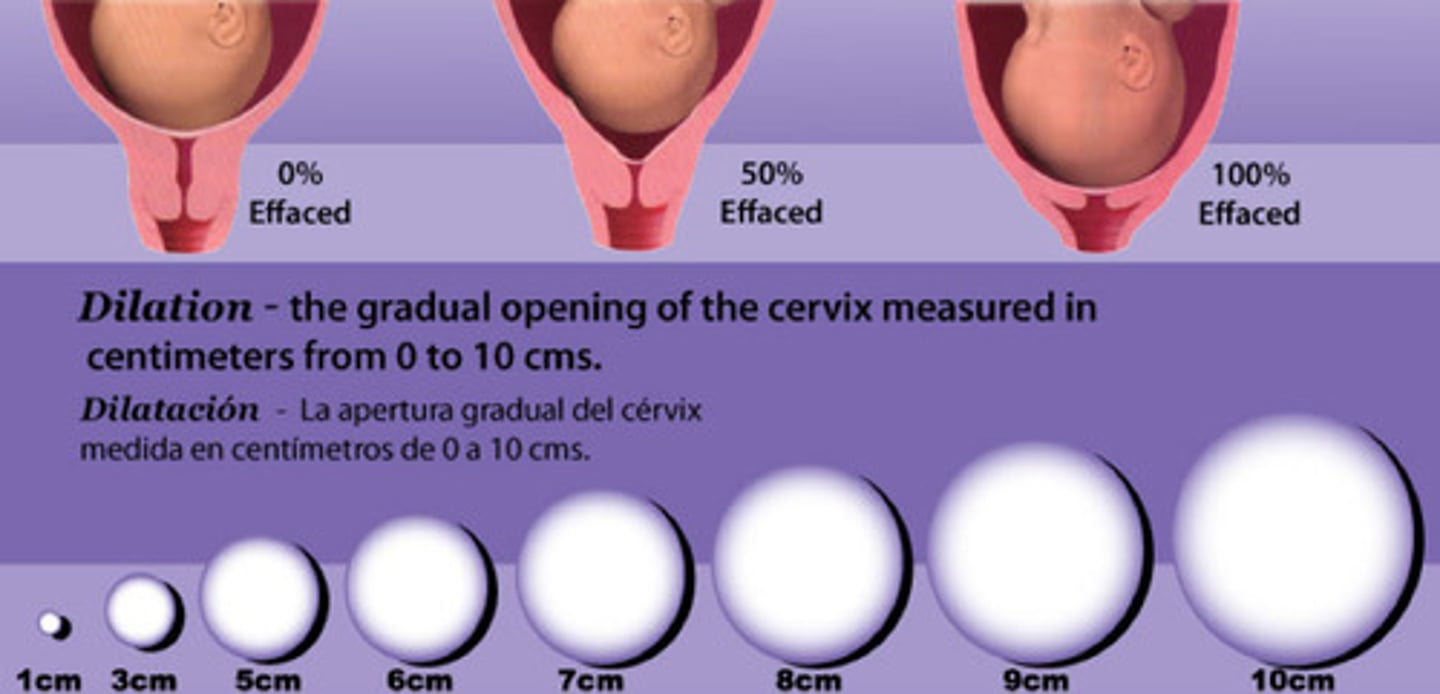
Effacement vs Dilation
Effacement: shortening of the cervix (%)
Dilation: diameter of the os (in cm)
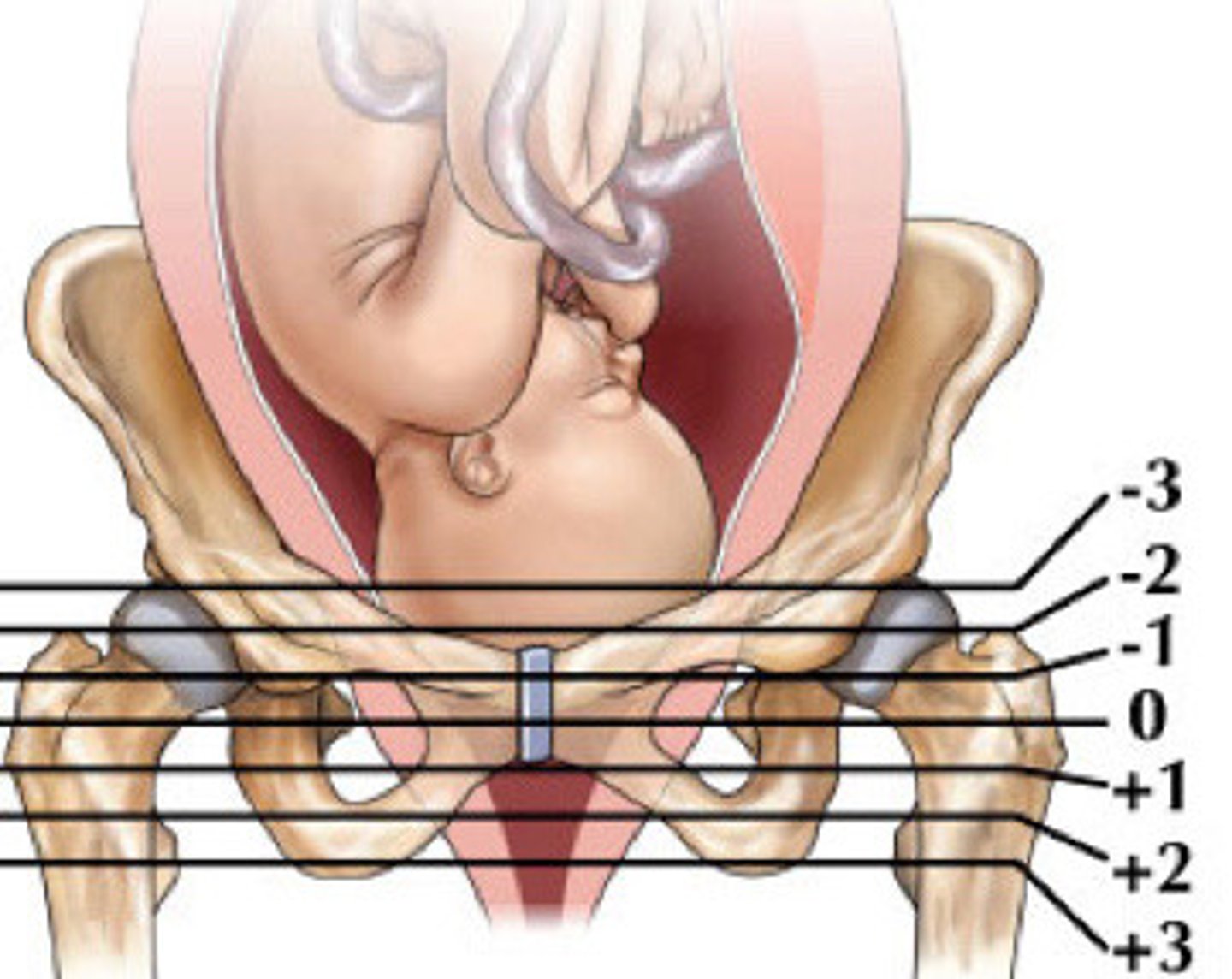
What is the distance of the fetus in relation to the ischial spines called?
Station, measured in cm
What does the umbilical arteries and vein carry
Arteries: deoxygenated blood to placenta, from baby
Vein: oxygenated blood to baby, from placenta
How does estrogen affect cortisol levels
Increases plasma cortisol levels
What happens to GFR levels, CrCl, plasma renin and angiotensin levels during pregnancy
Increased
What happens to BUN, serum creat, and uric acid levels during pregnancy
Decreased
T/F: pregnancy can crease respiratory alkalosis d/t mild hyperventilation
TRUE
Dec CO2, Inc pH
when is DVT risk the highest during pregnancy?
Delivery - 6 weeks postpartum
What hormone is responsible for inc risk of cholelithiasis in pregnancy
Estrogen
Progestin causes cholestasis
What hormones are responsible for insulin resistance during pregnancy
-Resistin
-human placental lactogen
-cortisol
-estrogen
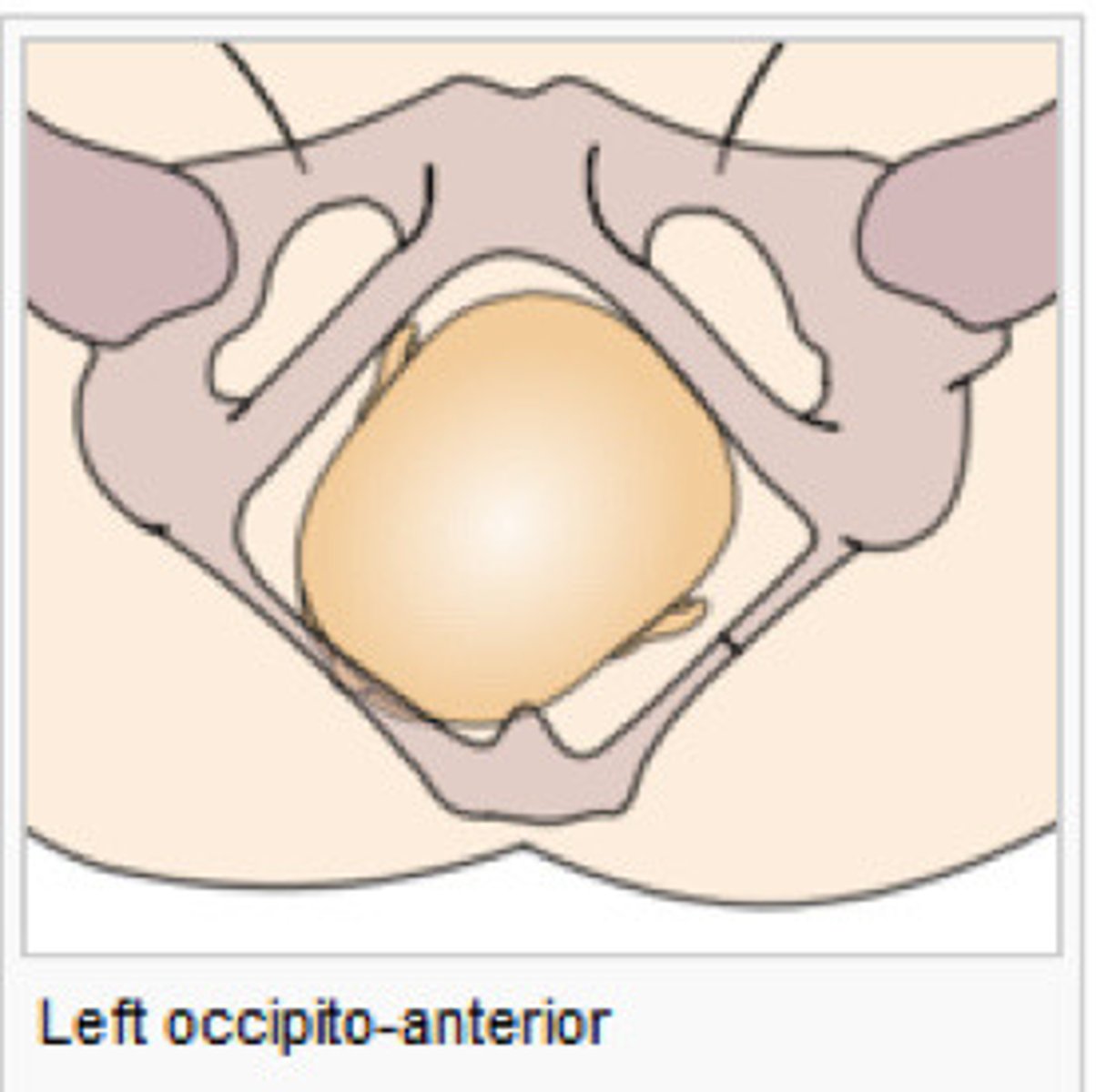
MC cephalic presentation
Left occipital anterior (LOA) vertex
(Baby is looking down to the right)
Cardinal Movements of labor
ED FIRE REx
Engagment
Descent
Flexion
Internal Rotation
Extension
Restitution (external rotation)
Expulsion
4 degrees of perineal tears
1st: skin/mucosal break
2nd: submucosa
3rd: anal sphincter
4th: through sphincter, into rectal mucosa
MC risk of shoulder dystocia
Macrosomic (big) babies (GDM)
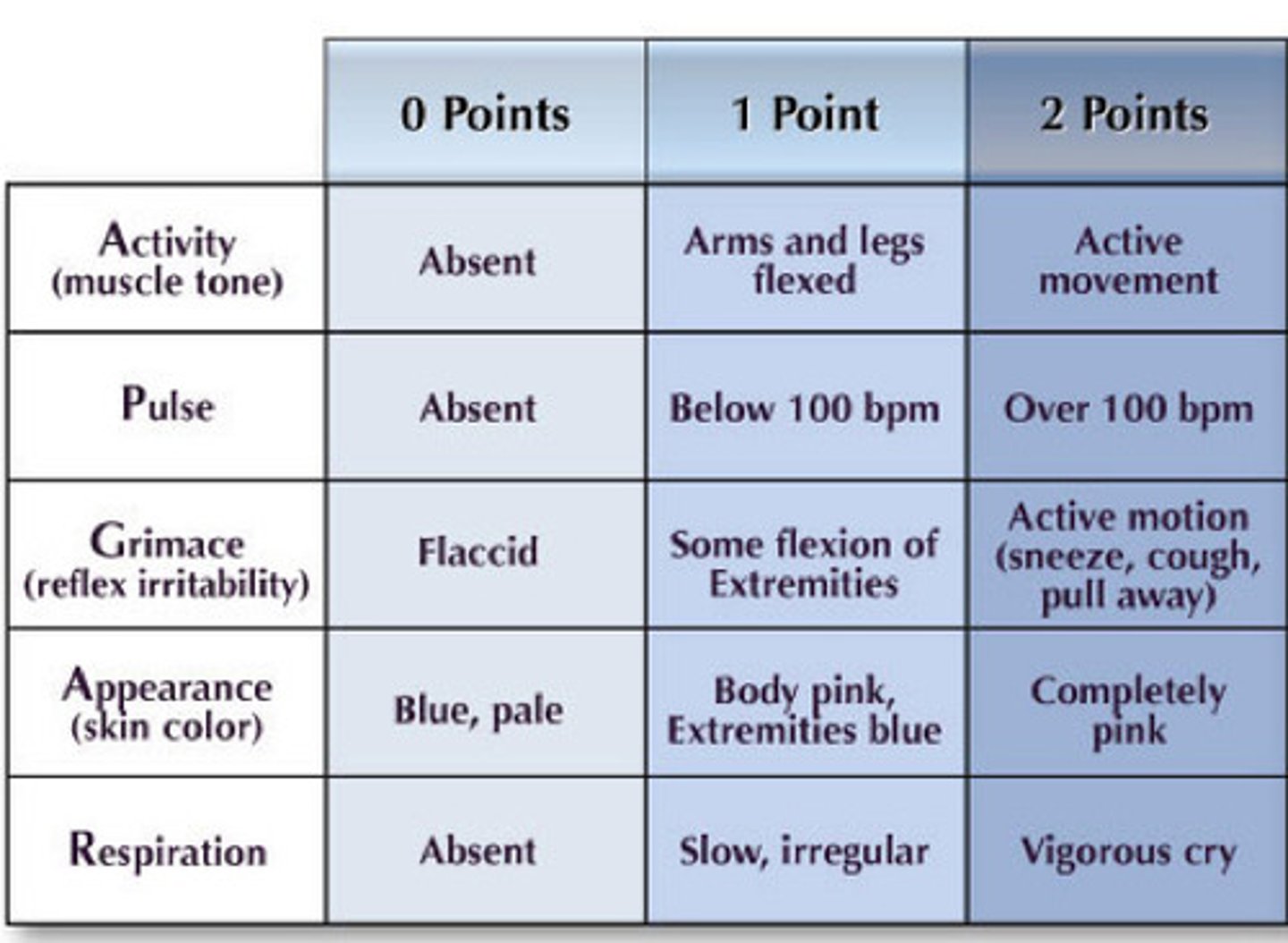
APGAR scoring
What are the universally mandated newborn screenings
PKU and hypothyroidism
Routine newborn prophylaxis
Silver nitrate & erythromycin for gonn/chlamydial blindness
Hep B vax
Screen for bilirubin if jaundice
MCC of excessive postpartum bleeding
uterine atony
Contraindications to breastfeeding
- HIV, CMV, areolar HSV
- galactosemia in infant
- maternal need for CI drug
+/- Hep B/C
First line rx for BV and trichomonas
Metronidazole
BV is after 1st trimester
First line rx for syphilis
PCN
First line rx for chlamydia / gonorrhea
Chlamydia: azithromycin (NO DOXY IN PREG)
Gonorrhea: Rocephin
First line rx for HSV
Oral suppressive therapy at 35-36 weeks
C-Section if active lesions
First line rx for candidiasis
Miconazole cream
What is considered chronic HTN in pregnancy
BP > 140/90
Before 20 wks or after 20 wks x 12 wks PP
Treatment of choice for chronic HTN
Methyldopa
What is considered gestational HTN
140/90 after 20 weeks but NORM within 12 weeks PP
What is considered pre-eclampsia? How to dx?
BP >140/90 + proteinuria on UA dipstick / 300 ml per day
How to treat severe preeclampsia or eclampsia
Hydralazine + Mg sulfate + delivery
Lorazepam for seizures in eclampsia
BP goal in preeclampsia
BP < 160 / 105-110
BP > 160/110 = severe preeclampsia
What is HELLP syndrome?
Hemolysis
Elevated LFTs
Low Platelets
>> can result in DIC
What is considered eclampsia
Preeclampsia + seizure / coma
Best dx for eclampsia
24 hr urine (protein)
>300mg mild
>5g severe
Causes of gestational diabetes
-human placental lactogen
-cortisol
-human GH
RF of developing gestational DM
Excessive weight gain
FMHx
Prior baby >9 lbs
Maternal and fetal risks of gestational DM
Maternal: inc risk for T2DM
Fetal: shoulder dystocia
GS dx of GDM
3hr GTT (100g)
Screening with 50g OGTT @ 24-28 wks
Management of GDM
Class A1: diet
Class A2: insulin IF...
- FBG >100
- post prandial glucose >140
What increases risk of transmission of GBS
-prematurity
-maternal fever intrapartum
-prolonged membrane rupture
-PMHx of GBS
Prevention of GBS
Swab @ 36-37 wks
PCN / AMP @ delivery if +
What fetal infections can occur if GBS is transmitted
Meningitis
PNA
Sepsis
Presentation of congenital rubella
Deafness
Vision impairment
Neuro / cardio defects
Mental retardation
Microcephalic
2 day old infant presents with microcephally, failed the hearing test, and a purple maculopapular rash. What was most likely transmitted to the baby and how do you treat?
CMV
Tx with ganciclovir
Fetal risks of varicella infection
Limb hypoplasia
Cutaneous scarring
Mental retardation / CNS abnormalities
Transmission and treatment of toxoplasmosis
Cat poo
Tx: spiramycin +/- sulfadiazine
What can fetal transmission of parvovirus cause
Fetal hydrops d/t infected reticulocytes
Does Rh isoimmunizatoin affect the first pregnancy?
NO > IgM forms in first preg
IgG forms in second which causes erythroblastosis fetalis (RBC hemolysis)
Presentation of Rh isoimmunization
Term preg: 300 mcg RhoGAM @ 28 wks & 72 hrs of delivery
1st trimester abortion/miscarriage: 50 mcg MICRogam
What is the accumulation of fluid in 2 or more fetal compartments
Hydrops fetalis
Results in 60-90% fetal mortality
What is considered macrosomnia? What are the RF?
BW > 4000 g
RF: inc maternal BMI, excess maternal weight
What are the 4 types of teratogens?
Radiation
Pharmaceuticals
Infection (TORCH)
Chemical (metals, pesticides)
What are the known pharmacological teratogens (6)
Isotretinoin
MTX
VPA
Tetracyclines (doxy)
ACEs
Live Vaxes
7 layers of closure of a c section
1: uterus
2: uterus again (needed for future vaginal births)
3: visceral peritoneum
4: parietal peritoneum
5: fascia
6: subQ tissue
7: skin
Bold is required
Down syndrome
Trisomy 21
Edward's syndrome
Trisomy 18 (10% chance of survival)
Patua Syndrome
Trisomy 13 (10% survival)
Presents with cardiac probs
MC sex chromosomal abnormality in females
Turner's syndrome (absence of an x - 45X)
How does Turner's syndrome present
Wide set nipples
Webbed neck
Short stature
Primary hypogonadism
Jacob's syndrome presentation
Extra Y >>
Phenotypically male, underdeveloped testes and breasts, learning disabilities
Klinefelter syndrome presentation
Extra X in males >>
-gynecomastia
-micropenis
-hypergonadotropic gonadism
MCC of pregnancy related death in 1st trimester
ectopic pregnancy
MC location of ectopic pregnancy
Ampulla of the fallopian tubes
Presentation of ectopic pregnancy
- pelvic / abd pain
- AUB
- palpable mass
- cervical tenderness
- syncope / dizziness
How long does it take an ectopic pregnancy to rupture?
Isthmic: 6-8 wks
Ampullary: 8-12 wks
Interstitial: 12-16 wks (hemorrhagic)
Pt presents with high HCG levels and US reveals an empty uterine cavity... what is the most likely diagnosis?
Ectopic pregnancy
When should an intrauterine sac be visible on US
Transvag: HCG >1000
Abd: HCG 1800-3600
Treatment for stable and unstable ectopic pregnancies
stable: MTX
Unstable: emergency surgery
What is the definitive management of ectopic pregnancies
Laparoscopy
Intrauterine bleeding before 20 weeks is known as
Threatened abortion
>> no dilation of cervix
Intrauterine bleeding before 20 weeks WITH cervical dilation
Inevitable abortion
What is considered a missed abortion
Embryo dies but POC is retained
MCC of spontaneous abortion
Aneuploidy
Treatment of abortion before 20 wks
Misoprostol +/- mifepristone