biology, cell membrane
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
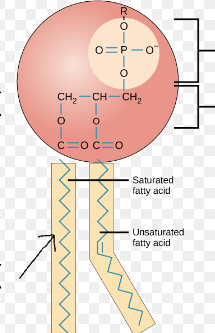
phospholipid head
polar, hydrophilic
phospholipid tail
non-polar, hydrophobic
plasma membrane
composed of a lipid bilayer, with embedded proteins and surface proteins
passive transport
does not require input of energy, moves with concentration gradient
active transport
does require input of energy, moves against concentration gradient
diffusion
movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until equilbrelum
facilitated diffusion
integral proteins help move moles that are too large
osmosis
movement of water from an area of high to low concentration through aquaporins
aquaporins
water protein channel
endocytosis
movement of materials in to the cell, low to high concentration
phagocytosis
moving food particles into the cell
pinocytosis
moving liquids into the cell
exocytosis
movement of materials out of the cell
cytolysis
swelling or bursting of cells
plasmolysis
shrinking of cells
passive diffusion
what type of trasnport?
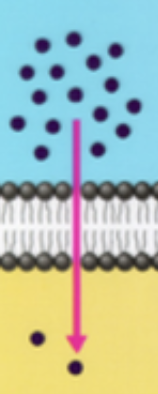
active transport
what type of transport?
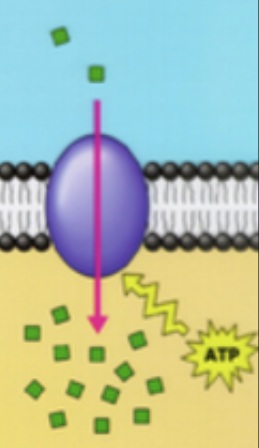
integral
what type of protein?
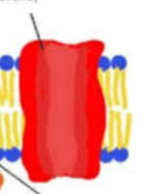
peripheral protein
what type of protein?

phospholipid head
what part?
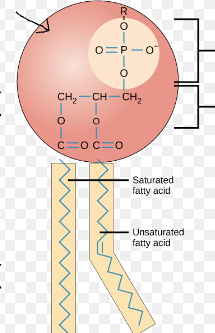
phospholipid tail
what part?
glycoprotein
name?
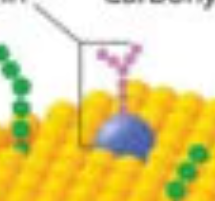
carbohydrate
name?

glycolipid
name?

cholesteral
name?

carbohydrates
allows cells to communicate with one another, helps cells identify cell types, provides sites for chemical messengers, hormones can attach
cholesterol
provides firmness and prevents membrane from freezing
sugar
what does glyco mean?
integral
proteins that extend across the membrane, moves across the membrane
peripheral
proteins that are attached to either side of the membrane, assists chemical reactions
protein channels
moves smaller molecules into the cell
protein carrier
moves larger molecules into the cell
protein pump
moves molecules out of the cell