Bio Study Guide
1/112
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
what are the 4 types of tissue
Nervous, connective, muscle, epithelial
nervous tissue
holds sensory info
connective tissue
connects, supports, protects
muscle tissue
muscles, help with movement
epithelial tissue
skin, organs
integumentary system
Made of skin protecting the body from antigens
Lymphatic system
lymph nodes in this system protect the body from disease causing antigens that make it past the skin
skeletal system
made of a variety of bones for support and protection and allow it to move
Muscular system
made of muscles, power the motion of bones and joints
respiratory system
lungs and all the tubes that bring in outside air allow the body to breathe. Gas exchange between blood and air occurs here
circulatory system
heart pumps blood through blood vessels to deliver nutrients throughout the body
Digestive system
stomach and intestines helped the body digest food, absorbed nutrients, and eliminate wastes
Urinary system
eliminates waste and uses the kidneys and bladder to maintain water balance in the body
Nervous system
Brain, spinal cord, and a network of nerves coordinate and control movement and process sensory info from the bodies environment
endocrine system
body functions are controlled and regulated by hormone secreting glands, like the thyroid
Reproductive system
each gender has appropriate organs to allow for reproduction or procreation
what are the levels of organization
cells, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
what is anatomy the study of
the human body
what is physiology
the scientific study of how living organisms function
what layers is the integumentary system made of
epidermis, dermis, subcutaneous layer
what is the epidermis made of
epithelial tissue
what is the dermis made of and what is found in it
made of connective, muscular, epithelial, and nervous tissues. Sweat glands, sebaceous glands, and hair follicles are found here
what is the sebaceous layer
under the dermis made of connective tissue; not skin but still part of the integumentary system
What does the integumentary system protect from
Antigens like bacteria, viruses, and foreign objects
What does integumentary system regulate
Temperature
What does integumentary system rid the body of
wet through sweat and sebaceous glands
how does the integumentary system warn us of pain
through touch
why does the integumentary system work with the lymphatic system
for protection
how does the integumentary system work with the nervous system
body temperature – makes a sweat or shiver
what does the skin use sunlight for
To make vitamin D which helps the skeletal system make bones in the digestive system absorb calcium
Where can hair be found
All over the body except on the palms of your hands and the soles of your feet
where is hair grown from
A hair follicle and found in the dermis
what is hair made of
Dead protein filled cells
what is melanin
pigment produced by cells in the epidermis that creates skin color
what can stimulate and produce melanin
sunlight
What are the three muscle types
Skeletal, smooth, and cardiac
What is voluntary tissue
controlled primarily by conscious thought
muscle types-size
major-large muscle
minor- small muscle
maximus- biggest muscle in a region
muscle types-shape
deltoid- triangular shaped muscles
trapezius- trapezoid shaped muscle
obliques- fibers arranged obliquely (in a slanting direction).
muscle types-function
adductor- draws in thigh
What are tendons
Extension of connective tissue surrounding muscles. Connect muscle muscles to the bone
what are muscle fibers
Have multiple nuclei and a large number of mitochondria
what is Actin
Thick filaments
what is myosin
Thin filaments
what are fascicles for
multiple together form a muscle
what is a sarcomere
The functional unit of muscle contraction
What is the role of ATP
ATP is needed for muscles to contract
A strong muscle contraction occurs when…
Many of the fibers in a muscle contract
A more gentle contraction occurs when…
Only a few of the fibers contract
Can muscles push?
no, muscles can only pull, they cannot push
What is oxygen debt
Additional need for oxygen resulting from strenuous activity
why do you become out of breath when you exercise
Reduction of oxygen in muscle cells
what are antagonistic pairs
One muscle or group of muscles pull in one direction, while another group pulls in another direction
How does the muscle system work with the respiratory system
Supplying muscles with oxygen
how does the muscle system work with the digestive system
supplying glucose to make ATP
how does a muscle system work with the integumentary system
Reaction to cold
how does the muscle system work with the nervous system
Properly functioning
what is Arrector pili
attached to hair follicles and contract, causing goosebumps
Why do goosebumps form
To an additional degree of insulation
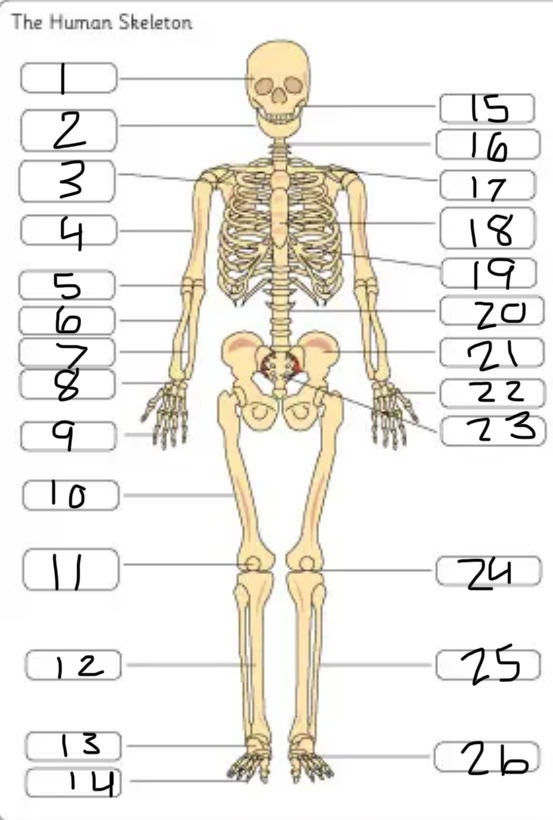
what is #1
the cranium
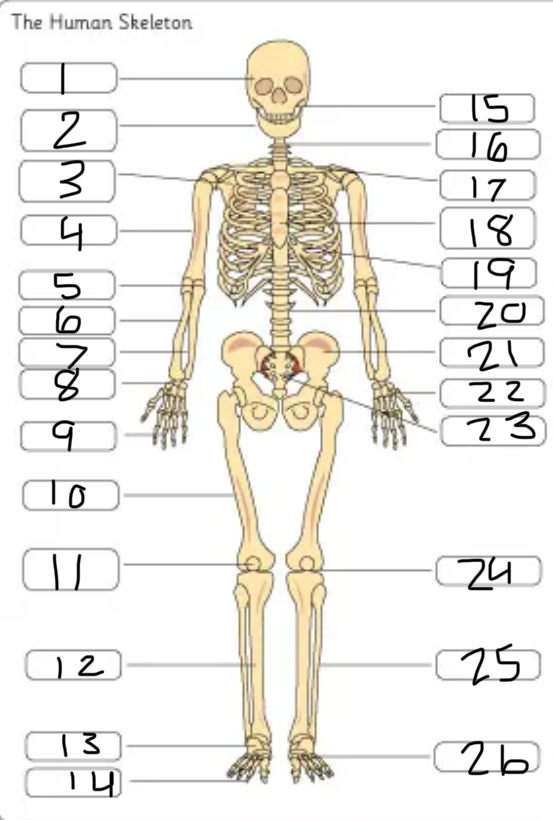
what is #2
the mandible
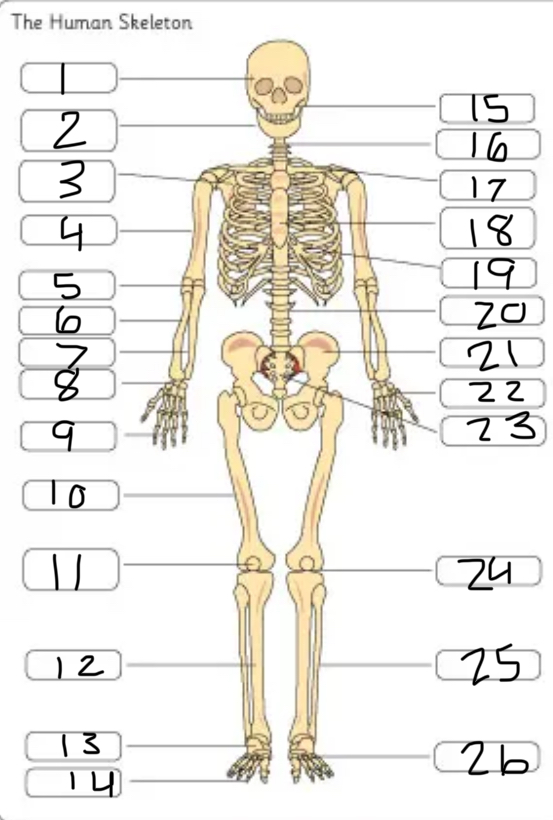
what is #3
the scapula
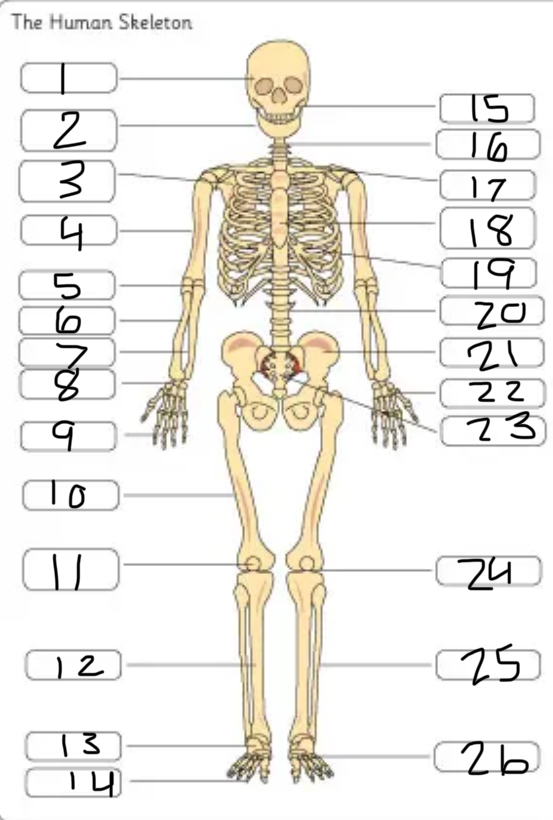
what is #4
the humerus
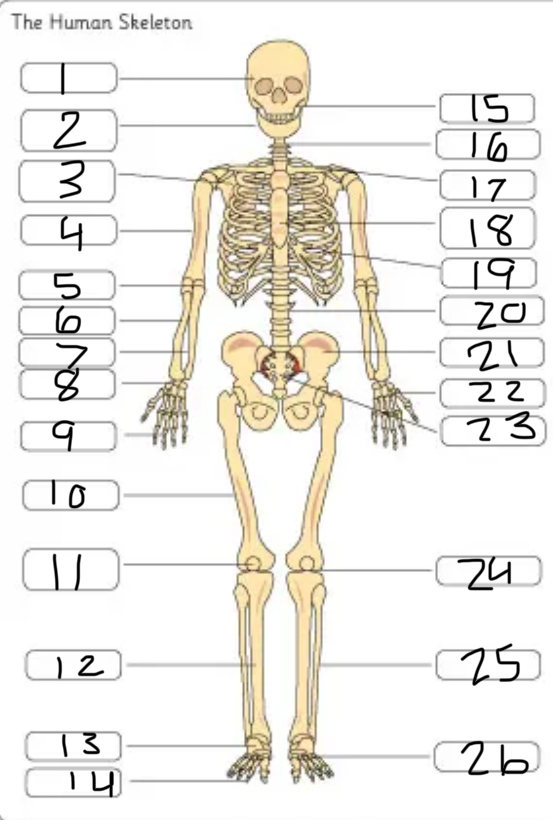
what is #6
the radius
what is #7
the ulna
what is #9
the phalanges
what is #10
the femur
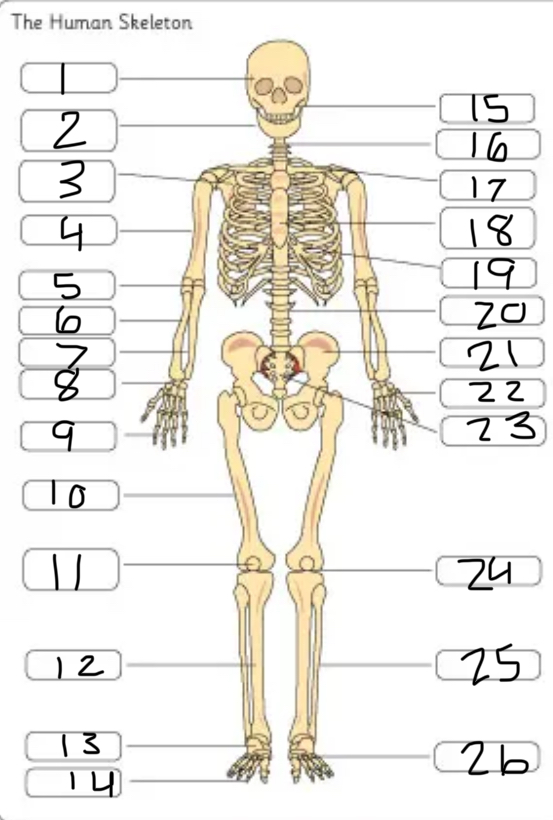
what is #11
the patella
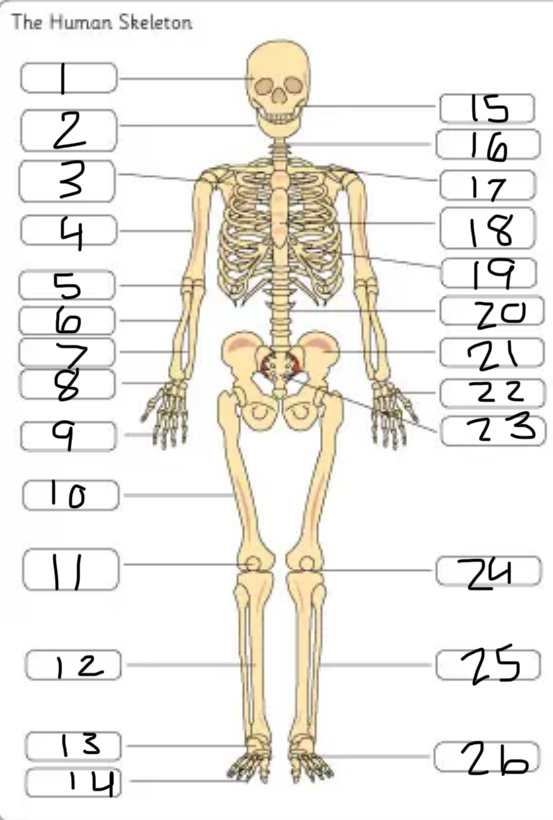
what is #12
the tibia
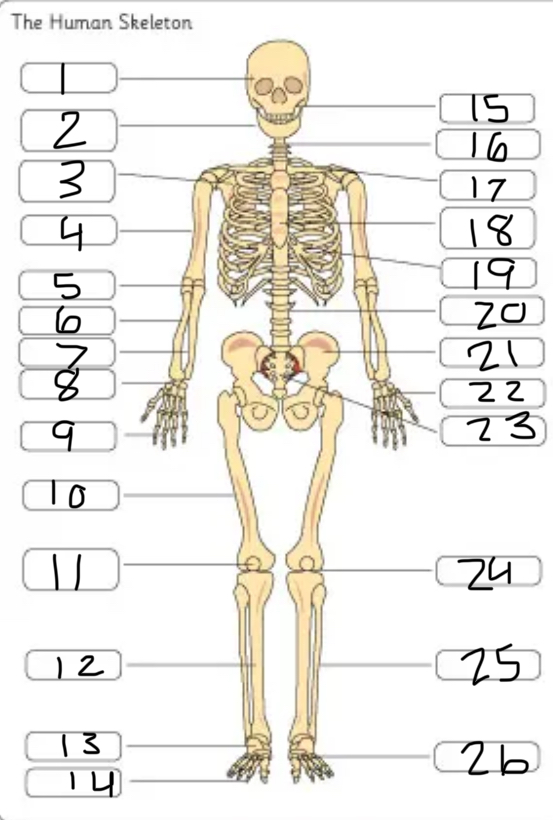
what is #13
the tarsals
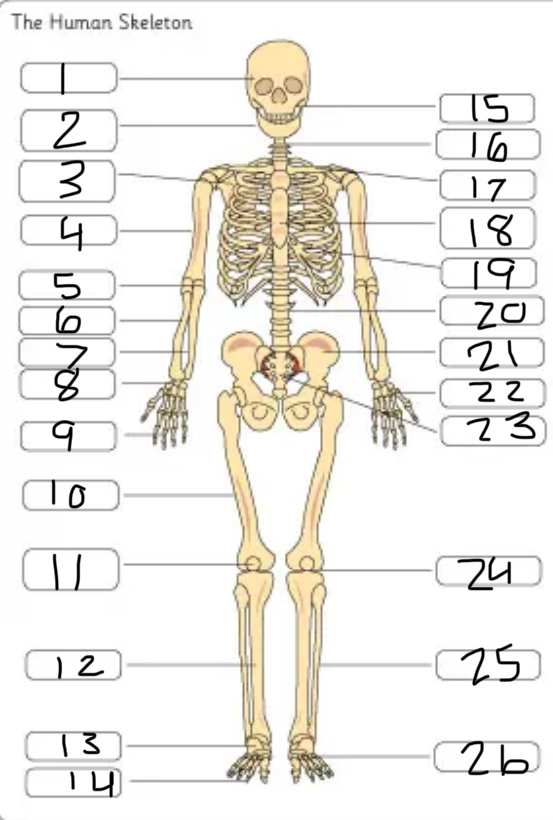
what is #14
the phalanges
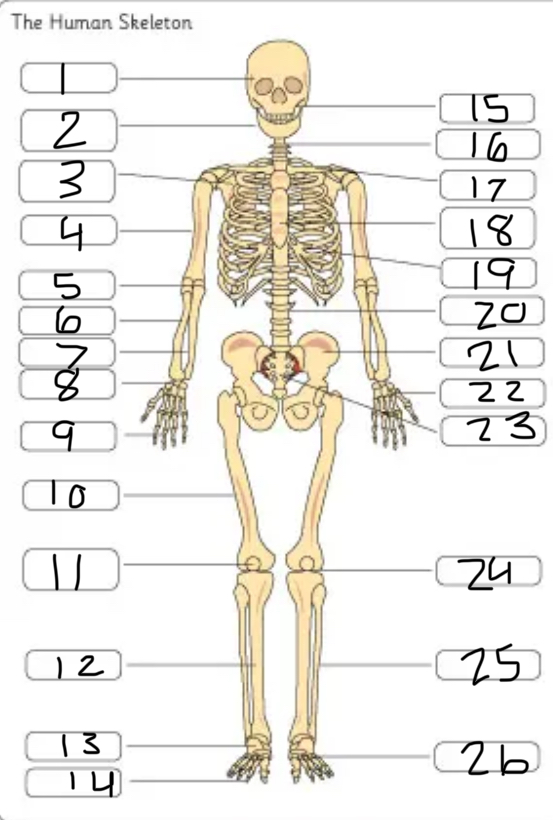
what is #17
the clavicle
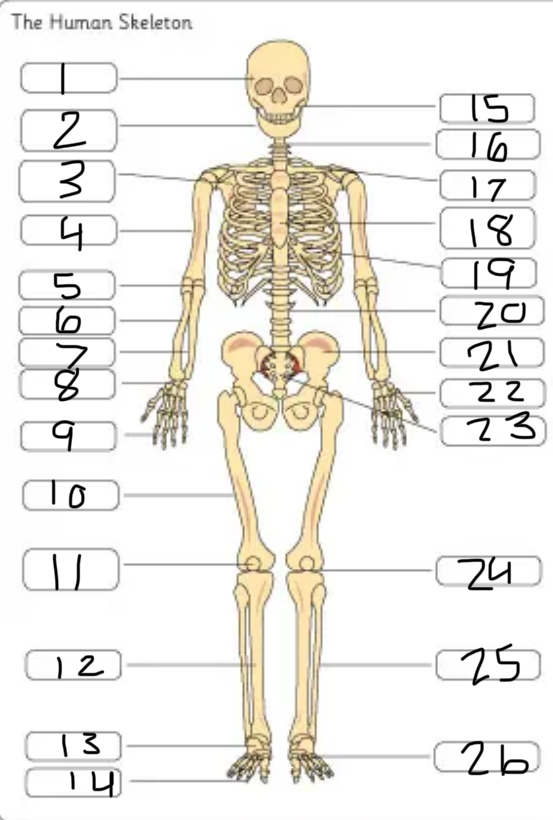
what is #18
the sternum
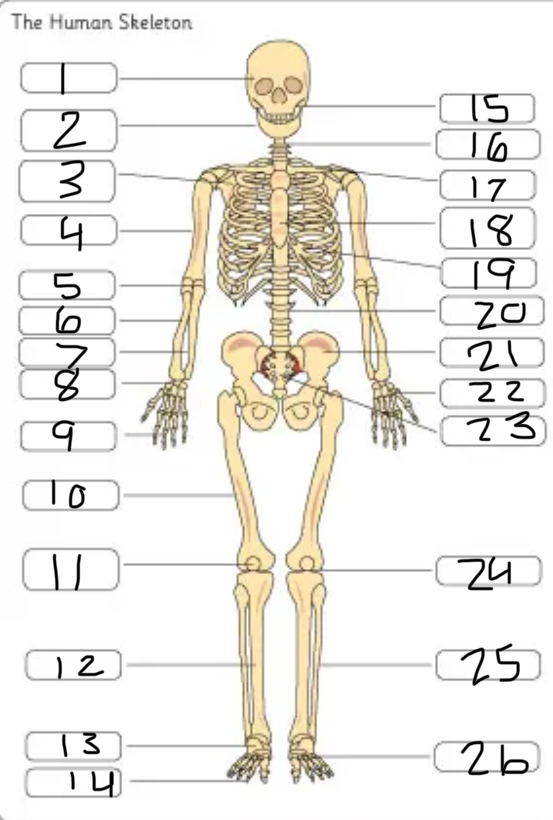
what is #19
the ribs
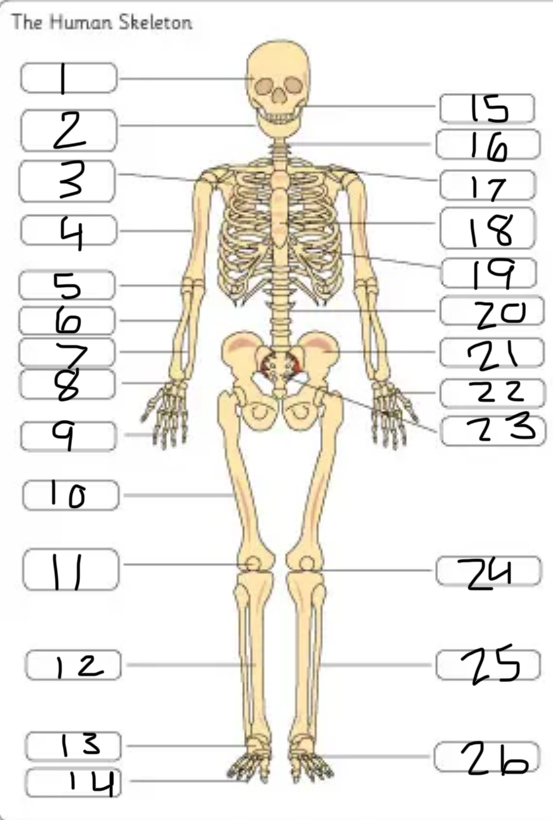
what is #21
the pelvis
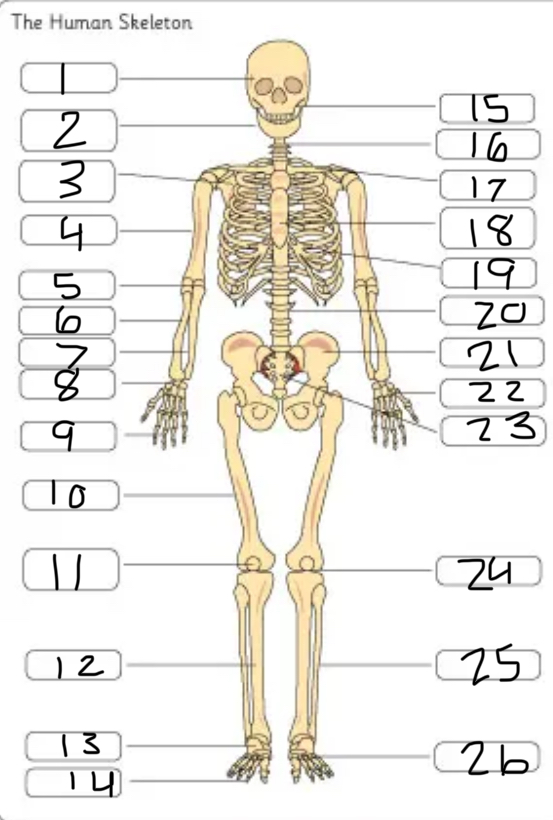
what is #22
the carpal
(top- carpals, middle- metacarpals, bottom-phalanges)
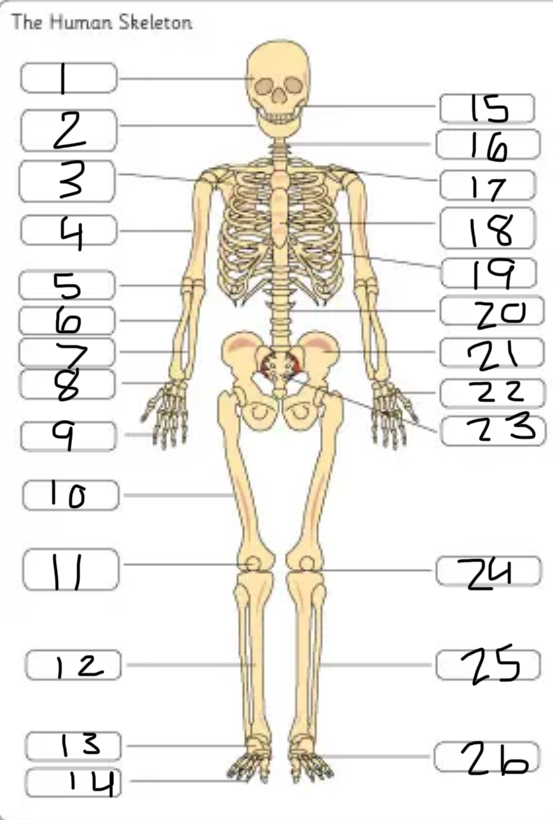
what is #23
the sacrum
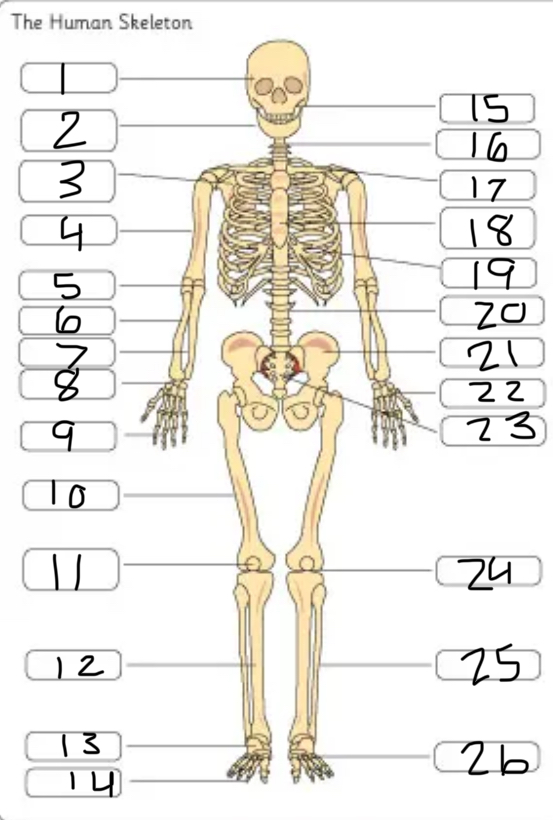
what is #25
the fibula
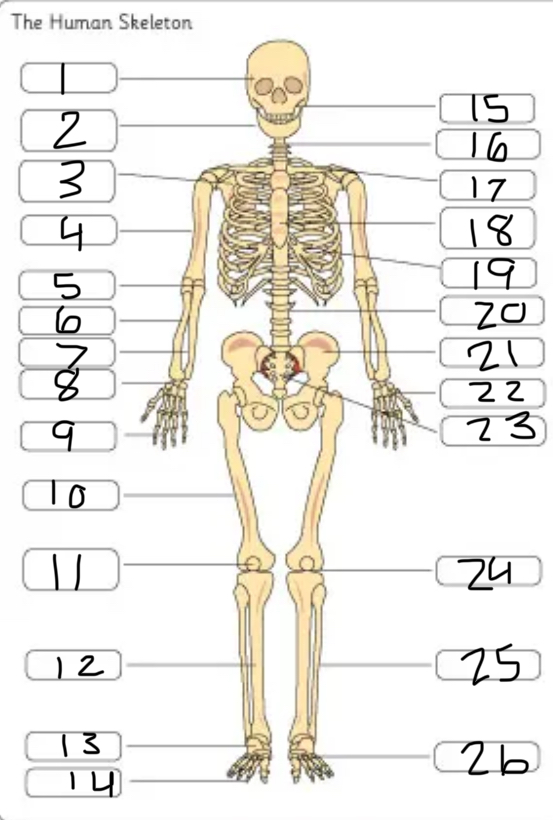
what is #26
the metatarsals
what is cartilage
a firm but flexible form of connective tissue
what is a joint
where bones meet, the bones have cartilage at the end
what is a ligament
strong bands of connective tissue
what is an immovable joint
also known as sutures, found in the skull, as a person grows the bones fuse
what is a pivot joint
Top two vertebrae, allows the head to rotate and swivel
slightly movable joints
vertebrae have pads of cartilage between them that allows limited movement
ball and socket joints
Rotating movement and allows free movement in all directions, hip and shoulder
hinge joints
Bend in only One Direction, knee and elbow are hinge joints
gliding joints
Limited vertical and lateral movement, wrist and ankle bones
What is an axial skeleton
made of 80 bones, skull, ribs, sternum, and vertebral column
appendicular skeleton
126 bones, arms, legs, and pectoral and pelvic girdles
Irregular bones
Jawbone, vertebrae, other bones that vary in shape and do not fit into any of the other categories
Long bones
Arms and legs
short bones
tarsals and carpals (feet and hands)
flat bones
ribs
What is an osteocyte
bone forming cells, live between lamellae, circular layers of hardened matrix
what are Osteoblasts
during ossification, the cells begin disintegrating cartilage with spongy bone
what are osteoclasts
Cells that destroy inner spongy bone to make a bone thicker
What is spongy bone
hard and strong, name comes from pitted appearance
compact bone
organized into circular units called osteons
what is a growth plate
small layer of cartilage between the diaphysis and each of the two epiphyses, continuously divides and older layers are ossified to increase the length of the bone. Once full height the growth plate becomes entirely bone.