Organelle Flashcards
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
What is the function of the nucleus in a cell?
The control center of the cell, contains all the cell's DNA and instructions for making proteins and other molecules.
What does the nucleus regulate?
Gene expression.
What surrounds the nucleus?
A nuclear envelope composed of 2 membranes.
Where is the nucleus typically located in a cell?
Near the center of all Eukaryotic Cells.
What is the function of the nucleolus?
Produces and assembles the cell's ribosomes.
Do all cells contain a nucleolus?
No, not all cells contain a nucleolus.
What type of nucleic acid does the nucleolus make?
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA).
Does the nucleolus contain chromosomes?
No, the nucleolus does not contain chromosomes.
What can the nucleolus move from the nucleus into the cytoplasm?
Ribosomes and ribosomal RNA (rRNA).
Where is the nucleolus located?
At the center of the nucleus.
Is the nucleolus separate from the rest of the nucleus?
Yes, the nucleolus is separate from the rest of the nucleus.
What is the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)?
The region of the endoplasmic reticulum that is studded with ribosomes.
What is the function of the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)?
Engages in protein modification.
What can misfolded proteins in the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) lead to?
Cell problems.
Why is it called 'rough' Endoplasmic Reticulum?
Because of the ribosomes that attach to it.
What is the significance of the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) in the cell?
because of its central role in protein synthesis
Where is the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) located?
Near the cell periphery (edges of the cell)
What does the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) synthesize?
Lipids and phospholipids
What type of cells contain Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)?
Eukaryotes
Does the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) contain ribosomes?
No, it does not contain ribosomes
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
It modifies and packages proteins and lipids for export by the cell through membrane-bound vesicles.
Where do proteins and lipids come from before reaching the Golgi apparatus?
They come from the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) in transport vesicles.
In which type of cells is the Golgi apparatus found?
Only in eukaryotic cells.
What is the function of a vacuole?
Stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates.
What encloses a vacuole?
A membrane.
In which types of cells are vacuoles found?
Both plant and animal cells.
Which type of cell typically has a larger central vacuole?
Plant cells.
What role does a vacuole play in plant cells?
Increases cell rigidity.
Where are vacuoles located within a cell?
In the cytoplasm.
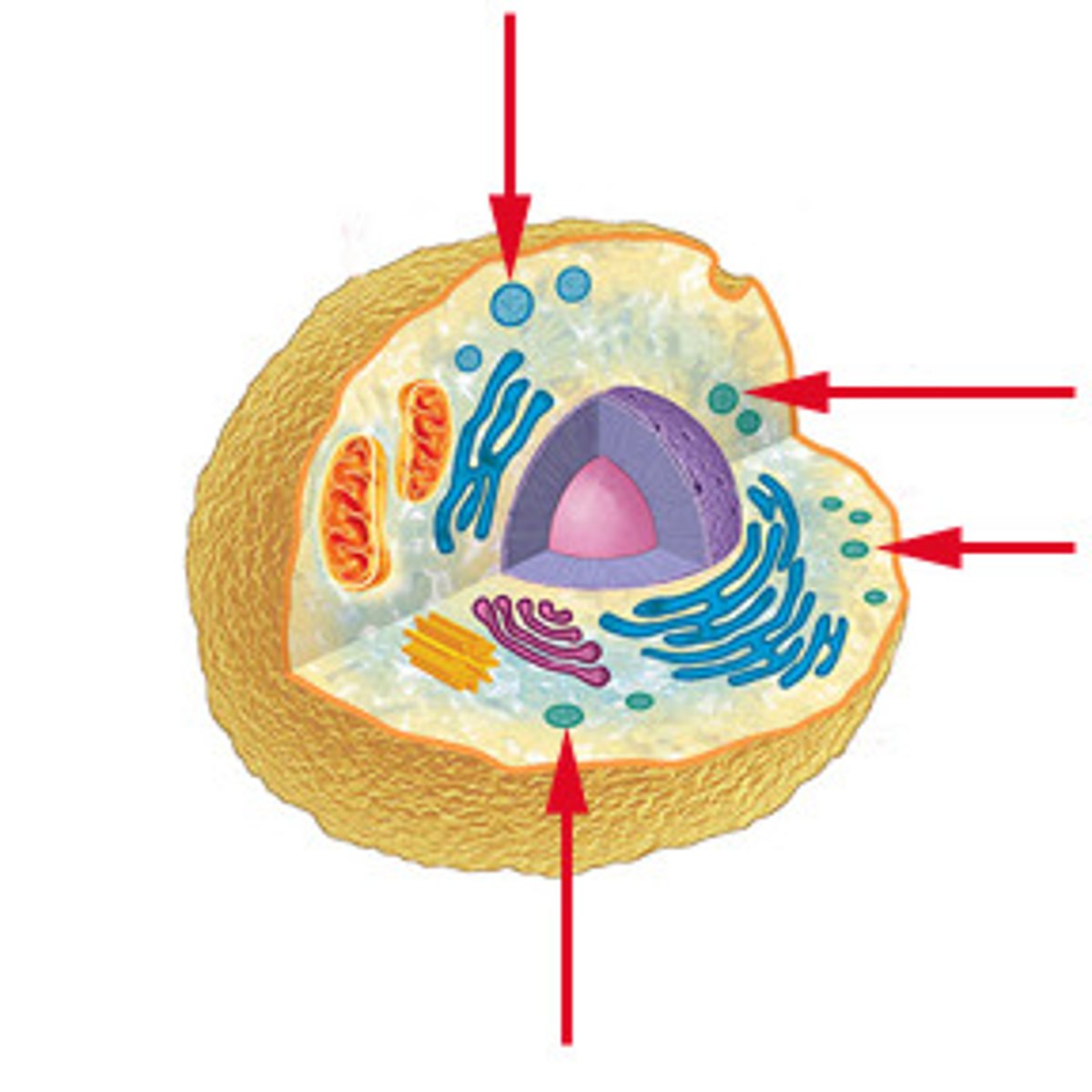
Vesicle
A membrane bound sac that contains materials involved in transport of the cell.
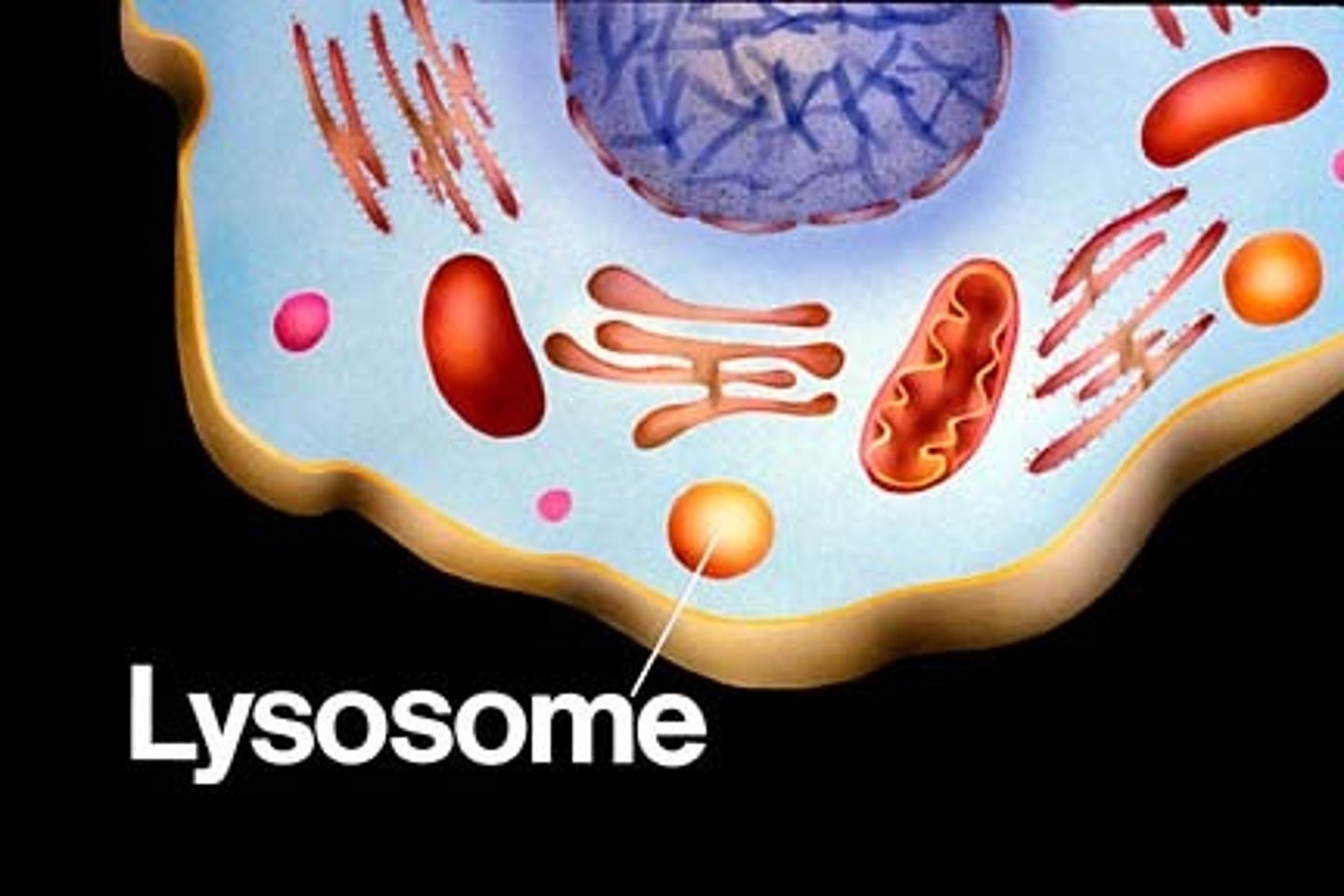
Lysosome
break down and recycle macromolecules, mostly eukaryotic, rarely prokaryotic
What are microfilaments?
Long, thin fibers that function in the movement and support of the cell.
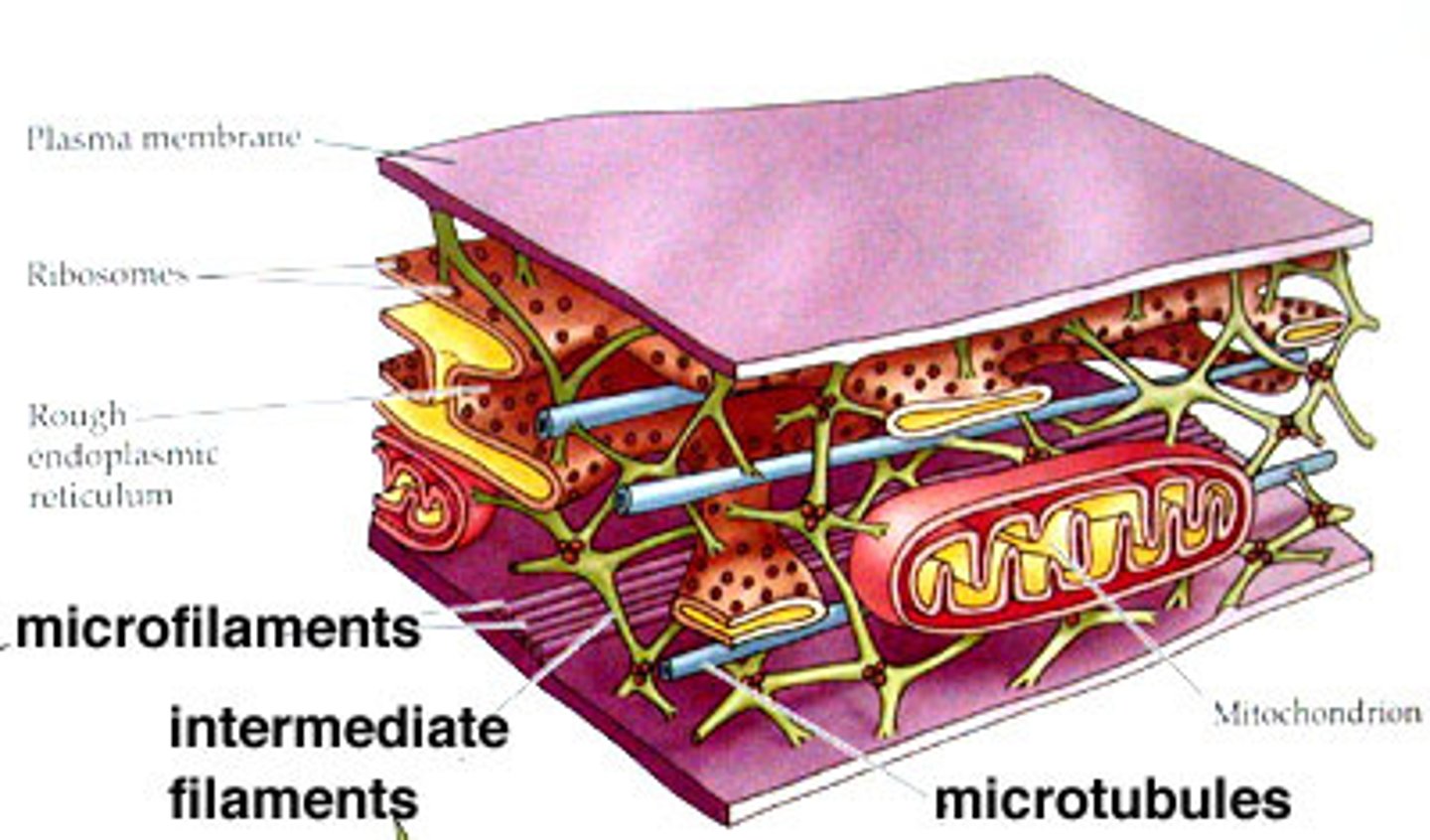
What protein are microfilaments made up of?
Actin
Are microfilaments considered prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
Eukaryotic
Where are microfilaments located in the cell?
Inside the thinnest part of the cytoskeleton in the cytoplasm.
What are the functions of microfilaments?
assembly and disassembly cause cytoplasmic movements, provide structure, facilitate cell diffusion, interact with proteins
What is the function of microtubules in regards to cell shape?
Microtubules help maintain cell shape by resisting compressive forces
What role do microtubules play in cell division?
Microtubules form the mitotic spindle and separate chromosomes.
What type of cells utilize microtubules to organize cell division?
Animal cells.
What structures do microtubules help build?
Cilia and flagella.
What is a function of cilia and flagella built by microtubules?
They help cells swim through liquids.
What organelle captures energy from sunlight in plant cells?
Chloroplast
In which type of cells are chloroplasts primarily found?
Eukaryotic plant cells
What process do chloroplasts play a large role in?
Photosynthesis
What do chloroplasts convert sunlight energy into?
Chemical energy
What is the primary function of mitochondria?
Powerhouse of the cell
In which type of cells are mitochondria found?
Only in eukaryotes
Where are mitochondria located within the cell?
In the cytoplasm
Do red blood cells contain mitochondria?
No, red blood cells have none
Which type of cells have a high number of mitochondria?
Liver cells
What processes are regulated by mitochondria?
Metabolism regulation, cell signaling, and apoptosis
What is the cell wall?
A rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms.
What are 2 functions of the cell wall?
It supports the shape of the cell and protecting it.
In which types of organisms is the cell wall found?
In both prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Which specific types of cells have a cell wall?
Plant cells, bacteria, fungi, and archaea.
Permeability of Cell Wall?
It can be rigid, tough, or flexible.
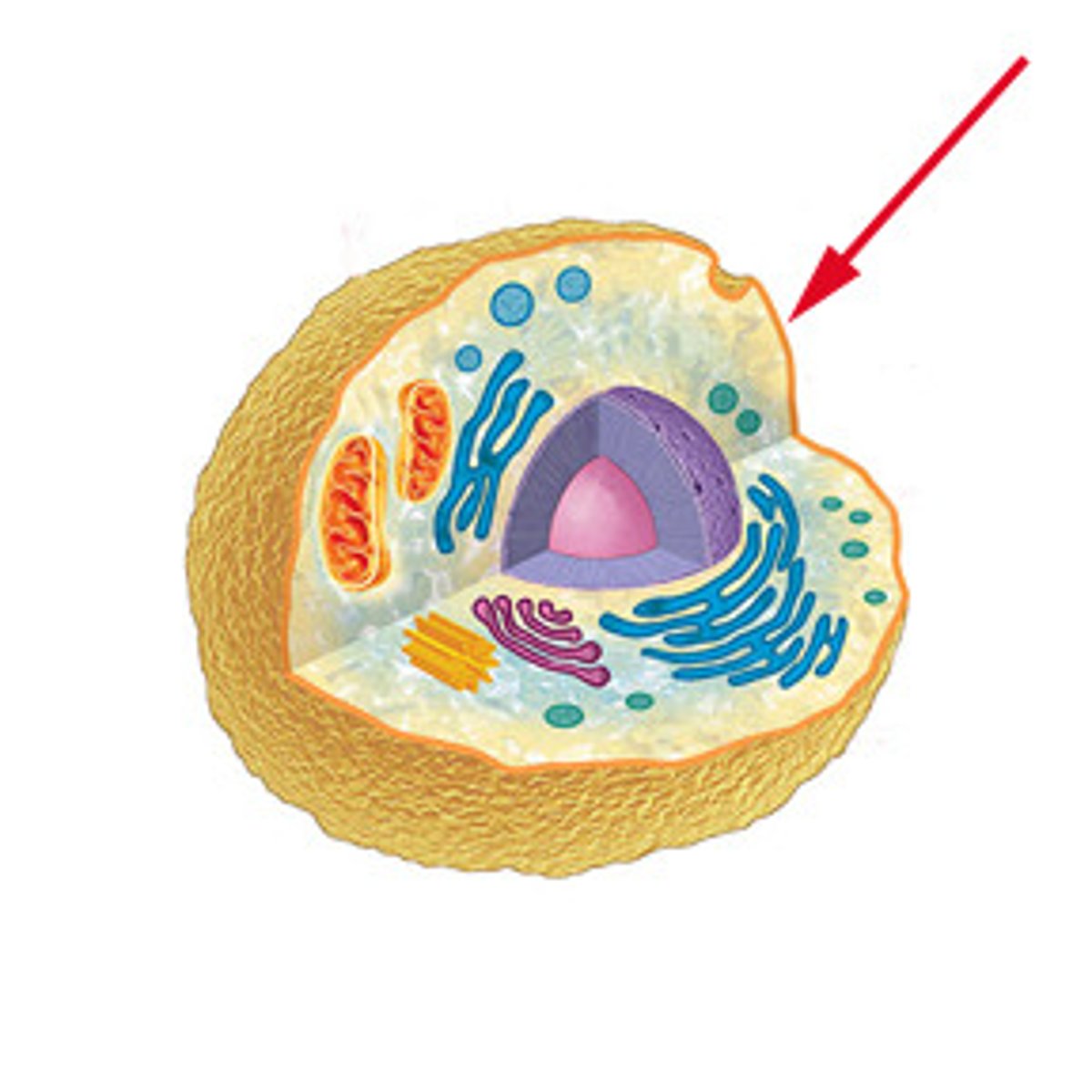
Cell Membrane (Structure)
double layered, lipid bilayer ( 2 layers of phospholipids with hydrophilic head and hydrophobic legs with the legs in the center, surrounding by the head )
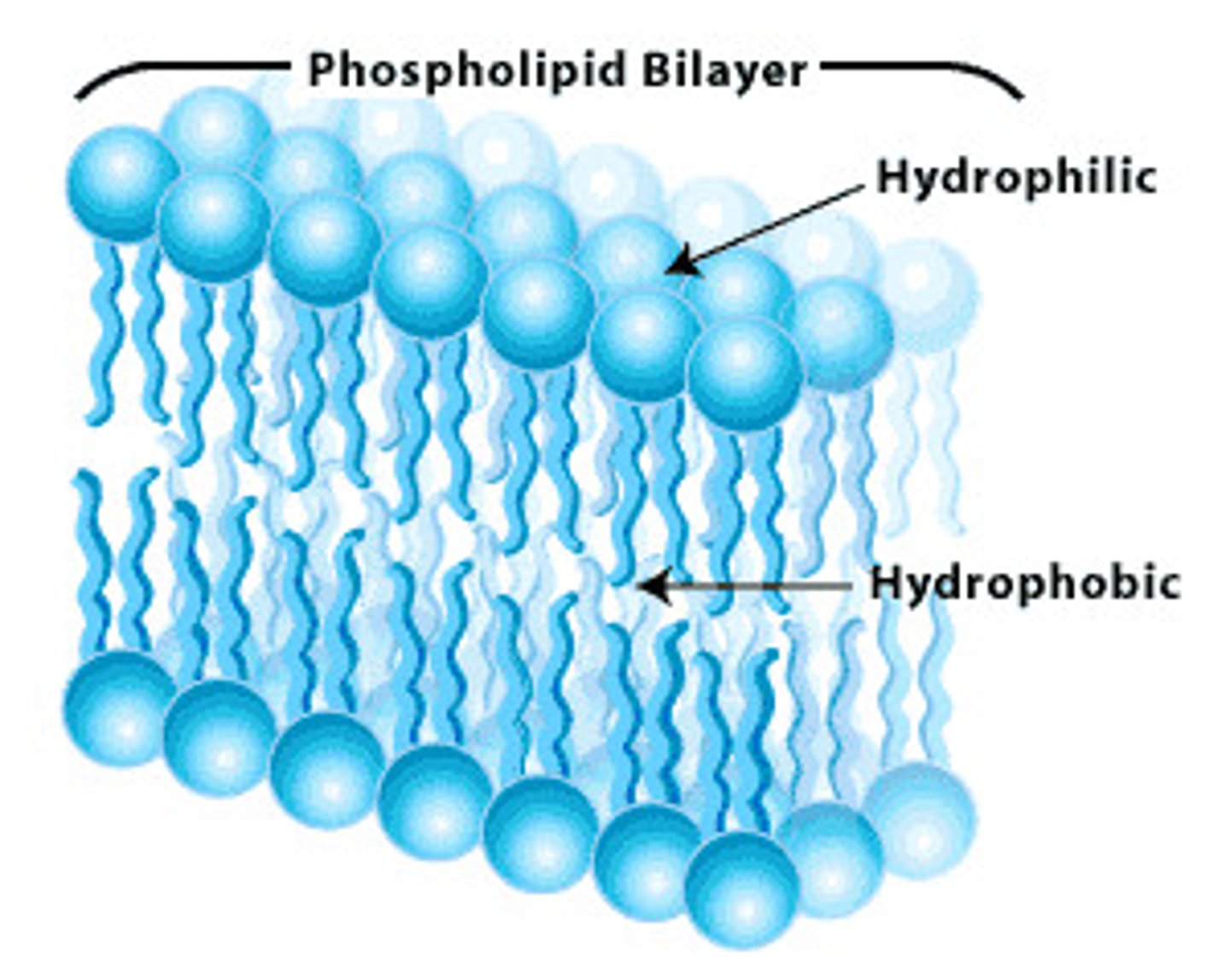
Cell Membrane (Function)
all cells contain cell membrane, allows substances to cross, regulates what leaves and what enters the cell