Unit 2: Biodiversity
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
richness (r)
the total number of different species found in an ecosystem
Evenness
relative abundance of each species
Simpson's Diversity Index
a measure of diversity between similar ecosystems
genetic diversity
The range of genetic material present in a gene pool or population of a species.
ecosystem diversity
variety of habitats, living communities, and ecological processes in the living world
species diversity
The number and relative abundance of species in a biological community.
resilience
the rate at which an ecosystem returns to its original state after a disturbance
inbreeding depression
when individuals with similar genotypes - typically relatives - breed with each other and produce offspring that have an impaired ability to survive and reproduce
overfishing & ocean depletion
capturing fish faster than they can reproduce
provisioning services
Benefits of biodiversity that humans use, including lumber, fur, meat, crops, water, and fiber
regulating services
the service provided by natural systems that helps regulate environmental conditions (air quality)
supporting services
the basic ecosystem processes, such as nutrient cycles and soil formation, that are needed to maintain other services
cultural services
ecosystems provide cultural or aesthetic benefits to many people
Overharvesting
harvesting a renewable resource quicker than the source can renew itself; often leads to the destruction of the resource
climate
Overall weather in an area over a long period of time
deforestation
The removal of trees faster than forests can replace themselves.
filter pollutants
one of the main functions of wetlands that helps to clean surrounded ponds, lakes and streams
Pollination
The transfer of pollen from male reproductive structures to female reproductive structures in plants
Specialists species
Species with a narrow ecological niche. They may be able to live in only one type of habitat, tolerate only a narrow range of climatic and other environmental conditions, or use only one type or a few types of food.
Generalists (omnivores)
consume a variety of foods
Biogeography
study of the distribution of organisms around the world
Niche
An organism's particular role in an ecosystem, or how it makes its living.
Immigration
Movement of individuals into a population
Community
All the different populations that live together in an area
positive correlation
A correlation where as one variable increases, the other also increases, or as one decreases so does the other. Both variables move in the same direction.
negative correlation
as one variable increases, the other decreases
pH scale
measurement system used to indicate the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in solution; ranges from 0 to 14
Extinction
A term that typically describes a species that no longer has any known living individuals.
inverse relationship
a relationship in which one variable decreases when another variable increases
physiological
having to do with an organism's physical/chemical processes
zone of intolerance
zone where organisms cannot survive
calcium carbonate
CaCO3
carbonic acid
a very weak acid formed in solution when carbon dioxide dissolves in water.
ocean acidification
decreasing pH of ocean waters due to absorption of excess atmospheric CO2 from the burning of fossil fuels
indicator species
Species that serve as early warnings that a community or ecosystem is being degraded.
Sentinel Species
A species whose presence, absence, or condition
in an area indicates certain environmental conditions. They
are often among the most sensitive species living in an area and can thus provide advanced warning
of environmental degradation to monitoring biologists.
endocrine disruptors
chemicals that interfere with the normal functioning of hormones in an animal's body
periodic disturbances
occurs with regular frequency (ex: dry-wet seasons)
episodic disturbances
occasional events with irregular frequency (ex: hurricanes, droughts, fires)
random disturbances
no regular frequency (volcanoes, earthquakes, and asteroids)
range of tolerance
Range of chemical and physical conditions that must be maintained for populations of a particular species to stay alive and grow, develop, and function normally
ecological footprint
the impact of a person or community on the environment, expressed as the amount of land required to sustain their use of natural resources.
Anthropogenic
derived from human activities
Endangered Species Act
(1973) identifies threatened and endangered species in the U.S., and puts their protection ahead of economic considerations
benthic zone
bottom of an aquatic ecosystem; consists of sand and sediment and supports its own community of organisms
profundal zone
a region of water where sunlight does not reach, below the limnetic zone in very deep lakes
r-selected species
a species that has a high intrinsic growth rate, which often leads to population overshoots and die-offs
K species
Species that produce a few, often fairly large offspring but invest a great deal of time and energy to ensure that most of those offspring reach reproductive age.
carry capacity
This is the population level that can be supported, given the quantity of food, habitat, water and other life infrastructure present. This is important because it tells how many people an area will be able to support.
logistic growth
Growth pattern in which a population's growth rate slows or stops following a period of exponential growth
medicinal
having the properties of medicine
nonrenewable resource
A natural resource that is not replaced in a useful time frame.
renewable resource
A natural resource that can be replaced at the same rate at which the resource is consumed
primary succession
An ecological succession that begins in an area where no biotic community previously existed
secondary succession
Succession following a disturbance that destroys a community without destroying the soil
pioneer species
First species to populate an area during primary succession
climax community
A stable, mature community that undergoes little or no change in species over time
lichen
symbiotic association between a fungus and a photosynthetic organism
Biomass
total amount of living tissue within a given trophic level
independent variable
The experimental factor that is manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied.
dependent variable
The outcome factor; the variable that may change in response to manipulations of the independent variable.
IUCN
International Union for the Conservation of Nature; a coalition of the world's leading conservation groups
Annuals
A flowering plant that completes its entire life cycle in a single year or growing season.
perennial
(adj.) lasting for a long time, persistent; (n.) a plant that lives for many years
vascular plants
have tissues made of cells that transport water and nutrients throughout the plant
nonvascular plants
Plants that lack a well-developed system of tubes for transporting water and other materials
intermediate disturbance hypothesis
the hypothesis that ecosystems experiencing intermediate levels of disturbance are more diverse than those with high or low disturbance levels
ecosystem engineers
a keystone species that creates or maintains habitat for other species
keystone species
A species that influences the survival of many other species in an ecosystem
control group
In an experiment, the group that is not exposed to the treatment; contrasts with the experimental group and serves as a comparison for evaluating the effect of the treatment.
adaptation
trait that helps an organism be more suited to the enviornment
natural
type of selection that happens in nature
population
all the members of a single species in a particular area
phenotype
the physical manifestation of genes
gene pool
the alleles in a population
mutation
primary source of genetic diversity in organisms that produce sexually
genetic drift
changes in allele frequence due to CHANCE
Bottleneck Effect
prevents the majority of genotypes from participating in the production of the next generation
founder effect
rare alleles occur at higher frequency in a population ISOLATED from the general population
Territory
area that is defended
Homologous structures
anatomical similarities inhertited by a common ancestor
analogous structures
anatomical features that serve the same purpose, but don’t suggest a common ancestor
life cycle
all the events in the growth and development of an organism until the organism reaches sexual maturity
gene flow
movement of alleles from one population to another
species
a group of similar organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspring
Study figure 14.2 and then describe or give an example to distinguish between species richness and species evenness
(for this theres now two species of deer in pittsburgh)There are a staggering number of white tail deer within a certain location(species richness), but within the same ecosystem there's only a handful of another species and the white tail deer dominate the area(species evenness)
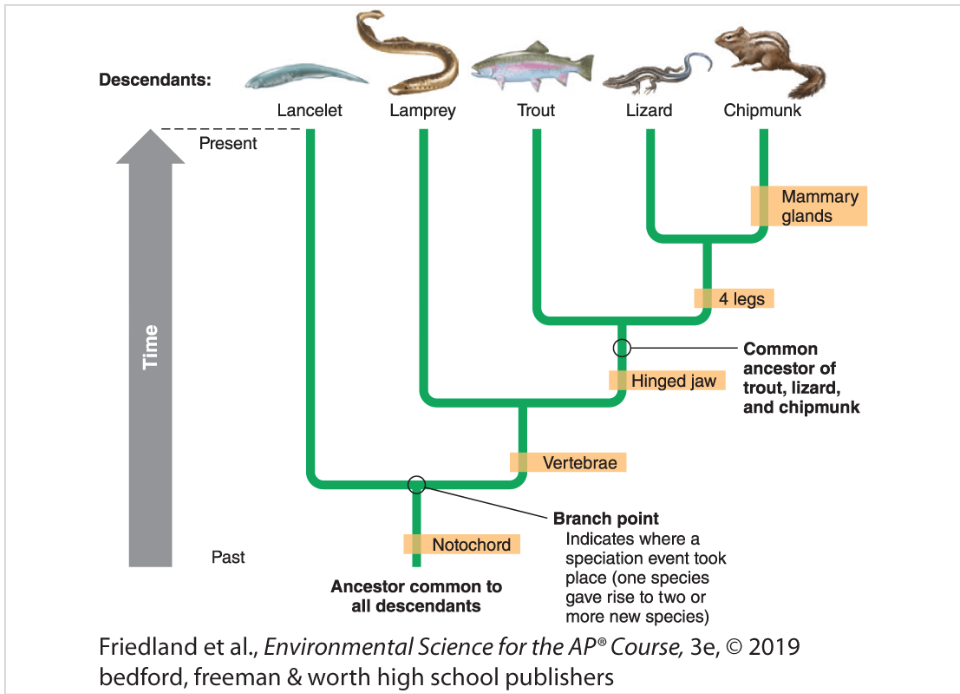
Define phylogeny
the branching pattern of evolutionary relationships
What is causing the sixth mass extinction
humans activities
Give at least 2 examples of how the US tries to conserve habitat and biodiversity
protecting areas as national, parks, national monuments, national forests, and wilderness areas. Also designated lots of marine waters to be protected as marine national monuments; creating marine reserves
What is the benefit of high genetic diversity
High biodiversity allows ecosystems to fight off or bounce back from natural or man made changes and higher genotype diversity allowing more differences between animals in ecosystems
Who is the IUCN and what do they do
International Union for Conservation of Nature and they bring together many forms of government to find pragmatic solutions to pressing environmental and developmental challenges(scientific research, managing field projects, producing data/tools like the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species)
What does it mean that some people think ecosystems have intrinsic value
believe that the land is independent of humans and want people to protect the lands instead of use them for human means
provisions(instrumental value)
Goods produced that can be used directly(ex. Lumber, food crops, medicinal plants, natural rubber, and furs)
Regulating services(instrumental value)
Natural ecosystems help to regulate environmental conditions(ex. nutrient cycles)
Support(instrumental value)
Natural ecosystems providing support services that would be extremely costly for humans to generate(ex. Crop pollination of bees, other insects, hummingbird, and bats is worth abt 3 B in added food production)
Resilience(instrumental value)
Ability to continue to exist in current state(ex. Several diff species can perform similar functions, but differ in susceptibility to disturbance)
Cultural(instrumental value)
Providing cultural/aesthetic benefits to ppl(A beautiful landscape leaves people in awe)
What is the purpose of the Marine Mammal Protection act
prohibits the killing of all marine mammals in the US and prohibits the import or export of any marine mammal body parts
Which is more dire: endangered or threatened species?
endangered species because they are closer to extinction meaning the species will never come back again
What is the Endangered Species Act and why can it be controversial
the act authorizes the government to purchase habitat that is critical to the conservation of these species and to develop recovery plans to increase the pop of threatened and endangered species and could be controversial because it has restrictions on human activities(how land owners use their land) and economic developments(lumbar industry and the workers that rely on those jobs)