PCOL:3102 Antibacterials
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
drug classes and their drugs that are cell wall synthesis inhibitors
beta-lactams
penicillins: penicillins, amoxcillin
cephalosporins: cefdinir
non beta-lactams: vancomycin, bacitracin
beta lactamase inhibitor: clavulanic acid
drug classes and their drugs that are protein synthesis inhibitors
tetracyclines: doxcycline
aminoglycosides: gentamicin
macrolides: erythromycin
lincosamide: clindamycin
others include linezolid, mupirocin
generalizations of cell wall synthesis inhibitors
maximum selective toxicity — good at targeting bacteria and not human cells
inhibits peptidoglycan synthesis and its cross-links
inhibits gram + >> gram -
bactericidal
non-beta lactam drugs
bacitracin
vancomycin
bacitracin
depletes lipid carrier for PDG synthesis
toxic / bactericidal
great for skin and eye infections
usually topical cuz toxic if taken internally
good in combo with polymyxin B
vancomycin
reserved drug for serious infections
blocks elongation and X-linking of PDG synthesis by binding the substrate
bactericidal
effective for gram + like MRSA (very narrrow spect)
toxicity for vancomycin
ear and kidney toxicity
vancomycin flushing syndrome (VFS)
beta-lactam drugs
ex. penicillins and cephalosporins
have a beta-lactam ring that binds to penicillin binding protein (PBPs)
inhibit the transpeptidases (PBPs) and block PDG strand X-linking
bactericidal
mainly gram +
how are beta-lactam resistance developed?
bacteria can make beta-lactamases to break down the drug
alteration of drug target (PBPs) to decrease affinity
decrease drug influx so it can’t get in
increase drug efflux so it’s pumped out
adverse effects of beta-lactams
generally minimal
allergy (usually delayed)
types of penicillins
penicillin V
amoxicillin
characteristics of penicillin V
gram + and some gram - cocci
first gen are mostly +++ but new gen includes + + / - -
adverse effects: allergies and stevens johnson syndrome
amoxicillin
extended spectrum penicillin
+ + / - -
destroyed by beta-lactamases but can be overcome with combination therapy
what is used with amoxicillin to overcome beta-lactamases?
clavulanic acid which is a beta-lactamase inhibitor
lacks antibiotic activity alone
doesn’t get degraded by beta-lactamase, just stops them (acts like a sponge)
cephalosporins
inhibits cell wall synthesis
large drug class, grouped into 5 gen
gen 1: excellent for +
gen 2, 3, 4: + + / - - but developed resistance
gen 5: developed against resistant strains like MRSA
ex. cefdinir
cefdinir
3rd gen cephalosporin
bacterial resistance cuz low PBP affinity
very safe
wide range of infections
bacterial vs human ribosome
bacteria: 70S ribosome with 30S + 50S (big) subunits
humans: 80S ribosome with 40S + 60S subunits
tetracyclines
aminoglycosides
50S ribosomal subunit inhibitor
macrolides
lincosamides
oxazolidinones
mupirocin → inhibits tRNA synthetase
tetracyclines
ex. doxycycline
reversible binding to 30S subunit of bacterial ribosome
bacteriostatic
broad activity ( + + / - - ) → superinfection risk
resistance by: poor uptake, increased efflux, drug inactivation, drug target alteration
aminoglycosides
ex. gentamicin
bind irreversibly to the 30S ribosomal subunit
inhibit protein synthesis at several levels
bactericidal
primarily gram -
if combined with cell wall synthesis inhibitor → gram +
resistance: poor uptake but develops slowly
adverse effects: ear and kidney toxicity
macrolides
ex. erythromycin
binds reversibly to 50S subunit
competitively inhibits ribosome binding of other protein synthesis inhibitors like clindamycin → antagonism
bacteriostatic (cidal at higher conc)
narrow spectrum: mostly gram +
cross resistance with clindamycin and modified drug target and develops quickly
can inhibit some CYPs
lincosamides
ex. clindamycin
cross resistance with erythromycin cuz they bind to same spot
narrow spect: mostly gram +
bacteriostatic but can be cidal in some
slow resistance
great for bone infections but prone to C. dificile outgrowth
oxazolidinone
ex. linezolid
binds to 23S rRNA of 50S subunit
no cross resistance with other protein synthesis inhibitors
bacteriostatic
used for serious infections like MRSA
mupirocin
inhibits tRNA synthetase
ointment form since it would metabolized into inactive form if orally
no cross resistance with other protein synthesis inhibitors
used for MRSA or Grp A strep
folic acid synthesis inhibitors
ex. sulfonamides and trimethoprim
act in sequential steps to block bacterial folic acid synthesis
inhibits DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis
high selective toxicity
if administered alone = static BUT if you combine the two = cidal
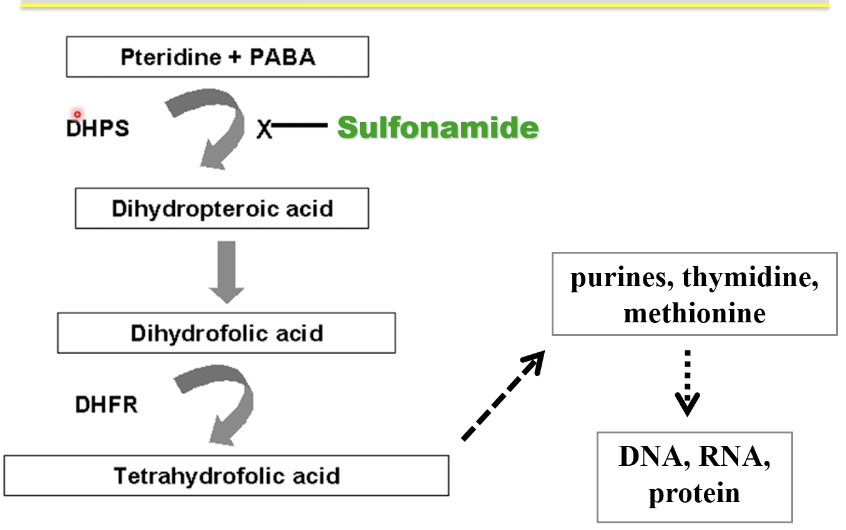
sulfonamides
ex. sulfamethoxazole
binds to DHPS enzyme to take the place of PABA in folic acid synthesis pathway to prevent DHFA synthesis
competitive inhibitor
high PABA levels inhibit sulfa activity
bacteriostatic
broad spect: + + / - - plus parasites NOT TICKS (cuz stimulates growth)
cross-resistance to all sulfas
resistace by: drug target amplifcation and alteration and increased efflux
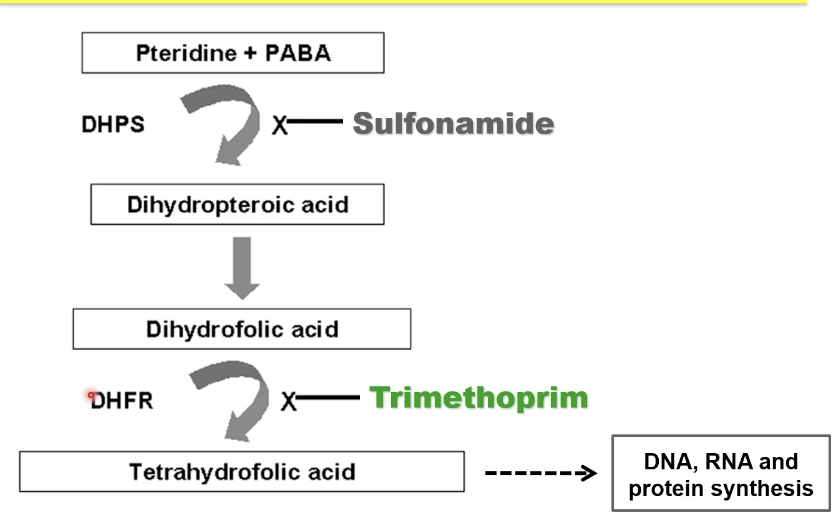
trimethoprim
takes DHFA place and competitively inhibits DHFR to make THFA
bacteriostatic
acts synergistically with sulfa → tmp-sulfa which is cidal
broad spec: + + / - - but not all
resistance by drug target amplification and alteration
tmp-sulfa common uses
MRSA
UTIs
fluoroquinolones
ex. ciprofloxacin
great potency (well tolerated) and expanded spec: better gram + coverage
earlier ones better at gram -
bactericidal
target bacterial DNA synthesis by inhibiting bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase to block DNA unwinding
induces irreversible DNA dmg / degradation
resistance by decreased drug influx, increased efflux, and drug target alteration
mutation in both gyrase and topoisomerase causes high level of resistance
nucleic acid synthesis inhibitors
sulfonamides
trimethoprim
fluoroquinolones
rifampin
cell membrane inhibitors
polymyxin B
daptomycin
pyrazinamide
polymyxin B
detergent that disrupts cell membrane
bactericidal
topical use only cuz very toxic
effective against gram neg
daptomycin
membrane depolarization
bactericidal
treats MRSA (superior to linezolid)
metronidazole
dna targeting agent
selective reduction and accumulation of toxic products in anaerobes = disrupts bacterial DNA
bactericidal
preventative and treatment
antimycobacterial agents
isoniazid
rifampin
pyrazinamide
ethamutol
for TB
rifampin
inhibits mRNA synthesis
most effective cyz it inhibits bacterial RNA polymerase
bactericidal
isoniazid
inhibits cell wall synthesis
bactericidal
prodrug that is activated by mycobacterial enzyme
ethambutol
inhibits cell wall synthesis
bacteriostatic but cidal at high doses
can cause red-green color blindness
pyrazinamide
disrupts cell membrane
prodrug activated by mycobacterial enzyme
bactericdial
how to treat TB?
combination therapy is best way and is prolonged since it takes a long time for the microbe to grow and actually give you an effect