bi205 axial skeleton
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
80
how many bones are in the axial skeleton
skull bones, auditory ossicles, hyoid, vertebral column, throacic cage
what does the axial skeleton consist of
supports and protects organs in the dorsal and ventral body cavities, protects special sense organs, attachment site for muscles, adjust the posture of the head, neck and trunk, move the thoracic cage for respiration and stabilize the appendicular skeleton
functions of the axial skeleton
face, cranium, hyoid, auditory ossicles
bones that make up the skull
suture
made of dense fibrous connective tissue
lambdoid suture
suture between the occipital and 2 parietal bones
sagittal suture
suture between the 2 parietal bones
coronal suture
suture between the frontal bone and the 2 parietal bones
squamos suture
suture between the temporal bone and the parietal bone
frontonasal suture
suture between the nasal bones and the frontal bone
calvaria
bones and sutures of the dome of the cranium are called
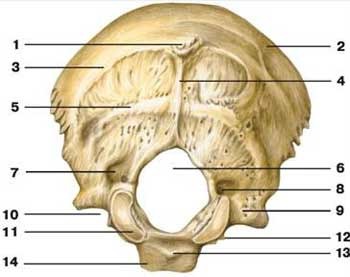
foramen magnum
what is label 6
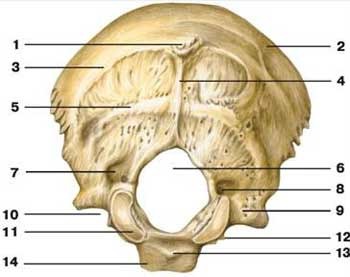
occipital condyle
what is label 11
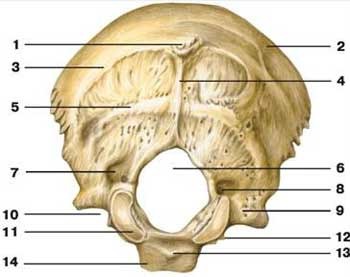
hypoglossal canal
what is label 12
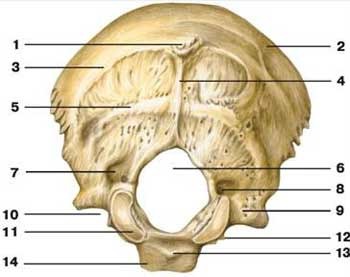
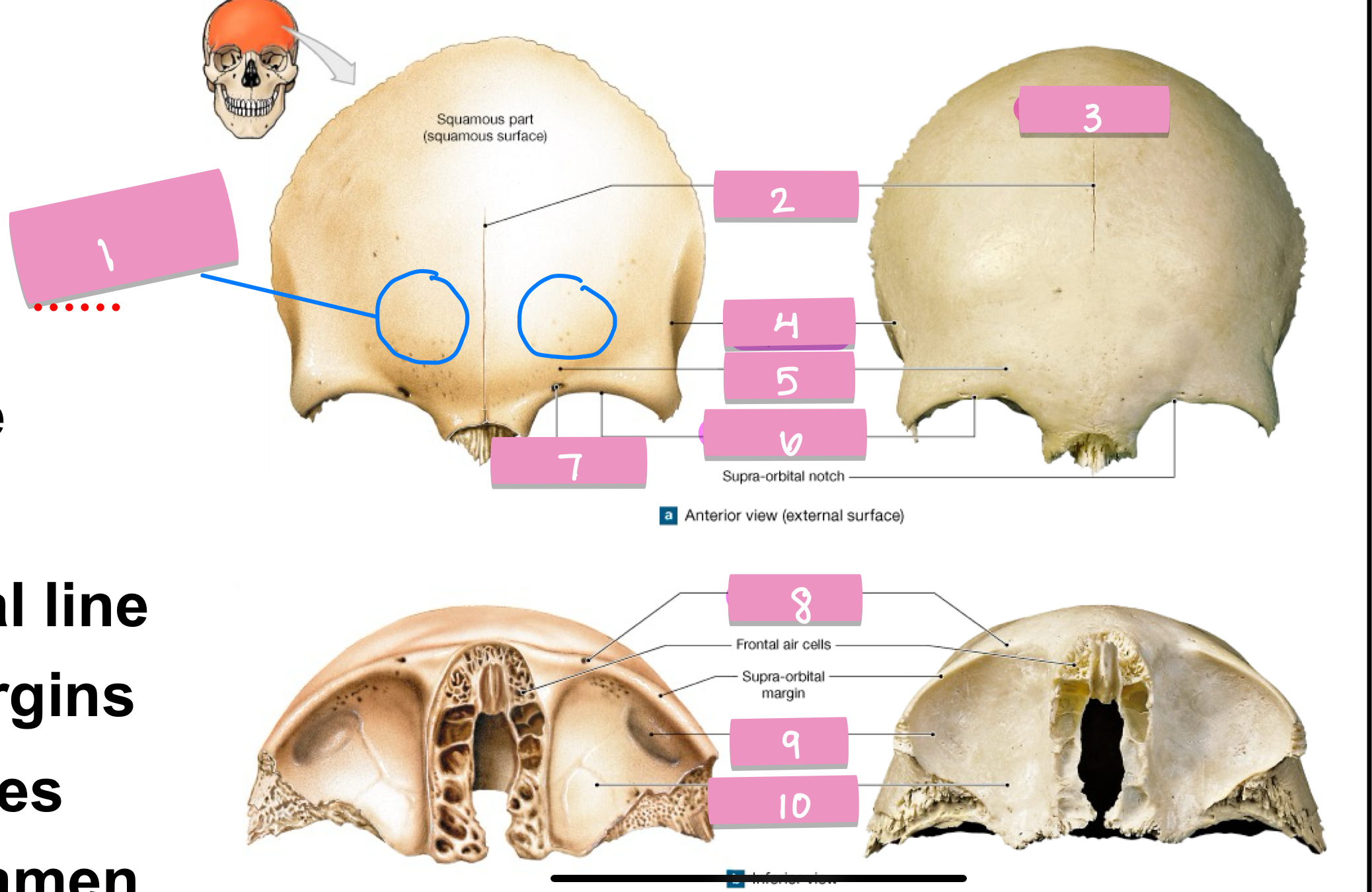
inferior nuchal line
what is label 5
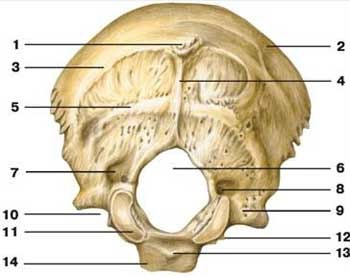
superior nuchal line
what is label 3
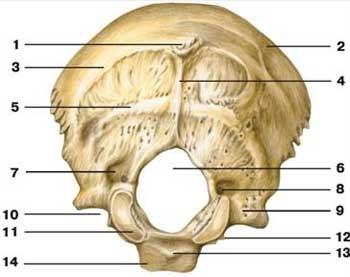
external occipital crest
what is label 4
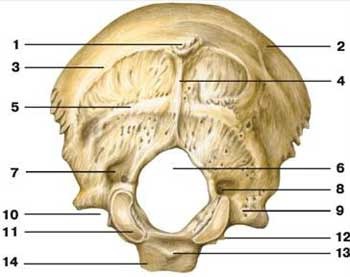
external occipital protuberance
what is label 1
squamos part
what is label 1
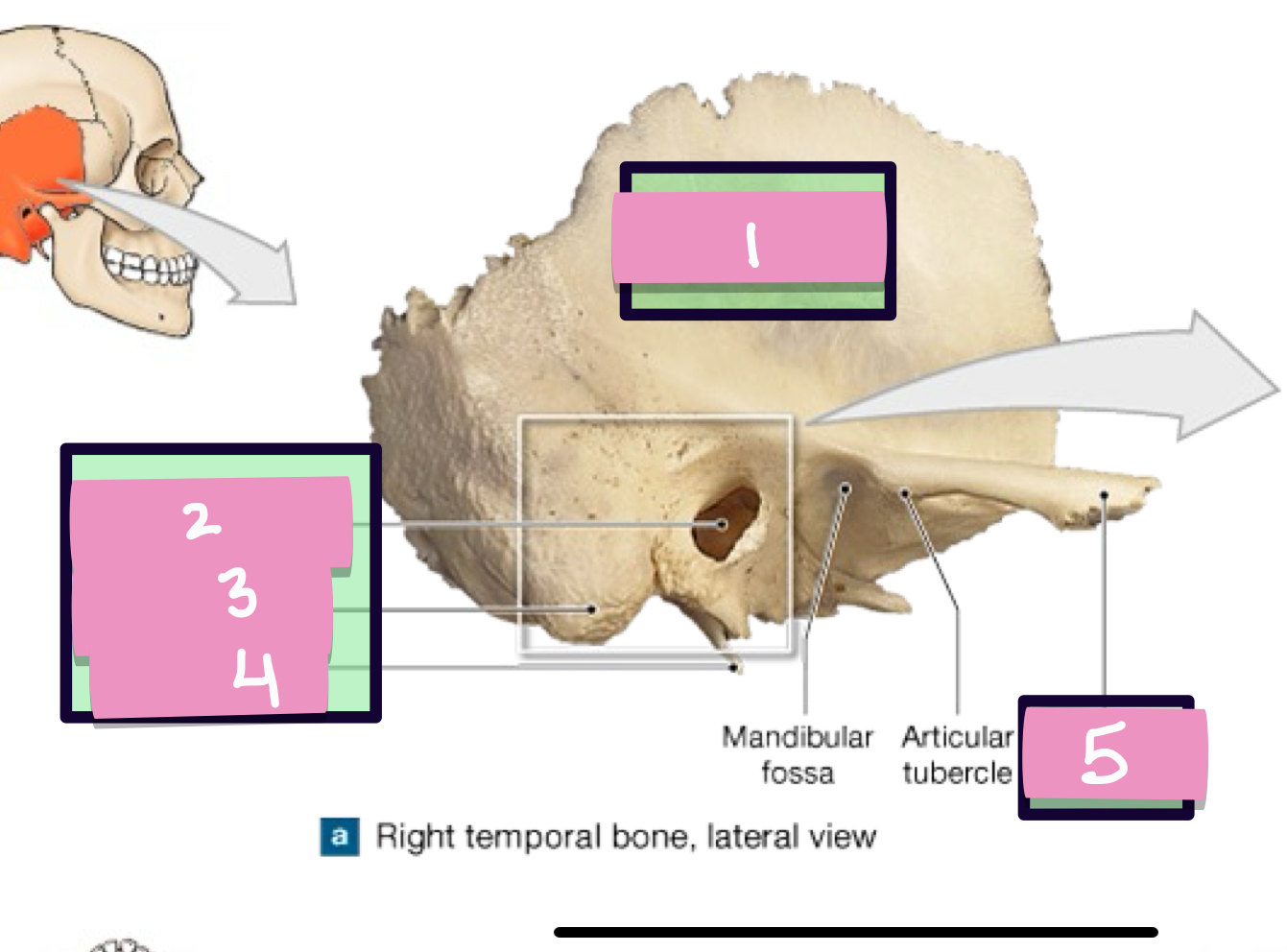
external acoustic meatus
what is label 2
mastoid process
what is label 3
styloid process
what is label 4
zygomatic process
what is label 5
frontal eminence
what is label 1
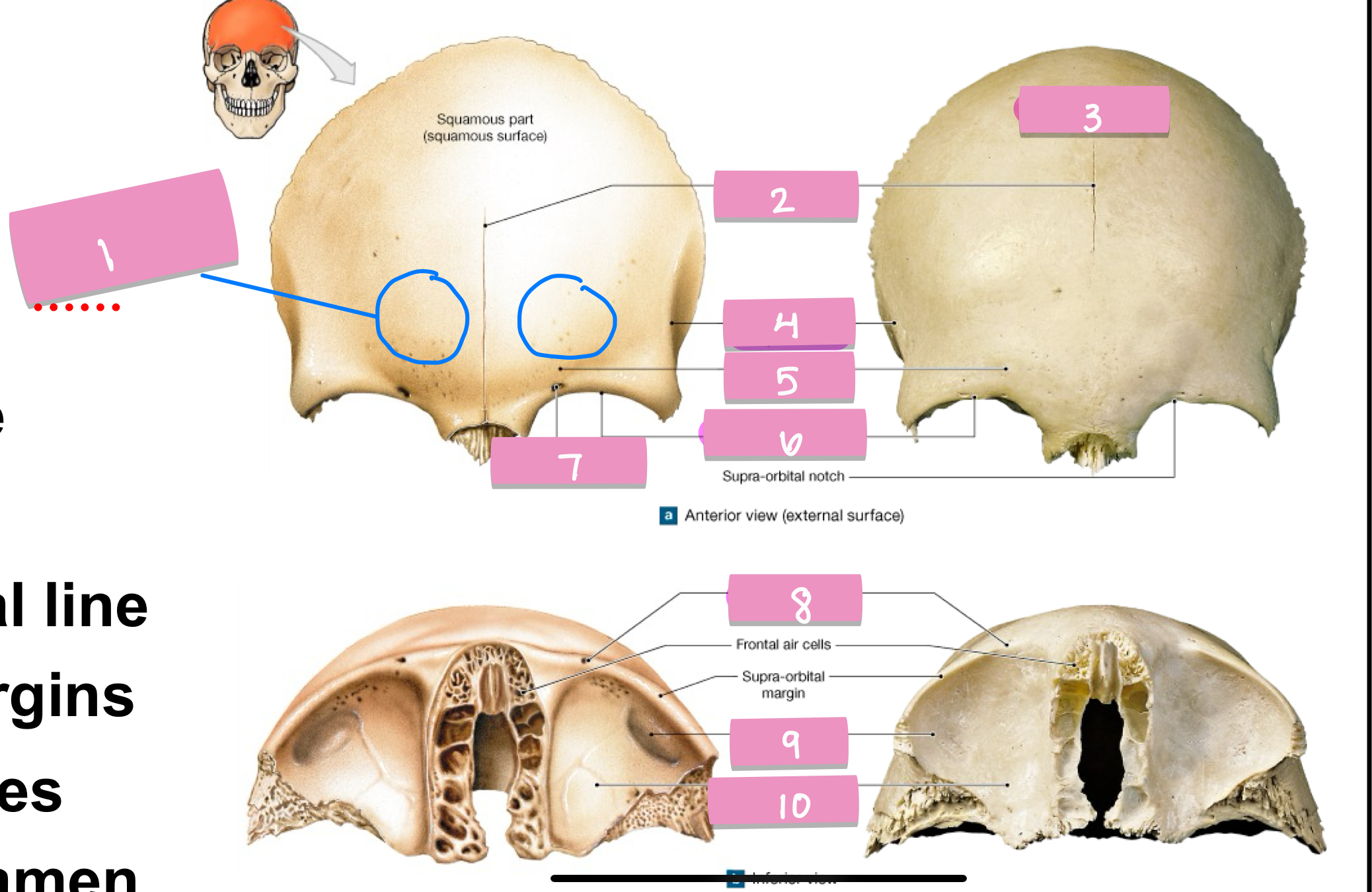
frontal suture
what is label 2
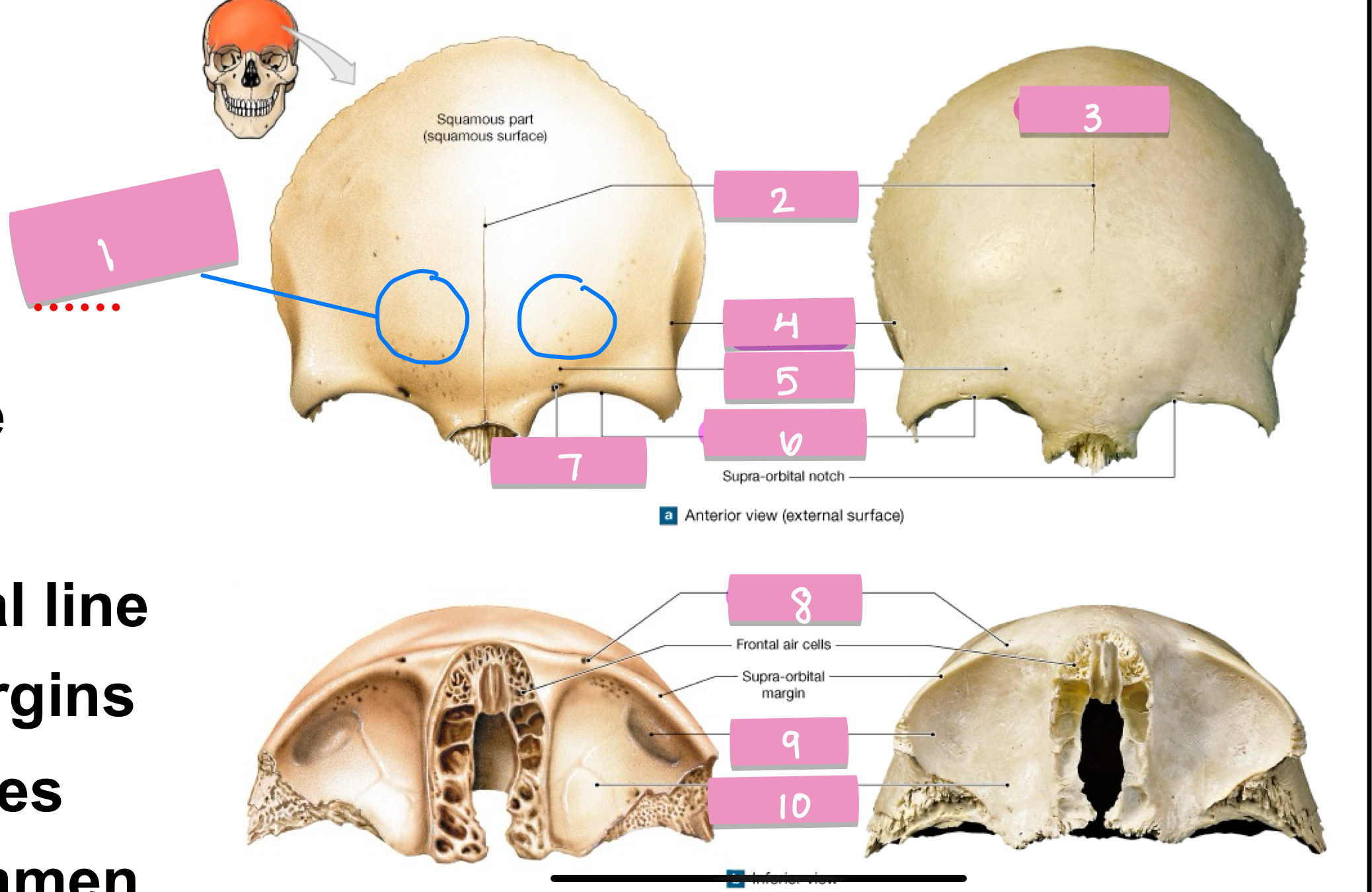
squamos part
what is label 3
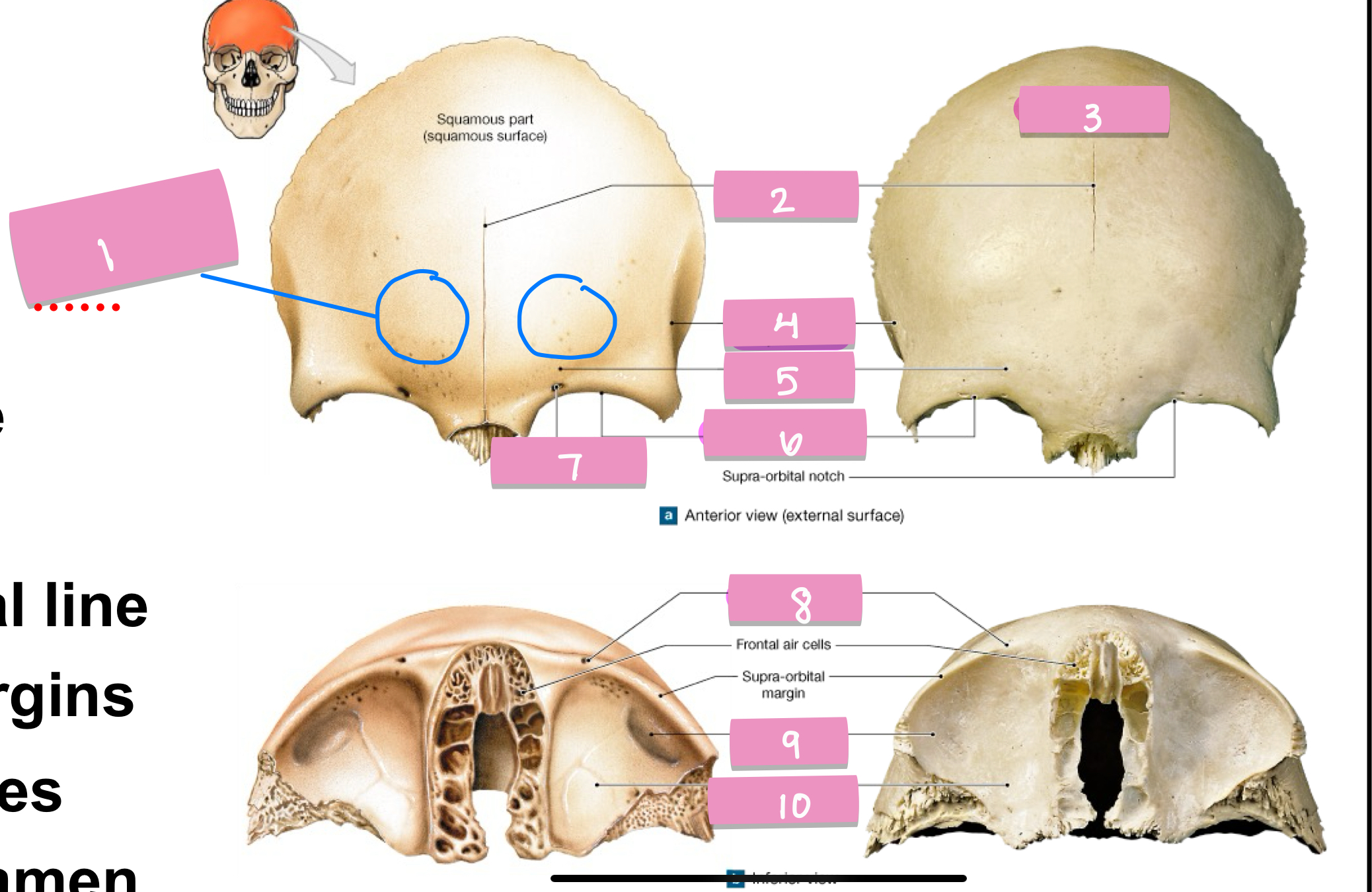
superior temporal line
what is label 4
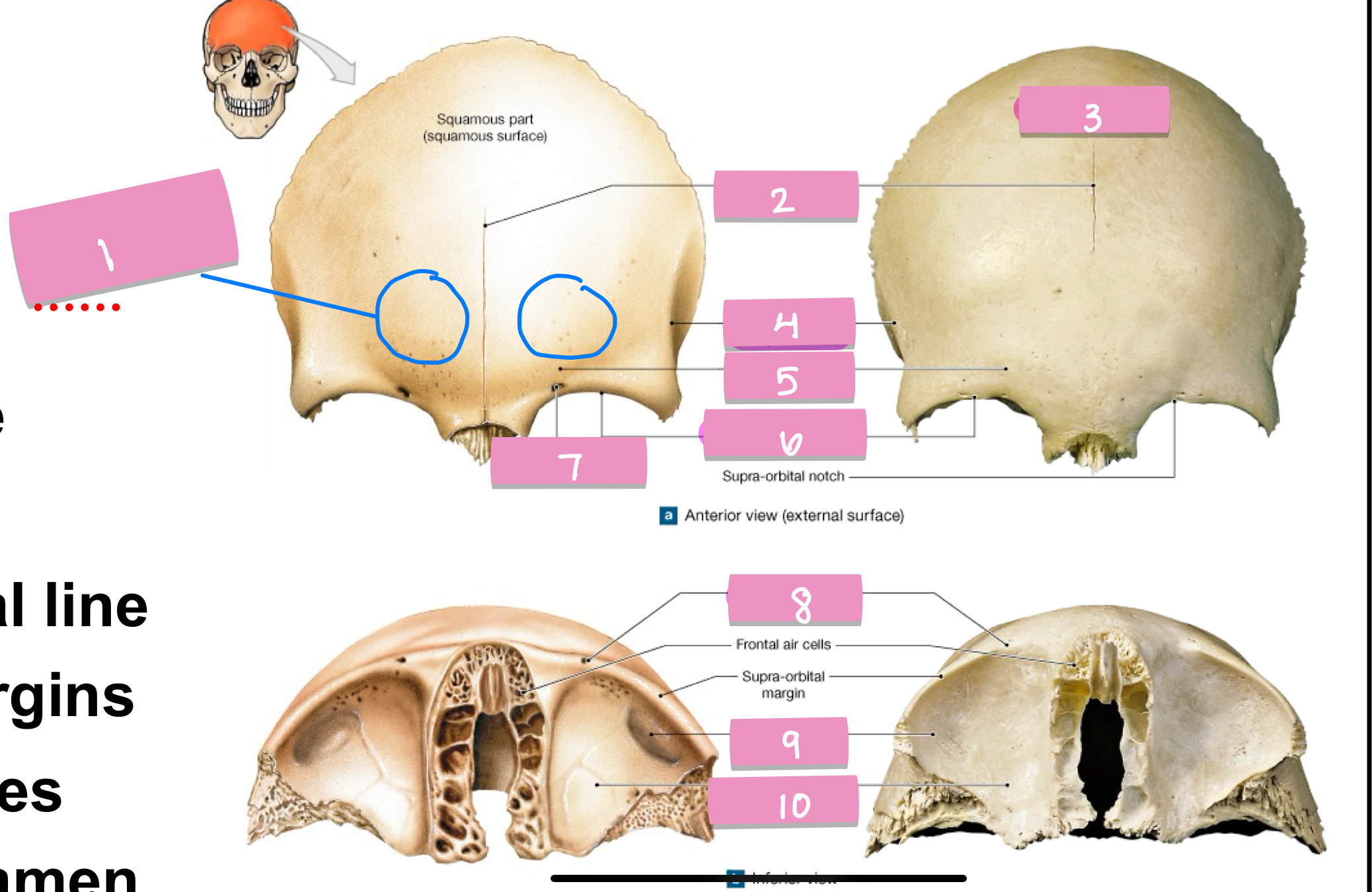
supercillary arch
what is label 5
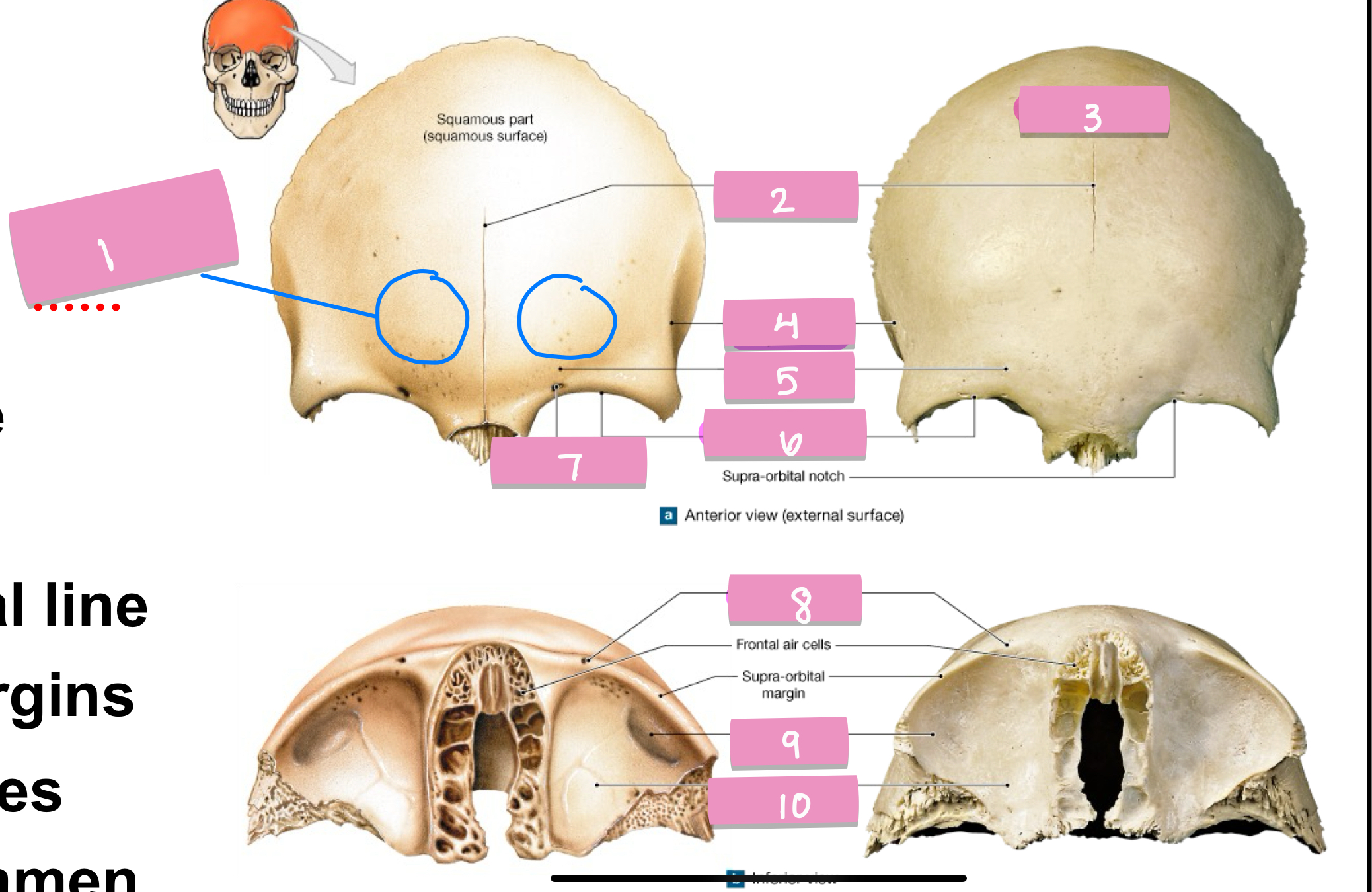
supra-orbital margin
what is label 6
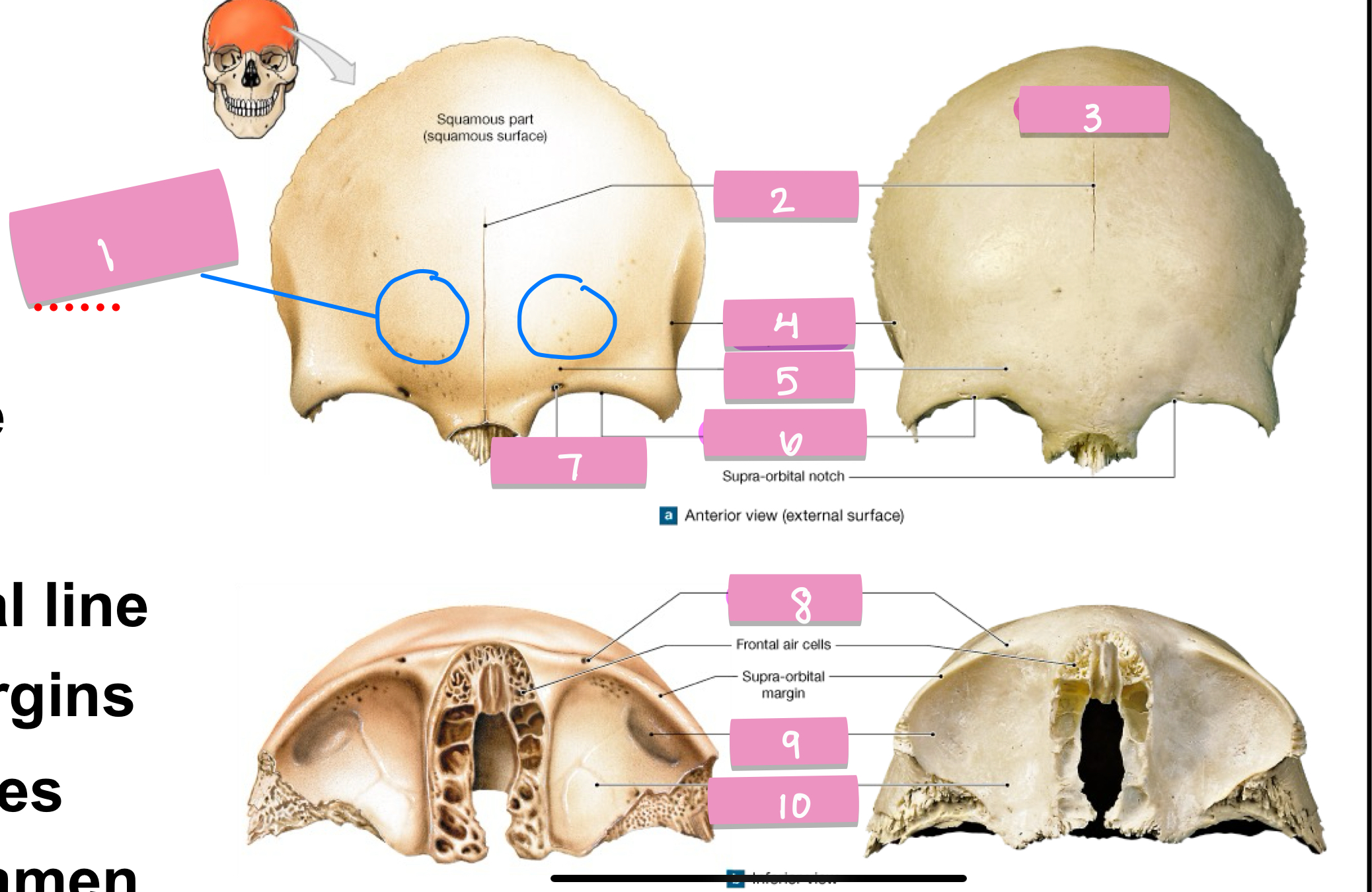
supra-orbital foramen
what is label 7
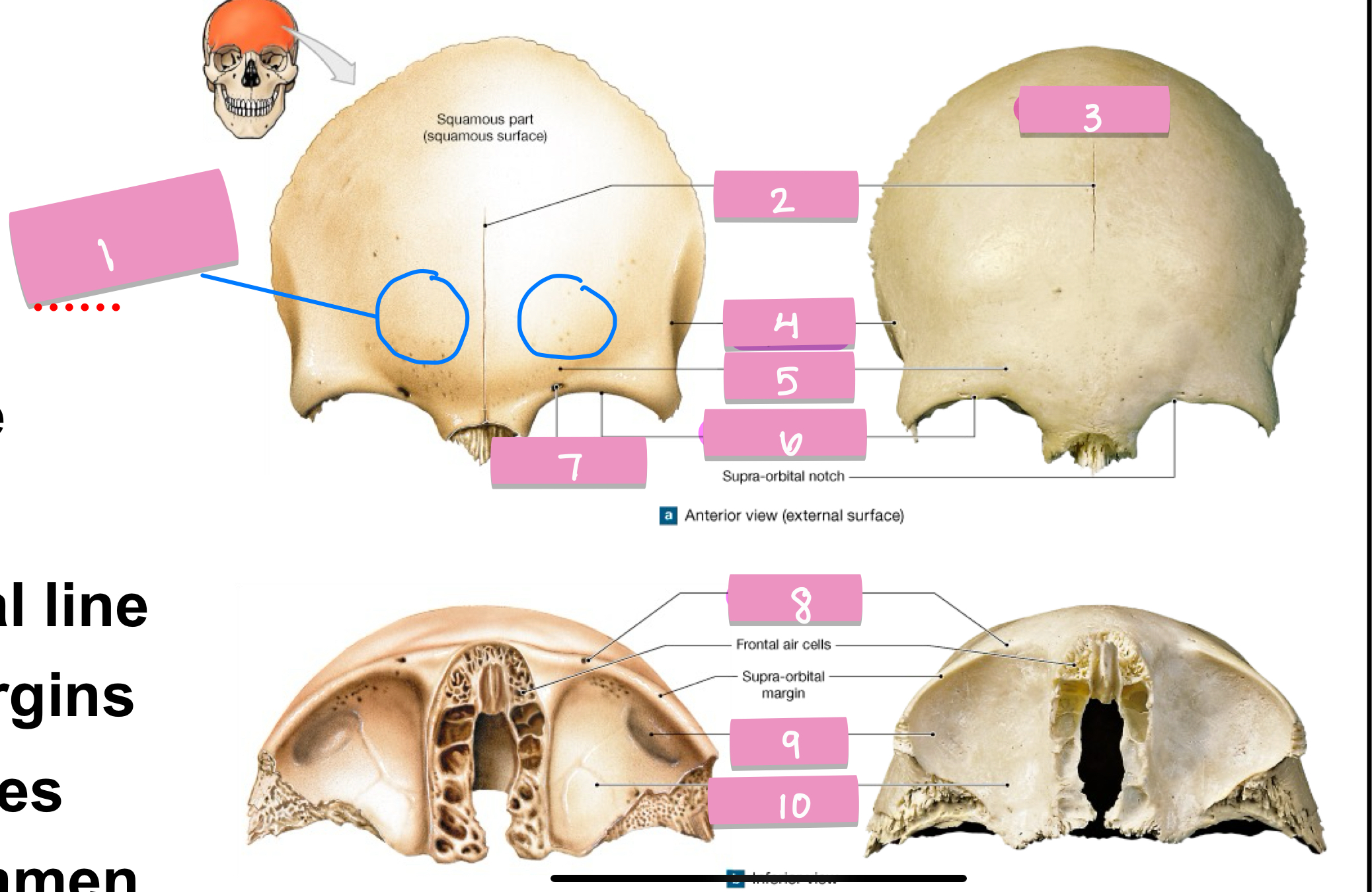
lacrimal fossa
what is label 9
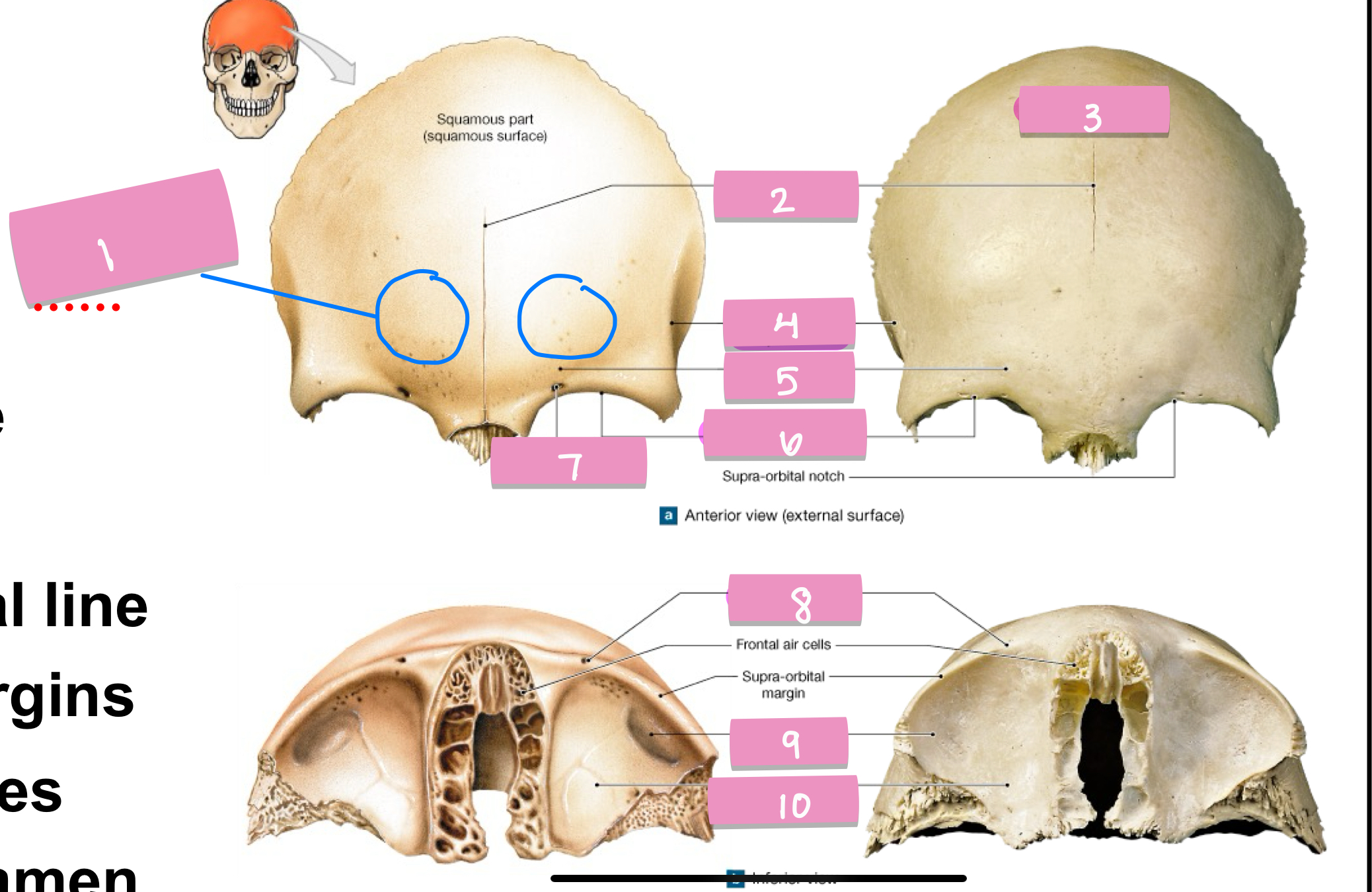
orbital part
what is label 10
zygomatic process
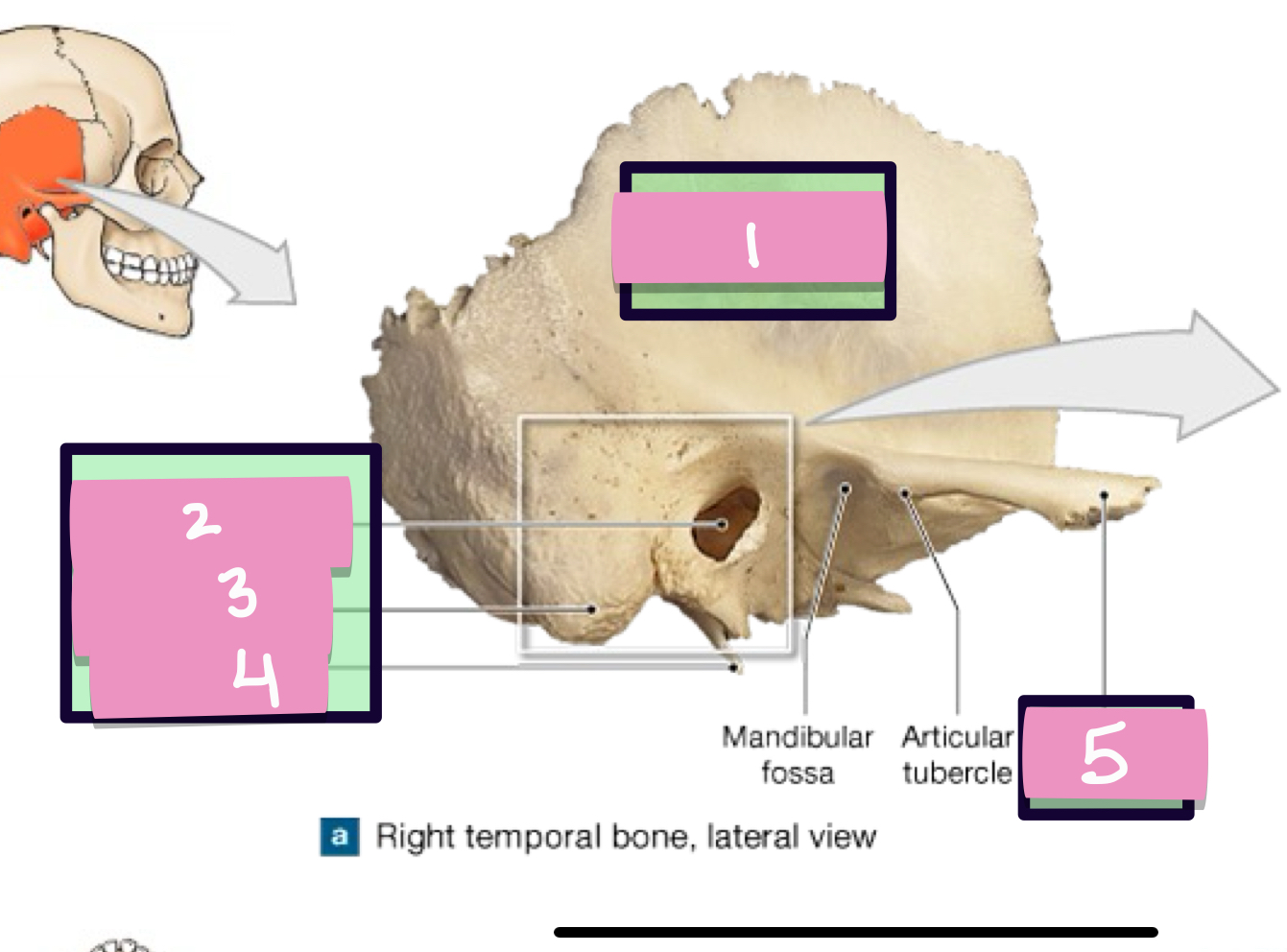
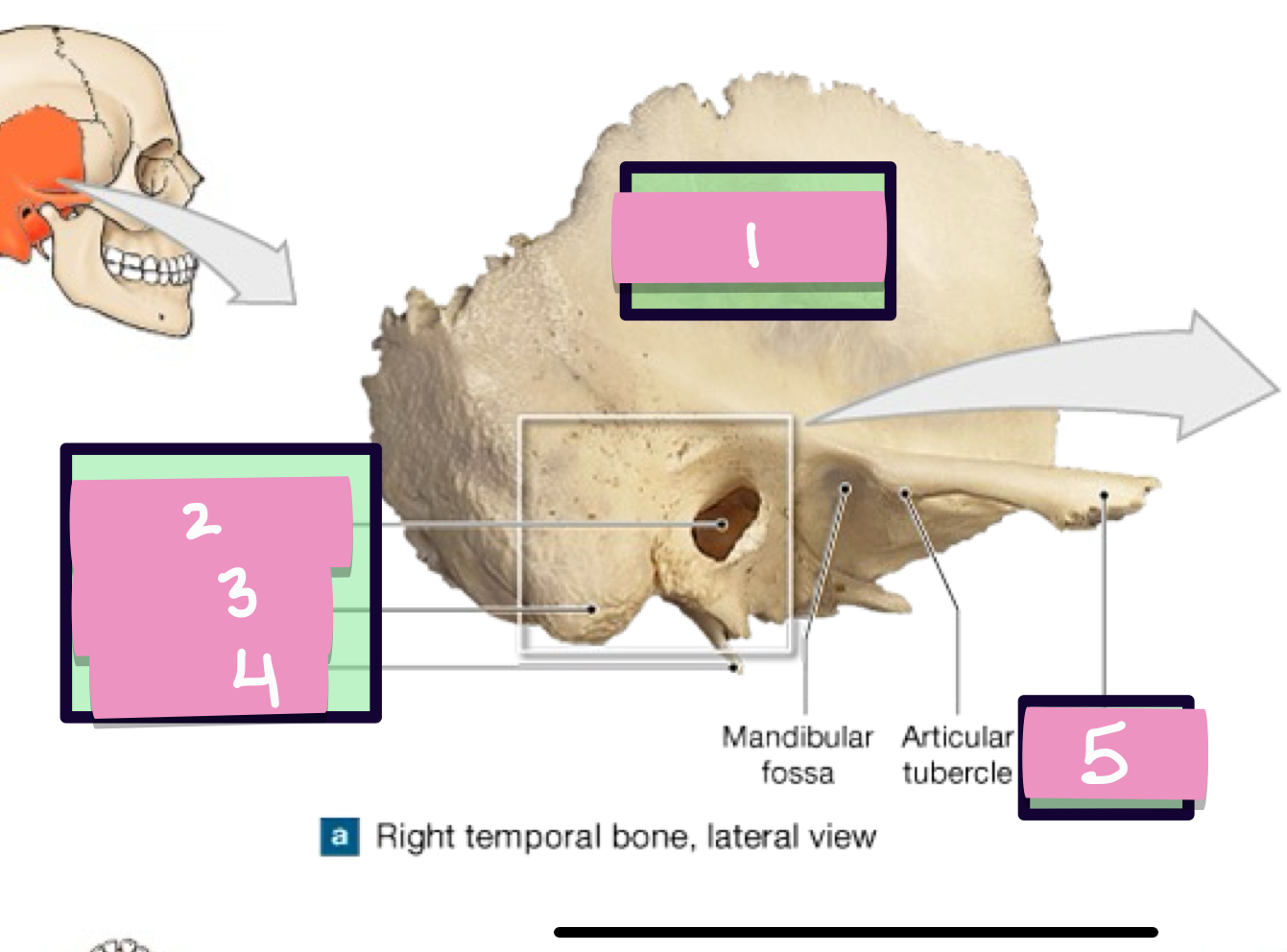
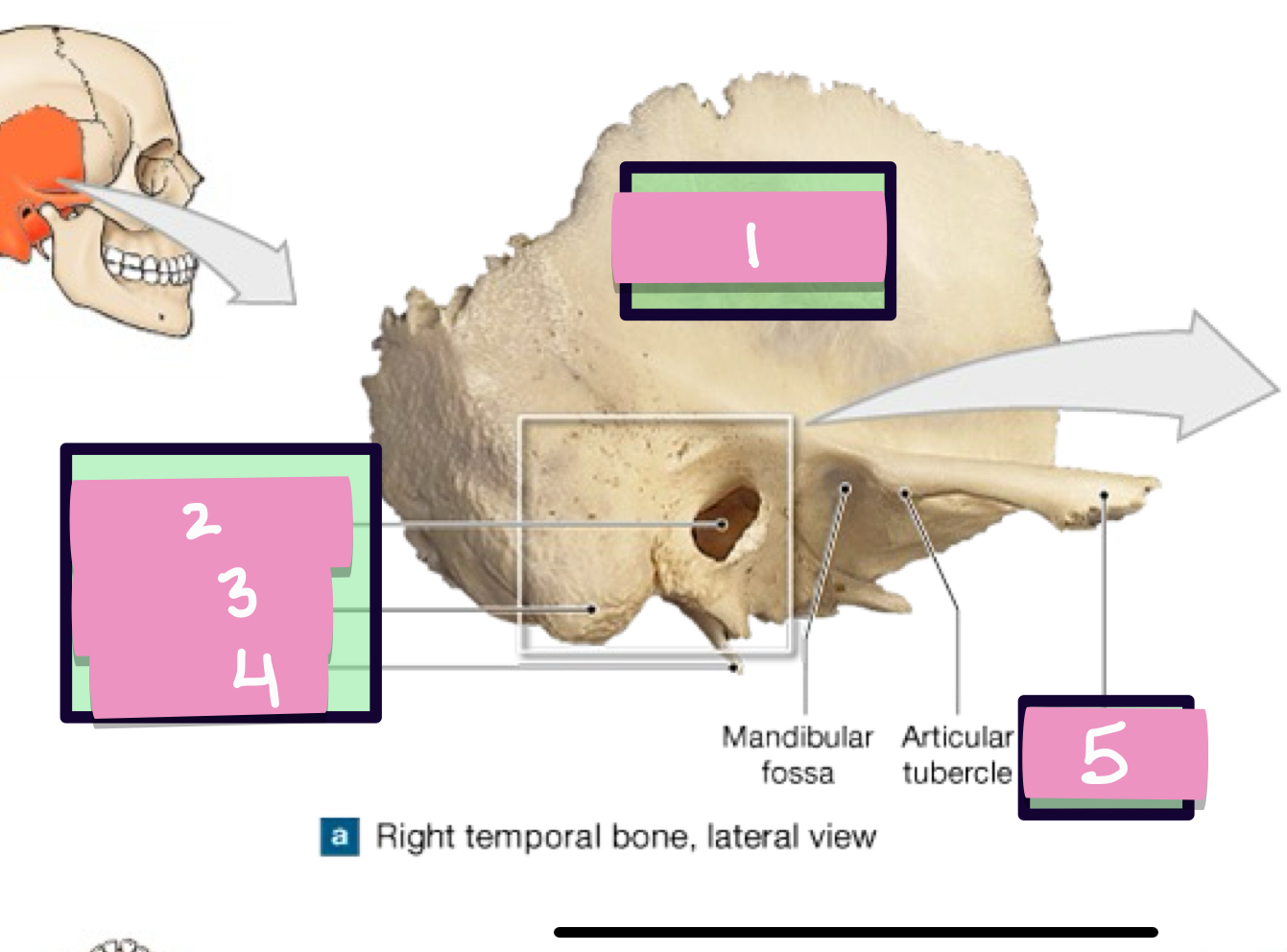
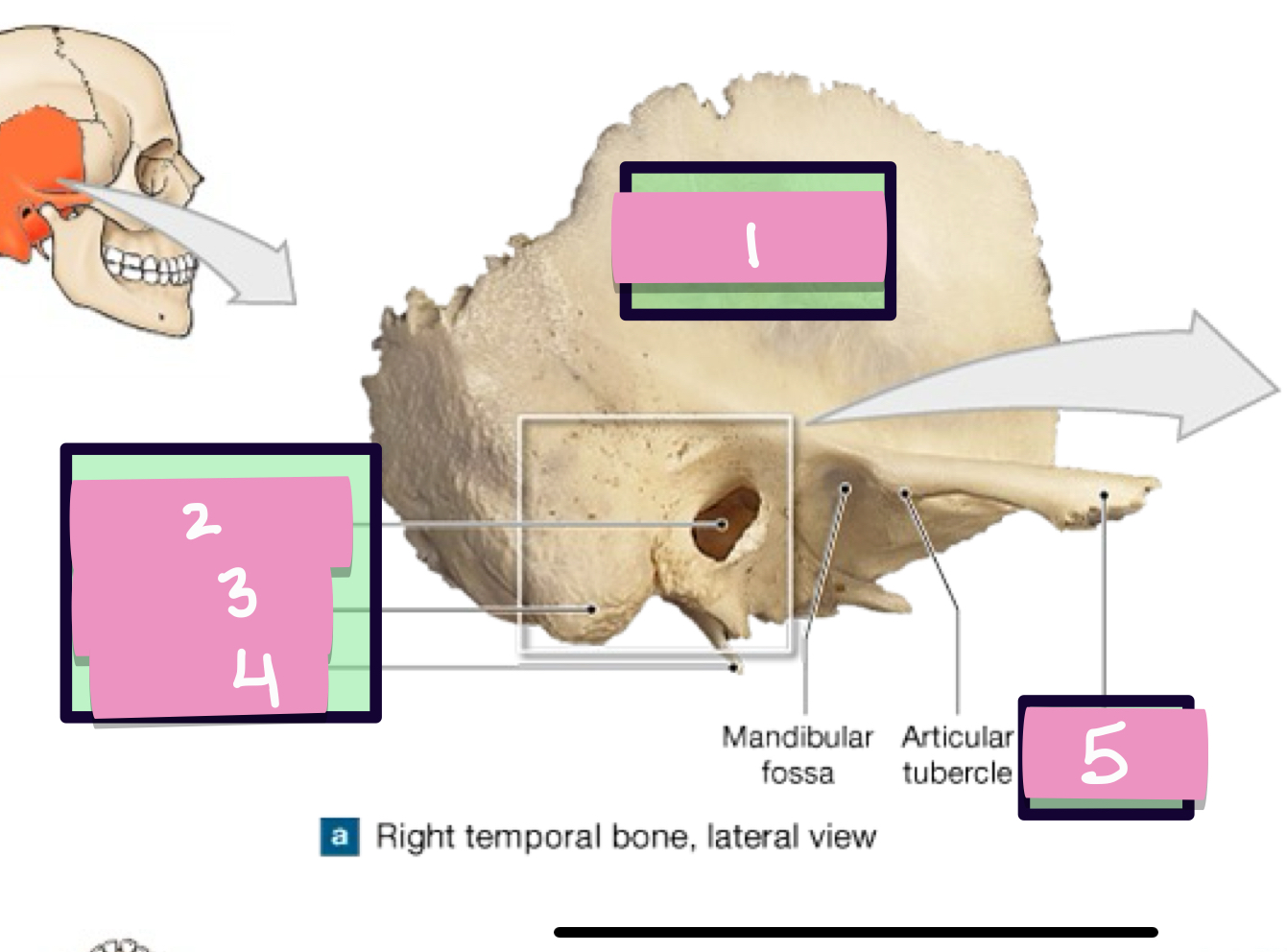
what is label 1
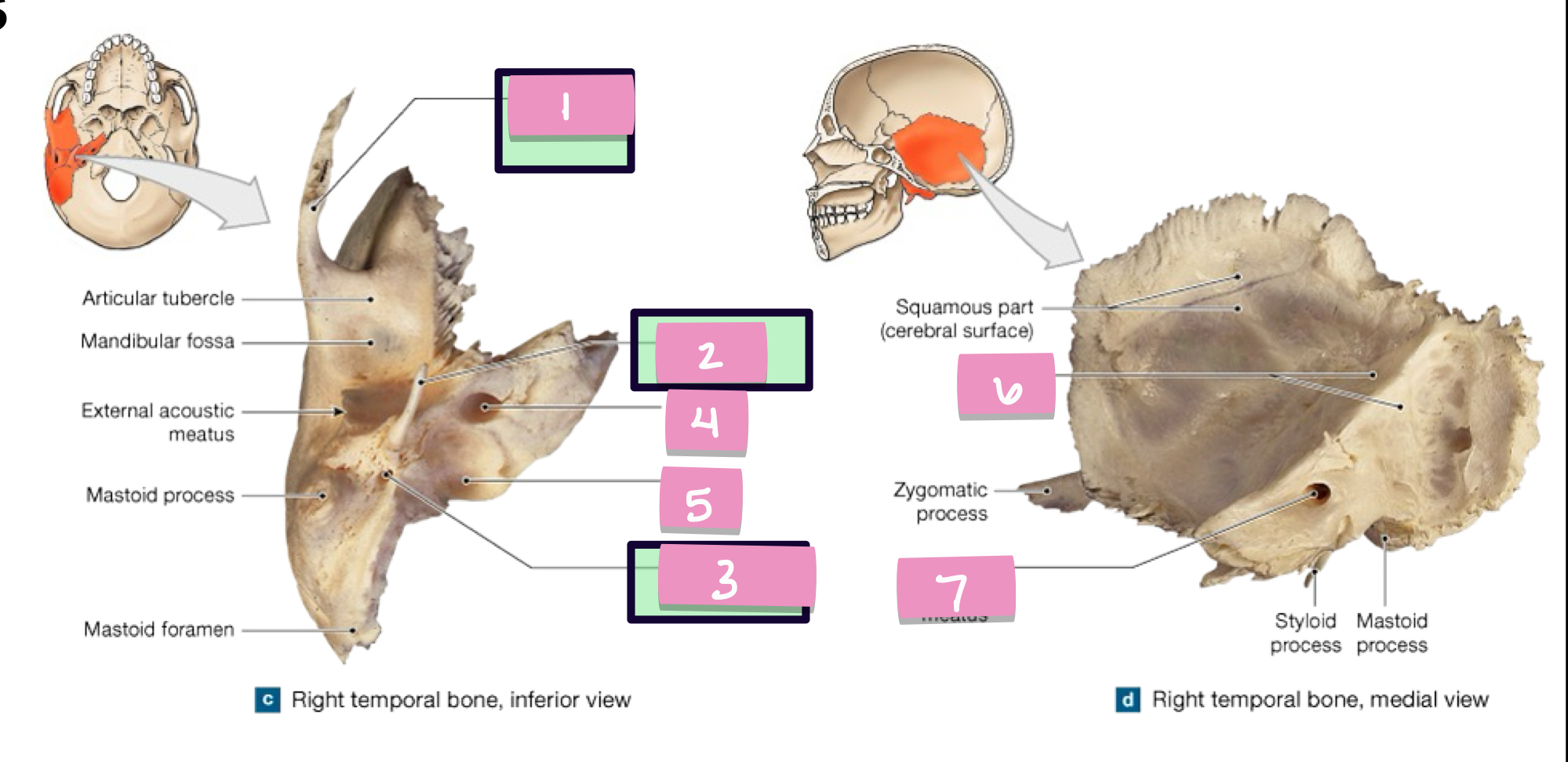
styloid process
what is label 2
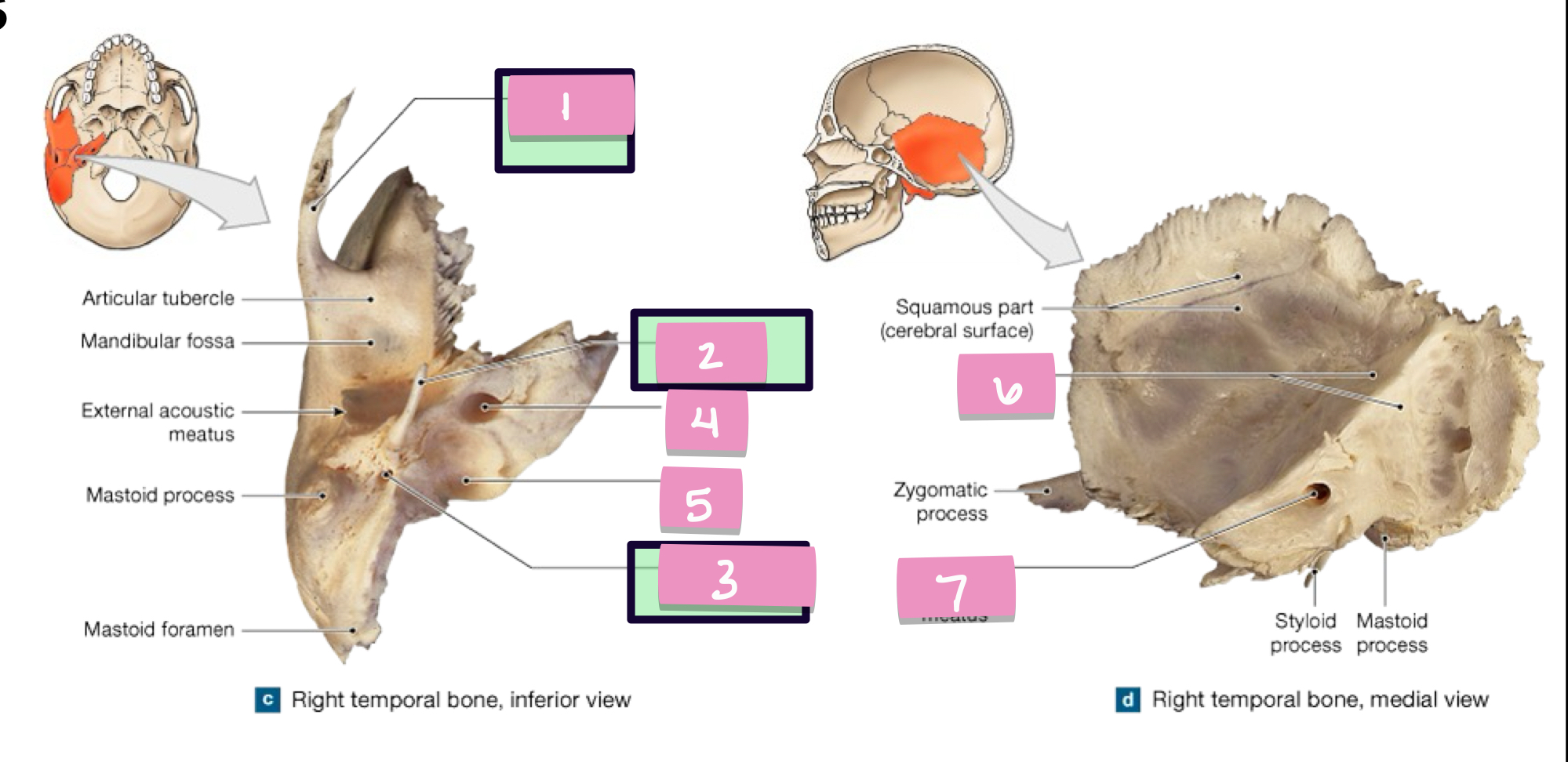
stylomastoid foramen
what is label 3
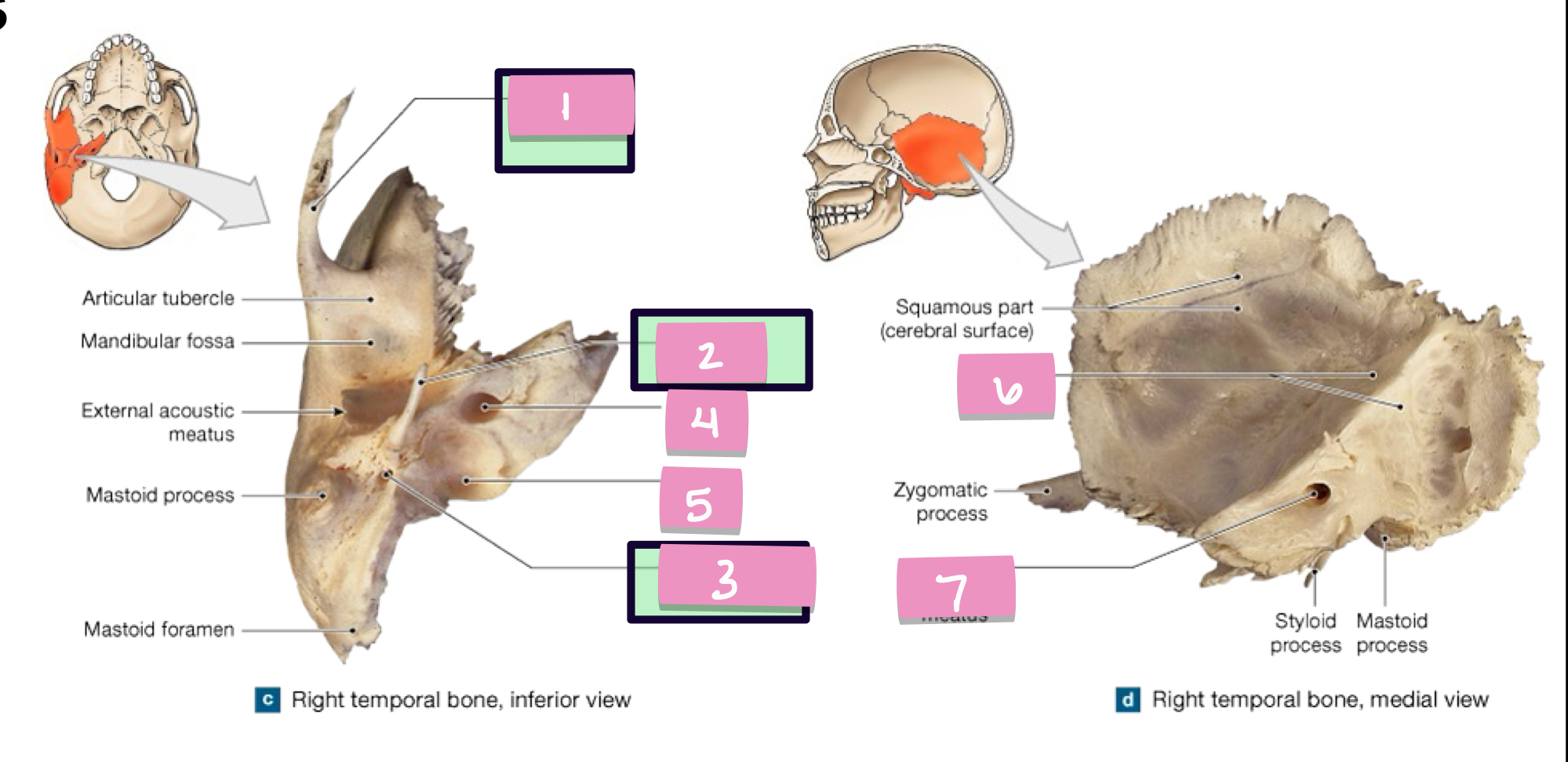
carotid canal
what is label 4
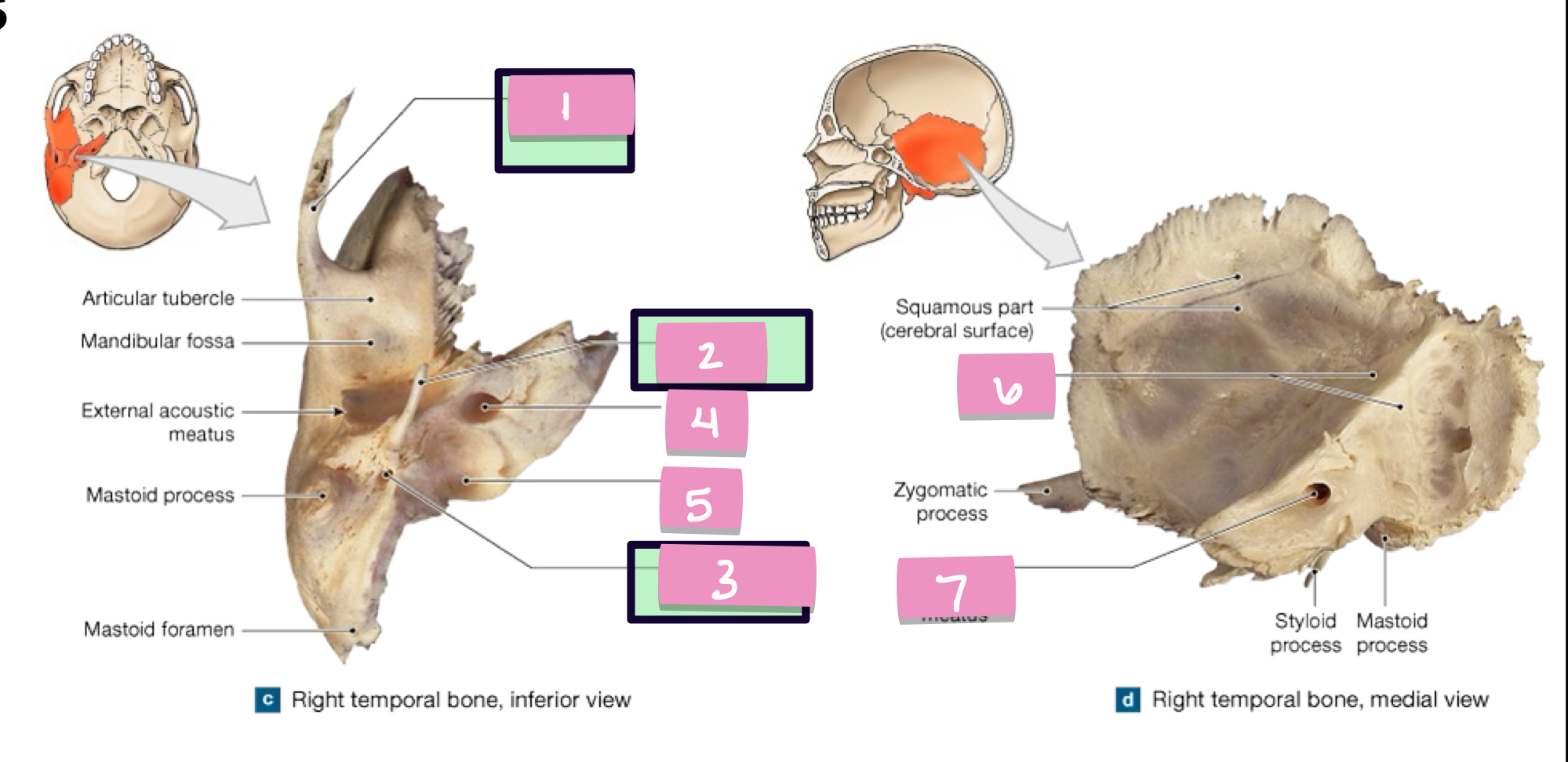
jugular fossa
what is label 5
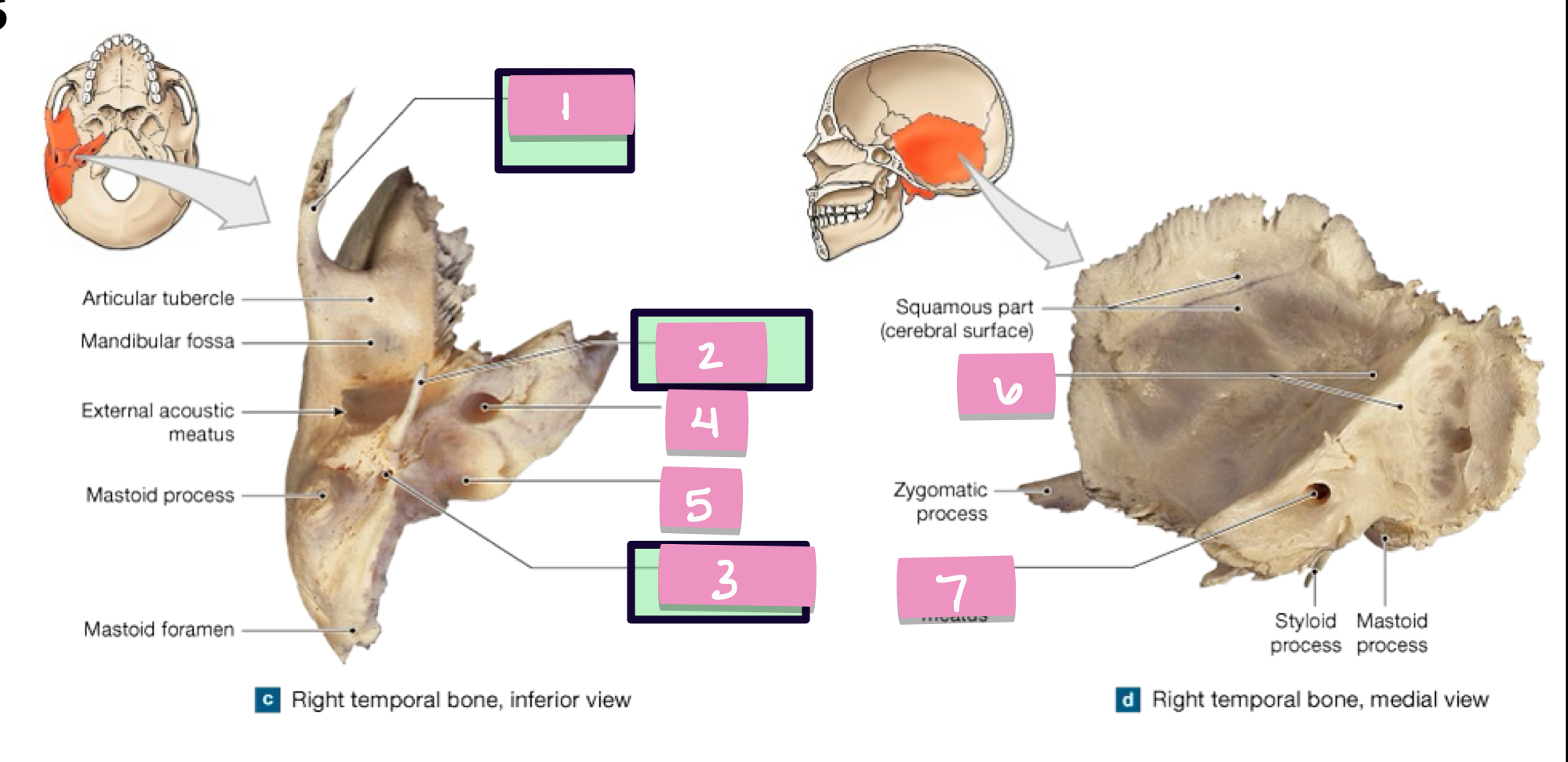
internal acoustic meatus
what is label 7
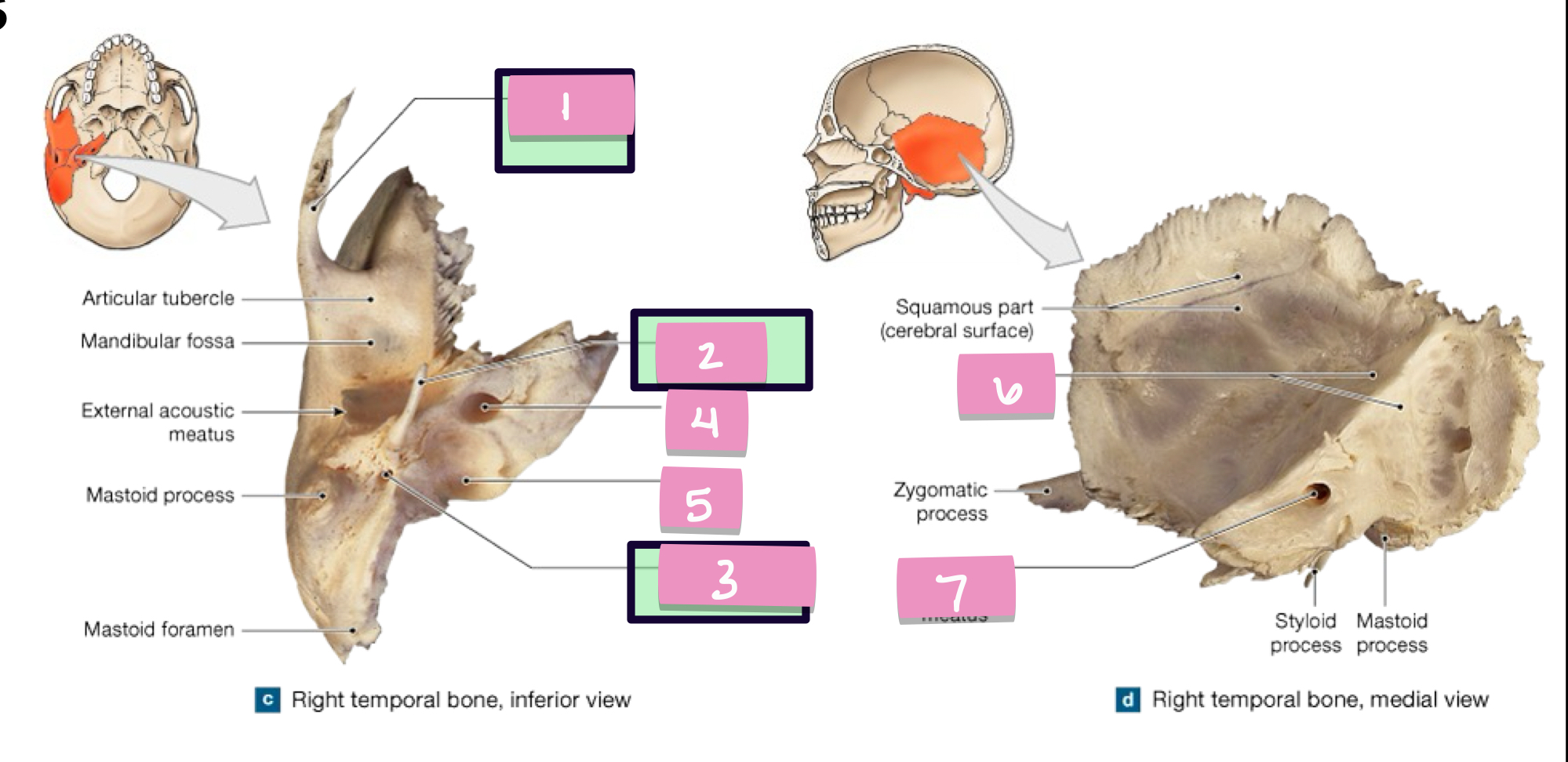
petrous part
what is label 6
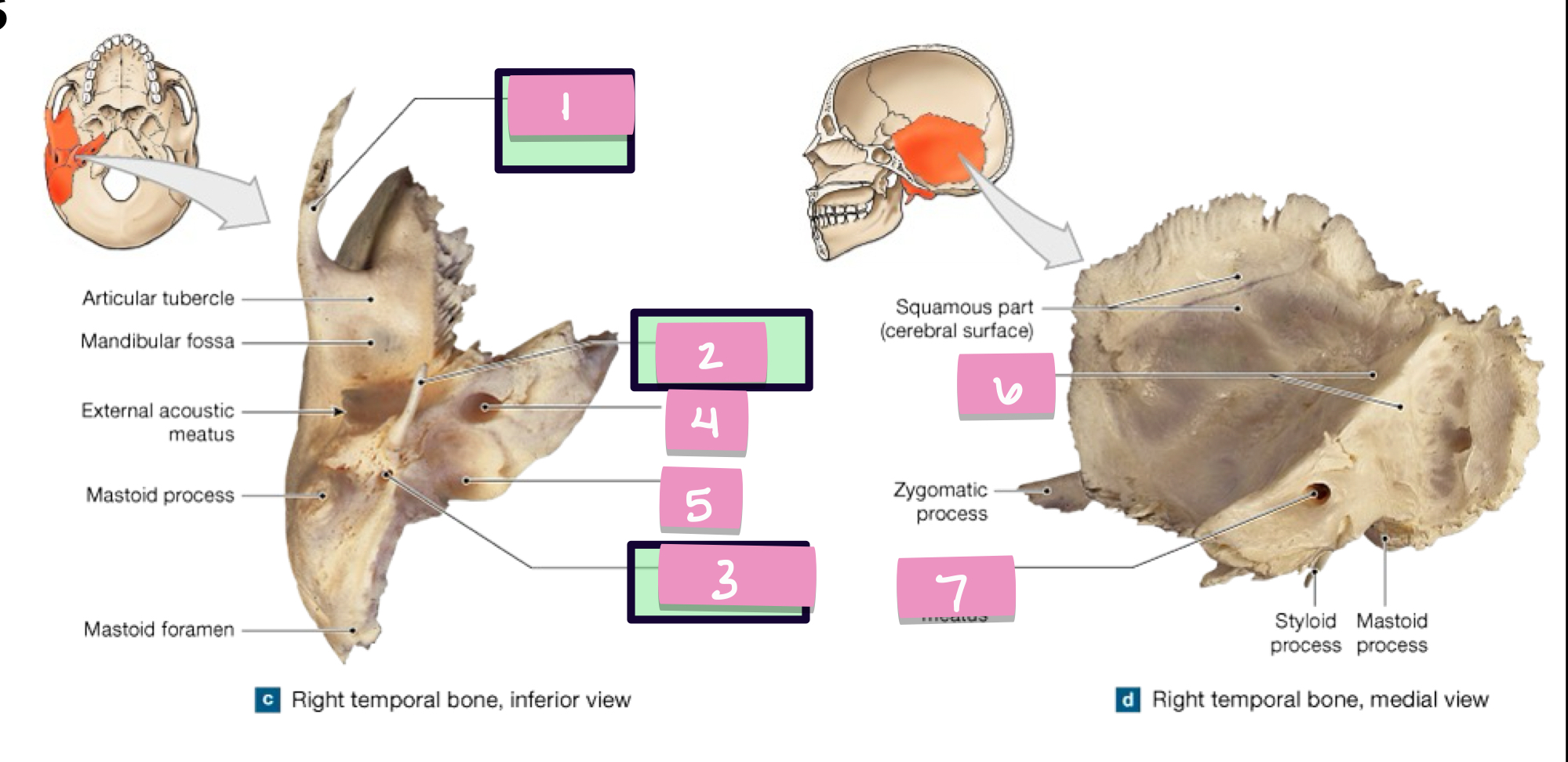
cribriform plate
what is label 1
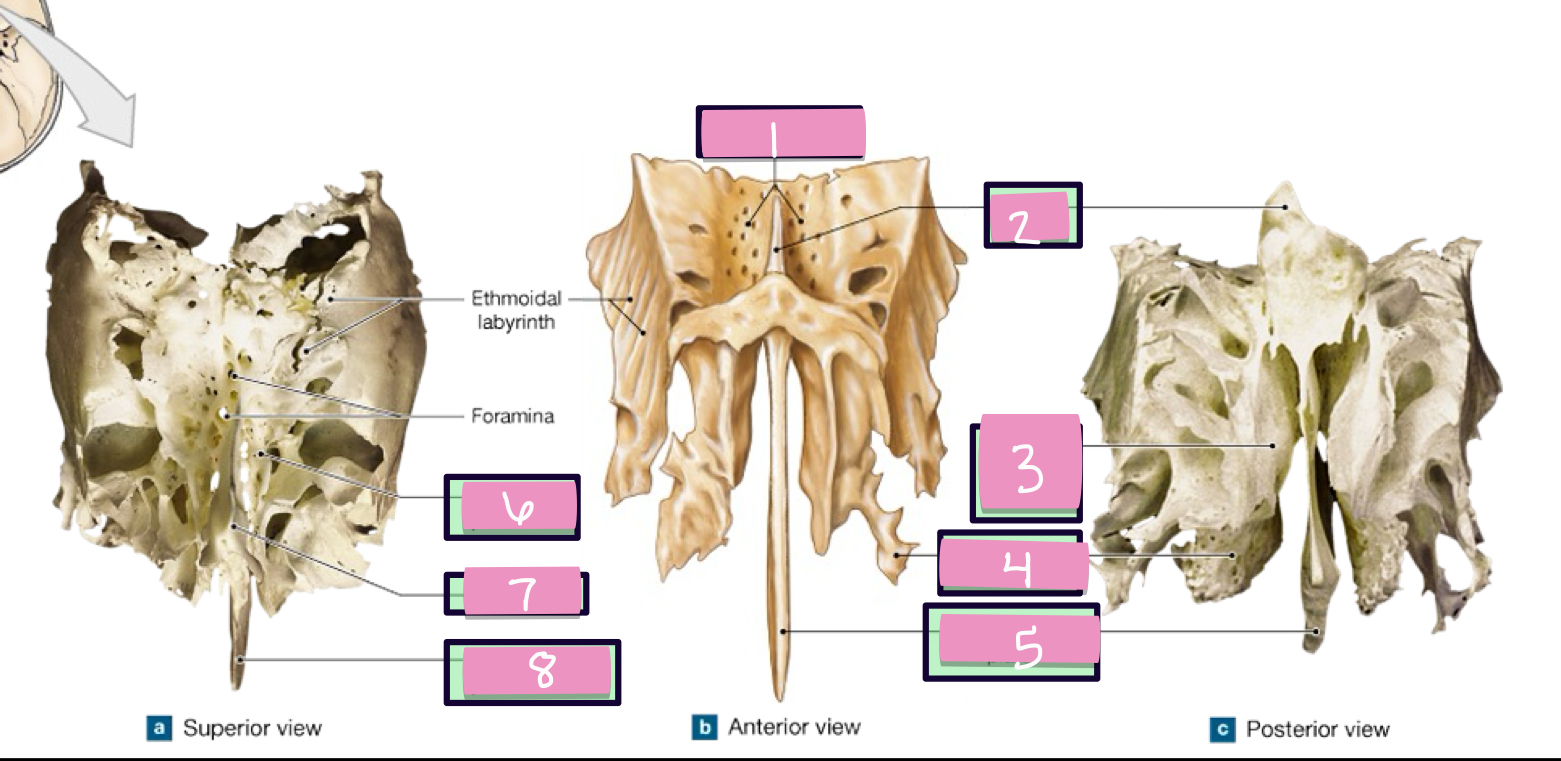
crista gali
what is label 2
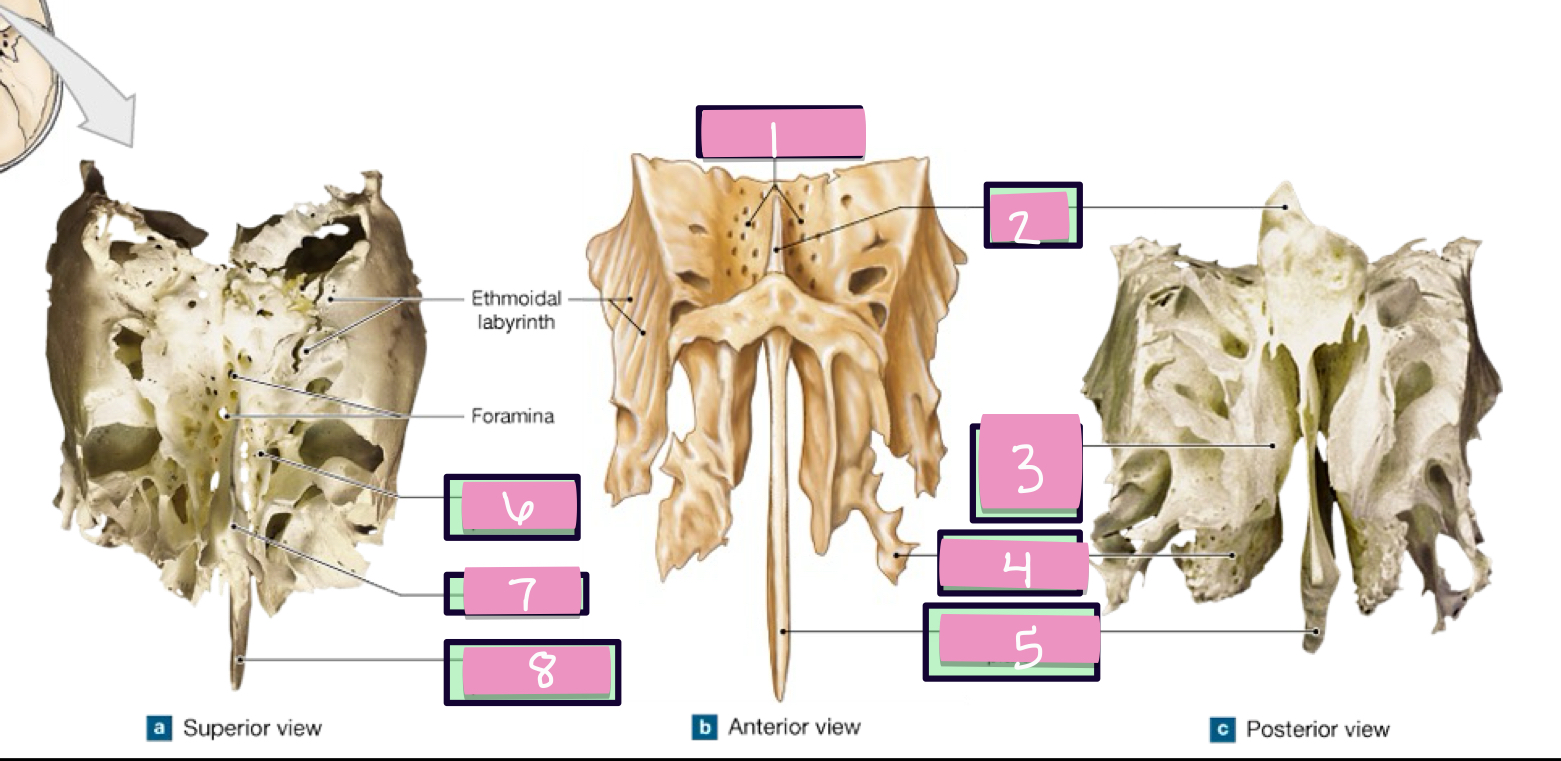
superior nasal concha
what is label 3
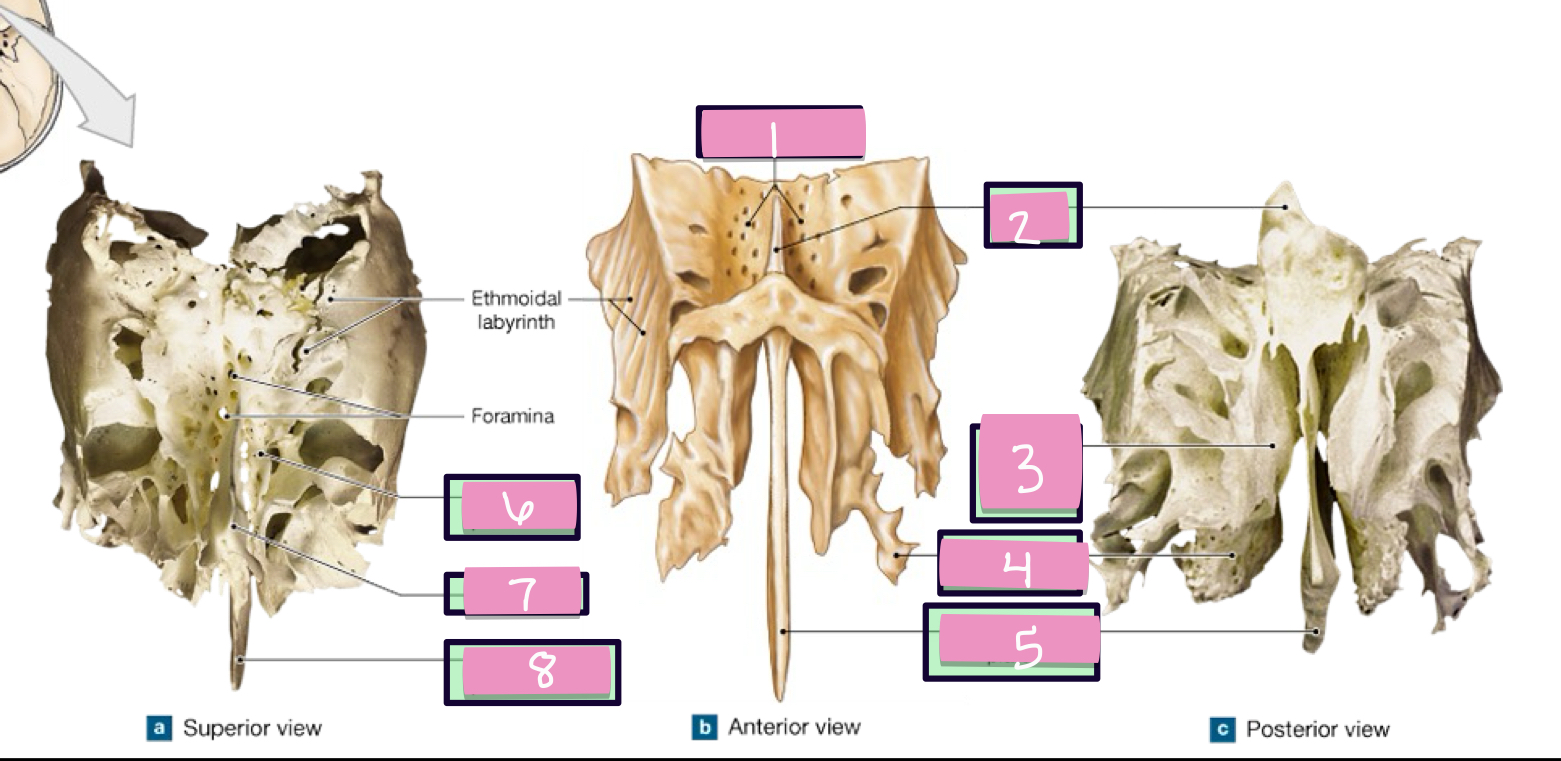
middle nasal concha
what is label 4
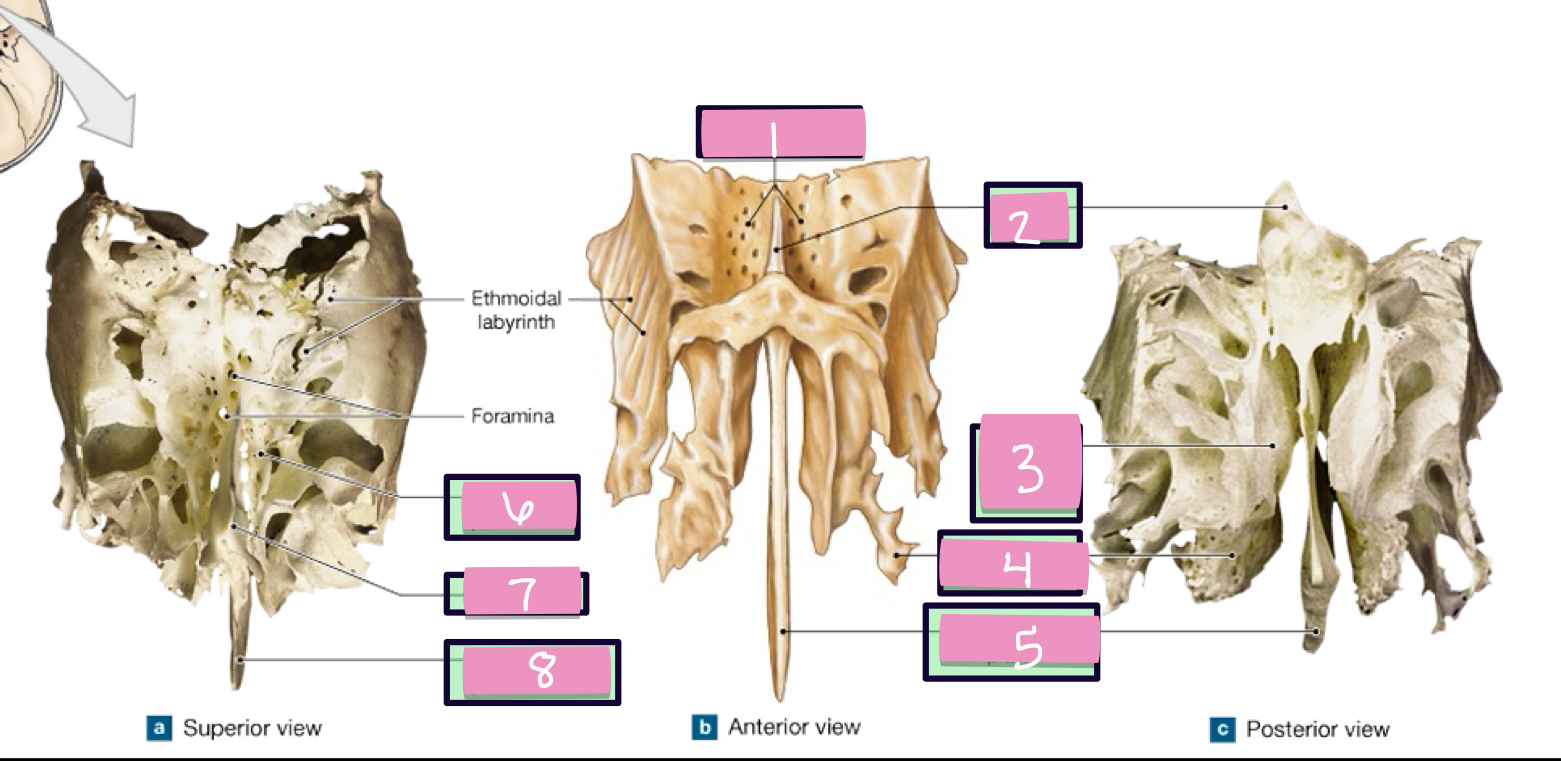
perpendicular plate
what is label 5
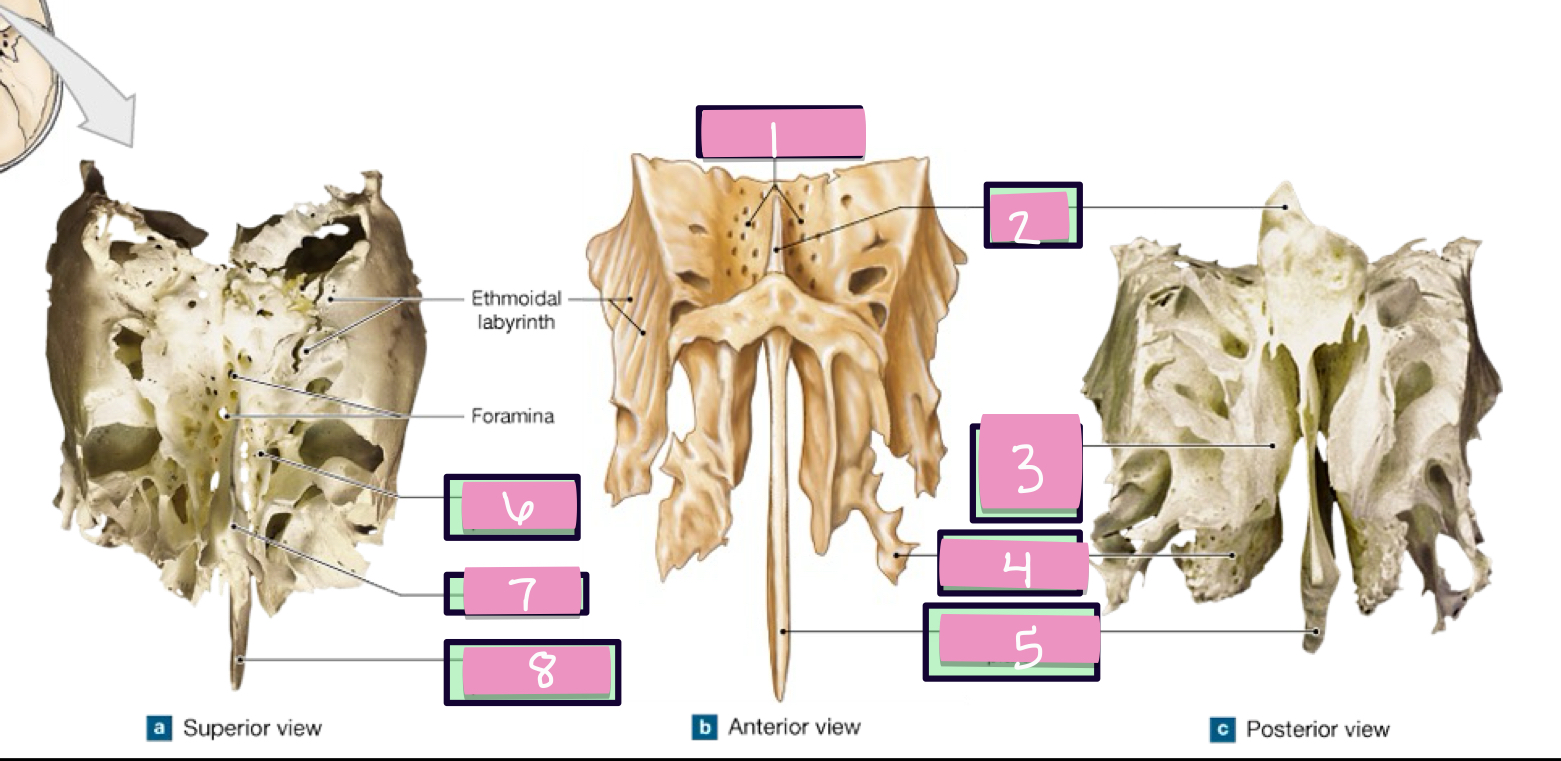
paranasal sinus
air filled chambers that open into the nasal cavity
stylohyoid ligaments
what ligaments is the hyoid bone suspended by
fontanelle
membranous areas where sutures will eventually form
24 vertebrae (7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar), 1 sacrum, coccyx
what makes up the vertebral column
encloses and protects the spinal cord
supports the skull
supports the weight of the head, neck, trunk
transfers weight to the lower limbs
helps maintain the upright position of the body
function of the vertebral column
cervical curve
a secondary curve develops as the infant learns to balance the head on vertebrae of the neck
thoracic curve
a primary curve accommodates the thoracic organs
lumbar curve
a secondary curve balances the weight of the trunk over the lower limbs, it develops with the ability to stand
sacral curve
a primary curve accommodates the abdominopelvic organs
intervertebral discs
a vertebral body is separated from another vertebral body by a pad of cartilage called
spina bifida
malformation of the structures making up the vertebral arch, where the vertebral arch fails to close completely
atlas
C1 is also known as
axis
C2 is also known as
ligamentum nuchae
large elastic ligament, begins at the vertebral prominens and extends to the external occipital crest if the skull
whiplash
sudden motion of the head resulting in vertebral damage
protects the heart, lungs, thymus, and other structures within the cavity
it serves as the attachment site for muscles involved in respiration, positioning the vertebral column, movements of the pectoral girdle and upper limb
functions of the thoracic cage
1-7
which ribs are true ribs
8-10
which ribs are false ribs
costal cartilages
connects false ribs to the sternum
11-12
which ribs are floating ribs
manubrium, body, xiphoid process, jugular notch
what does the sternum consist of