vesicular transport
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
cell bio lecture 5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
what protein is involved in facilitated diffusion
channel protein
what protein is involved in active transport
carrier proteins
vesicles
Proteins and polysaccharides and larger particles cross
the membrane using VESICLES
how do the membrane of organelles communicate
fusion of the vesicles
2 key processes of vesicular transport
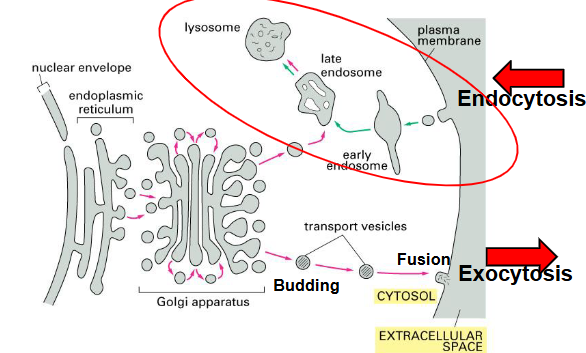
exocytosis
endocytosis
exocytosis
secretions of macromolecules through
fusion of vesicles with the plasma membrane
endocytosis
cell takes in macromolecules by
forming new vesicles from the plasma membrane
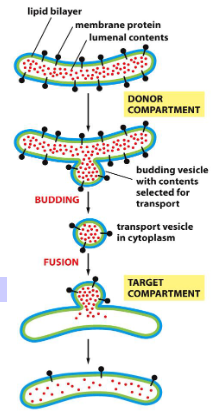
budding and fusion
• Budding from donor.
• Fusion with target.
• Membrane is transferred.
• Proteins retain original configuration.
• Soluble components transferred.
Main Pathways of Vesicular Transport
vesicles
• Form part of the endomembrane system.
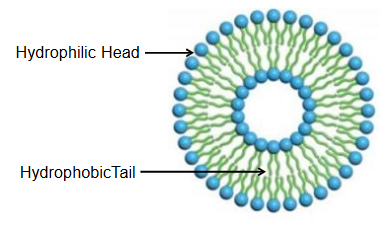
• Small membrane-bound sacs.
• Transport or store substances.
• Membrane is made of two layers = lipid bilayer.
• Vesicles can fuse with organelles to release their contents
within the cell and can also fuse with the cell/plasma membrane and
release their contents outside of the cell.
types of vesicles
Vacuoles
• Lysosomes
• Peroxisomes
• Endosomes
• Transport vesicles
• Secretory vesicles
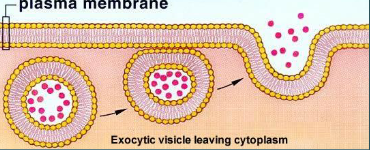
exocytosis
• A transport vesicle buds from the golgi apparatus and moves
to the plasma membrane.
• Vesicular membrane and plasma membrane make contact.
• Bilayers re-arrange to allow fusion.
• Cargo in the vesicle released into the extracellular fluid.
• Vesicular membrane becomes part of the plasma membrane.
what r the 2 types of exocytosis
constitutive
regulated
Constitutive exocytosis
• Steady stream of transport vesicles from trans Golgi to plasma
membrane.
• New lipids and proteins are continuously supplied to the
plasma membrane for membrane growth, rejuvenation and
remodelling
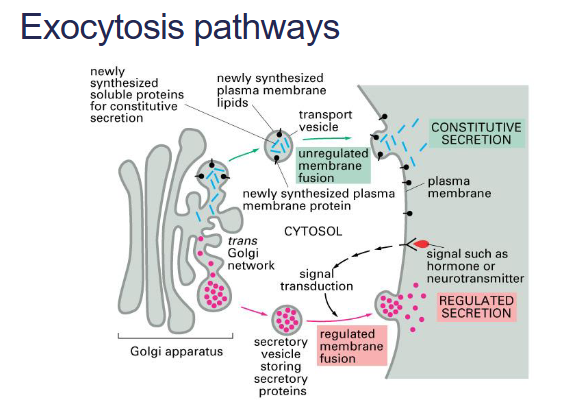
Regulated exocytosis
• Functions only in cells specialised for secretion.
• Lots of secretory vesicles found in specialised secretory cells –
hormones, mucous, digestive enzymes.
• Extracellular signal will stimulate their fusion with the plasma
membrane and release into the extracellular fluid.
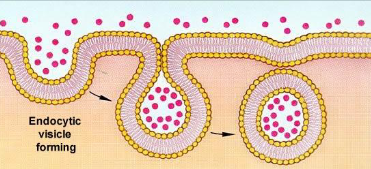
endocytosis
• New vesicles are formed by the plasma membrane.
• reverse process of exocytosis, using different proteins.
• Plasma membrane pinches in to form a vesicle containing
extracellular material.
what r the 3 types of endocytosis
phagocytosis
pinocytosis
receptor-mediated
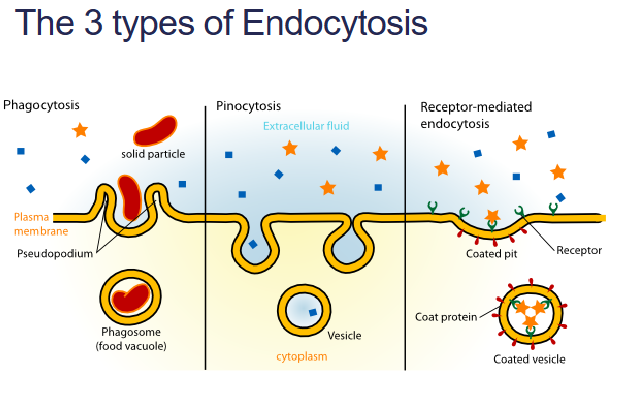
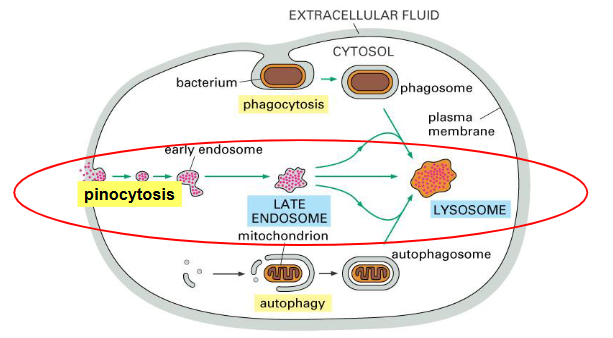
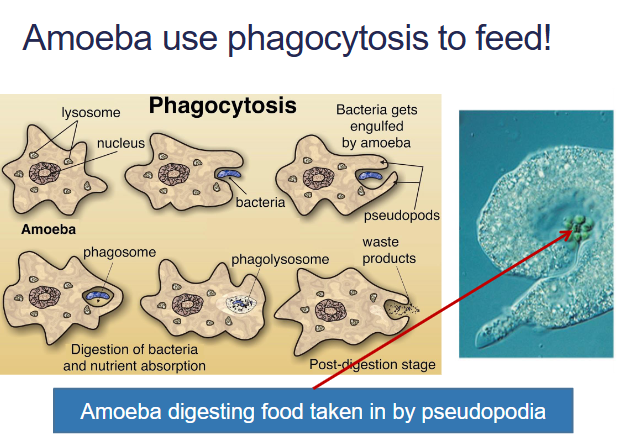
PHAGOCYTOSIS
engulfment of a particle, usually food or microorganisms, by wrapping cell membrane
around it to form a vacuole. Known as Cellular eating!The particle is digested after the vacuole fuses with a
lysosome containing hydrolytic enzymes• Protozoa use phagocytosis to feed.
• Macrophages defend against microorganisms.
• Macrophages/cleaner cells – engulf old RBCs
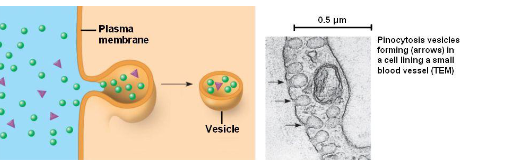
PINOCYTOSIS
same as phag except that fluids
are taken into small vesicles. Known as Cellular
drinking
• The cell ‘gulps’ droplets of extracellular fluid in tiny
vesicles.
• Example: Droplets of extracellular fluid enters the cells
via small vesicles.
• Pinocytic vesicles are returned to the cell surface after
ingestion.
• Macrophages swallow 25% of their own volume/hour.
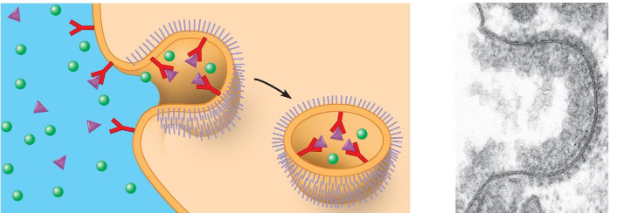
RECEPTOR-MEDIATED ENDOCYTOSIS
where receptors in a receptor-coated pit interact with a specific
protein, initiating formation of a vesicle.
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
• Selective uptake of specific macromolecules from extracellular
fluid.
• Receptor proteins in the membrane exposed to the
extracellular fluid.
• Extracellular substances (ligands) bind to the receptor sites on
receptor proteins.
• Receptor proteins are clustered in parts of the membrane
called ‘coated pits’.
• The cytoplasmic side of this area of membrane is coated with a
special protein
3 types of coated vesicles
clathrin
COP 1
COP 2
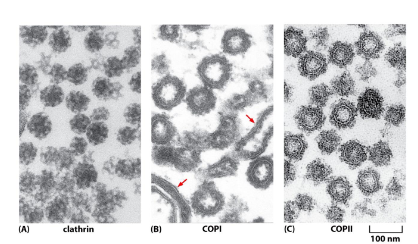
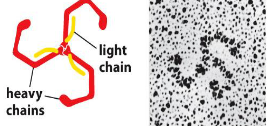
clathrin
3 light chains and 3 heavy chains
Clathrin coated vesicles traffic between the golgi network
and the lysosomes; and between the plasma
membrane and the endosomes.Triskelions form a framework
of hexagons and pentagons
to form coated pits on the
membrane surface.
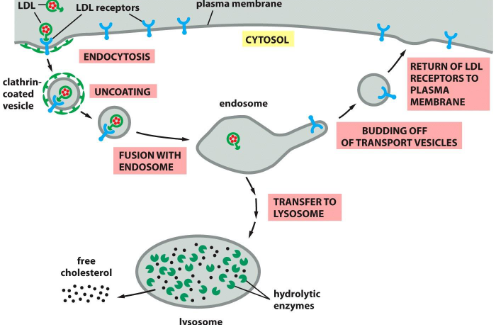
formation of a clathrin vesicle
1. Molecules bind to surface receptors of the plasma
membrane proteins located in areas of clathrin-coated
pits.
2. Pits bud to form clathrin-coated vesicles.
3. Fusion with endosomes or lysosomes.
LDL uptake into cells
Receptor mediated endocytosis
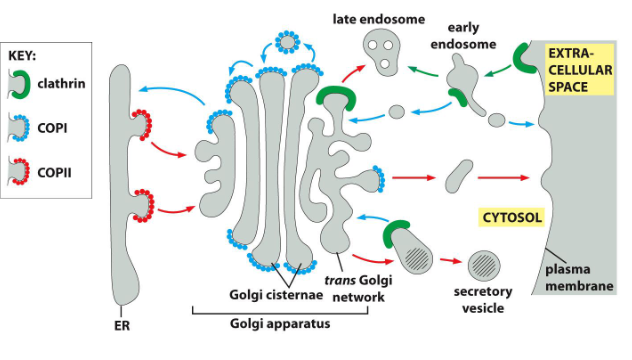
endosomes
Endosomes appear as a complex set of connected
membrane tubes and larger vesiclesmain sorting station in the endocytic pathway
Acidic environment promotes cargo release.
what are the 2 populations of endosomes
Early endosomes (beneath plasma membrane)
• Late endosomes (near nucleus)
Degradation of endocytosed material