Derm pathophys
1/157
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
158 Terms
Can all skin diseases be observed clinically?
mhm. yep. yeah. they can.
list the functions of the skin
maintain normal body temp
protective barrier against invading organisms, UV, and trauma
receive external sensory stimuli
control insensible water loss
How is skin distinct from mucosa?
contains adnexal structures, such as eccrine units that exude sweat and folliculosebaceous units that produce hair/oils
If you look into a light microscope and see stratified squamous epithelium, what layer are you looking at?
epidermis
If you look into a light microscope and see a layer of connective tissue, what layer of skin are you looking at?
dermis
Describe the epidermis
outermost layer that is superficial, tough, protective, made up of stratified epithelium that contains keratinocytes, melanocytes, has 5 layers, and is where exocrine sweat glands open
What is the undulating, basement membrane and epidermal junction that separates the epidermis from the dermis?
dermal layer (basal)
Describe the dermis
semi-fluid layer that binds the body together and contains nerve endings, oil/sweat glands, hair follicles, blood/lymph vessels, connective tissue, is where tattoos are and is not regenerative like the epidermis
What layer of the epidermis has anucleate, flattened keratinocytes?
cornified layer
What layer of the epidermis has cells w/ cytoplasmic granularity resulting from an accumulation of keratin complexes? (is also where skin heals/new skin grows)
granular layer
What layer of the epidermis has cells w/ ample cytoplasm and prominent desmosomes?
spinous layer
What layer of the epidermis has cuboidal germinative keratinocytes?
basal layer
What are the layers of the epidermis?
stratum corneum, (stratum lucideum), stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, , stratum basale (dermal layer)
What is an intercalated dendritic cell in the basal layer that provides a dispersed screen against UV rays?
melanocyte
What is an intercalated dendritic cell that is bone marrow-derived and antigen presenting?
langerhans cells
What layer consists of connective tissue gel, collagen types I and II, and elastic microfibrils, and serves as the scaffolding that supports complex neurovascular networks?
dermis
What cells are in the dermis?
fibrocytes, mast cells, dendritic immune cells
What are the three types of skin diseases?
inflammatory, infectious, neoplastic
What is a macule?
area of increased or decreased pigmentation w/o elevation or depression
less than 1 cm, not palpable, superficial layers only
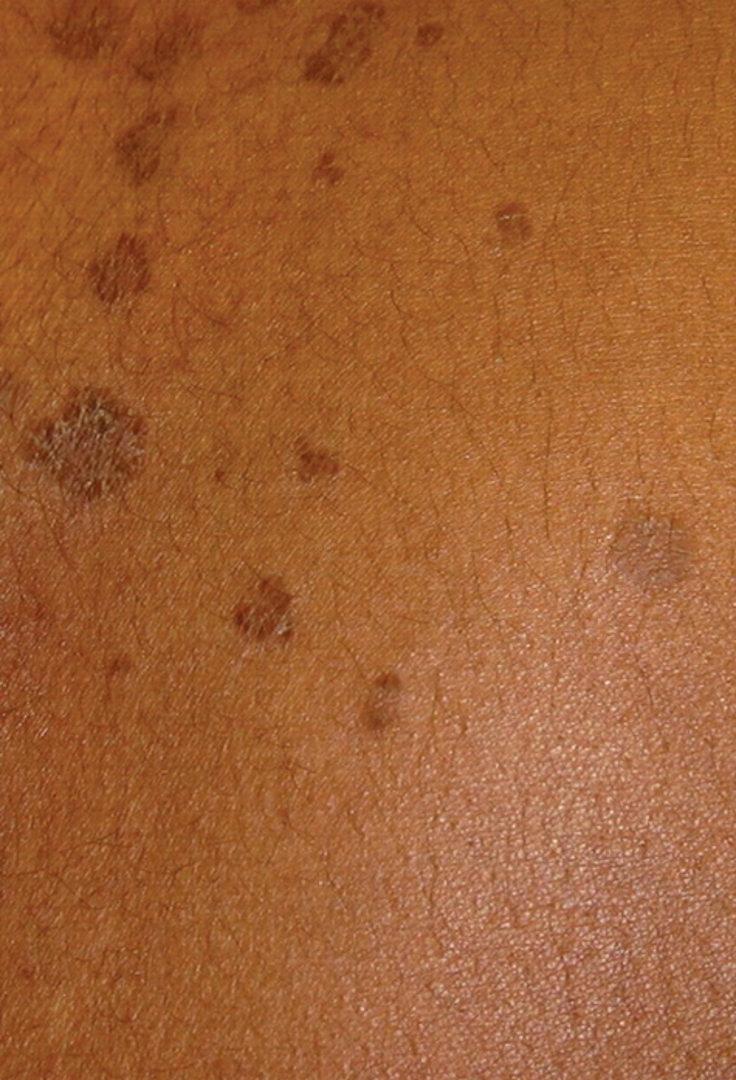
What is a patch?
macular type lesion that is flat, circumscribed and greater than 1cm
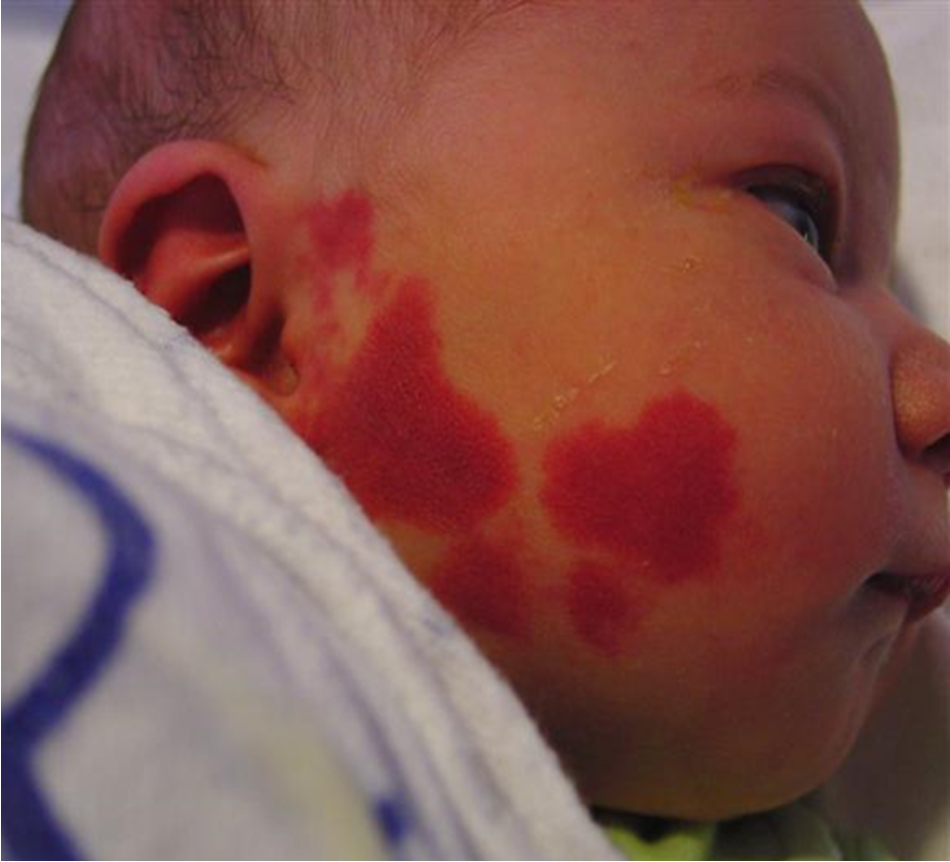
What is a papule?
superficial, solid lesion less than 1 cm, often occurs in clusters, and can accompany rashes
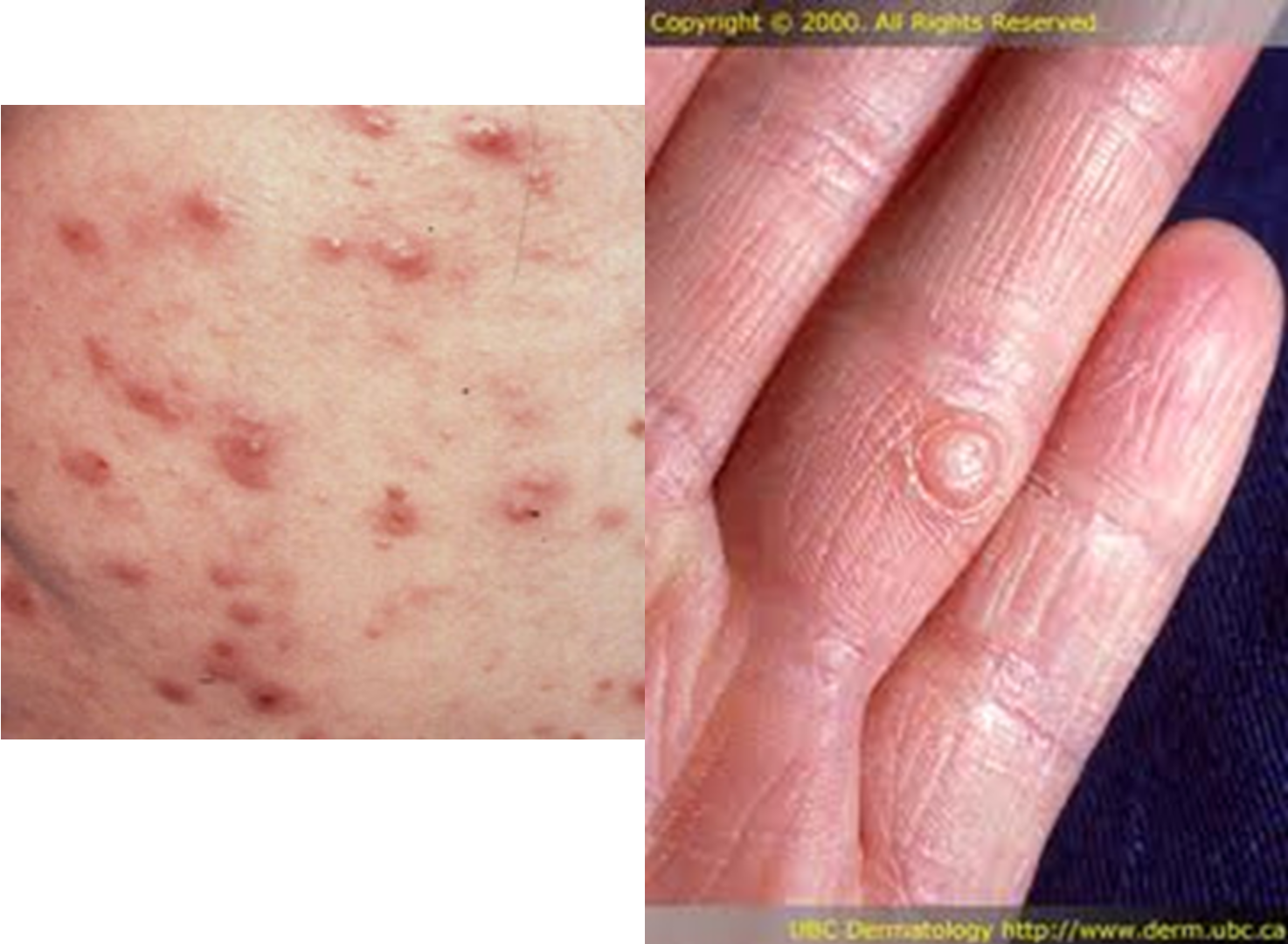
What may cause a papule?
inflammation from infected/abraded skin, accumulated secretions, infections such as disseminated histoplasmosis, hypertrophy of skin cells, acne
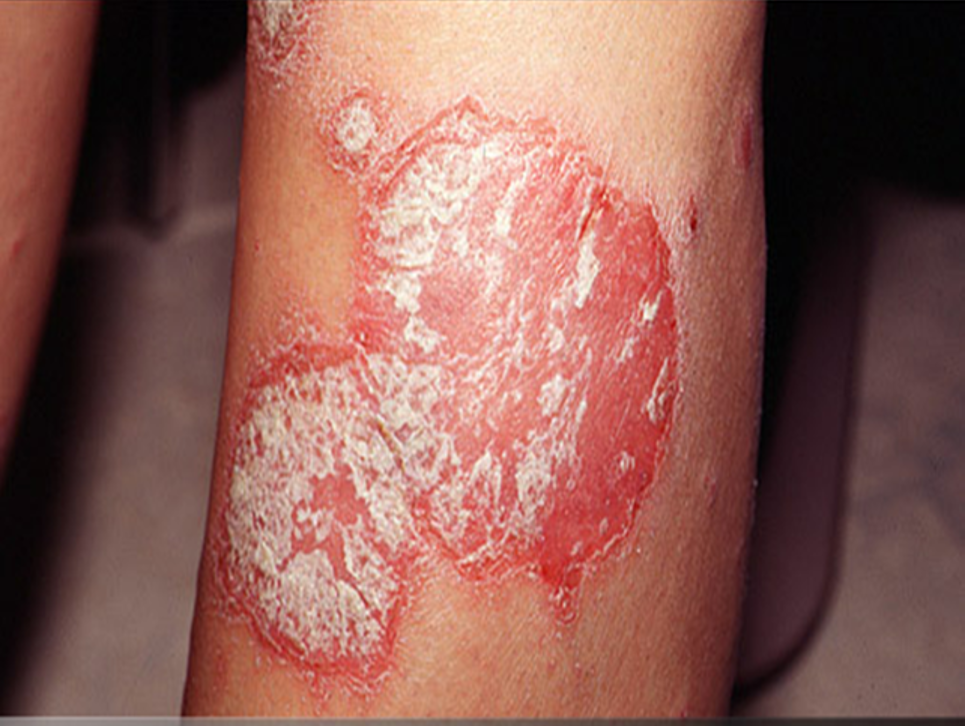
What is a plaque?
plateau-like elevation w/ a surface area greater than its height;
greater than 1 cm in size and frequently forms by confluence of papules
characterized by lichenification
What is lichenification?
rough and thickened skin that accentuates normal skin lines and resembles tree bark
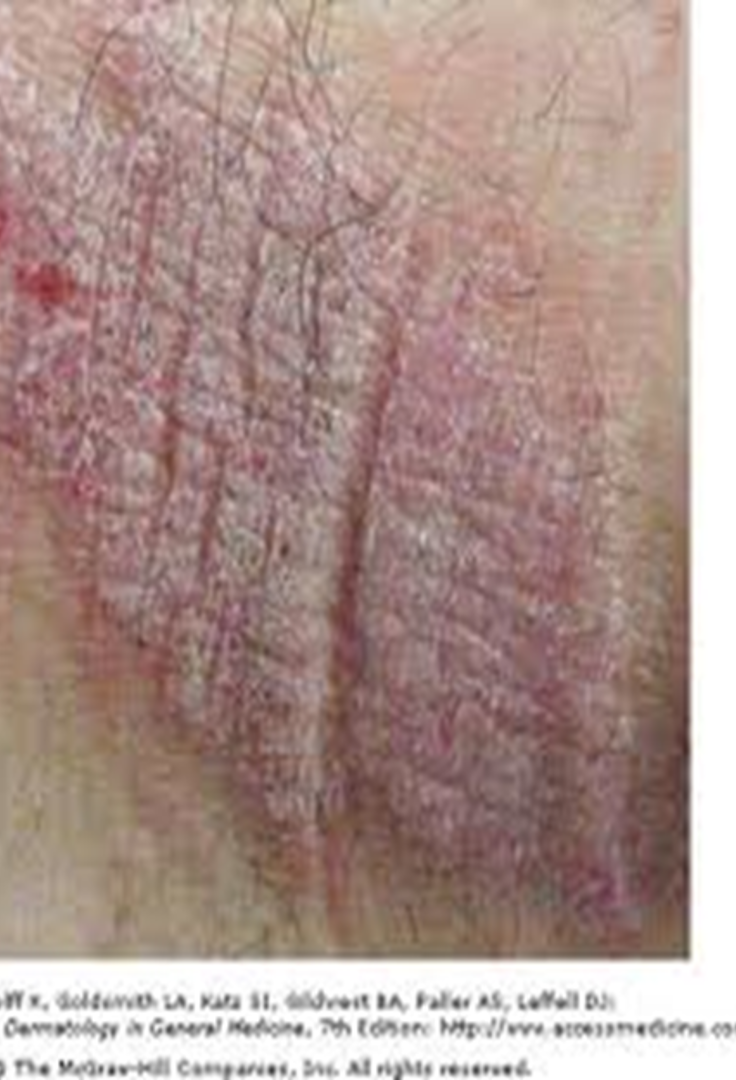
What disorders is lichenificaiton associated with?
pruritic disorders; chronic eczema, atopic dermatitis
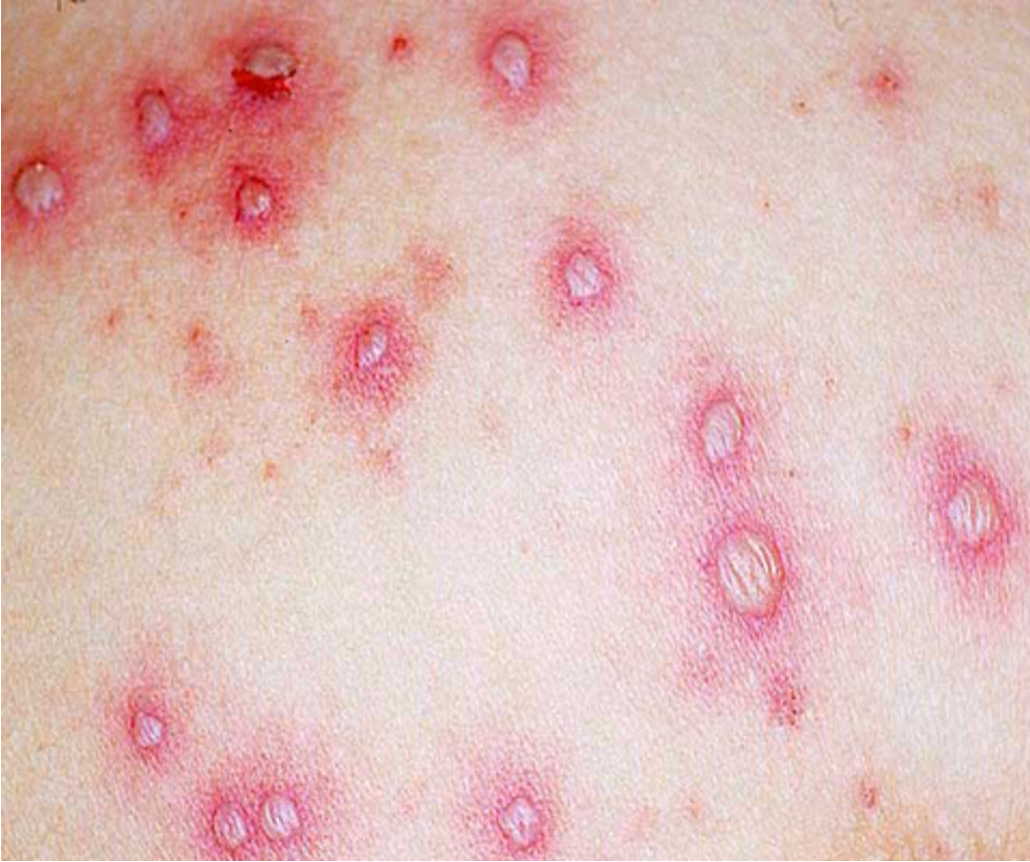
What is a vesicle?
small, circular, fluid filled lesion on or below the skin
less than 1 cm
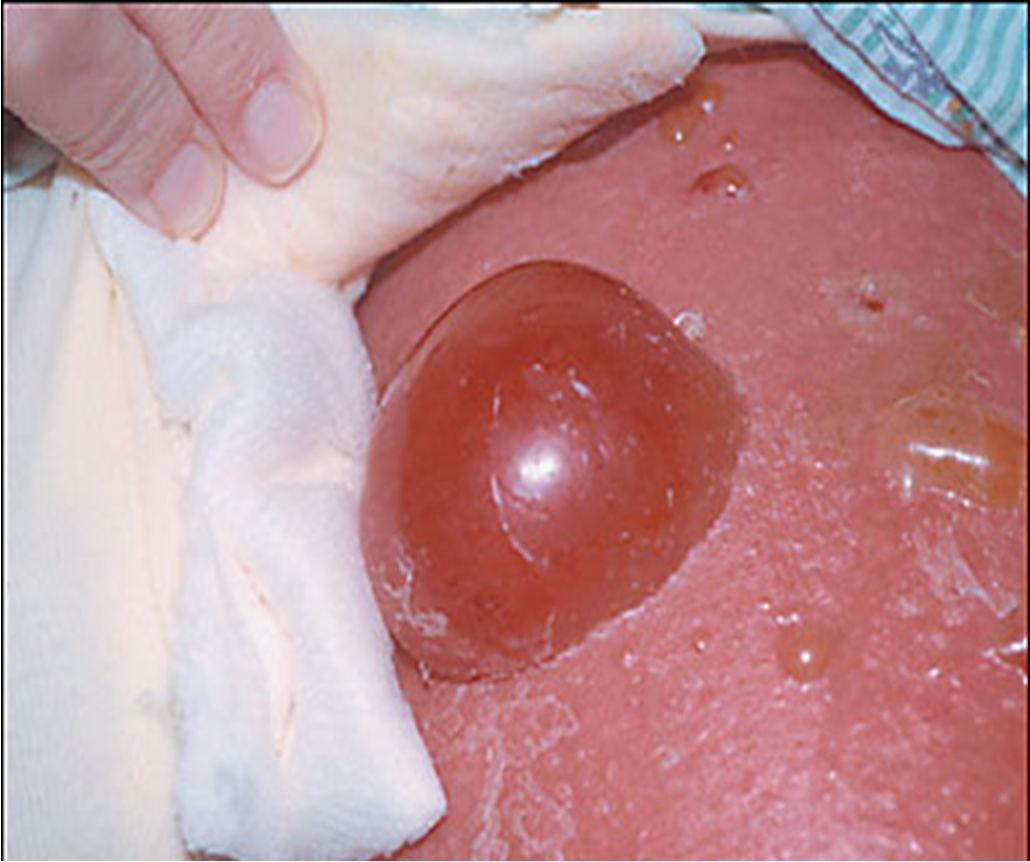
What is bulla?
circumscribed collection of free fluid greater than 1 cm
What is a pustule?
superficial skin cavity containing purulent exudate; may be yellow, white, green-white, or hemorrhagic
(vesicle or bulla containing purulent fluid)
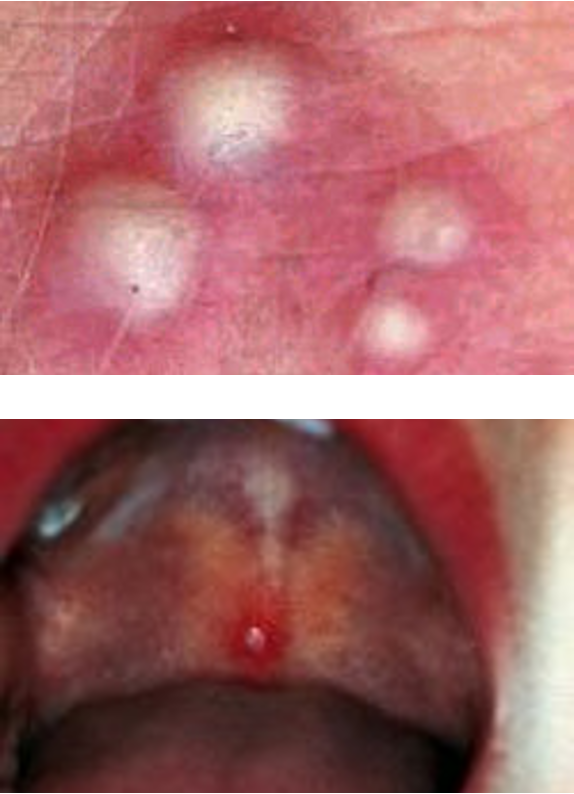
What would you call a vesicle or bulla that contains purulent fluid?
pustule
What is a blister?
both vesicles and bulla; defense mechanism of body where epidermis separates from the dermis and a pool of lymph and other fluids collect between the layers while skin regrows from underneath
What is etiology for blisters?
chemical or allergic rxn, physical injury (heat, frostbite, friction)
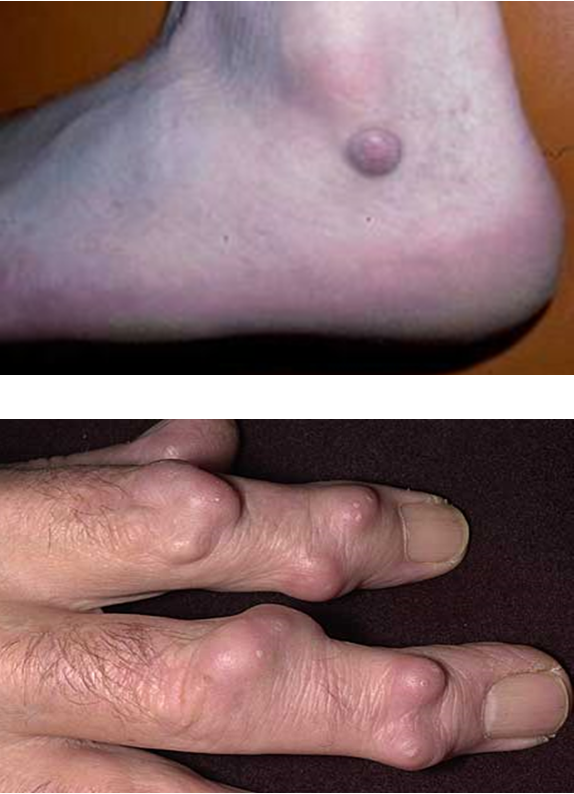
What is a nodule?
solid, circular lesion greater than 1 cm that usually invades epidermis and lower dermis
What is another name for a wheal?
urticarial exanthema, urticaria
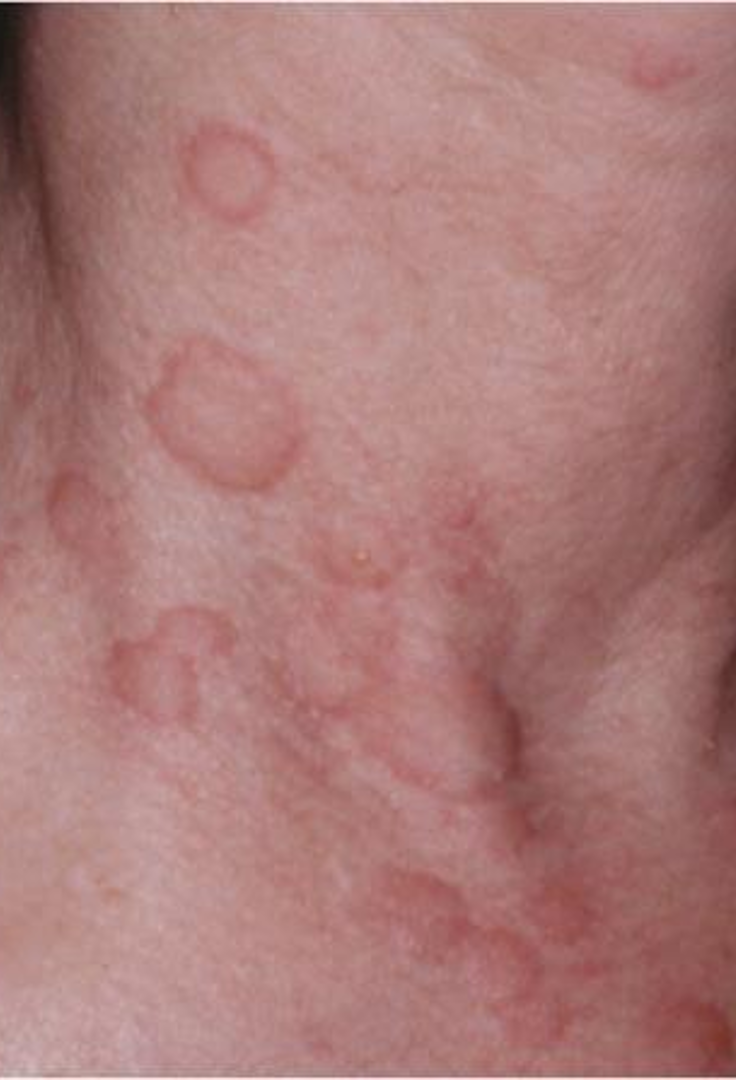
What is a wheal?
rounded or flat topped edematous plaque that is well demarcated; no scaling or epidermal involvement, color and shape varies
What shape can wheals be?
round, oval, gyrate, annular or serpiginous
What causes wheals?
allergic response
What is darier’s sign?
gentle rubbing or stroking of lesions is followed by local itching, erythema, and wheal formation w/in 2-5 min
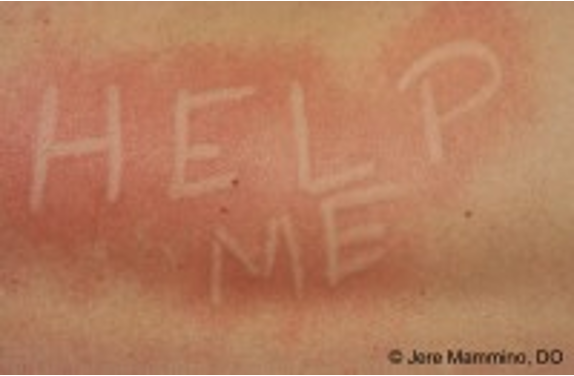
What is dermatographism?
“writing on the skin”; very common localized hive reaction
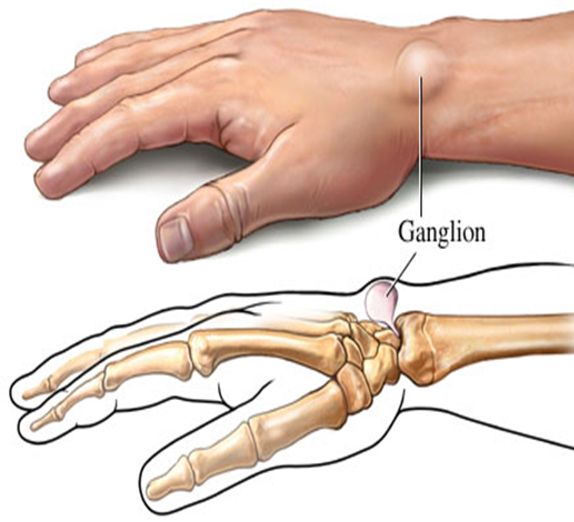
What is a cyst?
elevated, circumscribed and palpable encapsulated lesion filled w/ fluid or semisolid material /
enclosed sac w/ distinct membrane lining
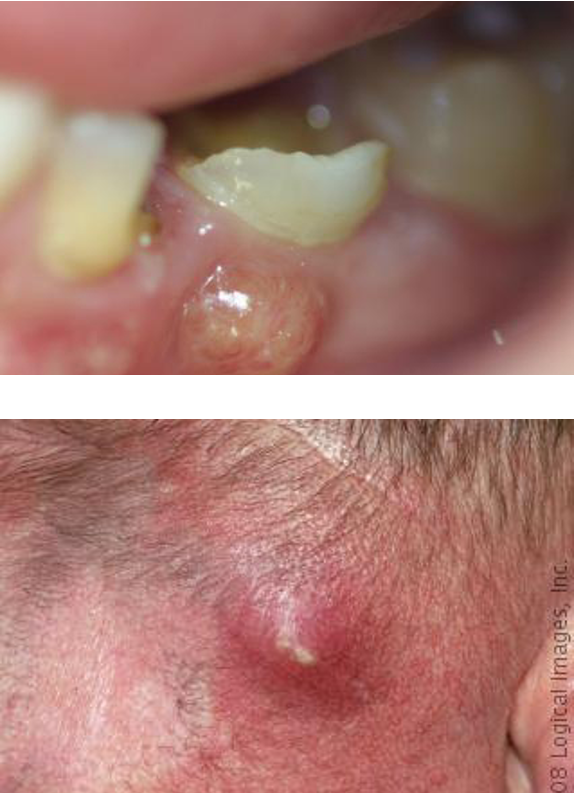
What is an abscess?
collection of pus
What is crust?
dried serum or exudates on skin surface; present after blisters rupture
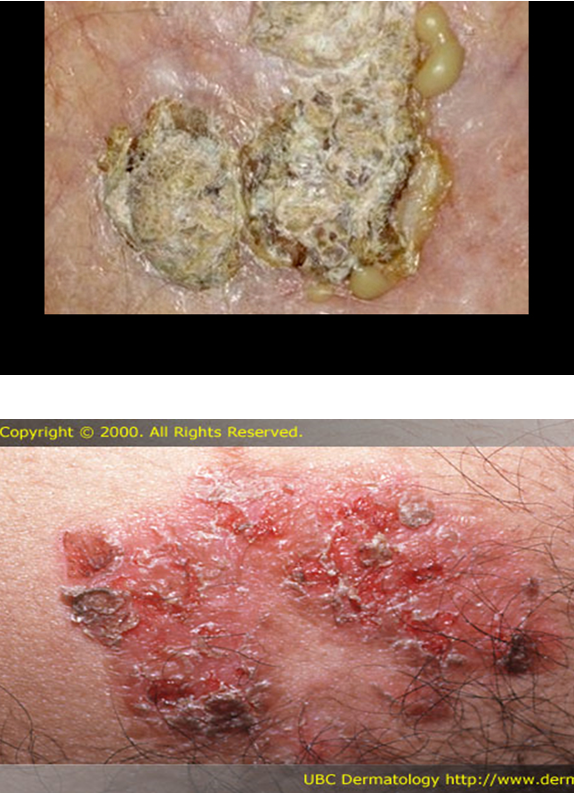
What color does crust from dried blood appear?
brown
What color does crust from dried serum appear?
honey colored
What color does crust from dried pus appear?
yellow-green
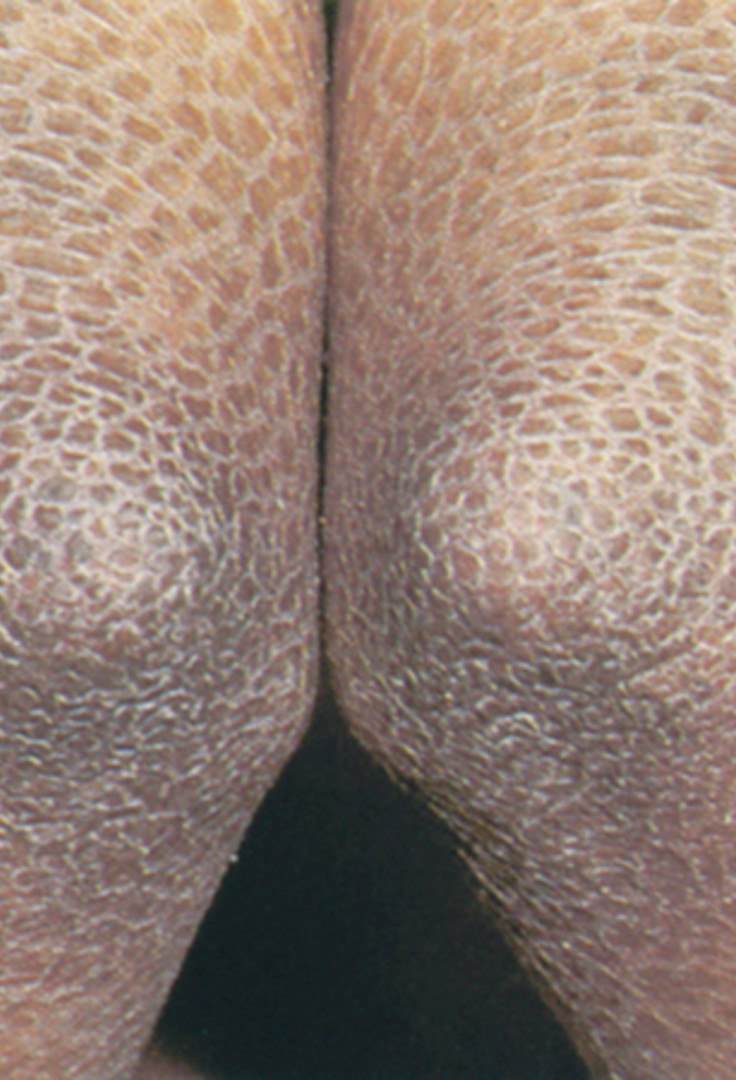
What are scales/ desquamation?
abnormal areas of stratum corneum, may be adherent or loose, large sheet like areas or tiny particles that peel
caused by inc rate of epidermal cell proliferation
What is an erosion?
skin defect with loss of epidermis only and heals WITHOUT a scar
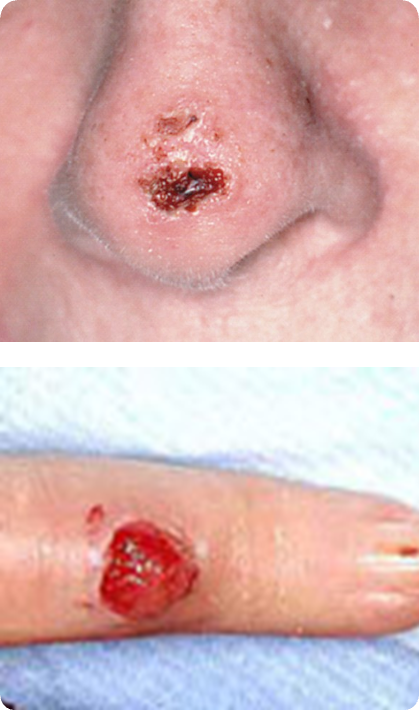
What is an ulcer?
skin defect with loss of epidermis and upper layer of dermis; always heals WITH scar tissue
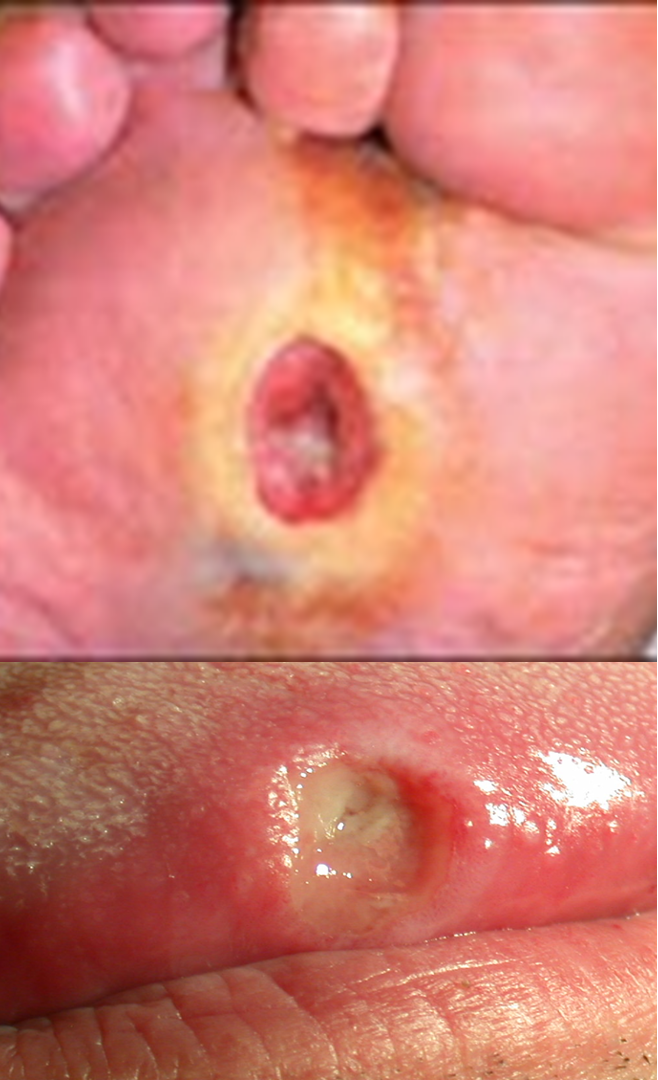
what are telangiectasis?
small enlarged blood vessels near surface of skin often nose, cheeks, and chin; usually only mms in size; sign of chronic alcoholism
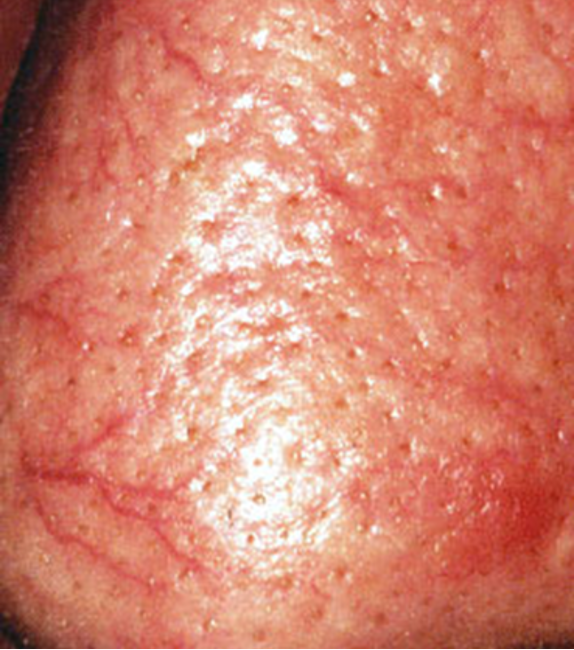
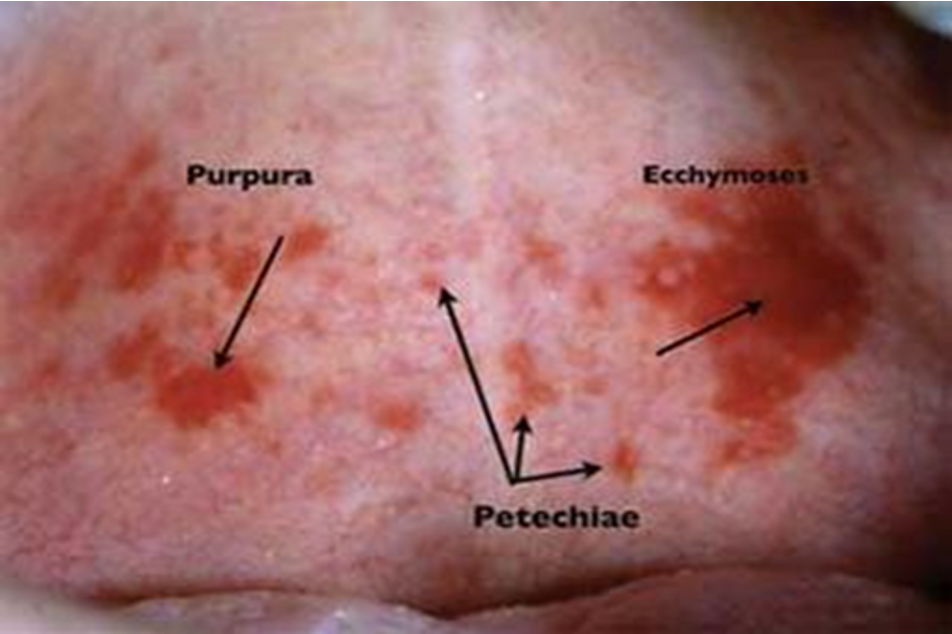
What is petechiae?
small red or purple spots on the body, less than 3 mm, caused by minor hemorrhage (broken cap), thrombocytopenia, or dec platelet function
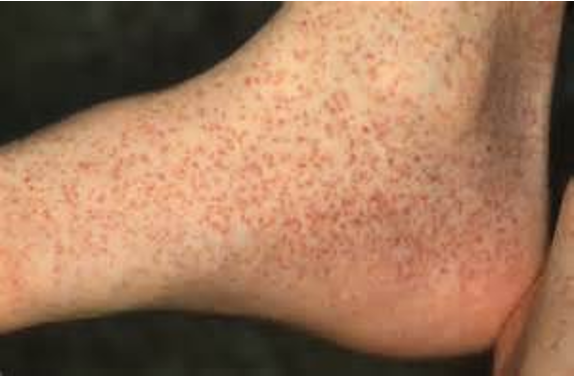
What is purpura?
larger red or purple discolorations on the skin, 3-10mm in size, caused by bleeding under the skin
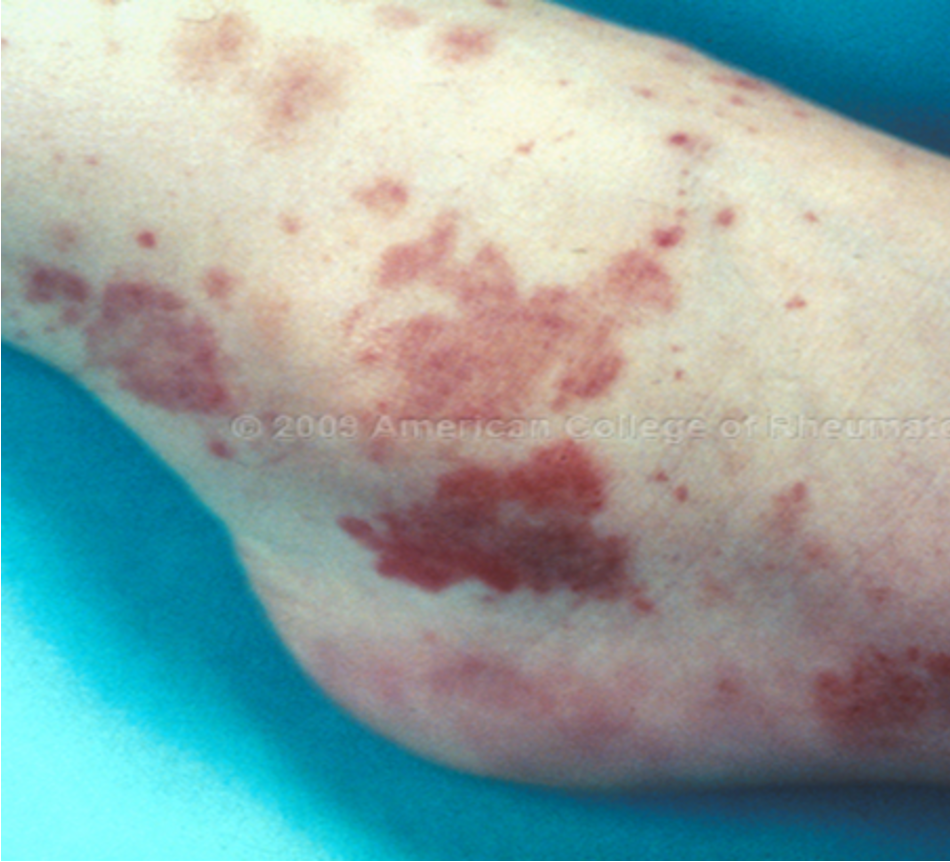
What is ecchymosis?
capillary damage that allows blood to extravasate into surrounding tissues, greater than 1 cm, usually caused by blunt trauma
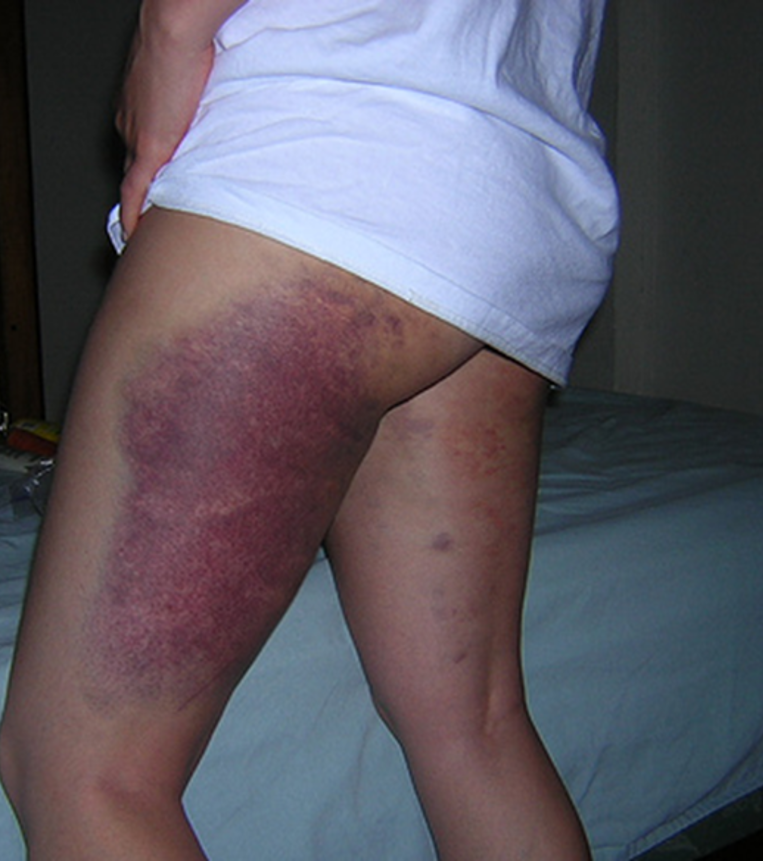
Do petechiae, purpura, and ecchymosis blanch with pressure? (disappear when you push on them)
sir no sir
What is a tumor?
solid lesion w/ elevation and depth, usually involves epidermis and dermis (possible SC), greater than 2 cm, and ± pigmentation
What is a serpiginous lesion?
irregular / wavy / snake like pattern (ex: hookworm)
What does zosterform mean when describing lesions?
only affects a specific dermatome
How many distinct patterns of dermatitis are there?
9
hives is an example of what pattern of inflammatory disease?
perivascular dermatitis
What is perivascular dermatitis?
perivascular inflammatory infiltrate w/o significant epidermal involvement
allergic contact dermatitis is an example of what pattern of inflammatory disease?
spongiotic dermatitis
What is spongiotic dermatitis?
associated with intercellular epidermal edema (spongiosis)
psoriasis is an example of what pattern of inflammatory disease?
psoriasiform dermatitis
What is psoriasiform dermatitis?
associated w/ epidermal thickening from elongated rete ridges
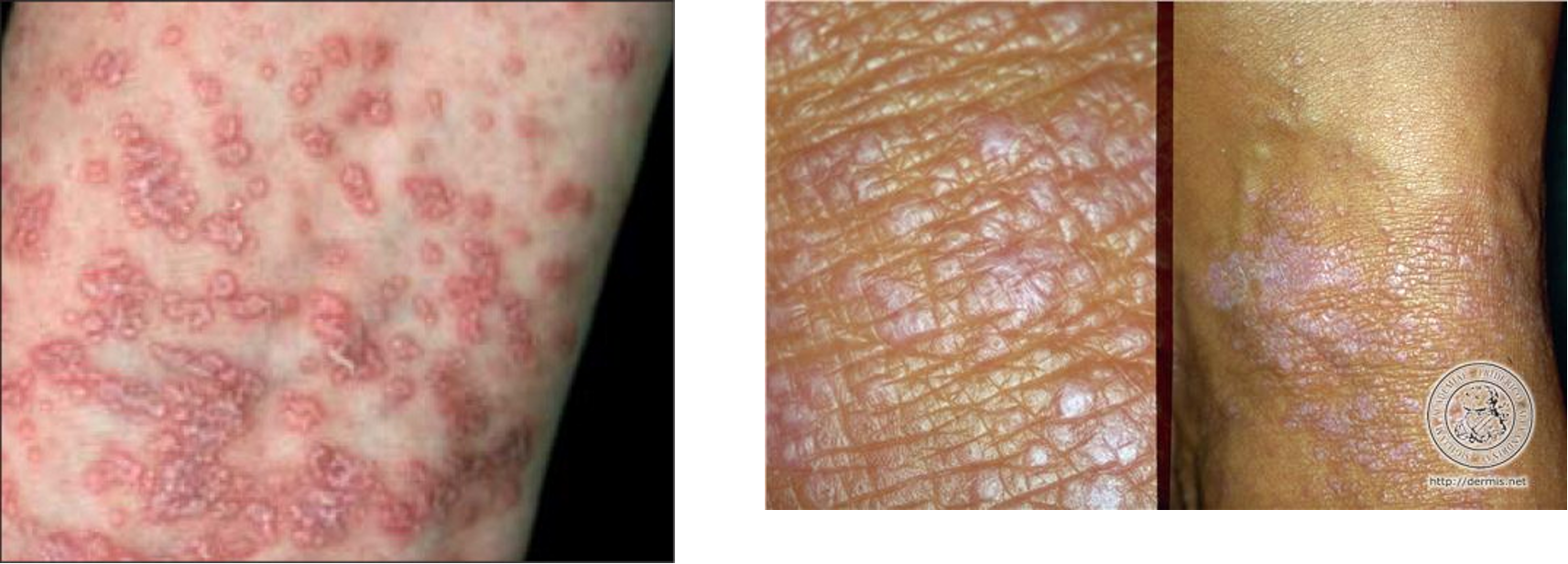
lichen planus is an example of what pattern of inflammatory disease?
interface dermatitis
what is interface dermatitis?
cytotoxic rxn that affects dermis and epidermis characterized bt vacuoles and lymphocyte infiltrates
bullous pemphigoid is an example of what pattern of inflammatory disease?
vesiculobullous dermatitis
what is vesiculobullous dermatitis?
intradermal or subepidermal cleavage
leukocytoclastic vasculitis is an example of what pattern of inflammatory disease?
vasculitis
what is vasculitis?
damage to cutaneous vessel walls
acne folliculitis is an example of what pattern of inflammatory disease?
folliculitis
What is folliculitis?
rxn directed against colliculo-sebacous units
cutaneous sarcoidosis is an example of what pattern of inflammatory disease?
nodular dermatitis
what is nodular dermatitis?
nodular or diffuse dermal infiltrate w/o significant epidermal changes
erythema nodusum is an example of what pattern of inflammatory disease?
panniculitis
what is panniculitis?
involves SC fat
What is the clinical presentation of psoriasis?
sharply marginated, erythematous, and surmounted by silvery scales
What is most common age of onset for psoriasis?
third decade (equal in sexes and ethnic groups)
what is etiology for psoriasis?
unknown, likely multifactorial inherited condition; FMHx is common
what is squirting dermal papillae? What disorder is it seen in?
migration of neutrophils from dermal papillae into overlying epidermis;
psoriasis
Besides silvery scales, what else is seen in psoriasis?
epidermal hyperplasia (thicker skin), changes in rete ridges, thinning of suprapapillary plate, squirting dermal papillae, and inflammatory cells in the epidermis
What surfaces are spared from psoriasis?
mucosal surfaces
what surfaces are often involved in psoriasis?
scalp, extensor surfaces of extremities, flexural surfaces, nails
what is the only extracutaneous manifestation of psoriasis?
psoriatic arthritis
What is psoriatic arthritis?
deforming, asymmetric (1 joint), oligoarticular arhtritis that can involve small or large joints; classified as seronegative spondyloarthropathy
what joints are characteristically involved in psoriatic arthritis?
distal interphalangeal joints of fingers and toes
What happens with lymphocytes in interface dermatitis?
they attack the basal/dermal layer of epidermis causing vacuolar change in the basal cells or necrosis of basal keratinocytes
What is an example of chronic interface dermatitis?
lichen planus
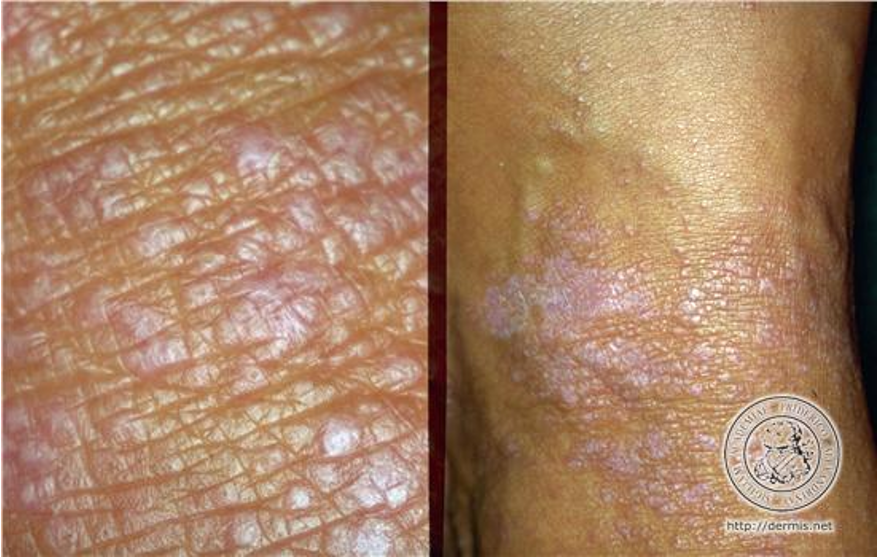
What is an example of acute interface dermatitis?
erythema multiforme
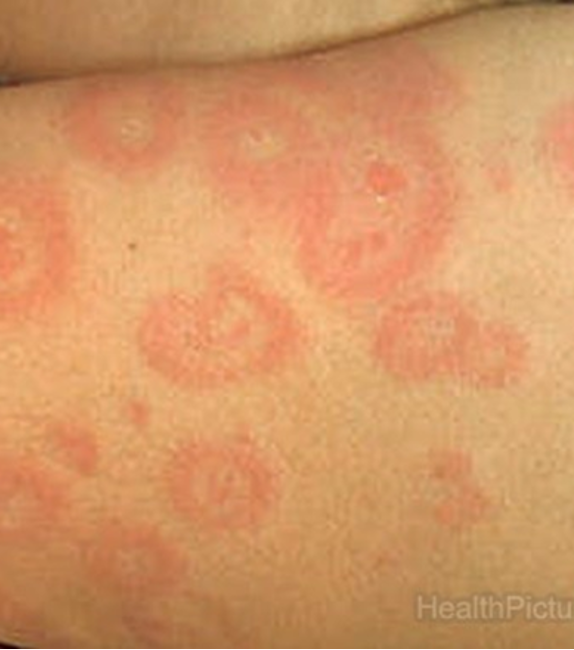
Describe the pathophysiology of many of the diseases in interface dermatitis
T cell mediated damage to keratinocytes and remodeling of the basement membrane zone;
injury to basal keratinocytes and other structures produces tiny vacuoles along the dermoepidermal junction on both sides of basal lamina (vacuolization or liquefaction degeneration)
Is lichen planus more common in men or women?
women
etiology of lichen planus
mostly unknown but drugs such as therapeutic gold and antimalarial agents are shown to play a role
pathogenesis of lichen planus
begins w/ dense infiltrate of T cells in papillary and superficial dermis, keratinocytes and melanocytes become damaged, vacuoles and colloid bodies appear in lower dermis, and mature lesions are composed of CD8 cytotoxic T cells
What are the PE findings of lichen planus?
pruritic polygonal violaceous (purple) flat topped papules w/ wickham’s striae (minute whitish streaks); usually bilateral and symmetric
solitary lesions combine to form larger plaques
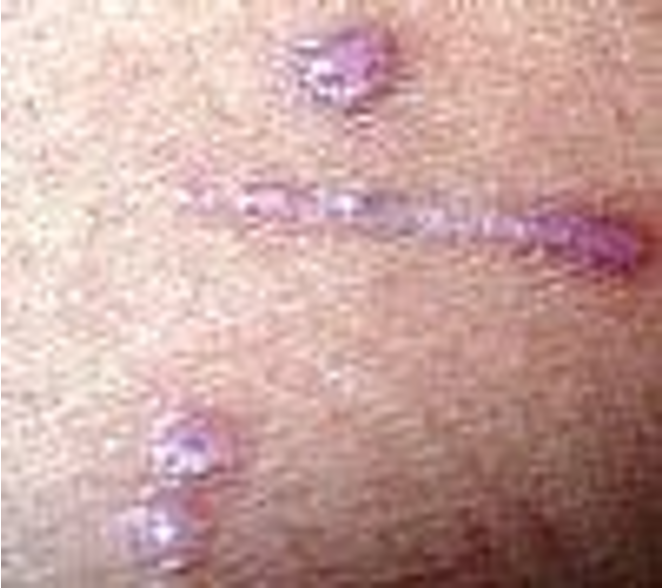
Where are common sites for lichen planus?
flexor surfaces of extremities, genital skin, mucous membranes
When do peak incidences of erythema multiforme happen?
2nd-4th decade of life (equal in men and women)
What is erythema multiforme?
cell mediated immune rxn that results in necrosis of epidermal keratinocytes; example of acute interface dermatitis
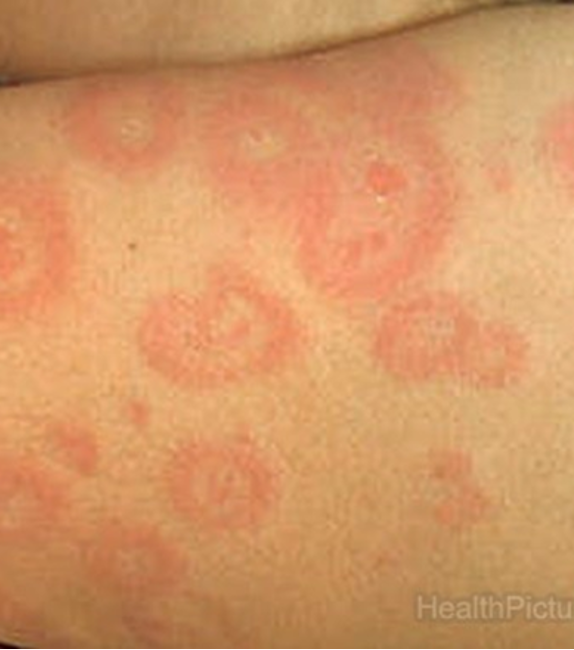
What is etiology for erythema multiforme?
HSV, rxn to meds, idiopathic
What are PE findings of erythema multiforme?
acute cutaneous eruption to skin or mucous membranes that is benign and self limited
lesions develop in crops on acral surfaces (affects distal portions of limbs);
monomorphous pattern- red macule o thin papule that expands from center outward, center becomes dusky or necrotic appearing “target-like”
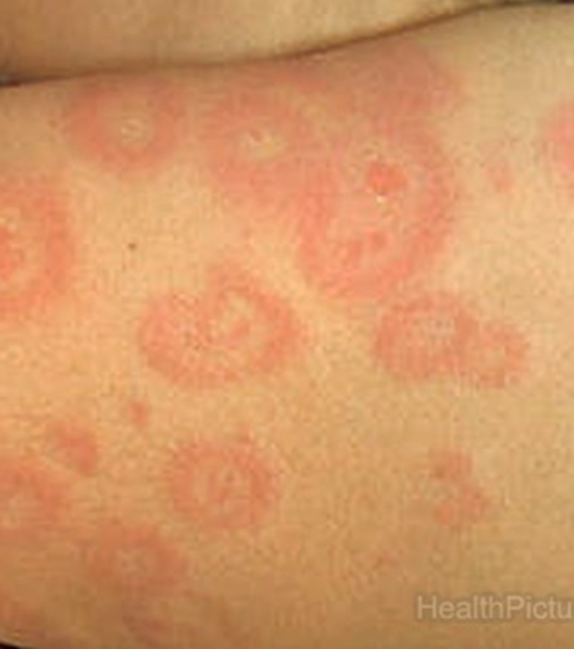
What is EM minor?
scattered lesions w/ limited mucosal involvement
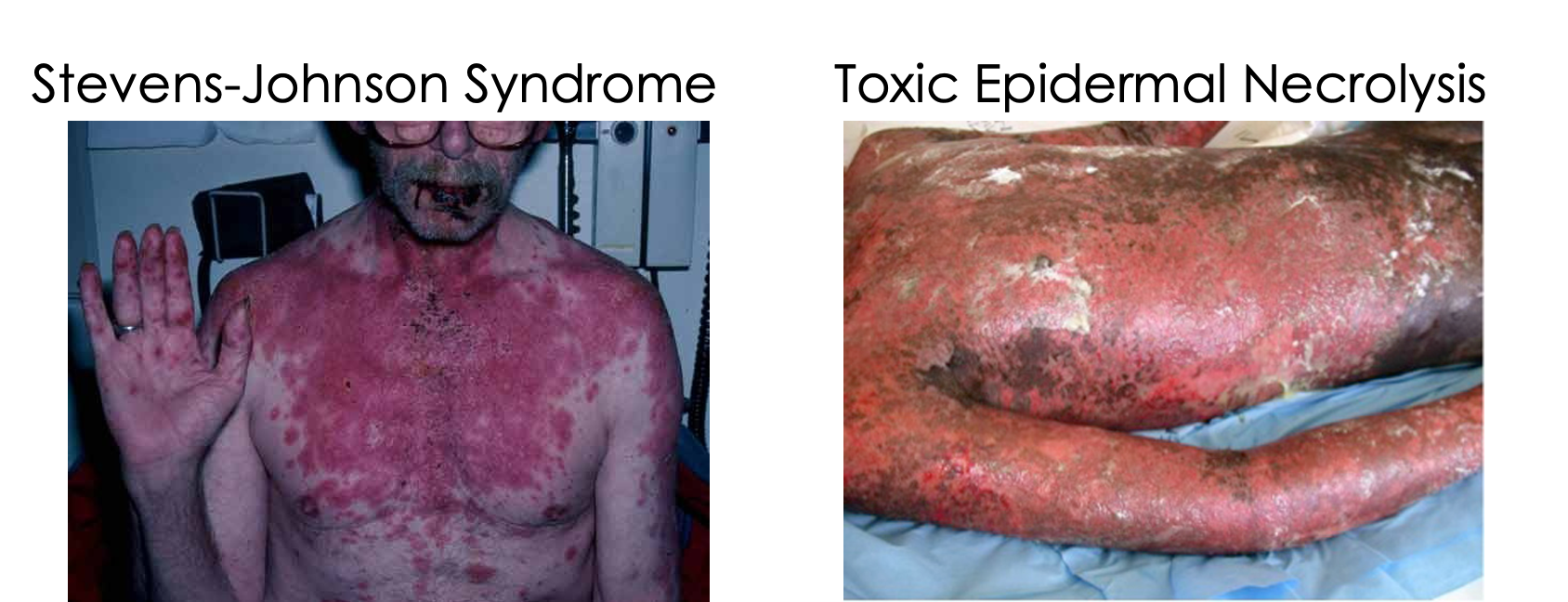
What is EM major?
prominent involvement in at least 2-3 mucosal sites (oral, anogenital, conjunctival); encompasses Steven-johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis
What is the pathogenesis of erythema multiforme?
sparse inflammatory infiltrate leads to necrosis of keratinocytes and creates widely distributed vacuolated keratinocytes;
CD4 & CD8 compose the infiltrate
target like appearance reflects zones of inflammatory rxn and damage