Unit 1: Intro to Cells
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
basically just review of cells and organelles
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
cell
small, membrane enclosed unit
filled w/ aqueous solution
building block of life
vary in size & shape
all come from a single ancestor
central dogma
DNA → RNA → protein
dna synthesis (replication), transcription, translation
DNA
store genetic info
made of nucleotides (A, T, C, G)
codons interpret genetic code
filler DNA does not code for RNA, but it can have other functions
mutation
change in the DNA sequence of an organism
beneficial, harmful, or neutral
genome
entire library of genetic info in its DNA
___ size varies across organisms
comparing ___ sequences reveals heritage
instructions for cell formation, function, & behavior
each cell contains a complete copy of the ___, but different cells express different genes
gene expression is affected by internal & external signals
cell theory
All organisms consist of one or more cells
Cells are the basic unit of structure for all organisms
All cells arise only from preexisting cells
Matthias Schleiden: botanist, studied plant cells
Theodor Schwann: studied animal cells
cell membrane
phospholipid bilayer that surrounds the cell
defines the boundary of the cell
cytoplasm
aqueous solution within cell membrane, contains things that arent membrane bound (both the liquid component & other stuff)
cytosol
just the liquid part of the inside of the cell
site of chemical rxns such as glycolysis
prokaryotic
no nucleus or membrane bound organelles
more simple
varying shapes & sizes
can live in a variety of environments
can live in colonies

eubacteria
prokaryotes
true bacteria
live in “normal” environments (soil, water, humans)
archaea
prokaryotes
extremophiles
like environments similar to early earth
also found in the gut
eukarya is more similar to ___ than bacteria
eukaryotic
DNA contained in nucleus
contains membrane bound organelles (endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosome, endosome, peroxisome, mitochondria, chloroplasts)
nucleus
where all the genetic info is stored in the cell
chromosomes are condensed into X shape during cell division (coiled), making them unavailable for transcription
only uncoiled DNA can be used for transcription
nuclear envelope
contains pores that allow molecules to enter & leave the nucleus
mitochondria
generate ATP from food to power the cell
double membrane
cristae: folds in the inner membrane of a mitochondria
has its own DNA
chloroplast
capture energy from sunlight
double membrane
more internal membrane
has its own DNA
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
assembles cell membrane components
continuation of nuclear envelope
next to nucleus
rough ER
contains many ribosomes
proteins move from rough ER → golgi apparatus
ribosome
makes proteins (location of translation)
smooth ER
lacks ribosomes
synthesizes lipids & phospholipids
golgi apparatus
modifies & sorts molecules (proteins) sent by the rough ER
contains vesicles which deliver the proteins (like an uber) to their final location
lysosome
breaks down molecules
peroxisome
where hydrogen peroxide is isolated
cytoskeleton
responsible for directed cell movements
constantly shifting, allowing for cell movement
consists of three filaments: microfilaments (actin), intermediate filaments, and microtubules
microfilaments (actin)
muscle contraction & cell movement
smallest size of the three filaments that make up the cytoskeleton
intermediate filaments
tensile strength
middle size of the three filaments that make up the cytoskeleton
microtubules
mitosis spindles (pull apart chromosomes
direct vesicle transport
largest size of the three filaments that make up the cytoskeleton
model organisms
easy to study
easy to propagate (breed)
results are widely applicable
E. coli
model organism
gram neg bacillus
used to study DNA coding & cell replication
Saccharomyces
model organism
fungi genus, includes yeast
used for cell division studies for mitosis
common water cress
model organism
used to study plant mechanisms
Drosophila (fruit fly)
model organism
used to study genetics
Nematodes
model organism
used to study development & apoptosis
Zebra fish
model organism
used to study development
transparent for the first two weeks of life
mice
model organism
manipulate their genes & mimic human diseases
human cell lines
population of human cells grown in a lab (in vitro) that can divide and replicate indefinitely, used for study
most originated from cancer cells or embryonic cells
fibroblasts
make up connective tissue
myoblasts
develop into muscles
epithelial cells
skin cells
light microscope
led to the discovery of cells
Robert Hooke (1665) viewed “cork” cells
Antoni van Leeuwanhoek (1674) viewed live cells in canal water
fixed specimen, limited resolution
phase contrast microscope
light microscope enhanced w/ optics
live specimen, limited resolution
look at living tissue
allows internal structures to be seen
fluorescence microscope
see molecules labeled w/ fluorescent dyes
see ~20nm objects
clear image; confocal scanning, 3D
electron microscope
fixed or dead images
transmission EM: scans thru specimen
scanning EM: scans surface
endosymbiont theory
mitochondria & chloroplasts most likely evolved from engulfed bacteria
first event: host cell engulf bacteria ( → mitochondria)
second event: host cell engulf photosynthetic bacteria ( → chloroplast)
mutual codependency: engulfed bacteria gain shelter, host cell gains resources
nitroplast: nitrogen fixing organelle
kind of went thru its own endosymbiotic theory
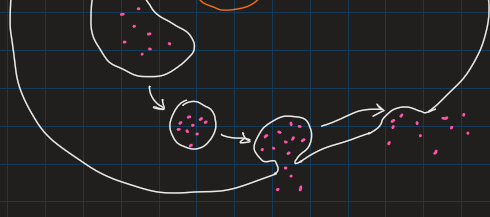
endocytosis
take in molecules thru the membrane
eukaryotes only: prokaryotic membrane lacks the fluid to form vesicles
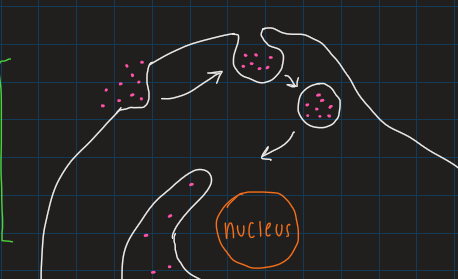
exocytosis
release molecules thru the membrane
eukaryotes only: prokaryotic membrane lacks the fluid to form vesicles