mol bio unit 3
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
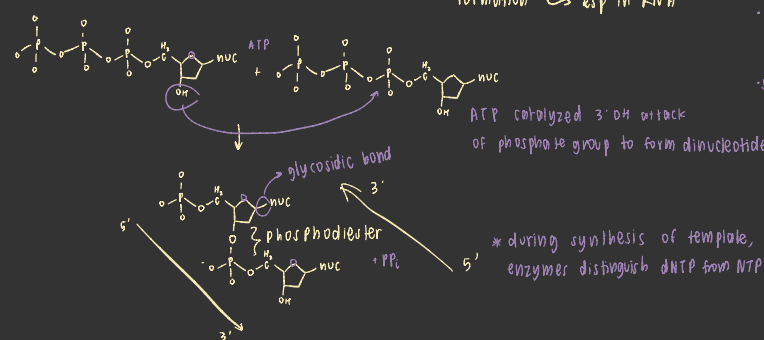
how do nucleotides link —> nucleic acids
3’OH attacks alpha phosphate of new nucleotide —> releases PPi and extends nucleotide via phosphodiester bond formation
RNA structure explains reactivity
existence of 2’OH allows lariat formation
backbones may spontaneously break
b form double helix
constant diameter
a form
dehydrated
z form
in vitro formation
minor vs major groove
diff amts of h bond donors + acceptors
seq- spec binding in major groove bc higher var of H bond donors + acceptors
non seq-spec in minor groove
DNA replication
one dsDNA —> 2 identical copies
DNA synth moves toward 5’ end of template on each strand
ori
used only once per cell cycle during S phase
have nearby GC righ regions
initiation of DNA replication
5’ end initiated by DNA primase
DNA pol can’t begin synth w/o existing 3’ end but primase can start anywhere
dna pol palm
active site w/ 2 atoms (usually Mg2+) allow phosphate groups’ charges to come tg
how DNA pol selects the right dNTP
finger and palm fit perf around correct dNTP
recognizes correct BP through minor groove by forming H bonds w it
proofreading via wrist
incorrectly paired base not stable in active site
wrong nucleoside enters editing site where backbone is cut by 3’ —> 5’ exonuclease (last nucleoside suffers same fate)
nucleosome re-establishment during replication
increase in histone synth in G1/S phase —> histone mod occur BEFORE replication fork is made
replisome isn’t blocked by histones
wave of H3k9ac precedes replication form
H3/H4 tetramers stay assoc w one strand or the other but h2a/h2b unbind + rebind
chr remodelling complexes aid with histone displacement
end replication problem (not in bacteria)
start with template strand with 3’ end
when primer removed —> 3’ overhang
solution to end replication problem
telomerase complex binds close to 3’ end of overhanging template strand
adds dNTPs to extend DNA strand using a bound RNA template seq
repeats many times to build repetitive telomere seq
3’ end becomes long
primer added near 3’ end of longer strand —> dna pol + ligase
DNA replication summary
opening/ separation of dna double helix at origin of replication
topiso in front of helicase to relieve supercoiling
DNA + pcna clamp on both leading and lagging
add dNTPs to 3’ end of primer strand
lagging strand has ssBPs
rna primers removed + replaced by DNA pol
ligase seals gaps
dna pol alpha
makes RNA primer
dna pol delta
makes lagging strand
dna pol epsilon
makes leading strand
RNAse
remove RNA primers
helicase
separates template strands
PCNA clamp
holds leading + lagging strand pol —> clamp loader helps PCNA
topoiso
cut DNA backbones to relieve overwinding/ supercoiling
tautomers
resemble normal bases
usually change back to normal and removed by proofreading before dna pol replicates more bases
if DNA pol moves on before removal —> mismatch
slippery seq
seq w multiple identical repeated seq —> strands can bind tg and loop —> indels when replicating and lead to 3, 4, 5 nt repeats
do somatic cells express telomerase
NO bc u dont want every cell replicating
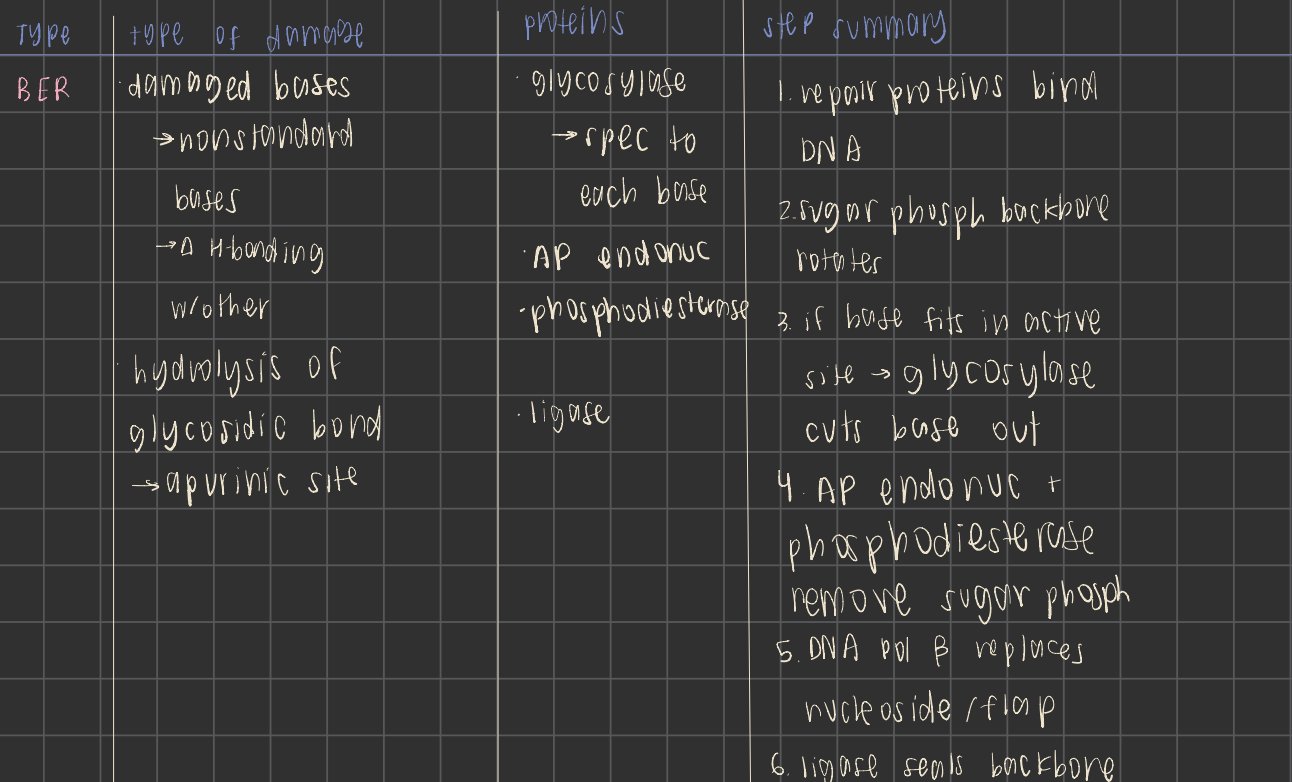
base excision repair
nucleotide excision repair

NHEJ

MMR

homology directed repair
occurs during s and g2 phases only

recombination
creates variation during M1
connections between homologous pairs provides tension necessary for meiosis
may occur within a gene
homologous recombination
eukaryotes vs prokaryotes

topo 1 vs topo 2
ssDNA vs dsDNA cuts
what happens if ssBP not present
degrades/ coils ssDNA
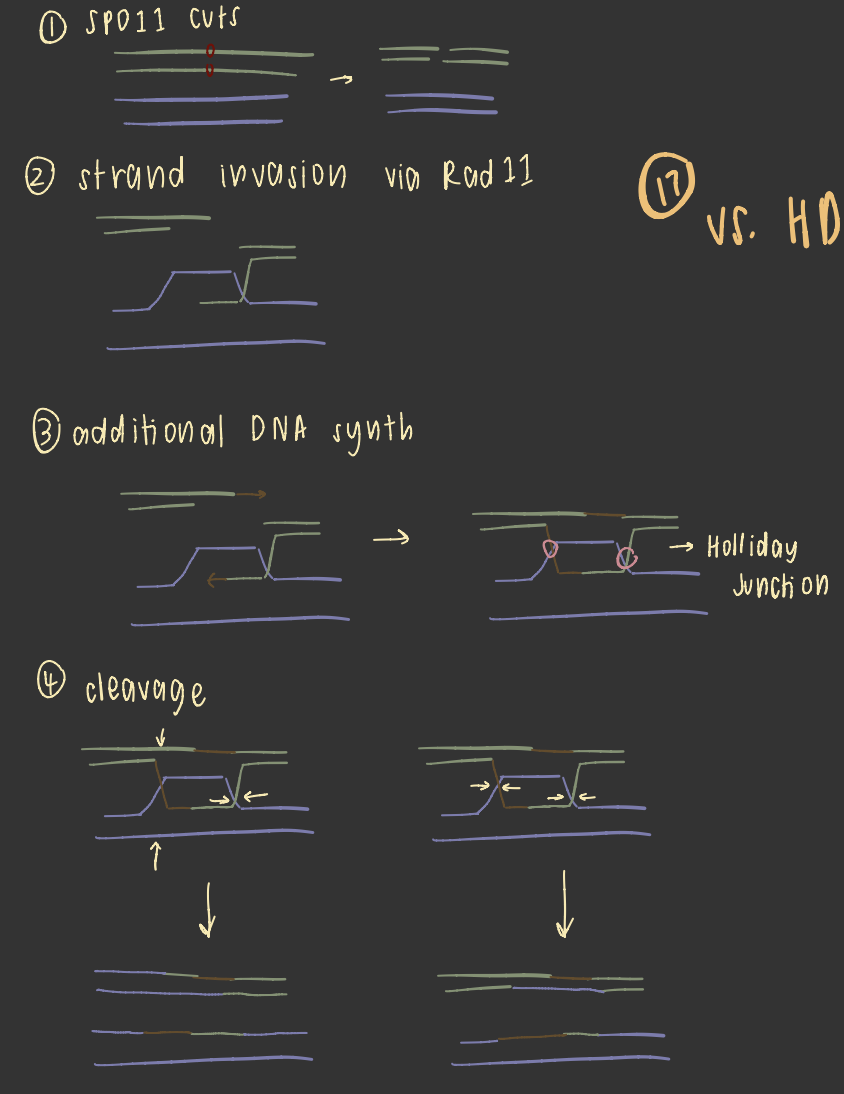
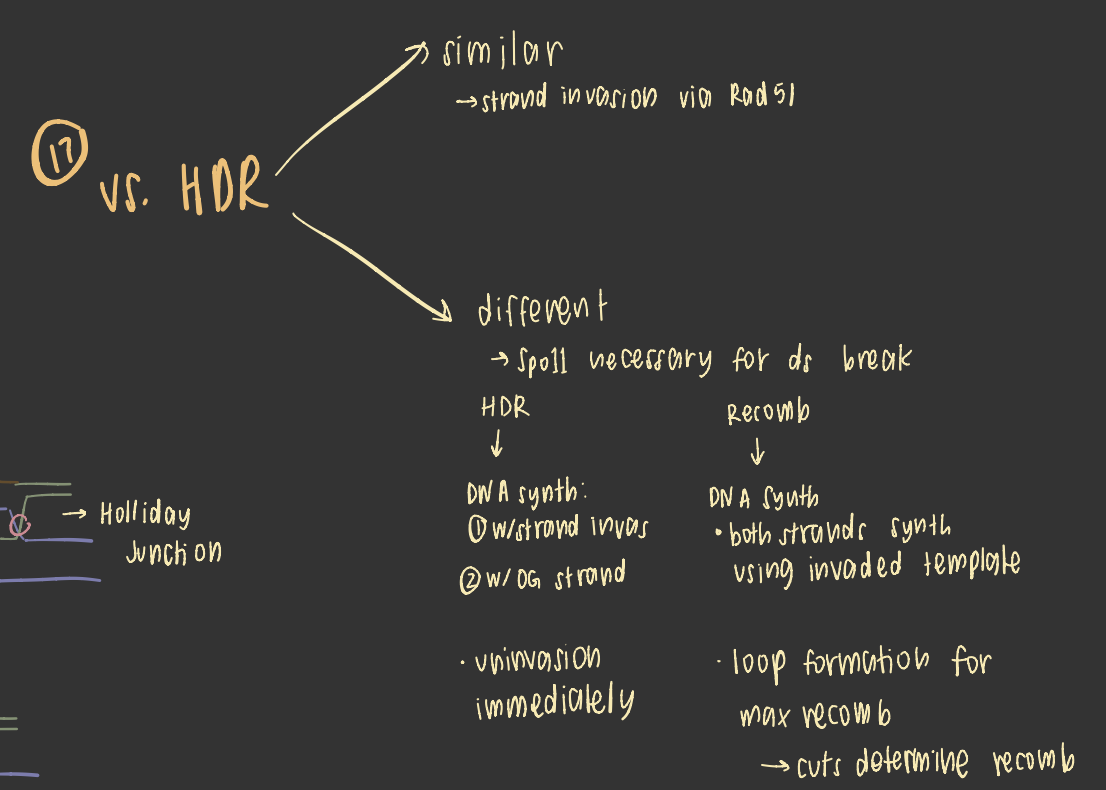
homologous recomb vs HDR
transposition
jumping genes
transposase —> loops and ds break
transposon in donor chr has ds break repair via nhej
new loc is cut and transposon is added
piRNAs
silence transposable elements (help maintain genomic stability)
longer than miRNAs
transcribed from uni/ bi directional transposons
bound by piwi proteins
allow transposon RNA degradation (post-transcriptional silencing)
can direct dna methylation of transposon + repetitive elements
important in germ line + stem cells
role in fertility and cancer
innate immunity

adaptive immunity

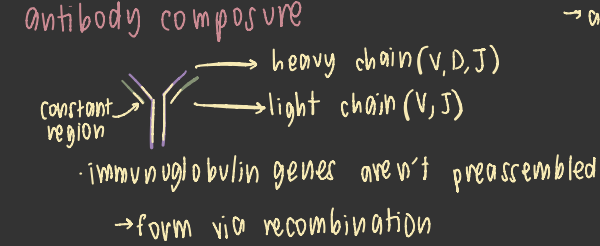
antibody composure
RSS (rexombination signal sequence)

RAG complex

mechanism of recombination
