Reactions Review
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Create a markovnikov alkyl halide
Start with an alkene. Add HX and CH2Cl2. This is nonstereospecific
Create a markovnikov alcohol
Start with an alkene. Add H2O and H2SO4 catalyst. This is nonstereospecific
Create a markovnikov ether
Start with an alkene. Add ROH and H2SO4 catalyst. This is nonstereospecific
Create a vicinal dihalide (on adjacent carbons)
Start with an alkene. Add X2 and CH2Cl2. This is anti
Create a vicinal halohydrin (alcohol on markovnikov carbon)
Start with an alkene. Add X2 and H2O solvent. This is anti
Create a vicinal haloether (ether on markovnikov carbon)
Start with an alkene. Add X2 and ROH. This is anti
Create an alkane (1. alkene 2. alkyne starting material)
Start with an alkene. Add H2, Pd/C. This is syn. Start with an alkyne. Add excess H2, Pd/C
Create an epoxide
Start with an alkene. Add a peroxyacid (mCPBA) and CH2Cl2. This is syn
Create an antimarkovnikov alcohol
Start with an alkene. Add 1. BH3/THF and 2. H2O, H2O2, NaOH. This is syn
Split a double bond to form ketone/aldehyde
Start with an alkene. Add 1. O3, -78 degrees C and 2. (CH3)2S
Create a Z-alkene
Start with an alkyne. Add H2 and Lindlar’s catalyst. This is syn
Create an E-alkene
Start with an alkyne. Add Na and NH3 (liq) at -78 degrees C. This is anti
Create an acetylide ion
Start with a terminal alkyne. Add NaNH2 and NH3 (liq)
Do chain elongation
Start with an acetylide ion. Add a methyl or primary alkyl bromide
Create a terminal aldehyde
Start with a terminal alkyne. Add 1. BH3/THF and 2. H2O, H2O2, NaOH. Tautomerization from enol
Create a terminal ketone
Start with a terminal alkyne. Add H2O and LAuX. Tautomerization from enol
Create a geminal dihalide
Start with an alkyne. Add excess HX
Relocate a double bond (more substituted to less substituted)
Add HX. Then add strong bulky base (tertbutoxide) and heat
Relocate a double bond (less substituted to more substituted)
Add HX. Then add a strong base (NaOH) and heat
Add an alkyl group to an -SH or -OH
Add NaH to deprotonate. Add a methyl or primary alkyl bromide
Form an alkene (less substituted)
Start with an alkyl halide. Add tertbutoxide
Form an alkene (more substituted)
Start with an alkyl halide. Add NaOH
What makes a bond more polarized?
Greater difference in electronegativity
What type of molecular orbital is this?
sigma

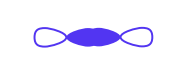
What type of molecular orbital is this?
pi
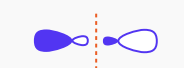
What type of molecular orbital is this?
sigma star
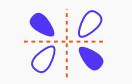
What type of molecular orbital is this?
pi star
To do an intramolecular reaction
Catalyze with H2SO4
Lower heat of hydrogenation means ______
more stable alkene
Reacting most rapidly with HX means ________
higher energy
How to form kinetic product; what type of addition?
50 degrees C, 1,2 addition
how to form thermodynamic product, and what is it?
-78 degrees C, most stable product
In a polar protic solution, look at ______ of nucleophile
Size, basicity
Strong bases
O- sp3, N- sp3, acetylide ion
SN2 transition state bond angles: Nuc-C-LG, R-C-R
180, 120
Replace an OH group with a halide
Add HI, HBr, or HCl and heat. Reaction will be Sn2 or Sn1 depending on substrate.
To replace a secondary OH with X, use PBr3 and pyridine to avoid Sn1.
Methyl is faster than primary!
Replace an OH group with a double bond
Add H2SO4 and heat. Reaction will be either E2 or E1 depending on the starting substrate
Create an ether from an alcohol (Williamson-Ether synthesis)
Deprotonate the alcohol with NaH. Add a primary or methyl alkyl bromide to do Sn2
Ether mechanism reaction rate order
secondary, primary, methyl, tertiary
With epoxide cleavage, under acidic conditions, the nuc attacks at ________, causing ______. use______
most substituted carbon, stereoinversion at attacked carbon; acid or water/alcohol catalyzed with h2so4
Create an alkyl halide (ONE halogen only) from an alkane
Add Br2 and light
Add an antimarkovnikov halide
Start with an alkene. Add HBr, peroxyacid, and light. Radical addition is nonstereospecific
Create a grignard reagent
Start with an alkyl halide. Add Mg and Et2O
Add carbons to chain along with OH group
Start with a grignard reagent. Add 1. epoxide 2. H3O+. Grignard reacts at lesser-substituted carbon of epoxide
Alcohol substitution ranking (slowest to fastest); secondary does ______
primary, methyl, secondary, tertiary; Sn1
Alcohol elimination ranking (slowest to fastest); secondary does _______
primary, secondary, tertiary; E1
Create an anti-markinov alkyl halide
Start with an alkene. Add HBr, ROOR, and light/heat. Radical addition is nonstereospecific
Create an allylic alkyl halide
Start with an alkene. Add HBr, light/ROOR, and NBS.