serology exam 3
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
Know the interpretation of lab results with previous algorithm (ELISA + Western Blot)
slide 41 ch 24
Why is there no vaccine for HIV
because the virus mutates rapidly, and it integrates itself into hosts DNA
Normal CD4:CD8 ratio, what ratio is most likely seen in AIDS
normal = 2:1
untreated = less than 1:1
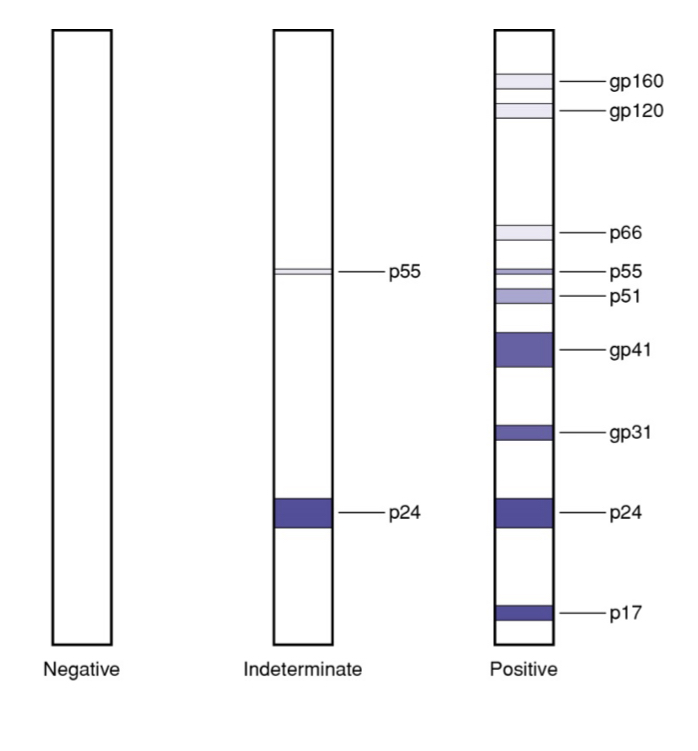
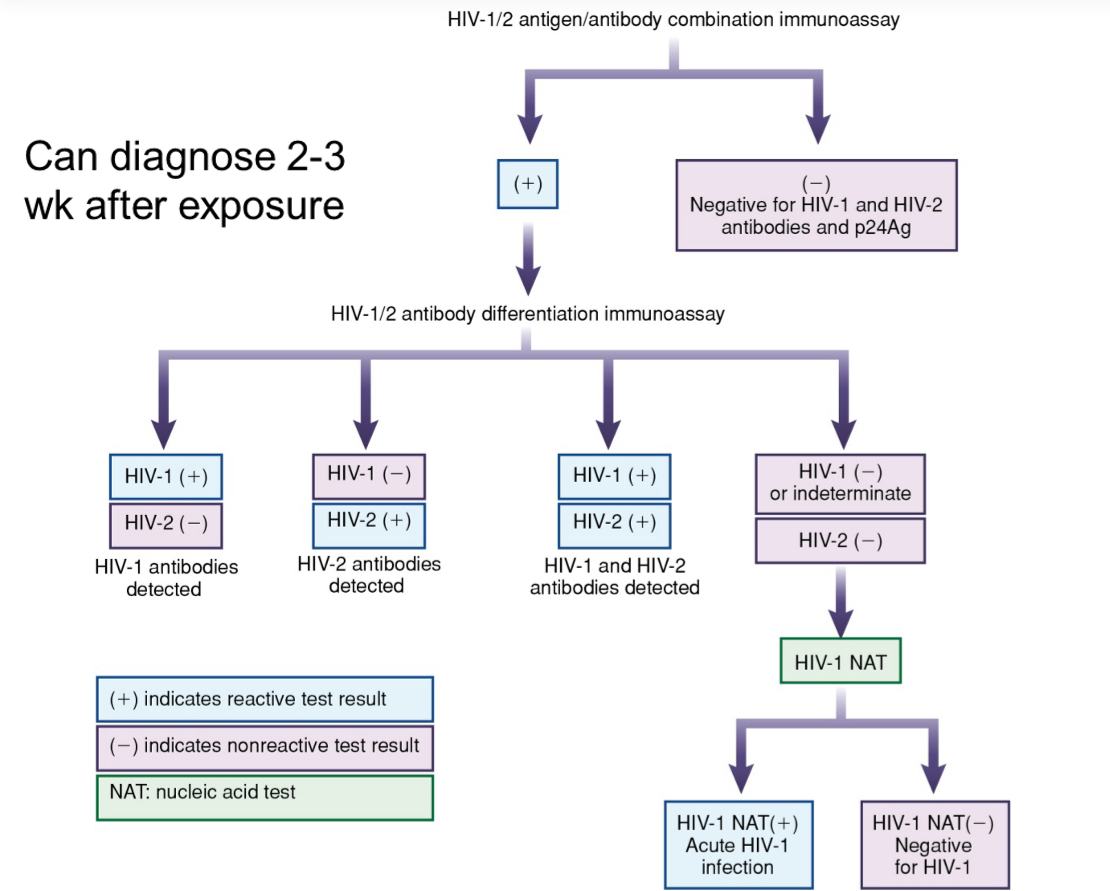
What is the advantage of 4th generation HIV tests?
it can diagnose 2-3 weeks after exposure and they test for both p24 antigen and HIV antibodies
What test is best test to monitor the effectiveness of antiretroviral therapy?
HIV viral load test
List some opportunistic infections associated with AIDS:
Kaposi sarcoma (HSV8), Histoplasma, Pneumocystis jirovecci, Cryptococcus neoformans, esophageal thrush, coccidiomycosis, toxoplasmosis
What cells does HIV preferably infect?
CD4 - T helper cells
Fact: One of the screening tests available for HIV is an ELISA method, we did it in lab
true
In terms of HIV what is a provirus
the form HIV takes after its DNA is integrated into host genome
Which method can detect infection with HIV sooner: antibody test or molecular?
molecular testing (nucleic acid test)
What do the reverse transcriptase, protease, and integrase enzymes do
reverse transcriptase = converts RNA to DNA
protease = cleaves viral proteins
integrase = aids in incorporation of viral DNA into genome of the infected cell
Know the current HIV testing algorithm
slide 42 ch 24
What are nucleic acid tests for HIV infection used for?
can detect HIV sooner, used when serological tests are inconclusive or to be used in infants
also for a recent HIGH RISK exposure, possible exposure, and have early symptoms of HIV infection, or to resolve discrpancies
Patients in the AIDS (3rd stage) of infection will most likely have __(increased/decreased) CD4 cells, about how many??
decreased
CD4 count of less than 200/uL
What does hepatitis mean?
inflammation of the liver
For which of the Hep viruses we have a high infection rate from mother to baby
HBV
hep A
fecal oral route, close person to person
risk = people who use drugs, homeless, and men who have sex with men
RNA virus
VACCINE
acute infection = + IgM anti-HAV
immunity = + total anti-HAV along with -IgM anti-HAV
hep B
DNA virus
sexual contact, IV drug use, needlestick injury, DURING BIRTH PROCESS
risk = infants born to infected mothers, infected sex partners, drug users, health care workers, hemodialysis patients
no treatment for acute
interferon a, inhibitor of polymerase, antiviral drugs, liver transplant = chronic
HAS VACCINE
hep C
RNA virus
most common bloodborne infection
chronic liver infection, infections not seem due to universal blood product testing
new cases are related to injection drug use
hep D
RNA but REQUIRES CO-INFECTION with HEP B = satellite virus
parenteral or perinatal
no vaccine for D but can vaccinate for B
hep E
RNA virus
HEV 1,2 fecal oral route, 3,4 by consumption of infected pork
acute infection = IgM anti-HEV
past exposure = IgG anti-HEV
NO VACCINE
Which are transmitted through fecal oral route? (hepatitis)
Hep A, Hep E
What is the mode of transmission for B, C, D hepatitis
contacted with infected blood and body fluids
For which Hep viruses is there a vaccine
Hep A, Hep B
Do all patients with Hep B and C have observable symptoms
no, in acute infections and chronic they can be asymptomatic
The majority of patient with antibodies to Hep_____will develop chronic infection and active liver disease
C
What is the “core window” in terms of hepatitis refer to?. What markers are available during this time?
core window- HBsAg is not detectable and just before other antibodies appear
total anti-HBc, HBc IgM, HBsAg, anti-HBs
What does it mean to be a chronic carrier of HBV
virus remain in the persons body after the acute infection has ended
persists for 6 or more months
typically remain asymptomatic
increased risk for chronic liver cirrhosis and hepatocelullar carcinoma
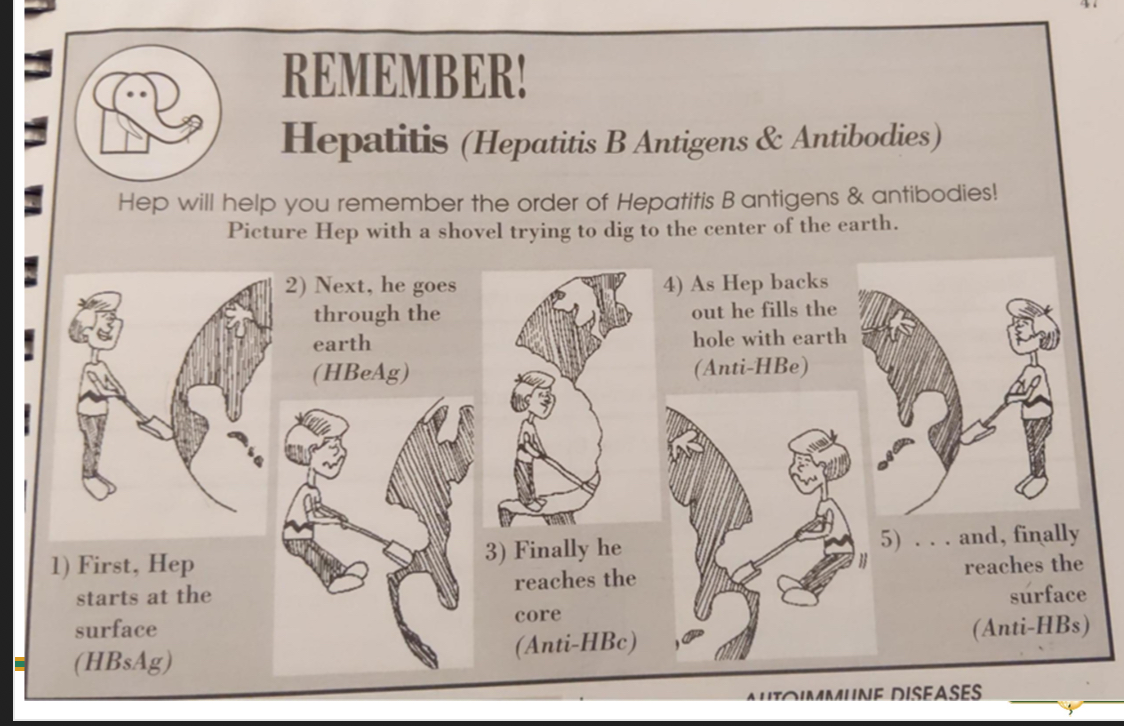
Know everything about appearance, disappearance of HBV antigens and antibodies in acute and chronic phase (a lot of questions here)
insert pics here
What is the expected serological response in an immunocompetent patient who has been vaccinated for Hepatitis B?
What Hep B markers are performed on blood products?
IgM anti-HBc and HBsAg
What are some of the clinical signs and symptoms seen in viral hepatitis (enzymes, jaundice….) basic info
What disease conditions are associated with EBV?
infectious mono, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, burkitt lymphoma
Presence of _____lymphs seen in patients with EBV
atypical (20% or more)
There is 1 question about the heterophile antibody testing with guinea pig kidney/beef bovine RBCs
What other infections may cause mononucleosis like syndrome
CMV, toxoplasmosis, HIV, rubella, Hep A/B/C, adenovirus
What is an heterophile antigen
antibodies (usually IgM) that are capable of reacting with similar antigens from 2 or more unrelated species
Diagnostic test most specific for EBV
How is EBV transmitted
intimate contact with salivary secretions (kissing disease)
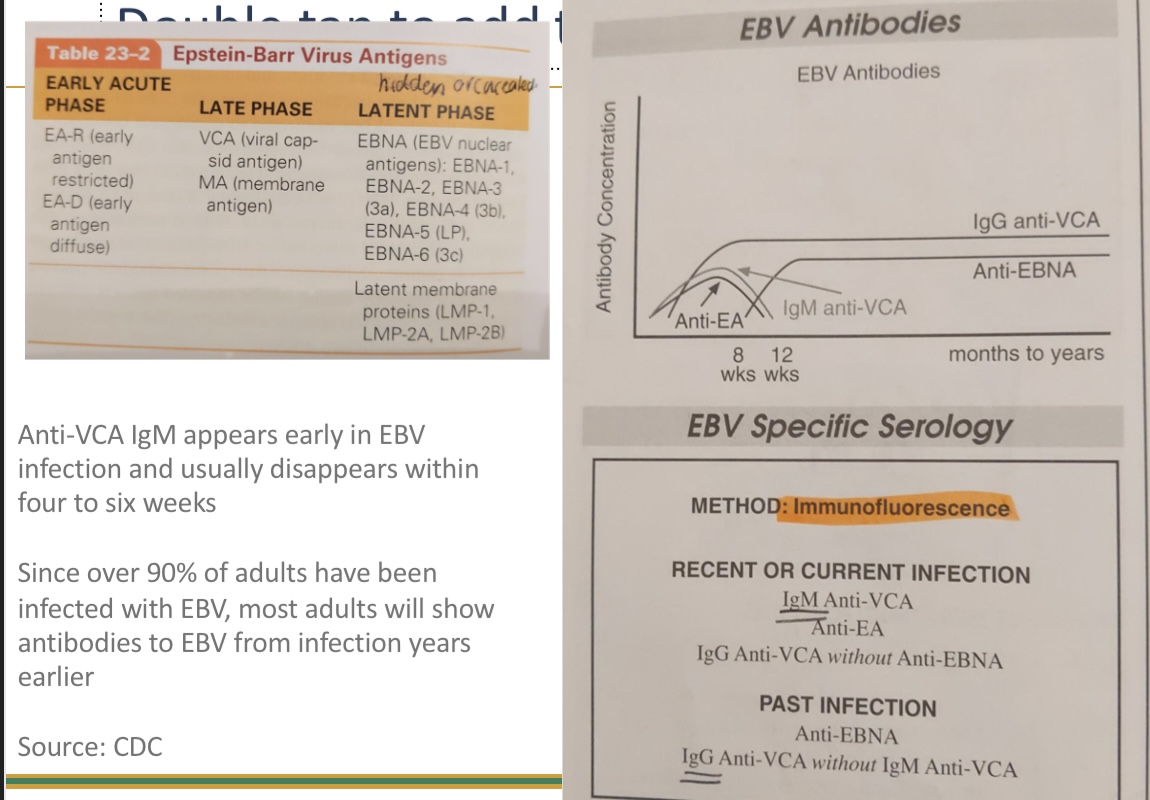
Know the sequence of antibodies for infectious mono, which are present in current vs past infection (VCA,EA,EBNA)
EA- early acute
VCA - late phase
EBNA - latent phase
recent - IgM anti-VCA, anti-EA, IgG anti-VCA without anti-EBNA
past. - anti-EBNA, IgG anti-VCA without IgM anti-VCA
What antibodies caused a positive heterophile antibody test for infectious mono?
Fact: EBV likes to attach to the receptor on B lymphocytes
true
What is the seroprevalence (%) in United States in adults in EBV
95% in adults
Fact: It is very important to screen blood products for CMV for
newborn/immunocompromised transfusion
true
Fact: Most common congenital infection in the United States
CMV - true
Fact: CMV appears to suppress cell mediated immunity, and you may see a decrease in both CD4 and CD8 lymphs. I know I did not mentioned this in class but I just notices this is a commonly asked question in review books
true
What is the seroprevalence (%) in United States in adults in CMV
over half of adults have been infected with CMV by age 40
initial disease is chickenpox. _______is the possible reactivation of virus
shingles
You see inflammation of ____glands (mumps)
parotid glands
Primary clinical manifestation (mumps)
parotitis (30-40%) - parotid glands
rubella is also known as
german measles or III day measles
Why are we concerned about transmission primarily in the 1st trimester of pregnancy (rubella)
it can cause congenital abnormalities, miscarriage, and stillbirth infants
in the 1st trimester is can infect the fetus through the placenta “congenital rubella syndrome”
how is measles transmitted
respiratory droplets
how contagious is measles
very, it can live for up to two hours in an airspace
90% of people close to one infected person will get it
infected people can spread 4 days before/after rash appears
fact: may cause immune amnesia (measles)
true
how do HSV 1 and 2 differ in location of the infection
what is the primary manifestation of HTLV
usually asymptomatic
very small amount will get adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATL) and HAM/TSP
what cells does HTLV preferably infect
CD4 T helper cells
antigenic shift vs drift
drift = result of minor changes caused by mutations
shift = result of reassortment in a doubly infected cell, creating a new virus
what are H and N surface glycoproteins
H (hemagglutinin) = which binds surface sialic acid
N which cleaves sialic acid
Fact: Examples of tests used to diagnose Influenza: Antigen tests, molecular, direct fluorescent tests (like the one we observed in the back microscope for RSV-you can do it for a lot of respiratory pathogens like parainfluenzae, adenovirus…)
true
direct vs indirect immunofluorescence (RSV)
how can we protect ourselves from RSV
When are respiratory viruses more prevalent
Fact: This virus is responsible for respiratory bronchiolitis in infants
RSV
does corona virus cause severe acute respiratory syndrome
yes it is SARS
what is the animal reservoir in west nile virus
birds
what is the most common manifestation in west nile virus
fever, joint pain
few very get severe encephalitis and meningitis
what is the vector for west nile virus
mosquito
What viruses are in the Herpes Virus family and what do they have in common?
8 Viruses
HSV 1 and 2, VZV, EBV, CMV, and human herpes viruses (HHV 6 7 8 and kapsoi sarcoma)
most common = latent infection that can be reactivated, and are surrounded by protein capsid and outer envelope
What viruses are associated with the TORCH panel?
T- toxoplasmosis
O- other
R- rubella
C- CMV
H- herpes
What does it mean to be in the window period
time between exposure to an infectious agent and when a test can accurately detect it
What are CD8 and CD4 cells?
CD4 - T helper cell, activate other immune cells
CD8 - cytotoxic T cells, directly kill
Cells involved in cell mediated immunity
T cells, CD4 and CD8
Newborns suspected of having a virus should be tested for what antibody type
IgM as it would be their antibody and NOT the mothers
A positive single titer in any healthy individual is mostly likely due to __________
What is latency
the ability of a virus or bacterium to remain dormant in the body without causing active symptoms
Fact: Mechanisms that viruses use to evade the immune system include downregulation of MHC class I molecules, latency, mutations, suppression of immune system
true
What does a low avidity IgG antibody indicate
recent infection
How do interferons alpha and beta help the host fight off viral infections
Know viruses for which we have a vaccine
varicella
flu
rubella
mumps
hep a and b
What does the presence of an IgM antibody mean? Current or past infection?
current or recent infection - IgM appear first
What does the 4th fold increase in IgG titer mean?
evidence of recent or current infection
What is the classic antibody response in infection?
Know the rise and fall of IgG and IgM antibodies and significance in disease (white paper that you have in your lab desk)
Would a patient that just got exposed to a virus develop antibodies right away?
no there is a lag phase, then IgM would be first after around 1-3 weeks and then IgG after a week-10 days
Would a patient receiving immunosuppressive therapy be able to mount a good antibody immune response?
no as the medications/therapy are suppressing the immune system
Would a patient infected with a genetically rare strain of a virus be able to test positive on a regular serological antigen test?
yes as it would be looking for antibodies produced to a viral infection
Do you think autoantibodies in individuals having an autoimmune disorder would exhibit cross reactivity in certain antibody serological tests?
yes - molecular mimicry, can lead to false positives and incorrect results
Do you think most antibodies present in the cord blood of a newborn baby are of maternal or fetal origin?
maternal origin
What are T lymphocytes and what are their main functions?
cell mediated immunity, directly killing infected or cancerous cells
When should acute and convalescent blood specimens be collected for the detection of antibody concentration (how far apart in days)?
acute = early in illness
convalescent = 2-10 weeks later
What molecule is the most immunogenic, proteins, carbohydrates or lipids?
proteins
What is the most significant class of microbial targets for NK cells
viruses
what is the order of ab/ag order in hepatitis