Treating depression notes
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT)
A psychological treatment for depression and other mental health issues combining cognitive and behavioral approaches.
A talking therapy that can help you manage your problems by changing the way you think and feel.
Aim of CBT
Building on the theories of Beck and Ellis, the aim of CBT is to change negative schemas people have and change the irrational thoughts people have
Focuses only on present problems, doesn’t explore any childhood traumas/issues
Length of CBT
5-20 sessions, so requires commitment
Both CBT and REBT involve homework
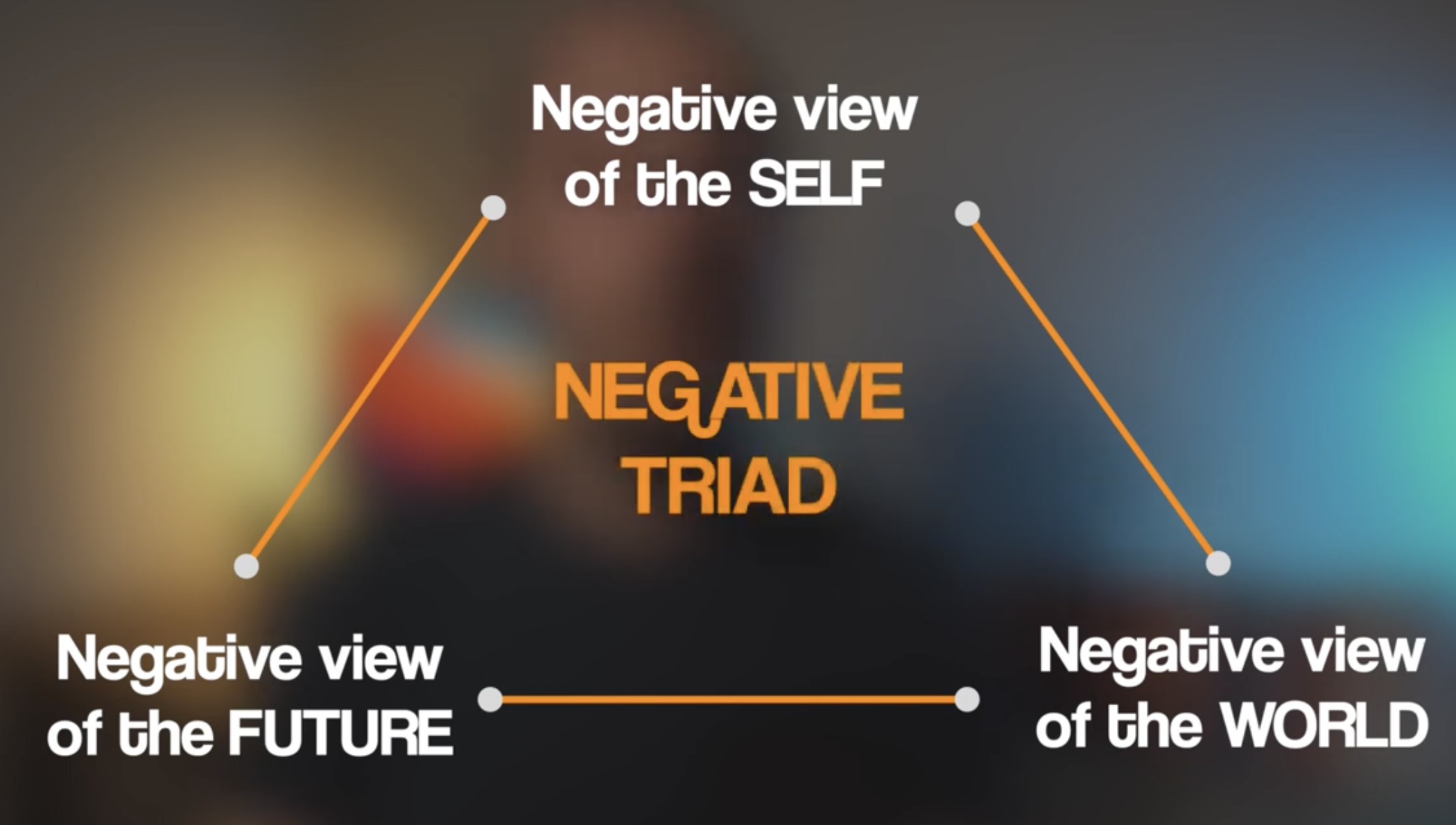
Treatment built on Beck’s cognitive triad theory
Negative Self-Schemas
Cognitive Biases
The Negative Triad
Process:
Thought Catching
The patient identifies their irrational thoughts and their negative triad by keeping a thought diary
Patient as Scientist
The patient is encourages to generate hypotheses to test how rational their thoughts are. They are set tasks or 'homework' to achieve this.
Behavioural Activation
The patient is set specific tasks to help change their behaviour.A CBT technique aiming to decrease avoidance and isolation in depressed individuals by increasing engagement in mood-improving activities.
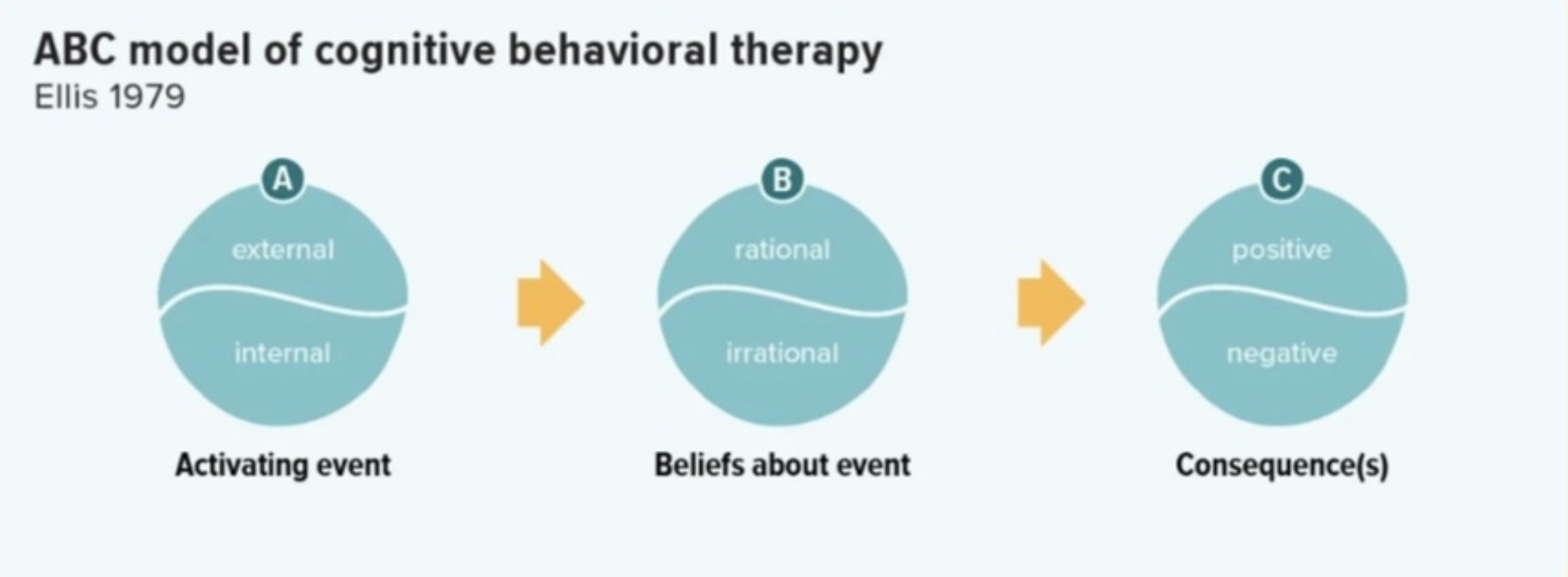
Ellis's Rational Emotive Behaviour Therapy (REBT)
Extends ABC model to ABCDE (Dispute, Effect) model, emphasizing identifying and disputing irrational thoughts through empirical and logical arguments.
Disputing Irrational Beliefs include:
Empirical Disputing
Involves disputing whether there is actual evidence to support the negative belief or is there any evidence for this belief?
Logical Disputing
Involves disputing whether the negative thoughts logically follows from the facts or is the belief rational?
Pragmatic Disputing
is this belief helpful?
Effects- The effect of disputing irrational thoughts is to help the person be more rational in their thinking about the situation. And to change the way they Feel about it.
Strengths of CBT
John March et al (2007)
Compared CBT to antidepressent drugs and also to a combination of both treatments when treating 327 depressed 12-17 y.o teens. After 36 weeks saw improvement of:
86% in the CBT group
81% in antidepressants group
81% in the CBT plus antidepressants group
So it was just effective as antidepressants
CBT vs Drug treatment
No negative side-effects that often come with drugs
For drugs, it’s difficult to get the dosage level correctly
Patient will need to gradually weaned off the drug once they’ve improved, which can be challenging as they can experience withdrawal-like symptoms
Cost-effective:
Requires six to 12 sessions
Limitations of CBT
Individual differences, may not be suitable for all patients
According to the same March et al study, it took 24 weeks for the improvement rate for CBT to almost match with drug treatment, and on 36 weeks to get up to around 80%. How many people are motivated enough and able to stick with the program for that lengths of time?
Drug treatment can work much quicker, doesn’t have the demands of motivation and commitment
CBT may not be as effective for severe cases or clients with learning disabilities, as rational thinking may be challenging.
Peter Sturmey (2005)
Suggests talking therapy is not suitable for people with learning disabilities