Cell Diversity (Bio 101)
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
things under a microscope
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
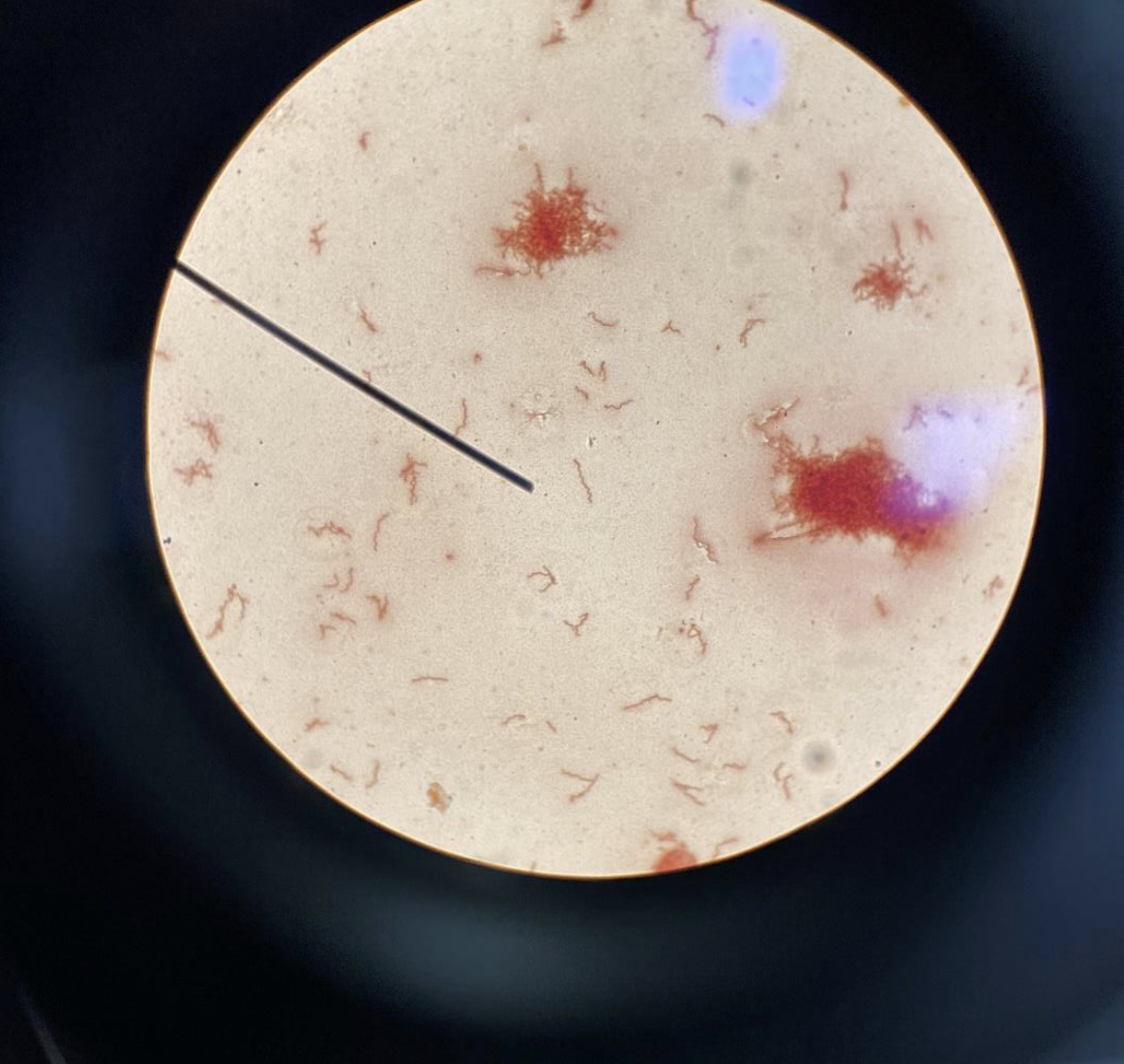
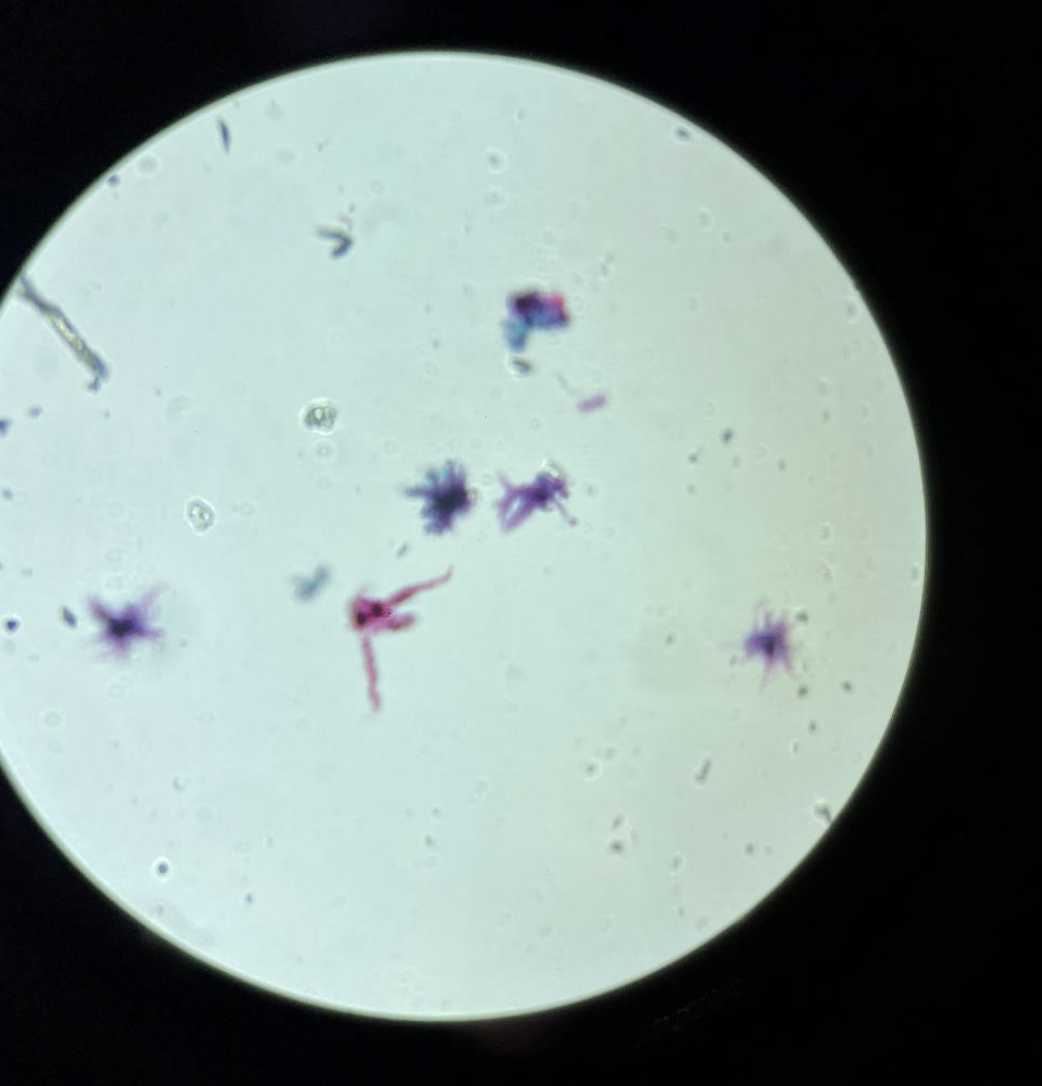
Spirillum shaped Bacteria 400x ( Blue Lens )
Are a type of bacteria characterized by their spiral shape. ( s or spiral type of shape and are in clusters, also thin )
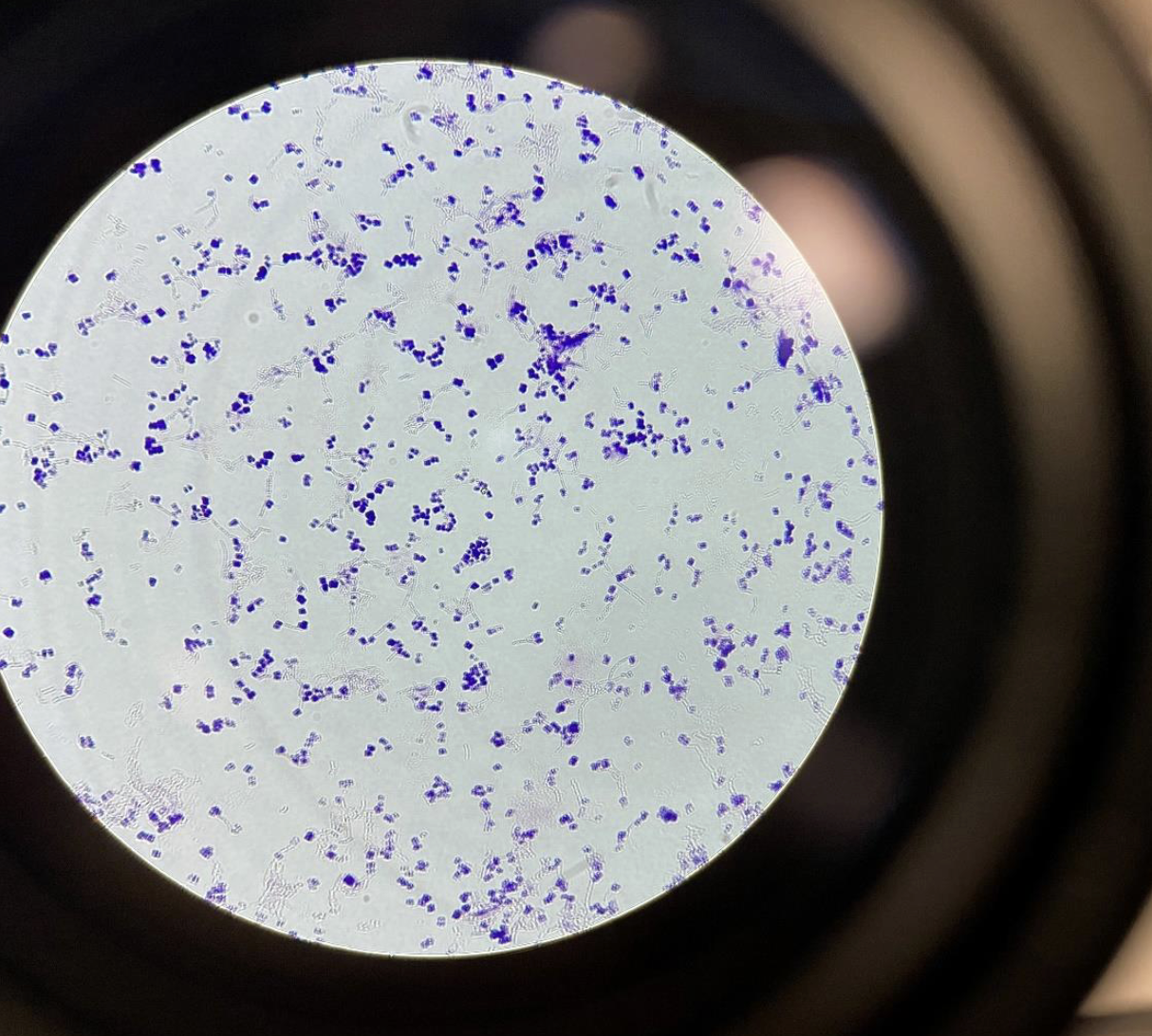
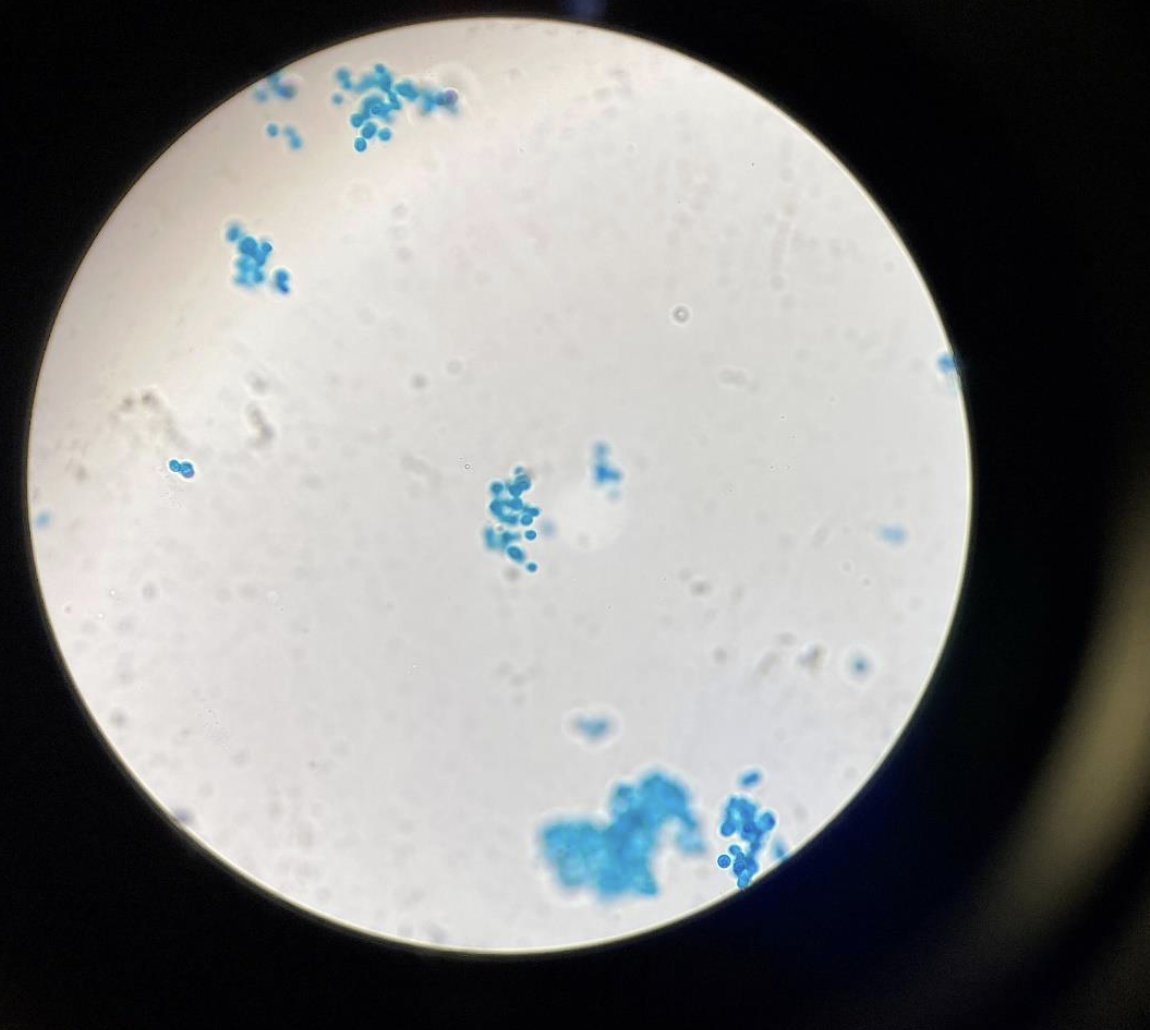
Cocci bacteria 400x
purple = gram positive Pink = gram negative
Dots everywhere
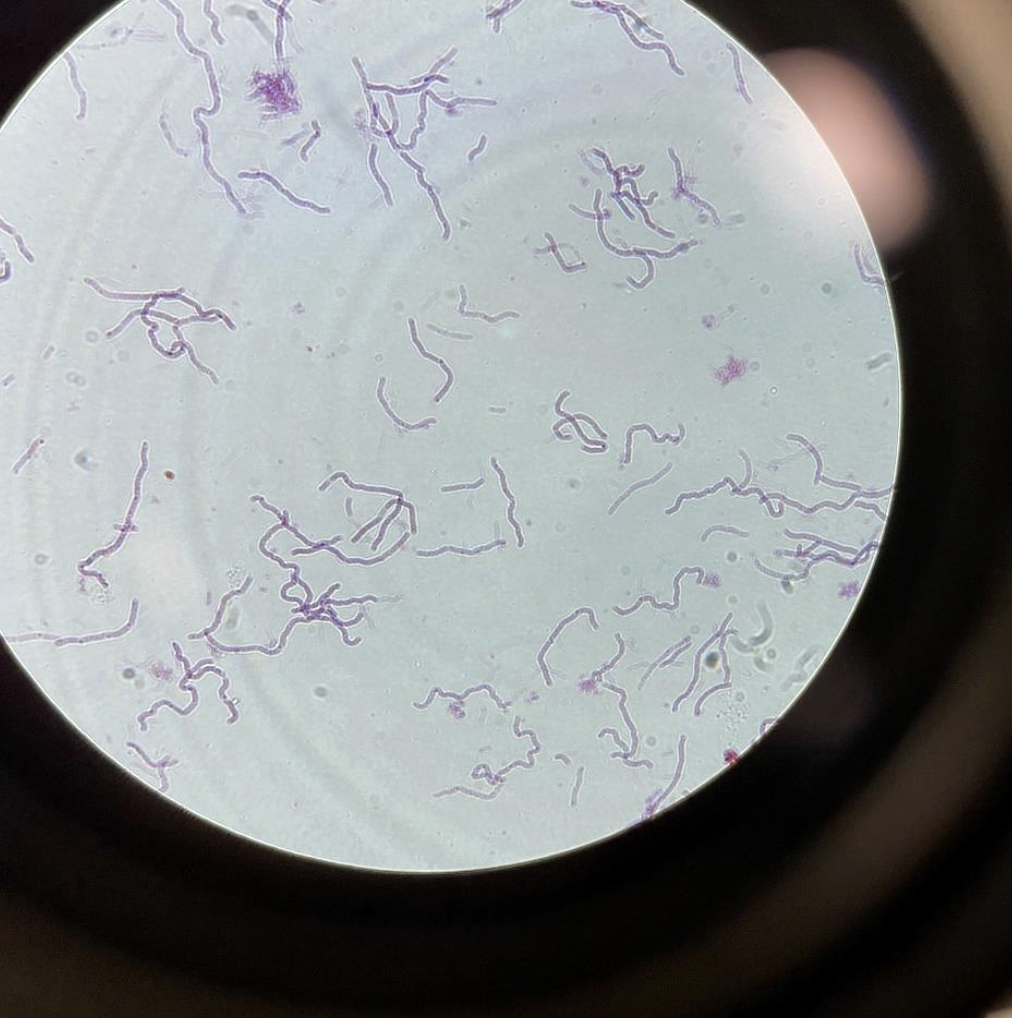
Bacilli gram negative 400x
rod shaped bacteria
slightly curved rods or straight lines
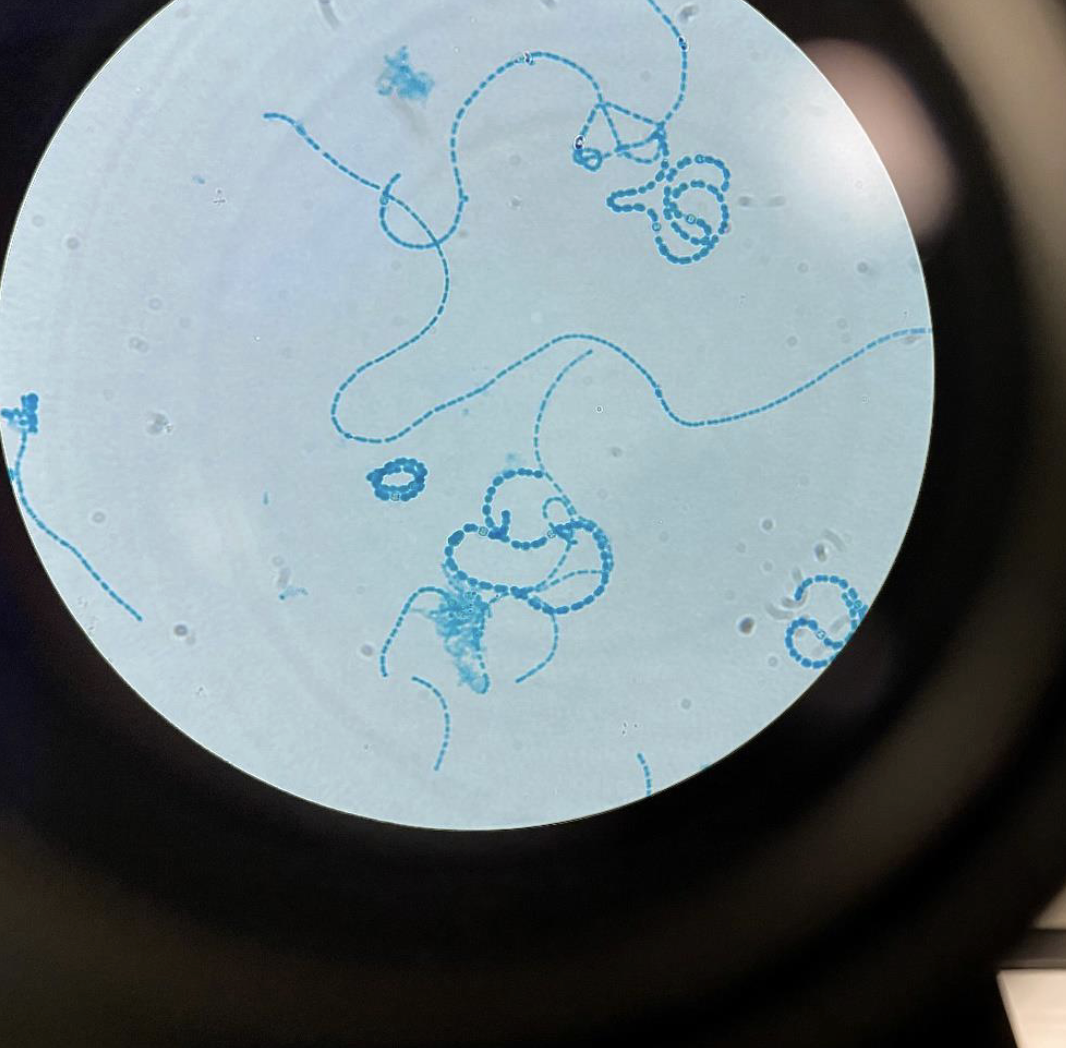
Cyanobacteria 400x
In long chains and are usually blue or green
Amoeba proteus 100x, Amoeba have pseudopodia (Kingdom Protista)
Sticks out its “legs” from the main body
blobby
( 100x is the yellow lens )
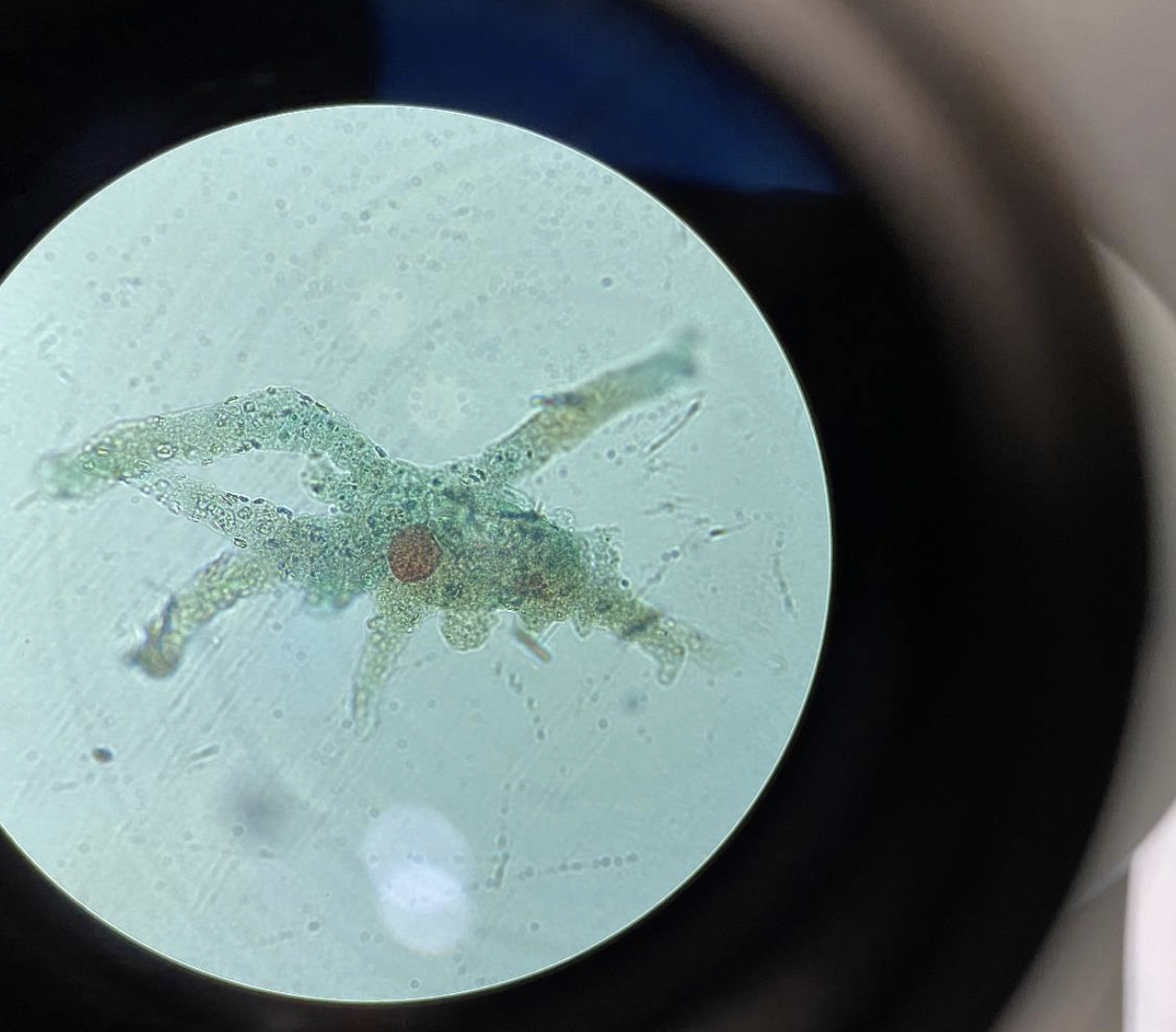
Live Amoeba 400x
looks like a spider
visible nucleus
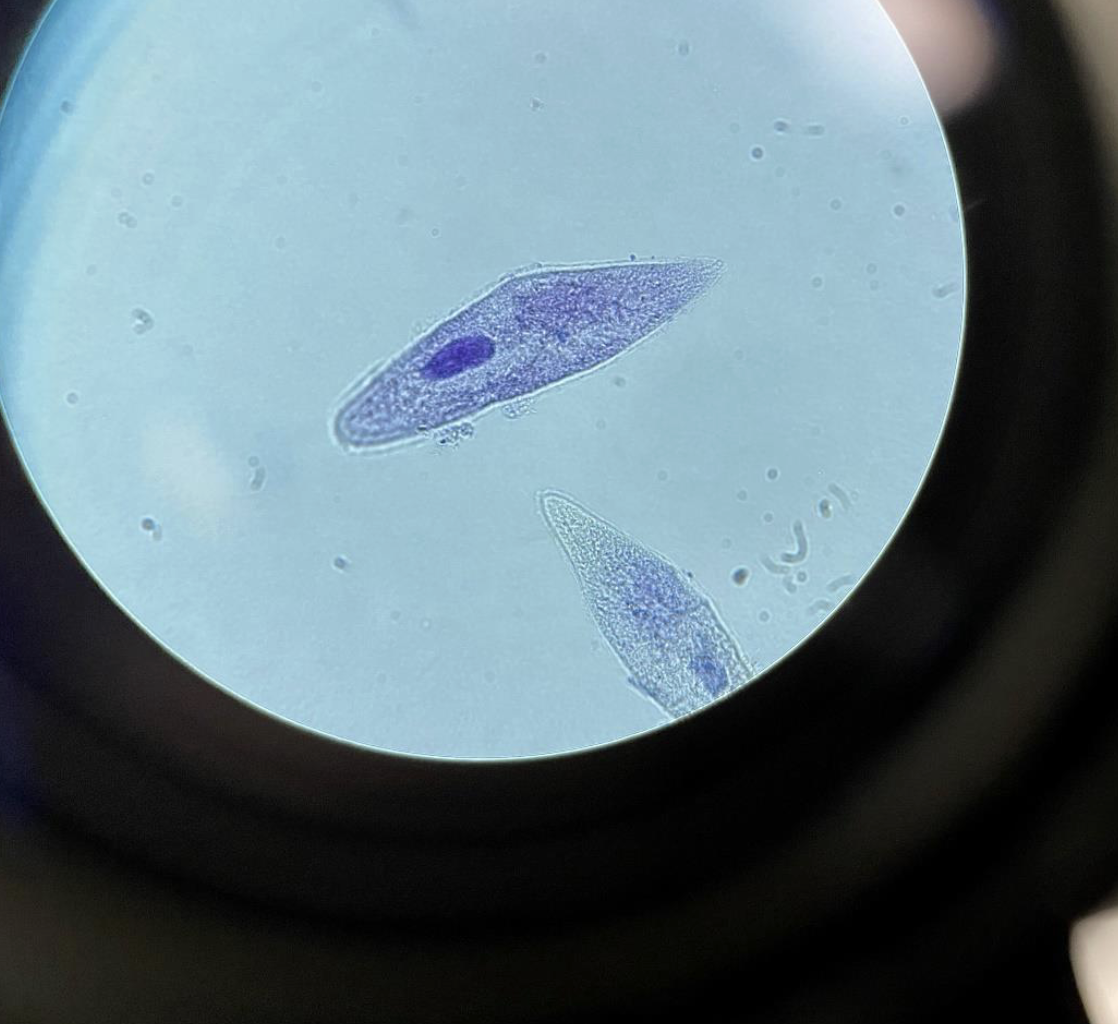
Paramecium 400x, Paramecium have cilia (Kingdom Protista)
long, oval, slipper shaped
usually have a visible nucleus
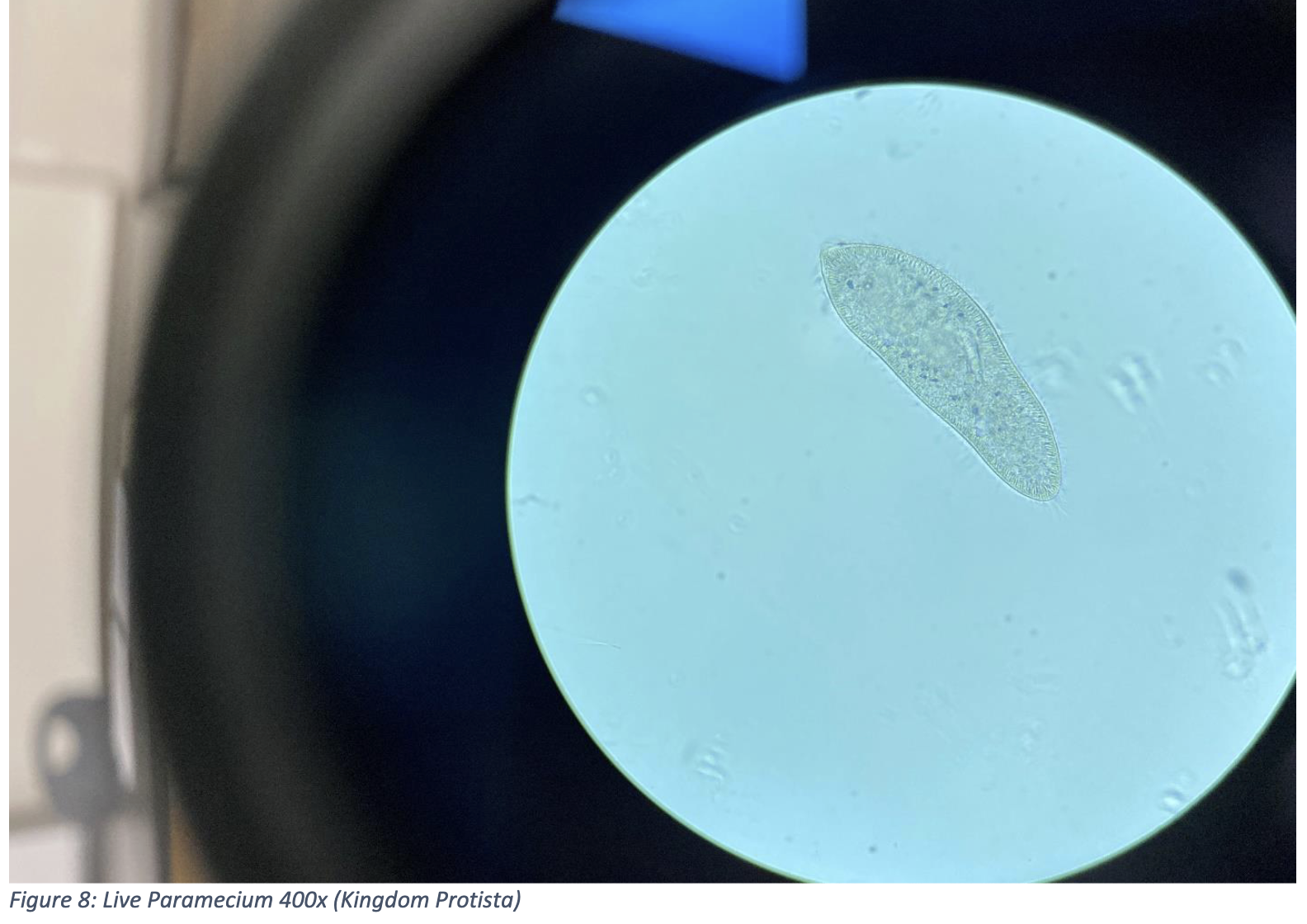
Live Paramecium 400x (Kingdom Protista)
long oval or slipper shaped
light gray or transparent
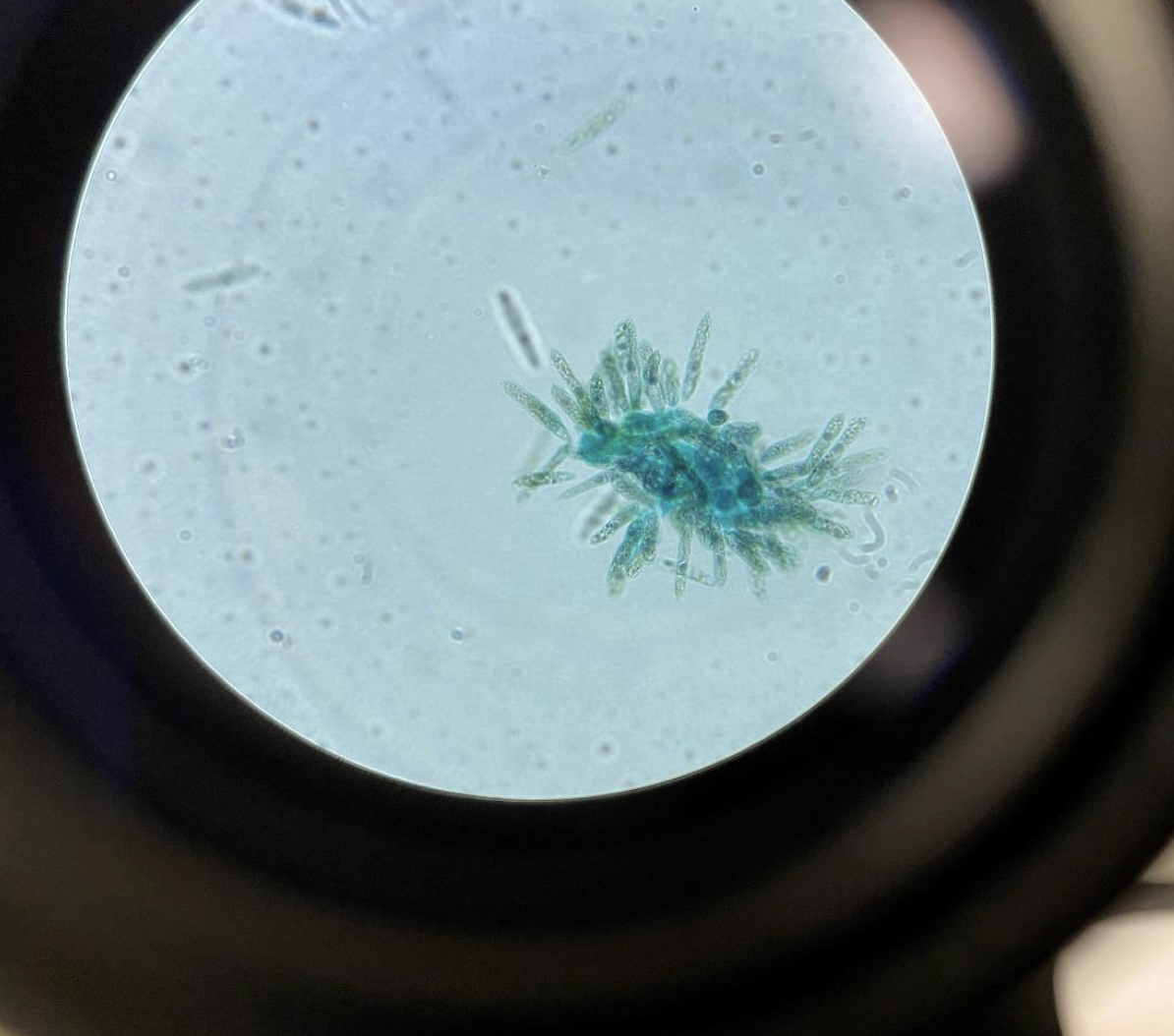
Euglena 400x, Euglena have a flagellum (Kingdom Protista)
It moves using a flagellum (tail-like structure)
usually green, looks like a cluster of rice
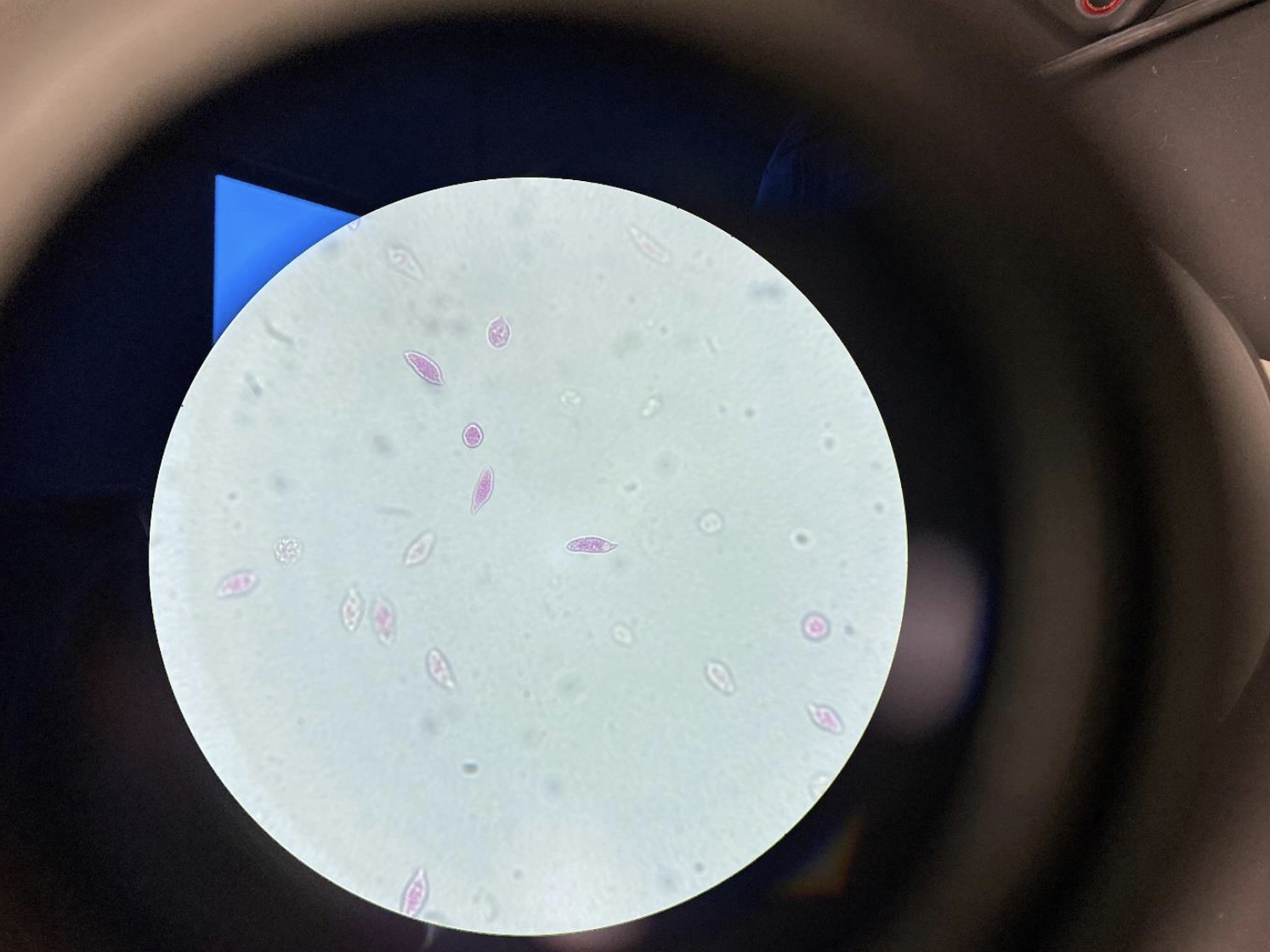
Euglena stained pink 400x
looks like small pieces of rice floating around
Chlamydomonas 400x, This Algae has two flagella (Kingdom Protista)
Swims using two flagella at the front (pulls itself forward)
usually green
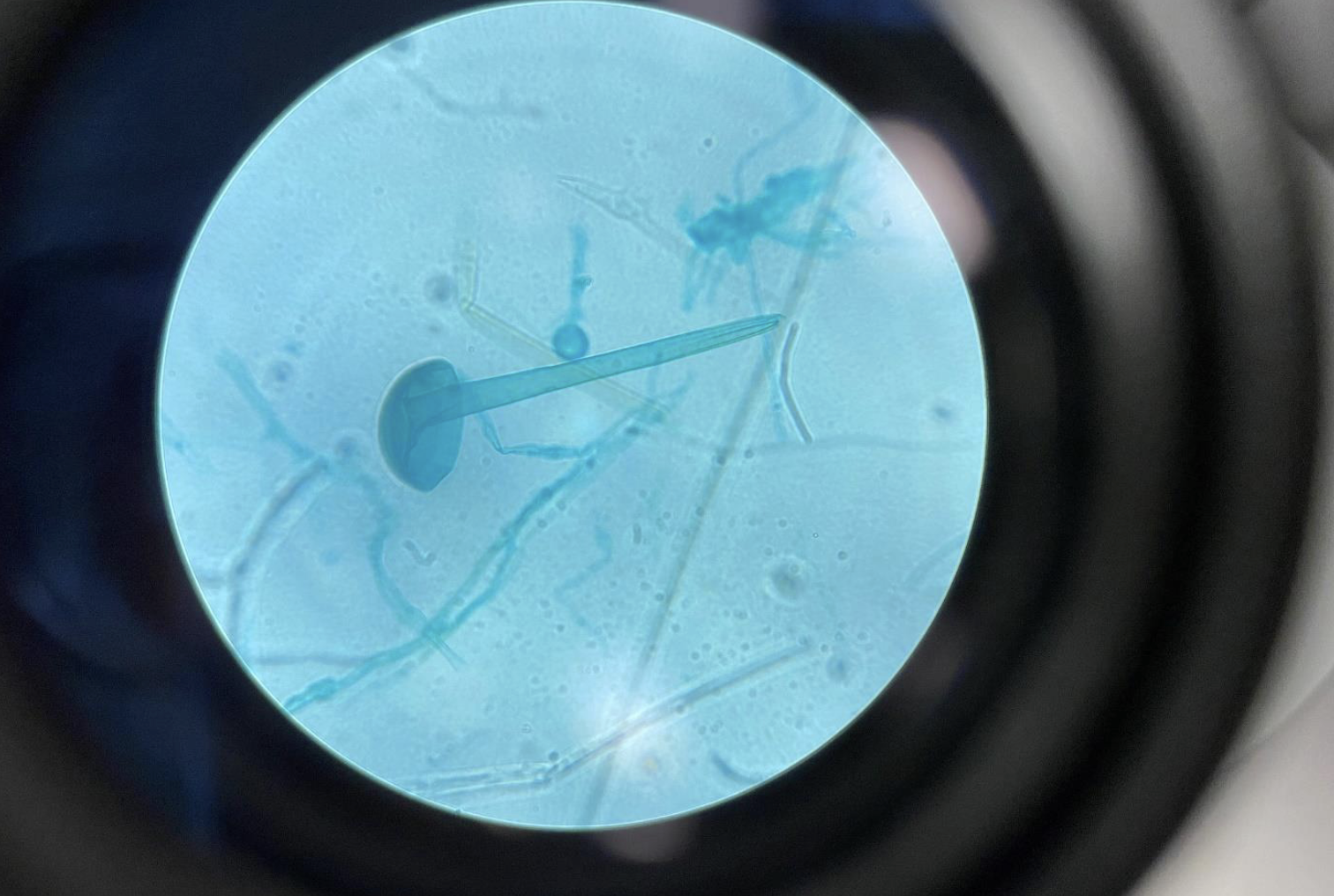
Rhizopus Fungi sporangia 400x (Division Zygomycota)
Looks like a lollipop or ball-on-a-stick structure
The round sporangium (ball) holds spores
The stalk is called a sporangiophore
Found in Zygomycota, a division of fungi
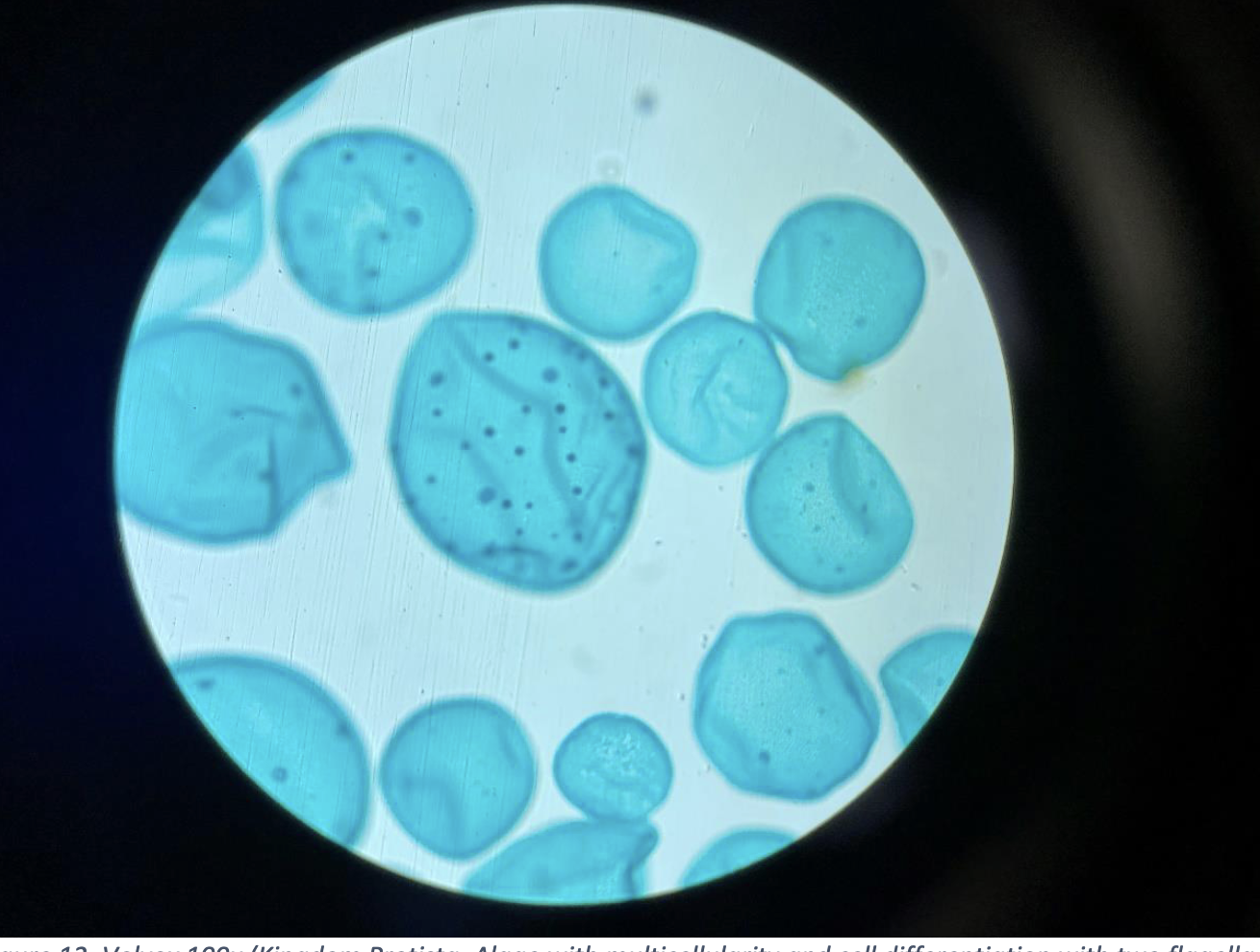
Volvox 100x (Kingdom Protista, Algae with multicellularity and cell differentiation with two flagella per cell)
large, round green colony made of many small cells arranged in a sphere
Each cell has two flagella, used to help the colony move
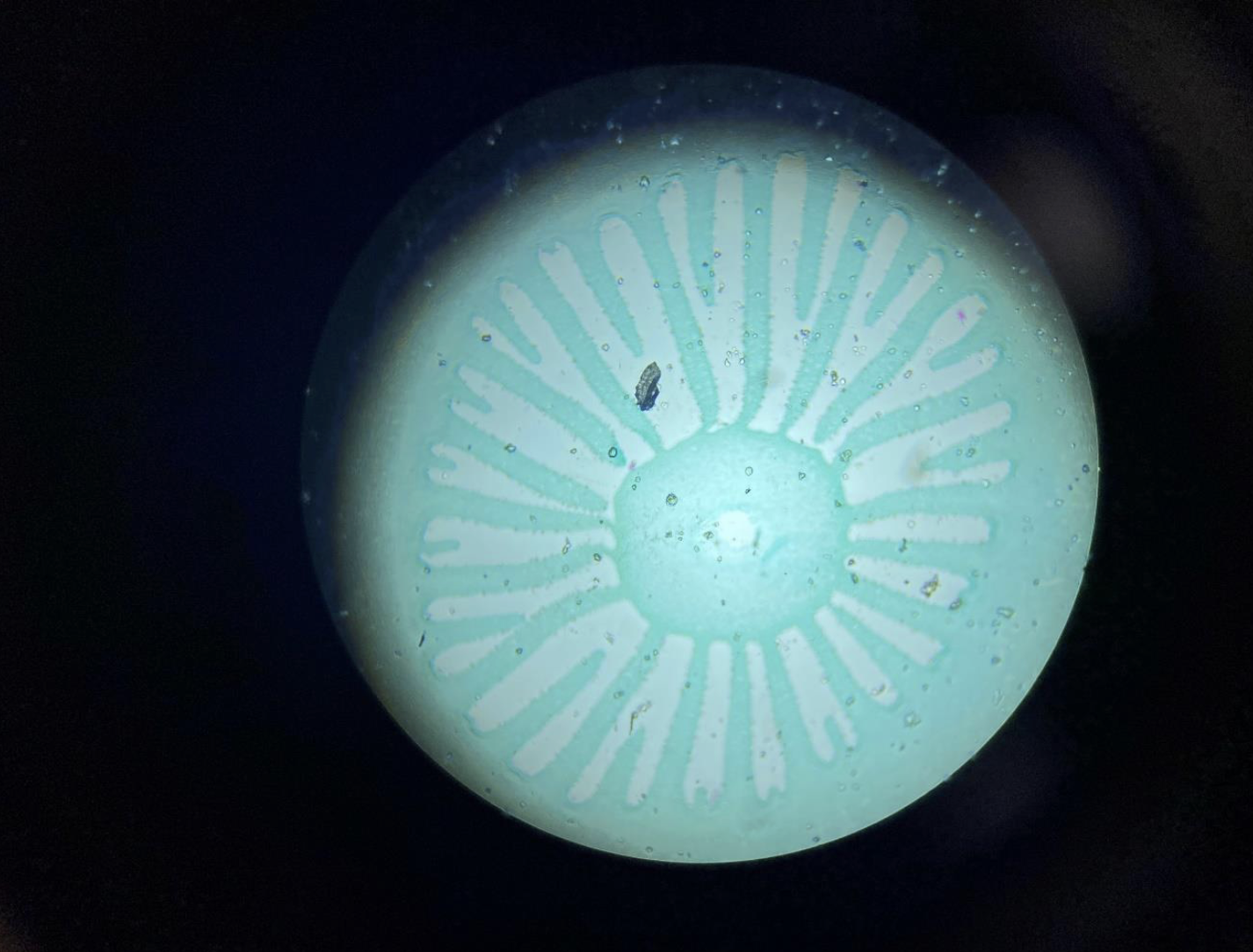

Fungi Basidiocarp 40x (Division Basidiomycota)
The visible fruiting body of mushrooms, like a cap and stem
Contains basidia, where spores are produced
Usually large enough to see without a microscope, but details visible at 40x
Part of the reproductive structure of Basidiomycota fungi
Includes common mushrooms, shelf fungi, and puffballs
Kingdom: Fungi
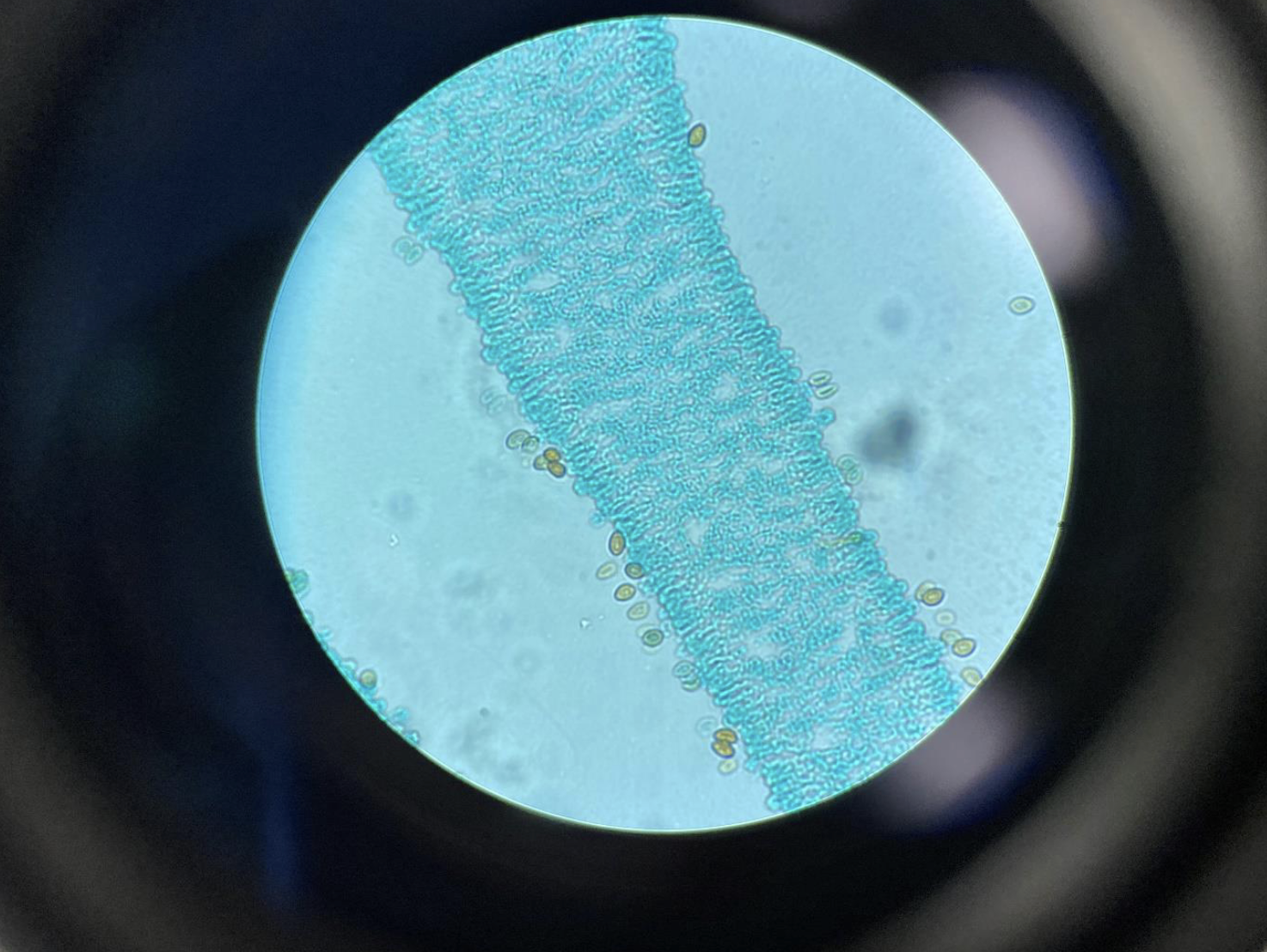
Fungi Basidiocarp with spores 400x (Division Basidiomycota)
Shows the basidia, the microscopic club-shaped structures on the gills or surface.
Each basidium produces basidiospores, which are often seen as small dots or grains around the basidia.
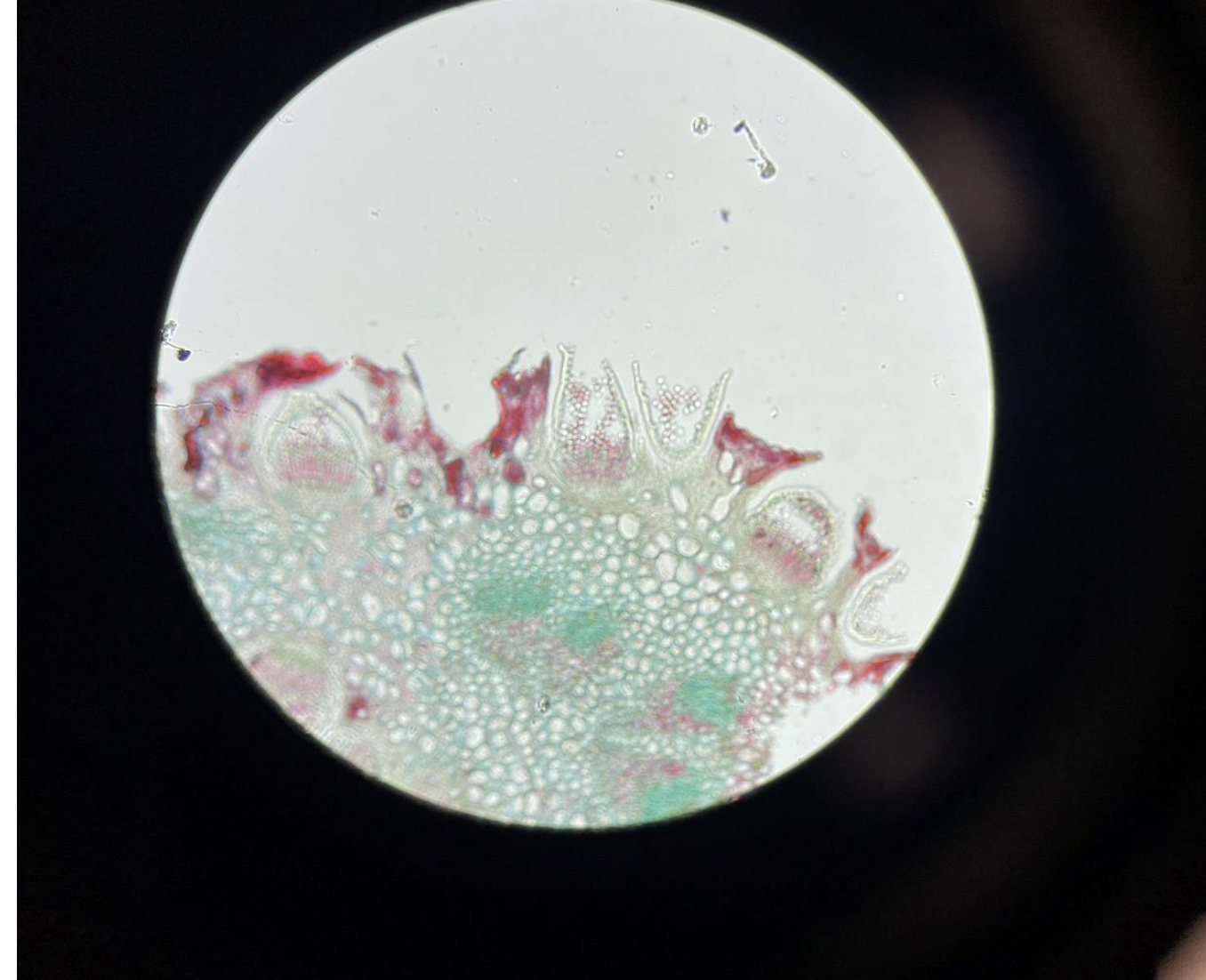
Puccinia Wheat Rust 400x (This is the Wheat Rust bursting out of the surface of the Wheat leaf, Division Basidiomycota)
You see rust-colored pustules bursting out of the wheat leaf surface.
These pustules release spores that spread the infection.
Puccinia is a fungal pathogen causing wheat rust disease.
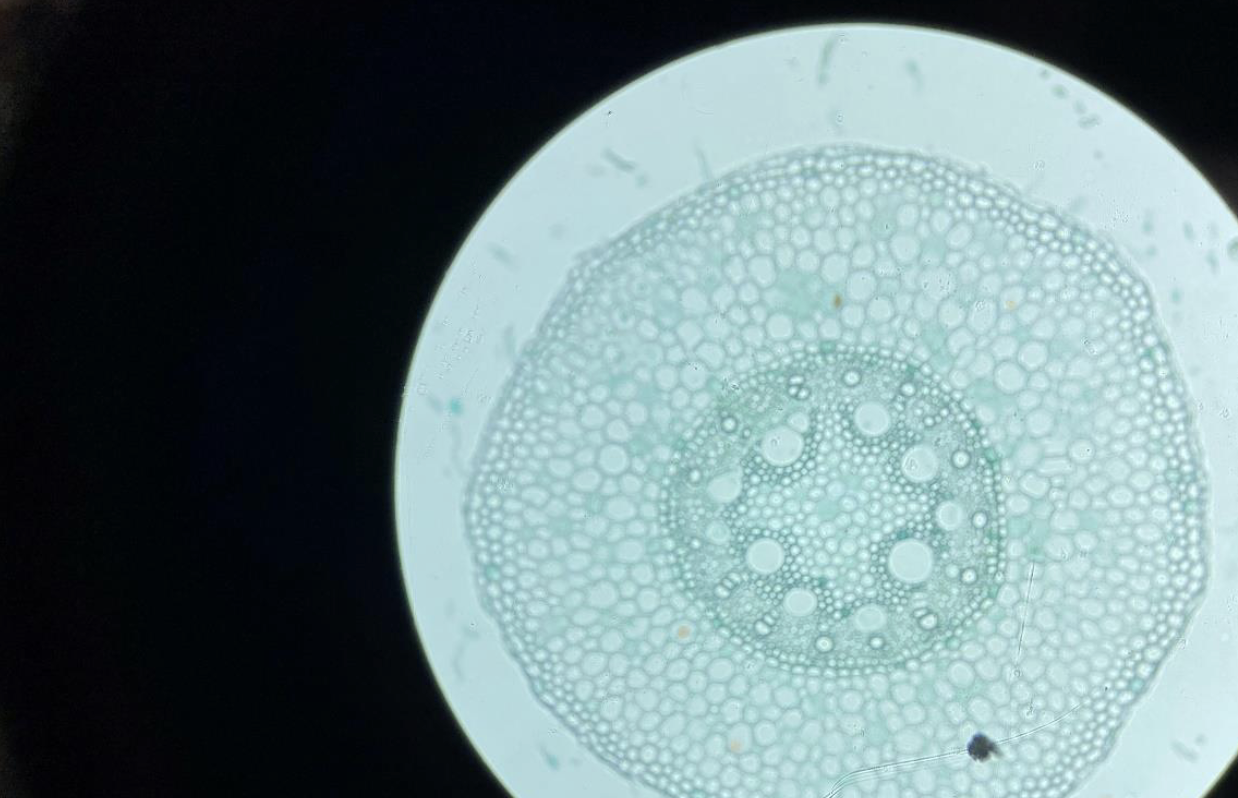
Monocot Plant Root 40x
You see many small circles (vascular bundles) spread out inside the root.
There is a big empty space (pith) in the middle.
The outside layer is the skin (epidermis).
This is how roots of monocot plants like corn or grass look.
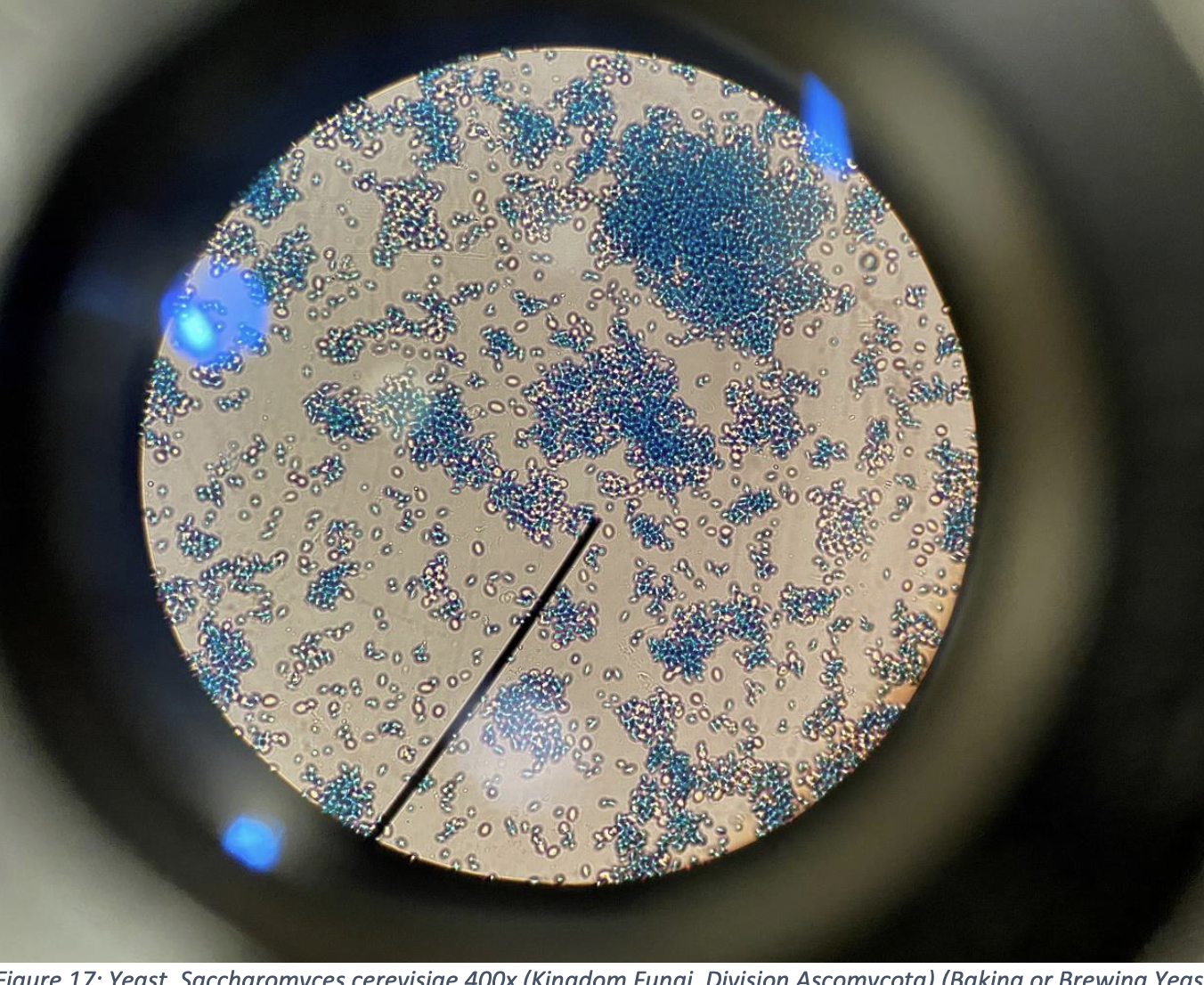
Yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae 400x (Kingdom Fungi, Division Ascomycota) (Baking or Brewing Yeast)
Small, round to oval-shaped cells, often seen as single cells or in small clusters.
Reproduction: Commonly reproduces by budding—small buds form and grow off the parent cell.
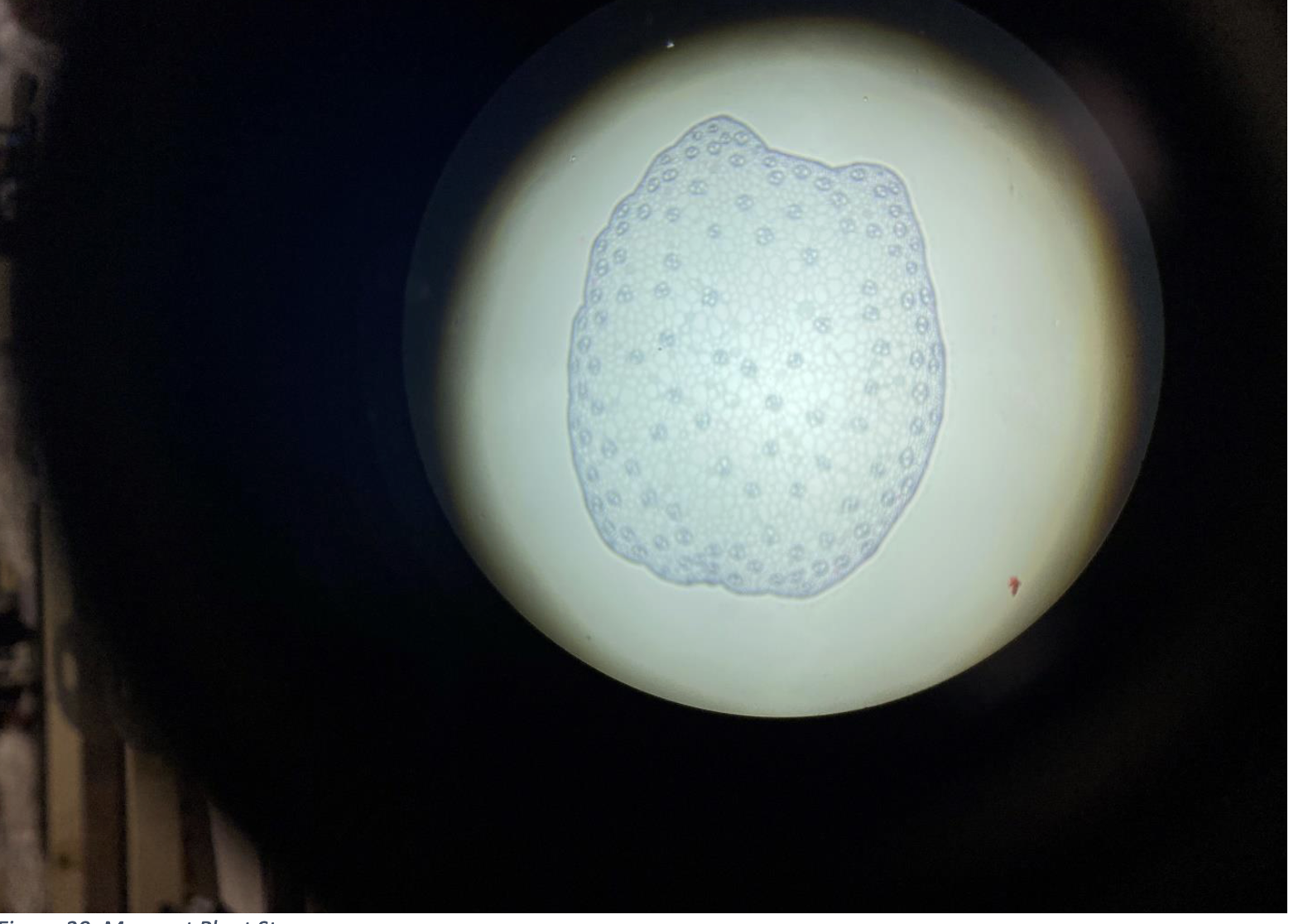
Monocot Plant Stem
The vascular bundles (xylem and phloem) are scattered all over inside the stem.
No clear ring or pattern.
The stem looks uniform inside with many small circles (vascular bundles).
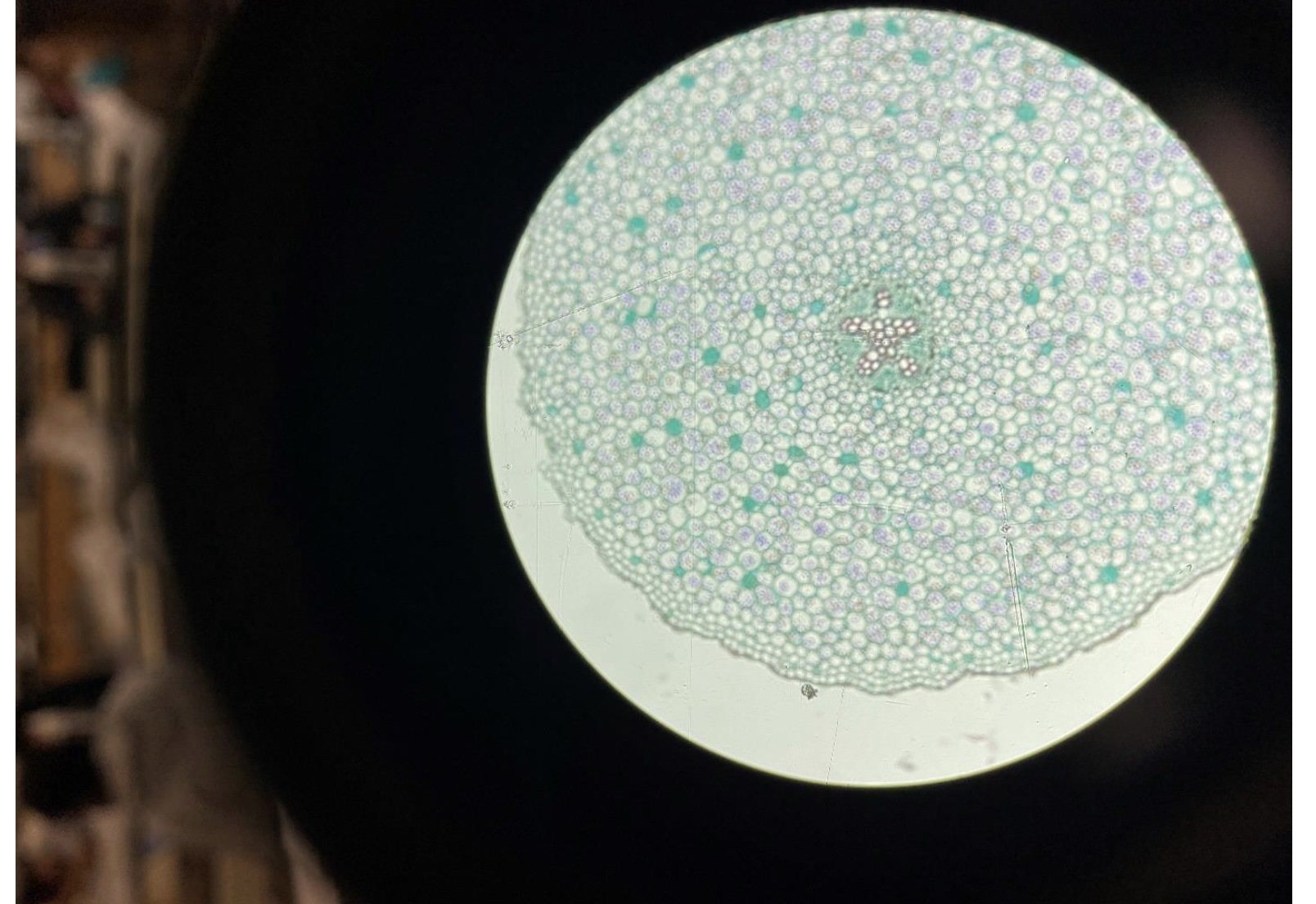
Dicot Plant Root
The vascular tissue (xylem and phloem) is arranged in a star shape in the center.
There is no big empty space (pith) in the middle.
The root has a clear cortex (layer between skin and center).
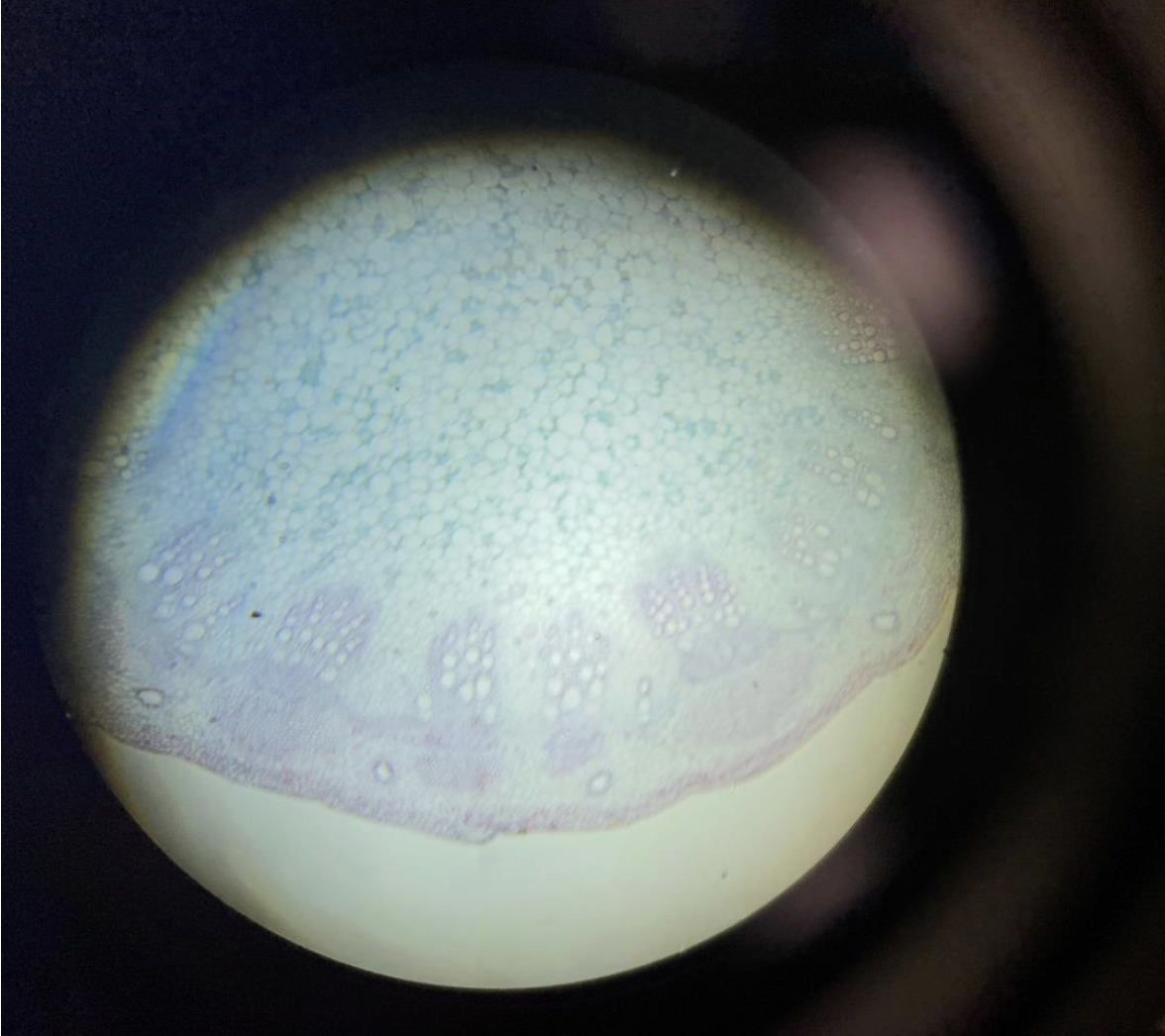
Dicot Plant Stem 40x
The vascular bundles (xylem and phloem) are arranged in a ring near the edge of the stem.
Inside the ring is the pith (central area).
Between the vascular bundles is the cambium, which helps the stem grow wider.
The outer layer is the epidermis (stem skin).
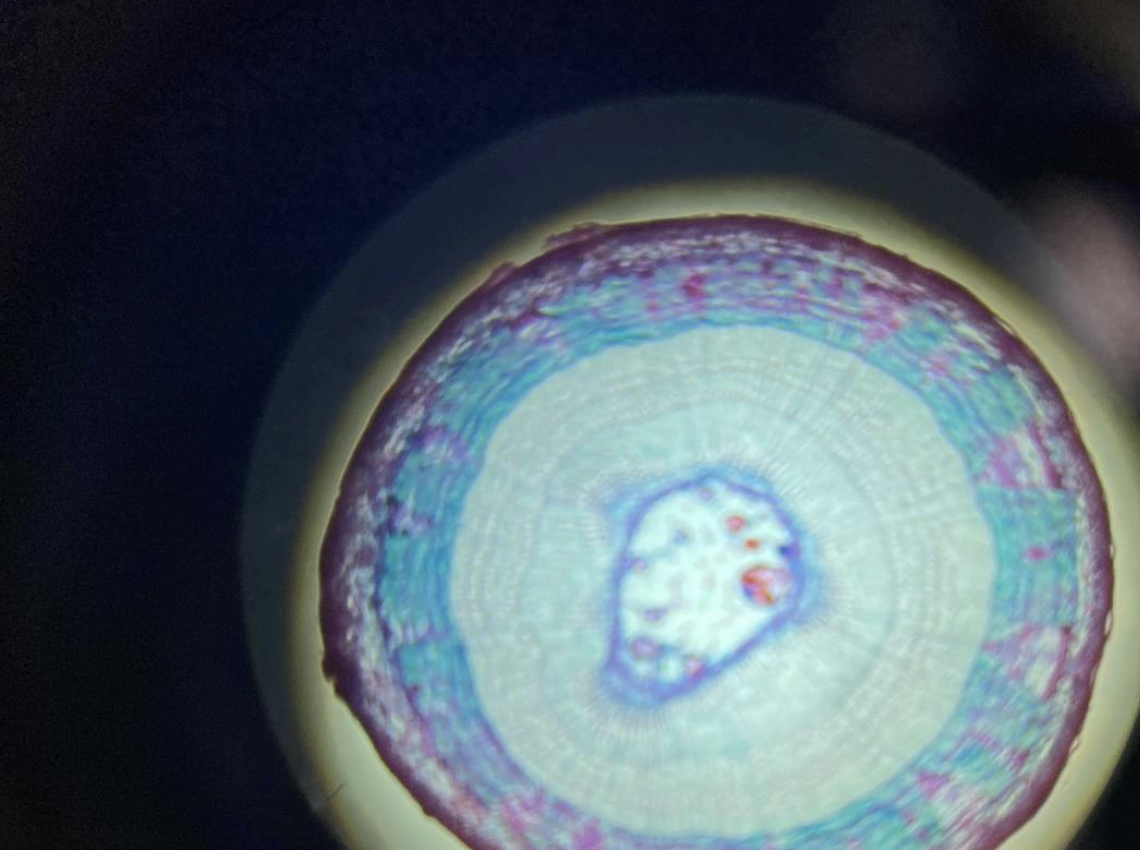
Woody Dicot Plant Stem 40x
Shows rings of growth (annual rings) made of wood (xylem) inside the stem.
Vascular bundles are arranged in a ring around the center.
Has a thick layer of bark on the outside.
Contains cambium, a layer that helps the stem get wider each year.
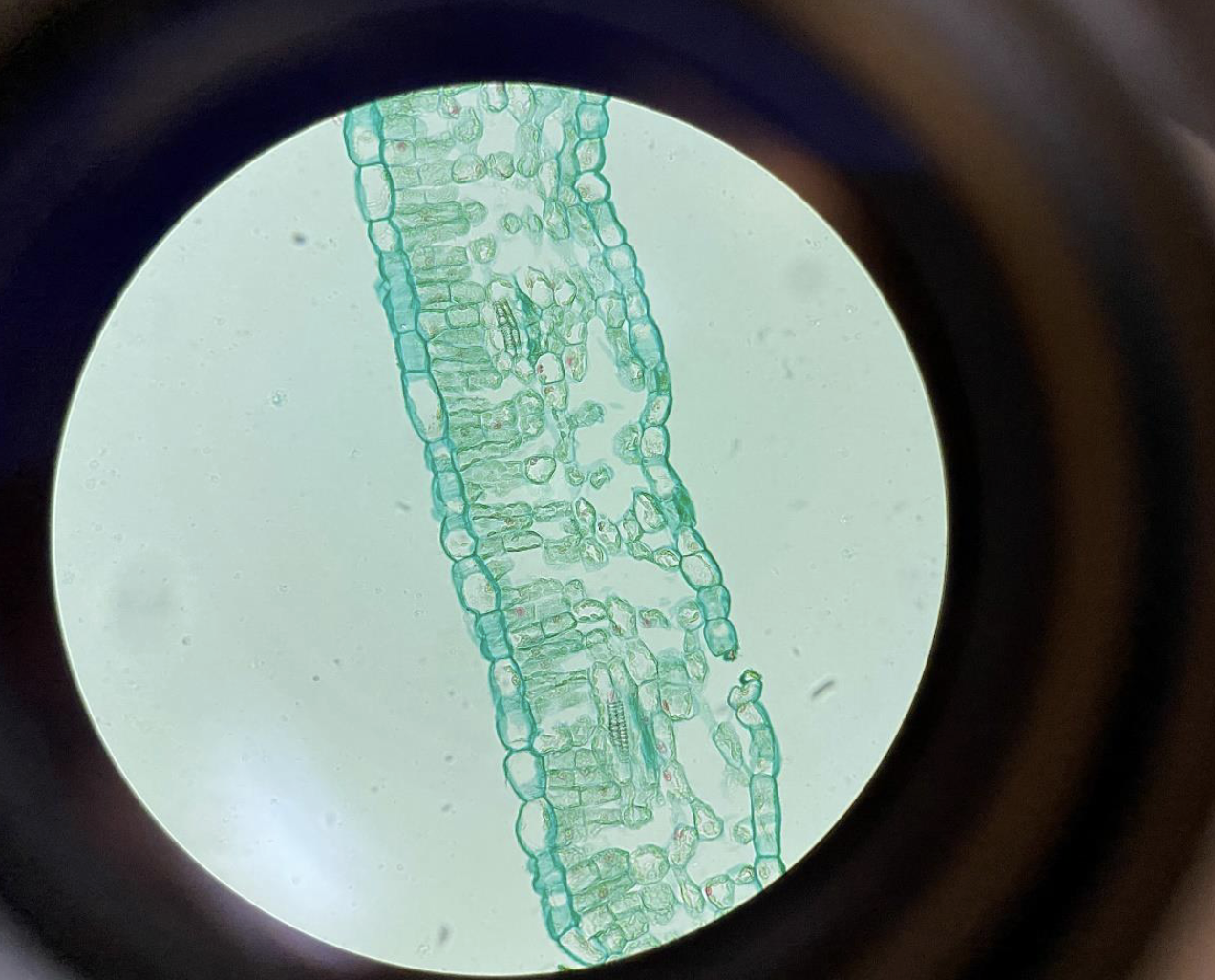
Dicot Plant Leaf 400x (Upper and Lower Epidermal Cells, Palisade Cells, Spongy Mesophyll Cells and Guard Cells)
Upper Epidermis: Thin, clear layer on top that protects the leaf.
Palisade Cells: Tall, tightly packed cells below the upper epidermis; where most photosynthesis happens.
Spongy Mesophyll Cells: Loosely packed cells with air spaces below the palisade layer; help with gas exchange.
Lower Epidermis: Thin layer at the bottom with guard cells surrounding tiny openings called stomata for breathing and water release.
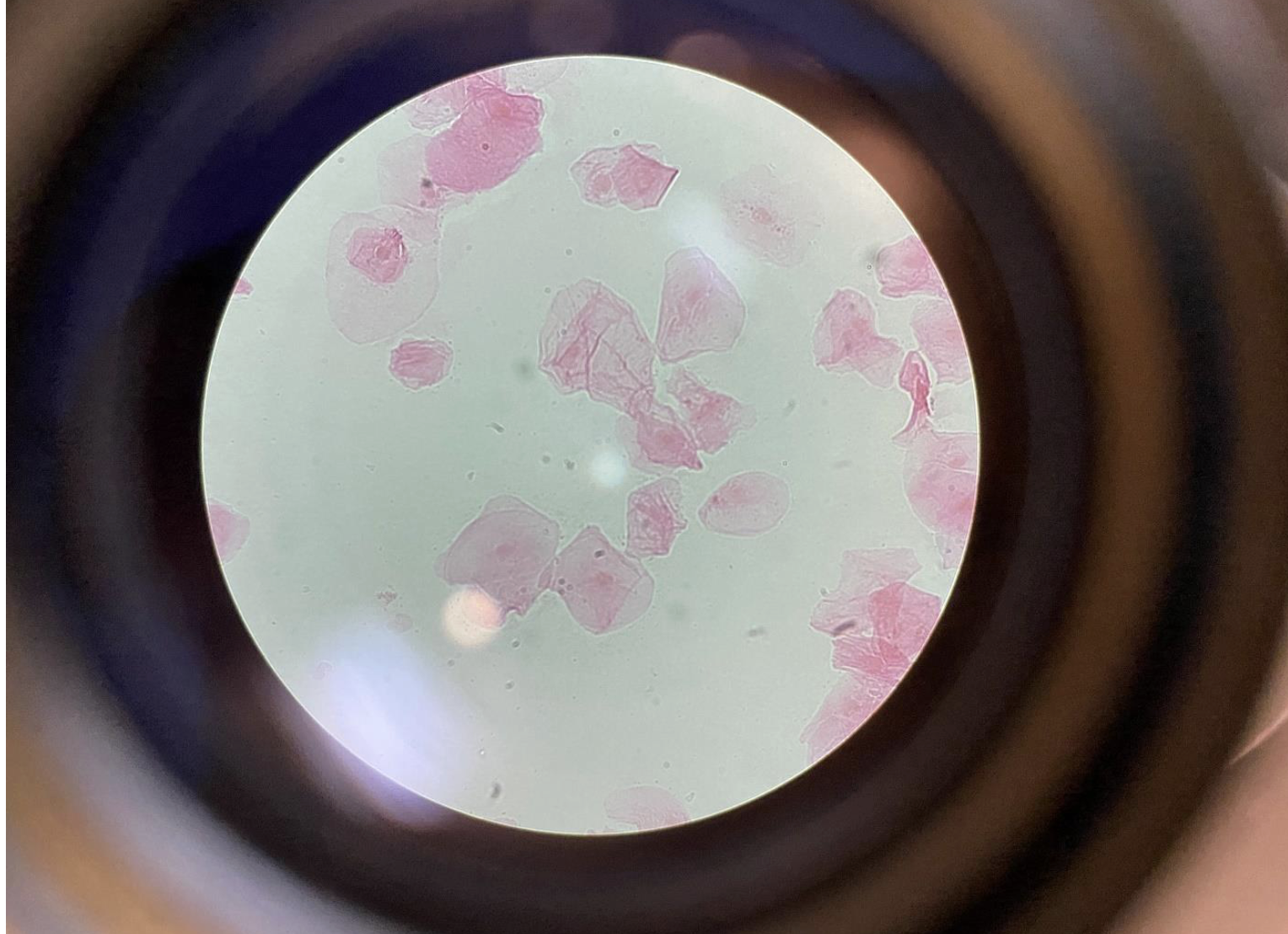
Squamous Cells from Human Cheek Epithelium 400x
Flat, thin, and irregularly shaped cells that overlap like tiles.
Transparent with a visible dark nucleus in the center of each cell.
Make up the lining of the inside of your cheek (epithelium).
Easy to see under the microscope because they form a thin layer.
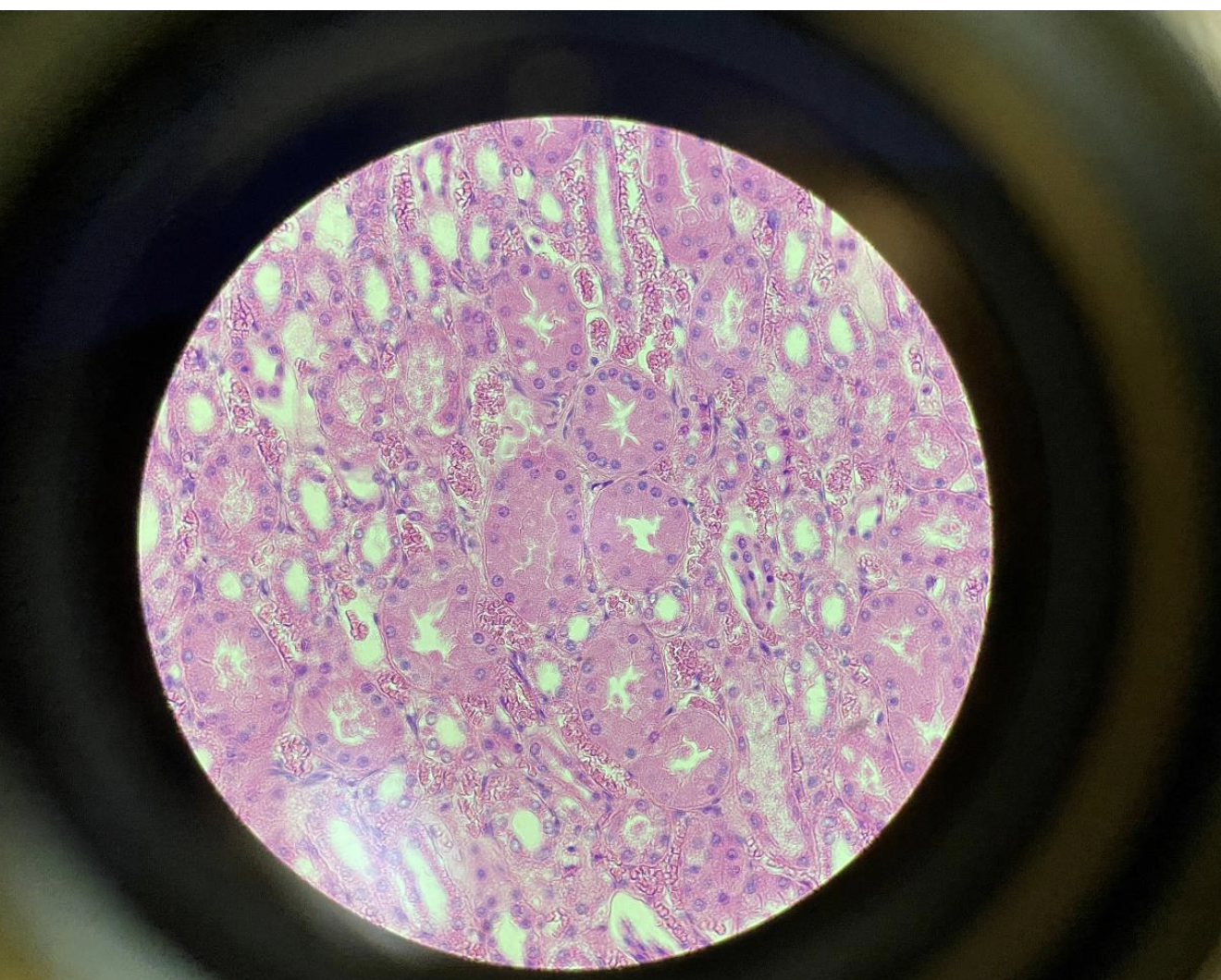
Cuboidal Epithelial Cells from the Kidney 400x
Cube-shaped cells with roughly equal height, width, and depth.
Have a round, central nucleus in each cell.
Form the lining of kidney tubules, helping with absorption and secretion.
Appear as a neat, regular layer under the microscope.
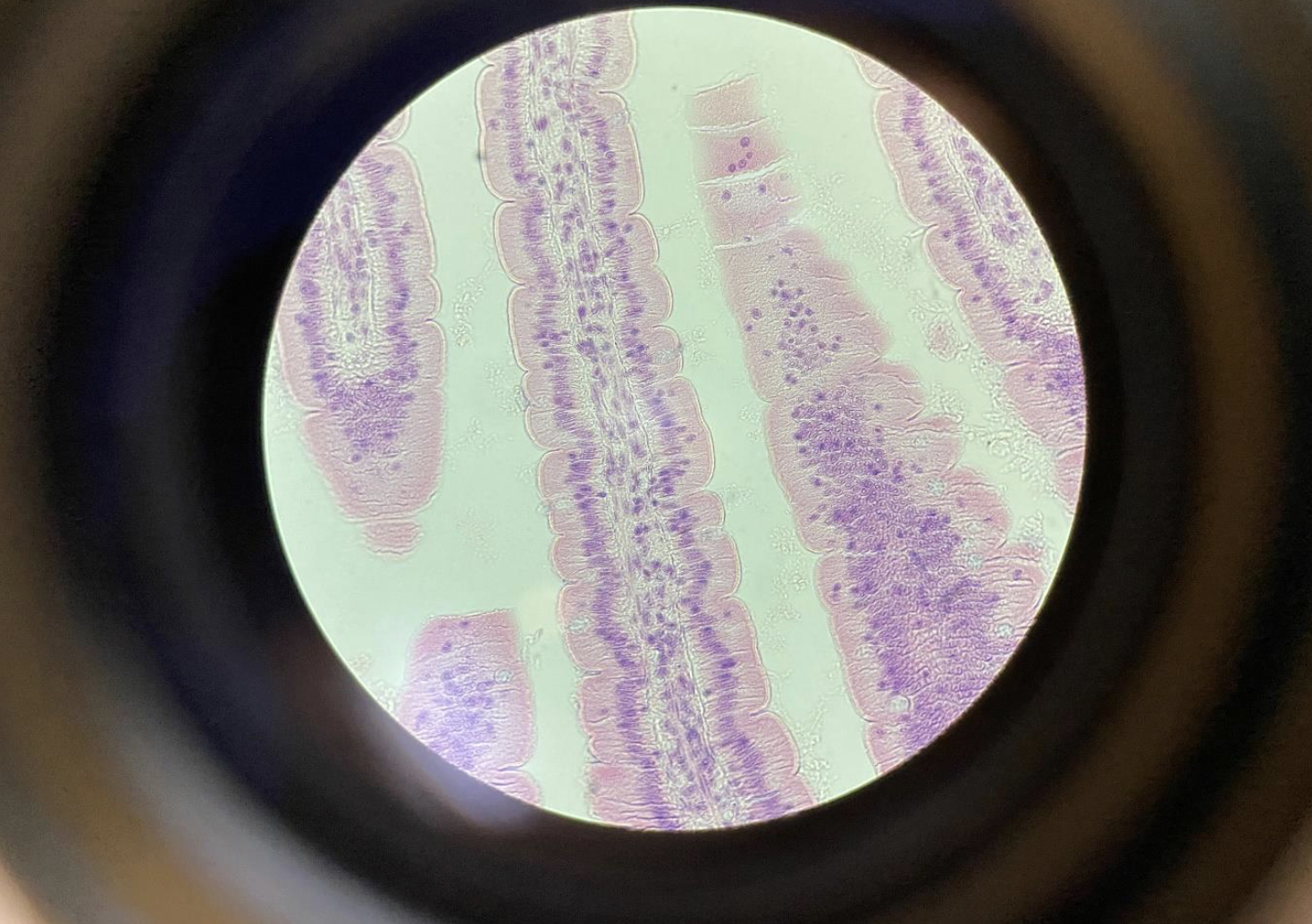
Columnar Epithelial Cells with Microvilli from the intestines 400x
Tall, rectangular-shaped cells lined up closely together.
Have microvilli on their surface—tiny finger-like projections that increase surface area.
Microvilli look like a fuzzy or brush-like border called the brush border.
Found lining the intestines, helping absorb nutrients.
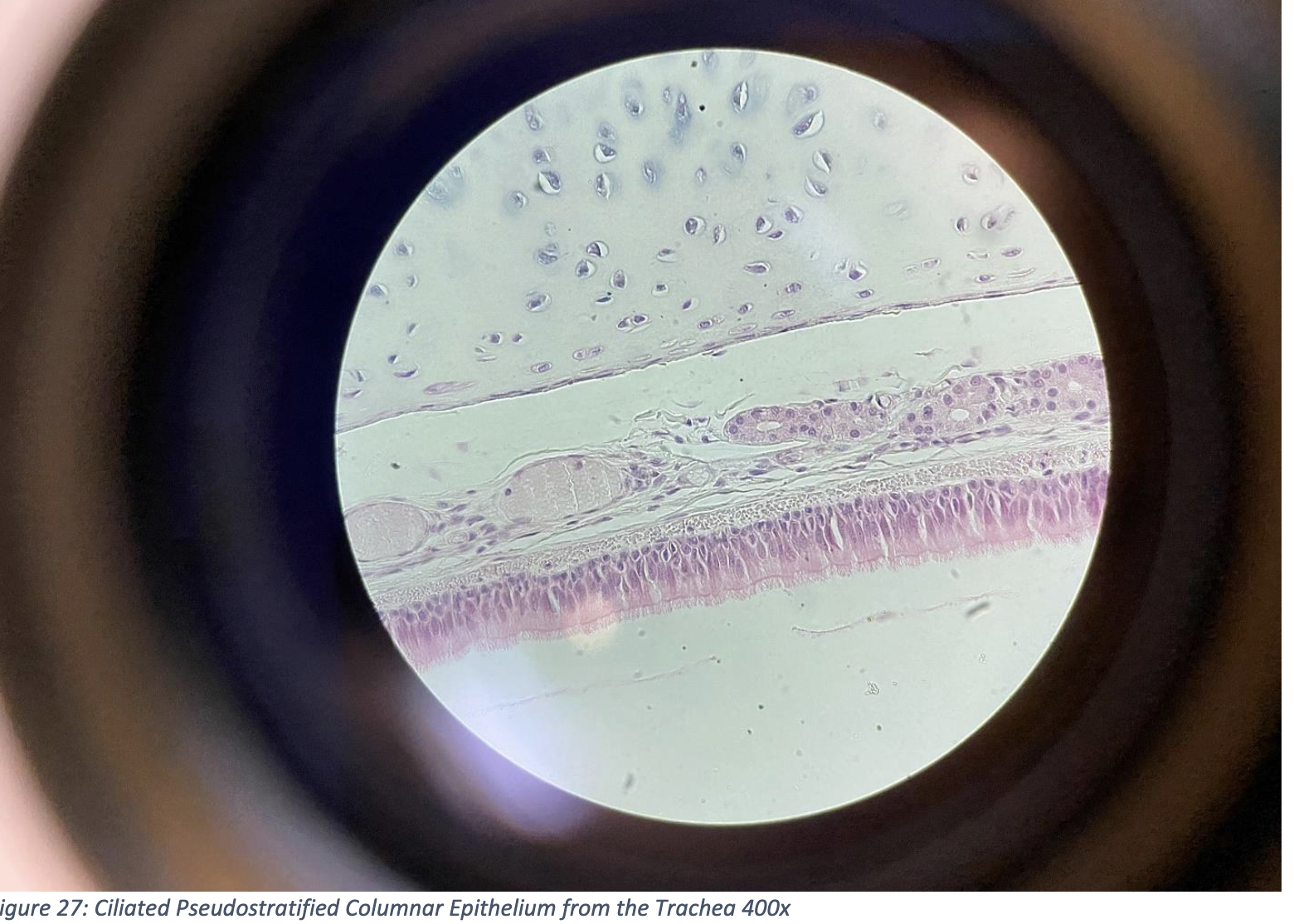
Ciliated Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium from the Trachea 400x
Cells appear in layers, but all touch the basement membrane — that’s why it’s called pseudostratified (falsely layered).
Column-shaped cells with nuclei at different heights, giving a layered look.
The top surface is covered in cilia — tiny hair-like structures that move mucus and dust out of the airway.
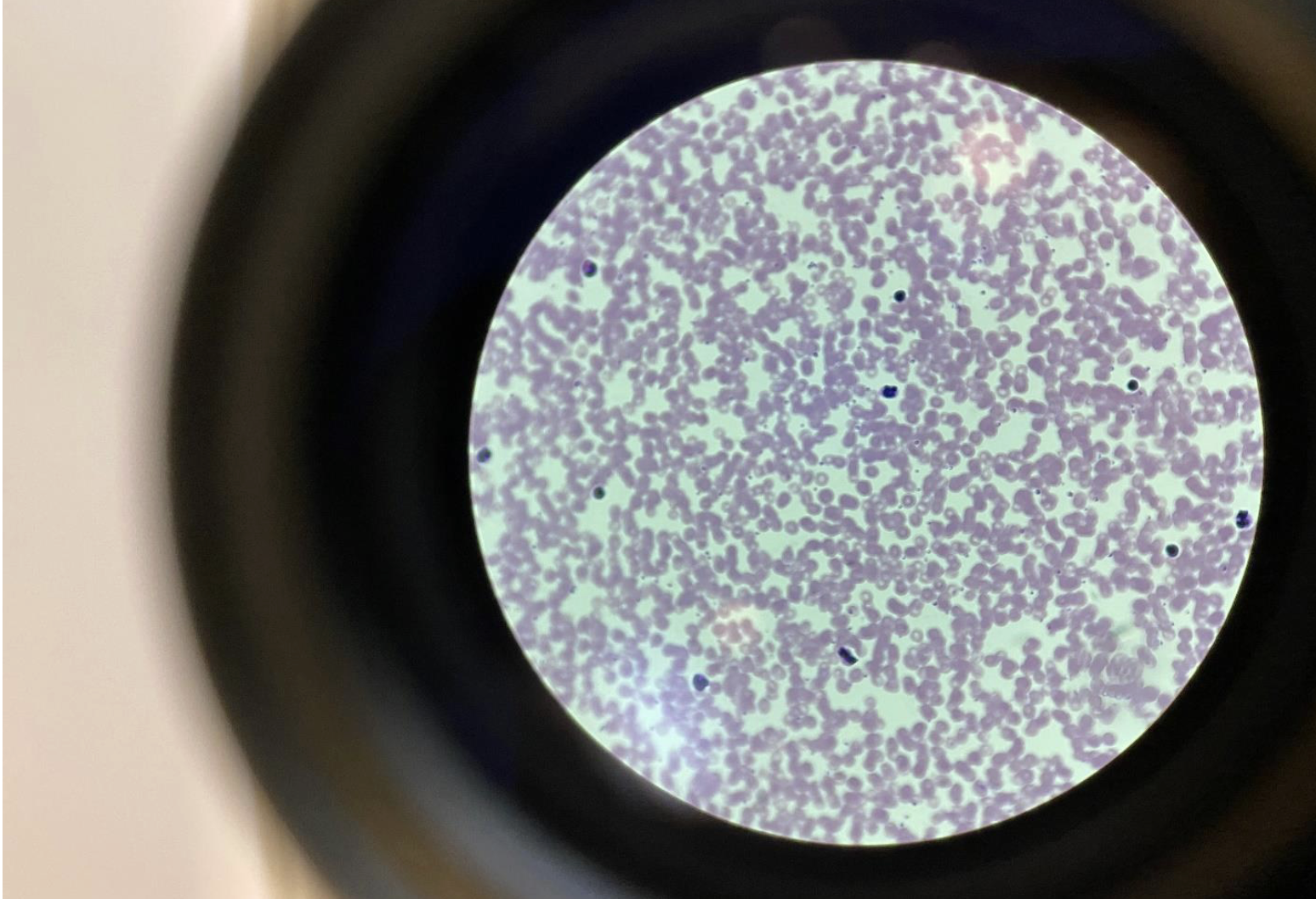
Human Blood, Connective Tissue with Liquid Matrix, 400x
Red blood cells (RBCs): Small, round, and pink with no nucleus — most abundant.
White blood cells (WBCs): Larger, fewer, with dark-stained nuclei.
Platelets: Tiny cell fragments involved in clotting.
Matrix: The liquid plasma, which is the non-living part — makes blood a connective tissue.
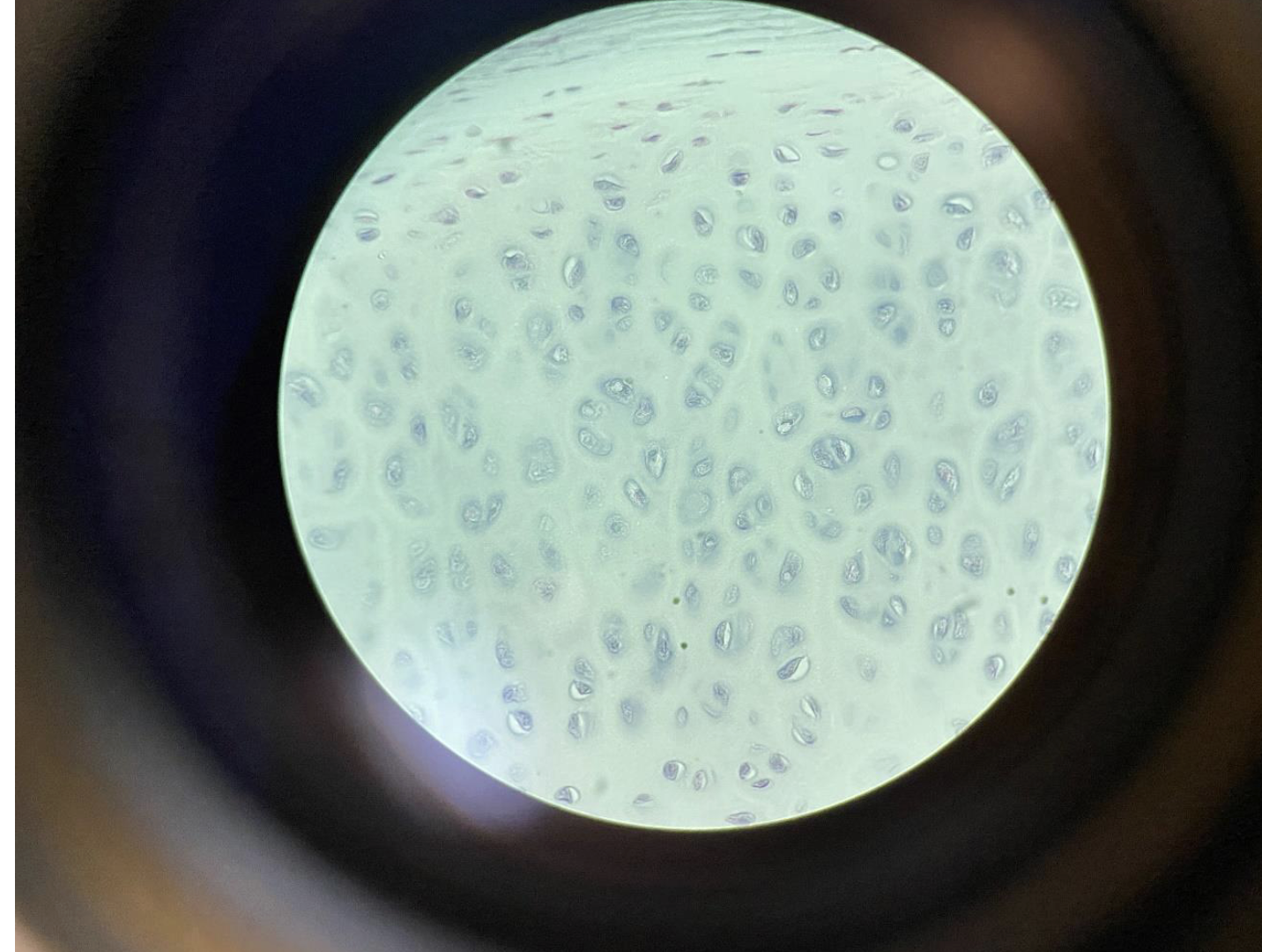
Chondrocytes in Cartilage – Trachea – 400x
(Connective Tissue with Flexible Matrix)
Chondrocytes are round cells found in lacunae (small spaces).
They sit inside a smooth, flexible matrix made of gel-like material.
The matrix provides support and flexibility, important for keeping the trachea open.
This is a type of connective tissue called hyaline cartilage.
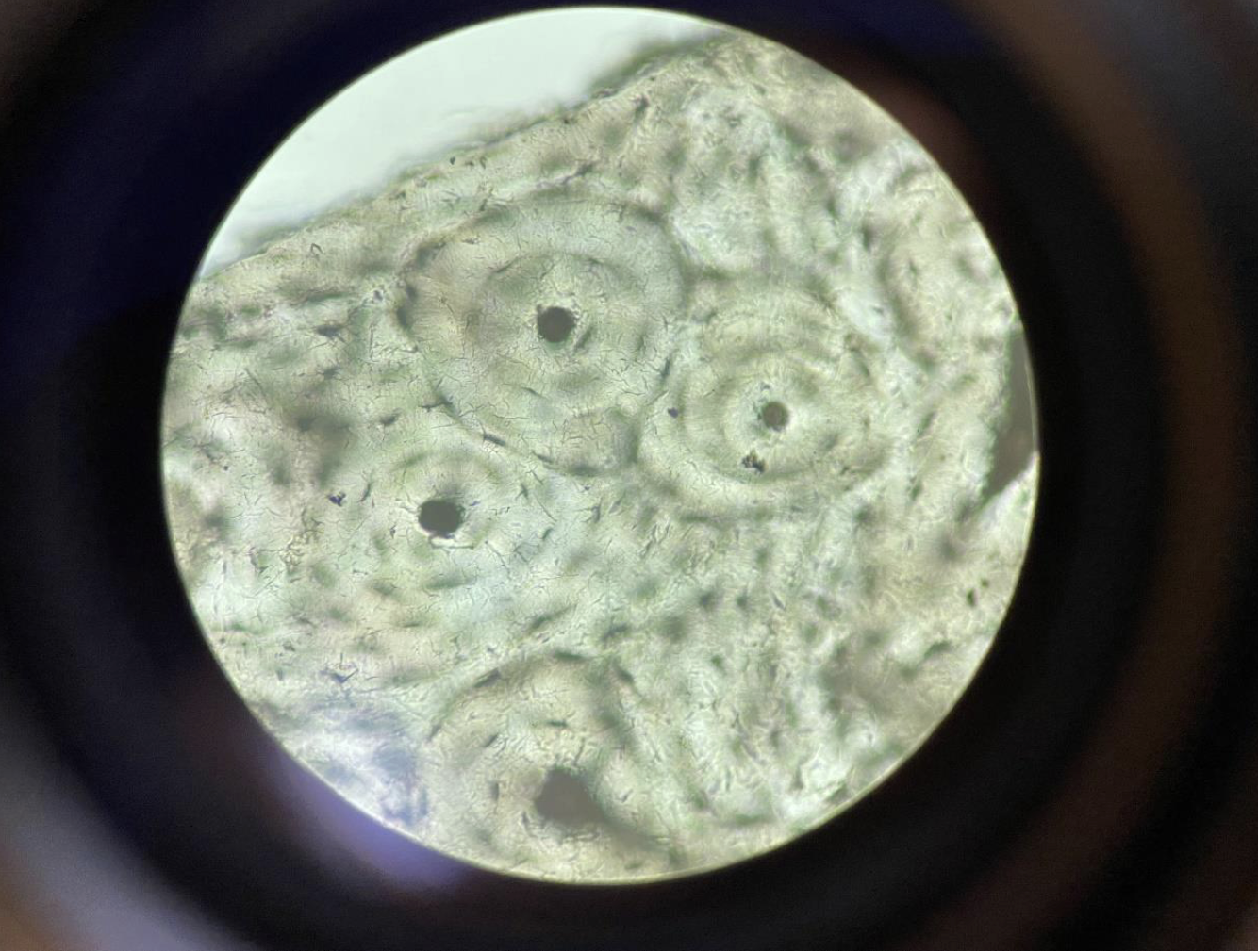
Osteocytes in Compact Bone with Haversian Systems, a solid connective tissue 400x
(Solid Connective Tissue with Haversian Systems)
Osteocytes (bone cells) sit in small spaces called lacunae.
Arranged in circular layers around a central Haversian canal (carries blood vessels).
These circular units are called Haversian systems or osteons.
The matrix is hard and solid, made of calcium and collagen.
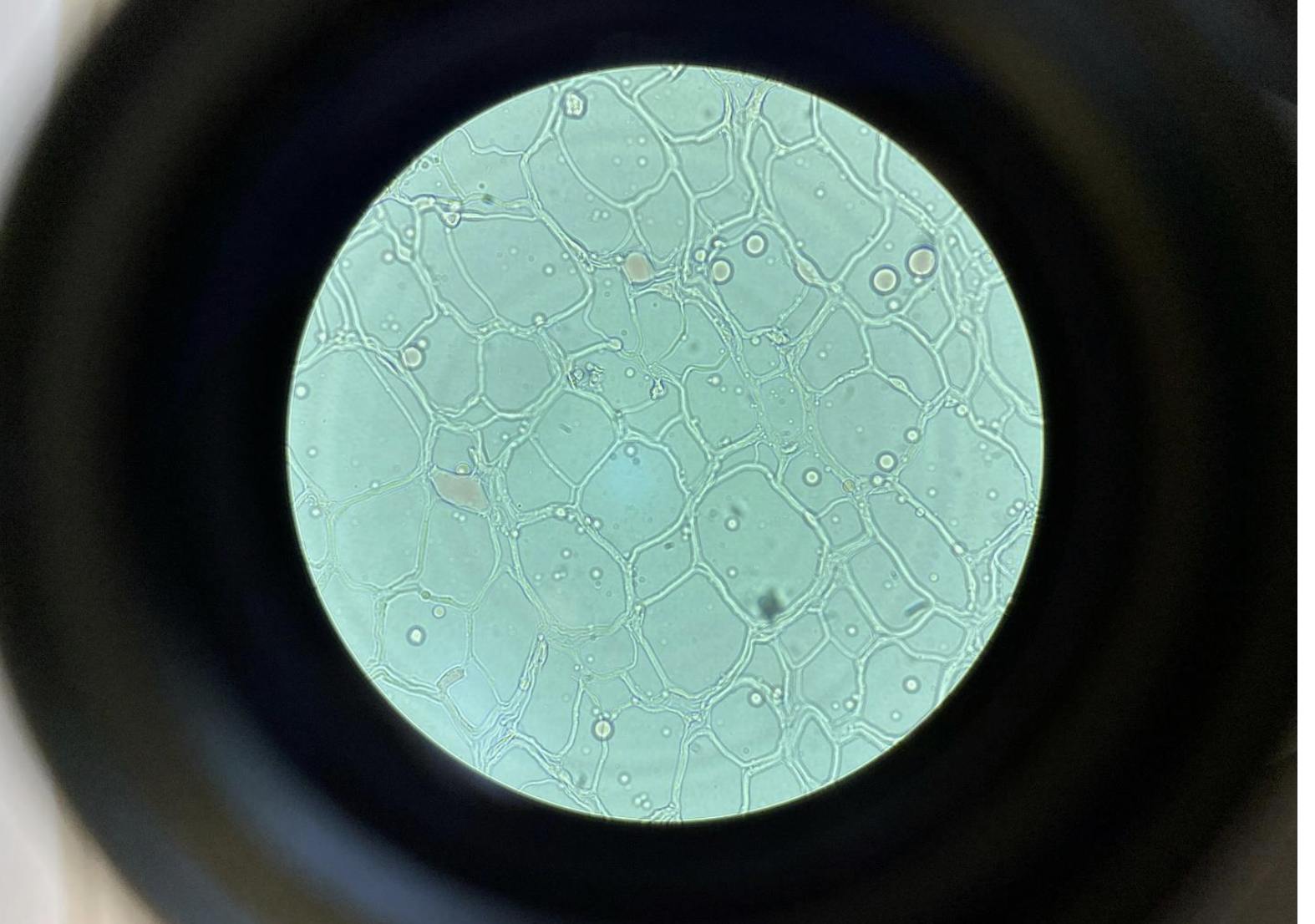
Adipocytes in Adipose Connective Tissue 400x
Adipocytes = fat cells
Appear as large, clear, round cells
Nucleus is pushed to the side (because the fat droplet fills most of the cell)
Cells are closely packed, and the tissue looks like a bubble wrap pattern
or a pool effect pattern
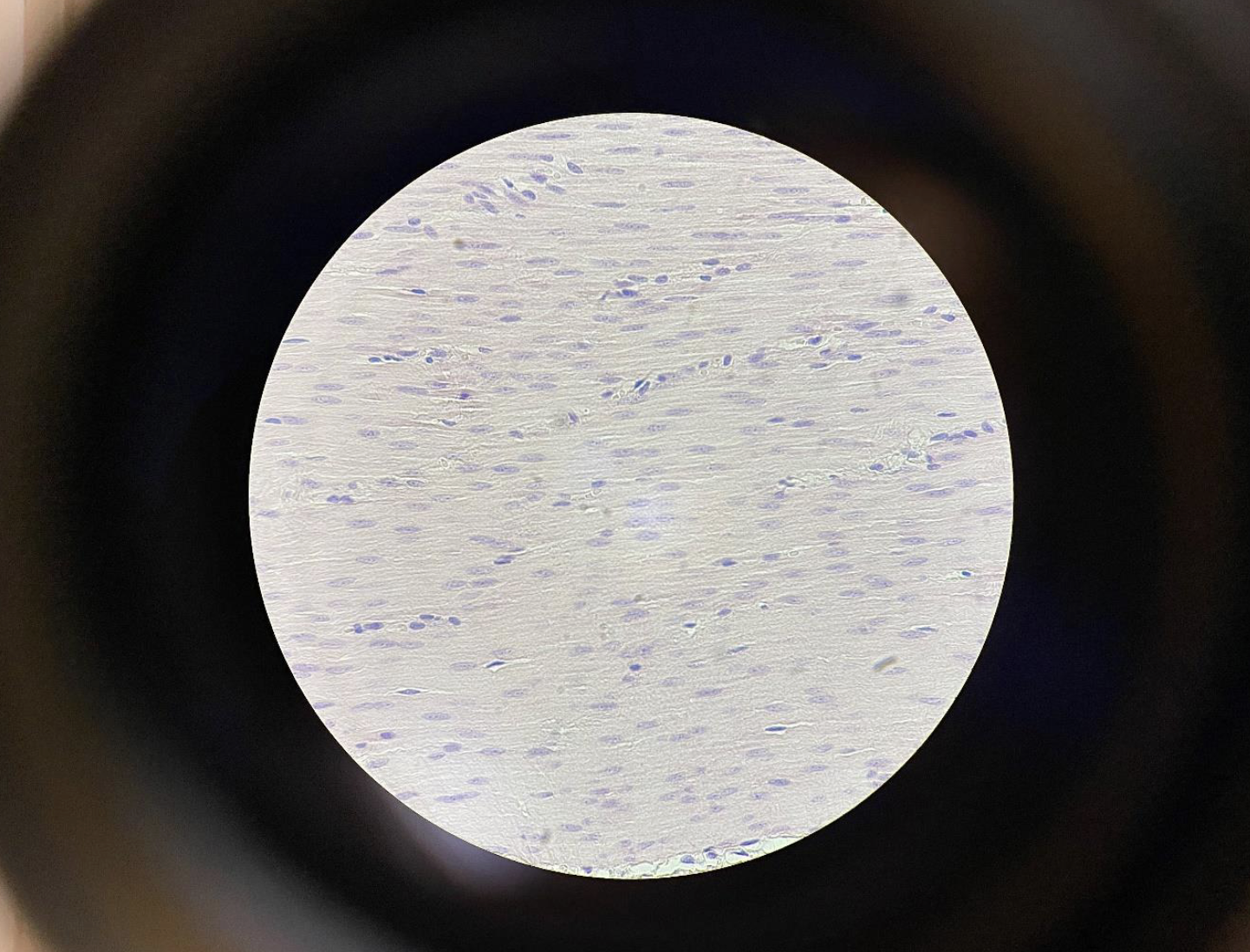
Smooth Muscle Cells 400x
Spindle-shaped cells (tapered at both ends)
One central nucleus per cell
Cells are closely packed and aligned in the same direction
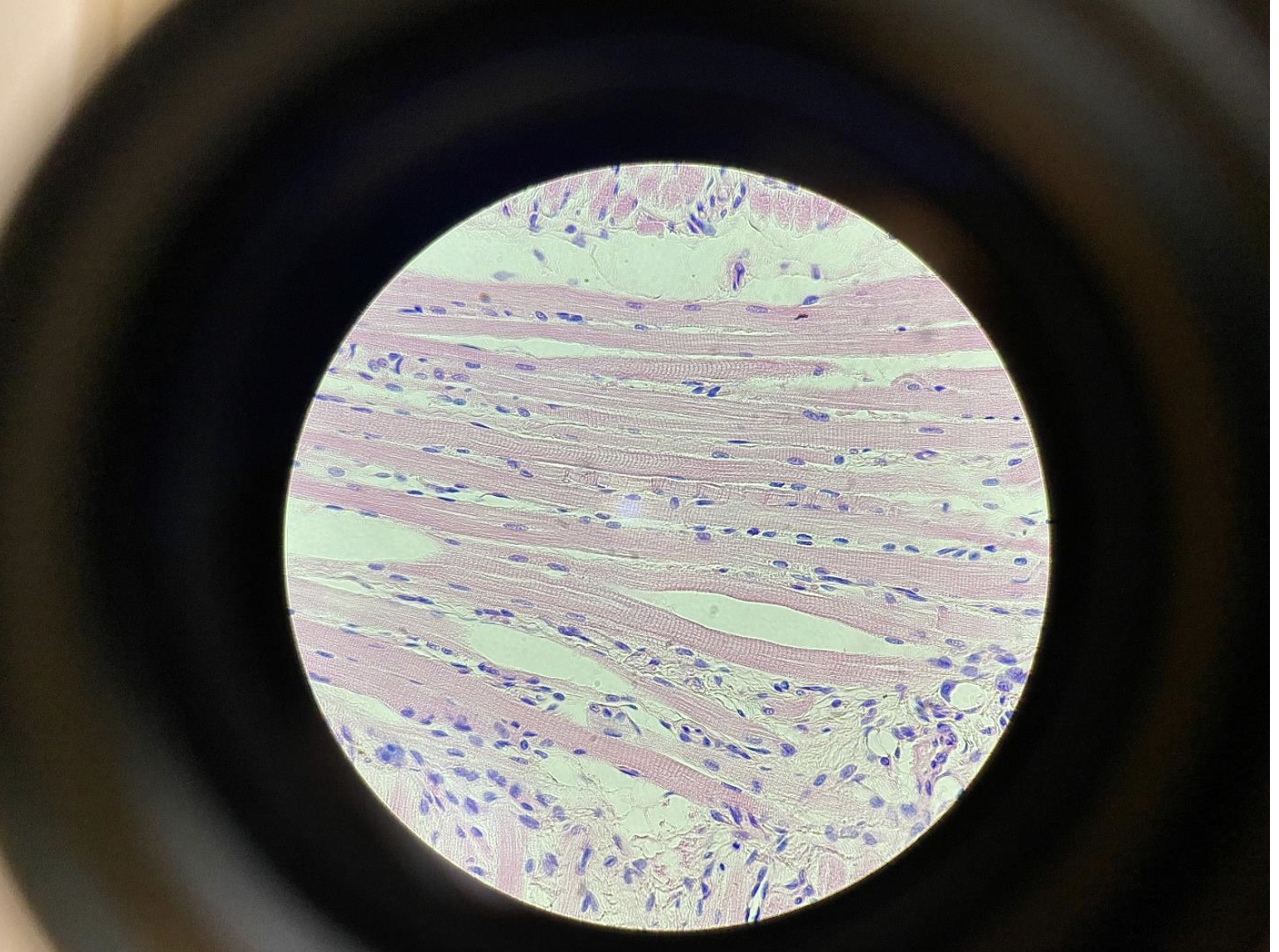
Skeletal Muscle Cells with Striations 400x
Long, cylindrical cells
Multiple nuclei per cell, located at the edges ( the purple lines )
Clear striations (light and dark bands running across the fibers)
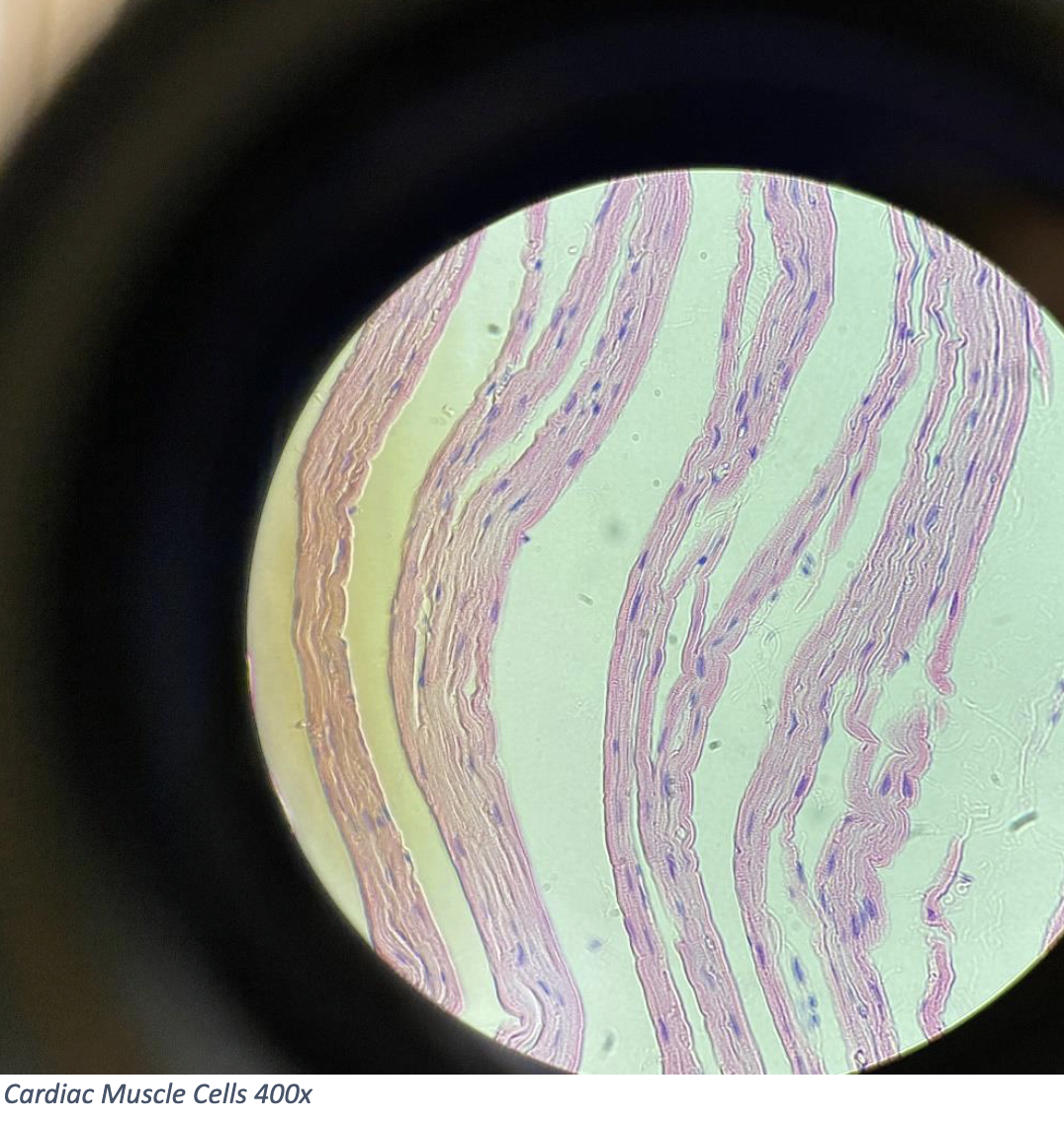
Cardiac Muscle Cells 400x
Branched, cylindrical cells
Usually one central nucleus per cell
Have visible striations (striped appearance)
Intercalated discs: dark lines where cells connect — help coordinate heart contractions
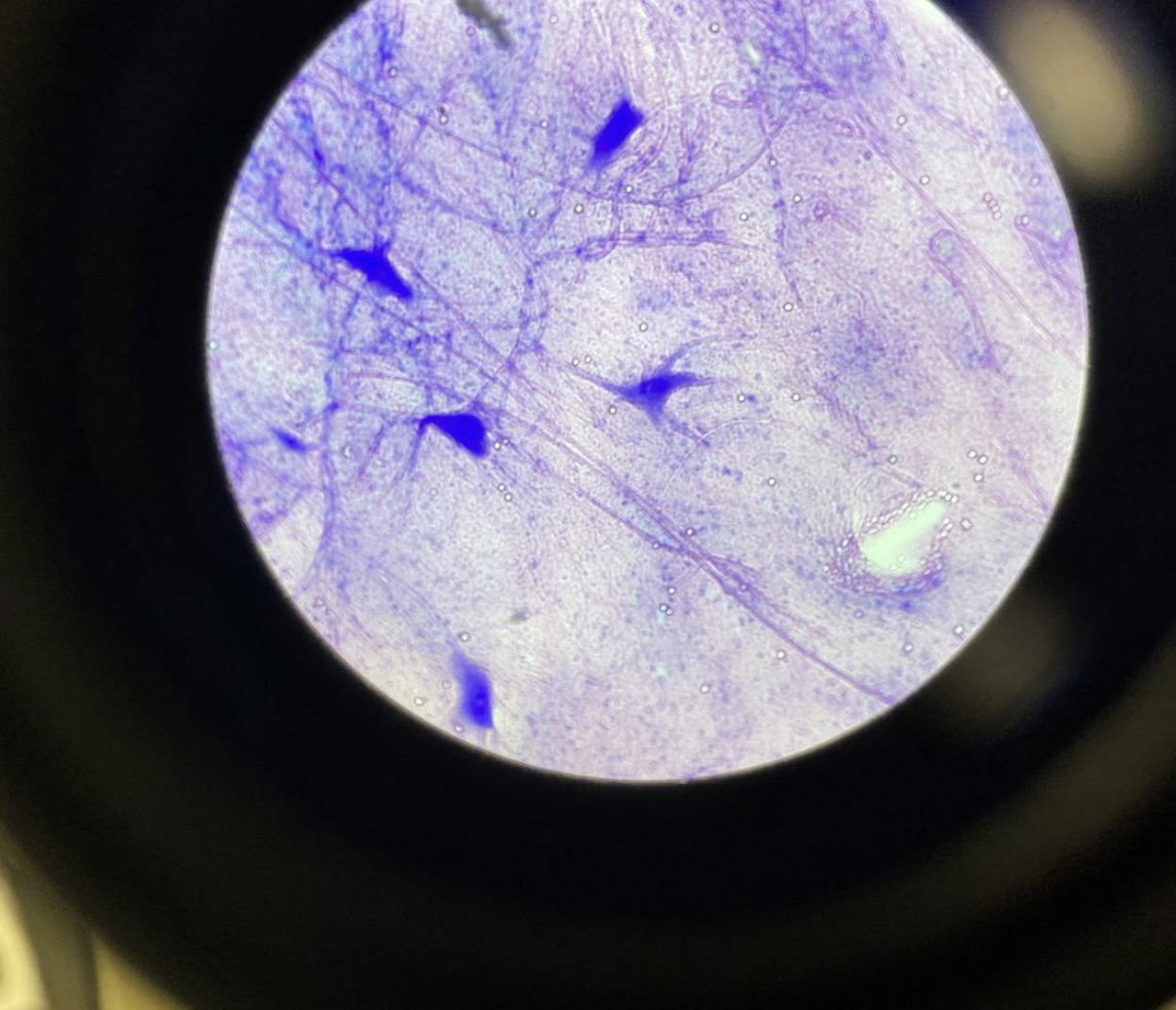
Giant Multi Polar Neurons 40x
Big nerve cells with many branches.
One long “arm” (axon) coming out.
Big round center with a visible dark spot (nucleus).
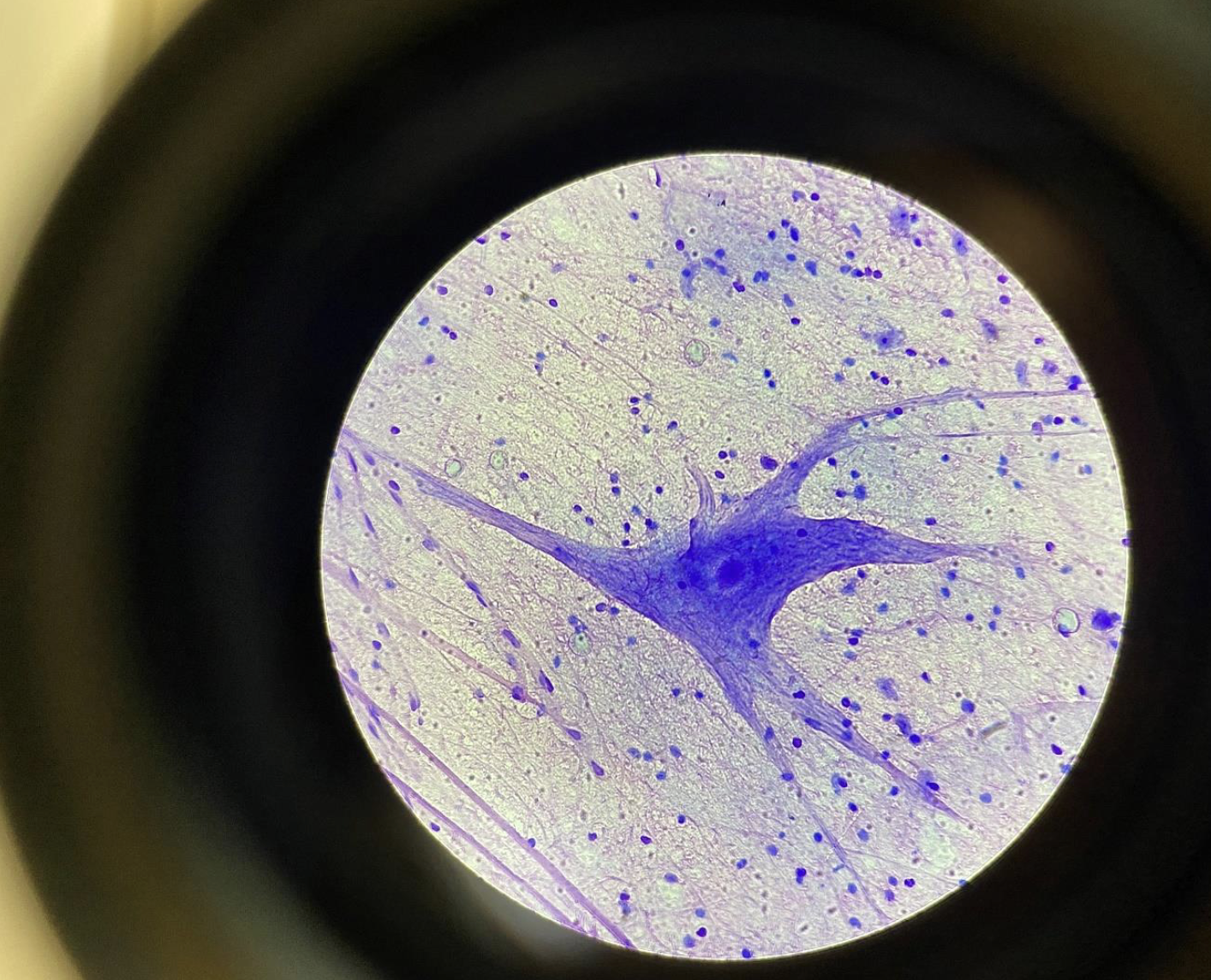
Giant Multipolar Neurons from the Spine 400x
Large nerve cells with many branch-like extensions (dendrites).
One long projection (axon) visible.
Big round cell body with a clear nucleus.
looks like an octopus
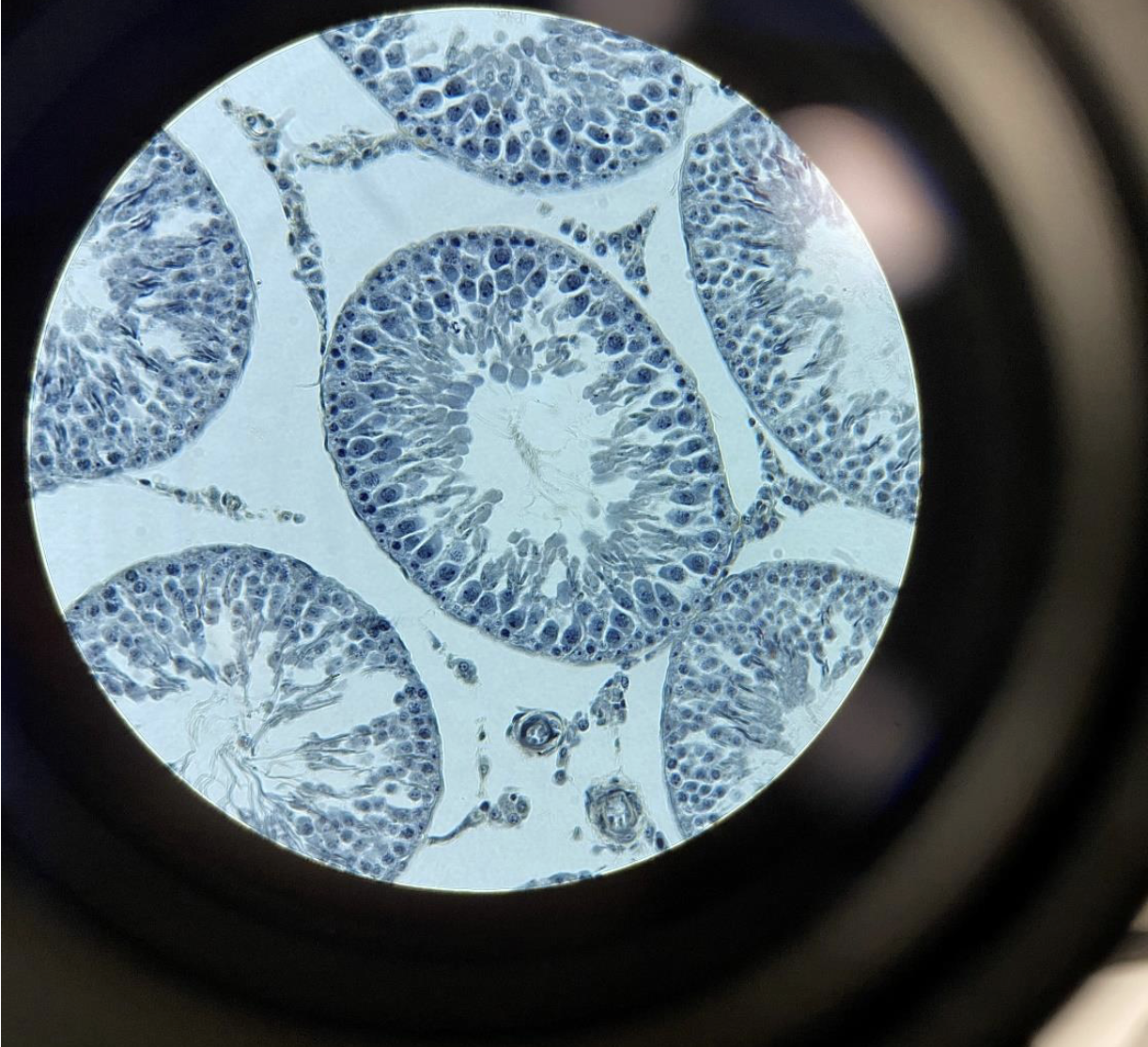
Rat Testis 400x,
sperm have flagella. Sperm with flagella can be seen in the center of the seminiferous tubule.
Flagella
are the most primitive structure for movement. Flagella can be found in some organisms of every kingdomFlagella are are the “tail” part of the sperm
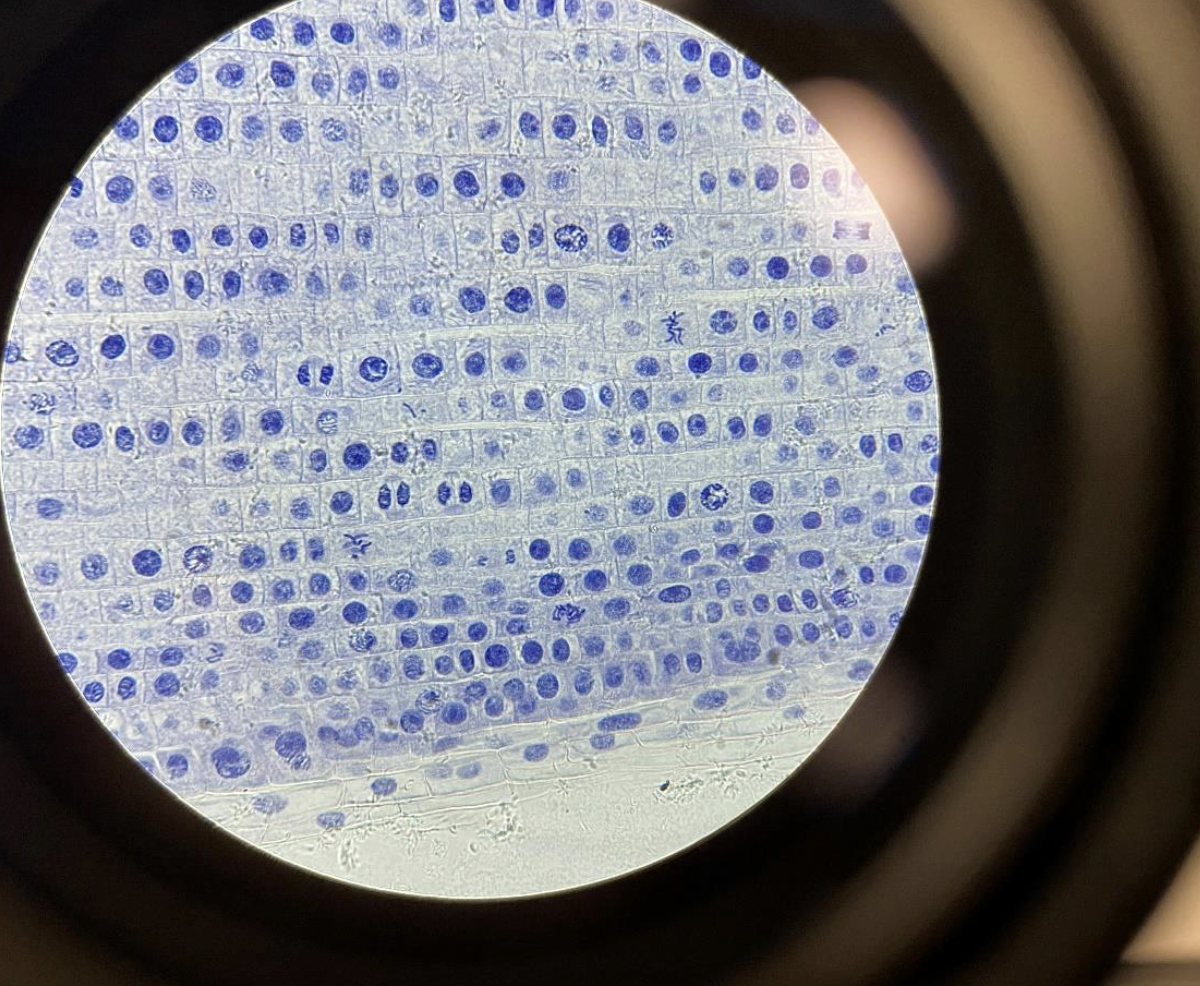
Mitosis in the Allium (onion) root tip 400x,
Cells at root tip showing mitosis — chromosomes visible in different stages.e.
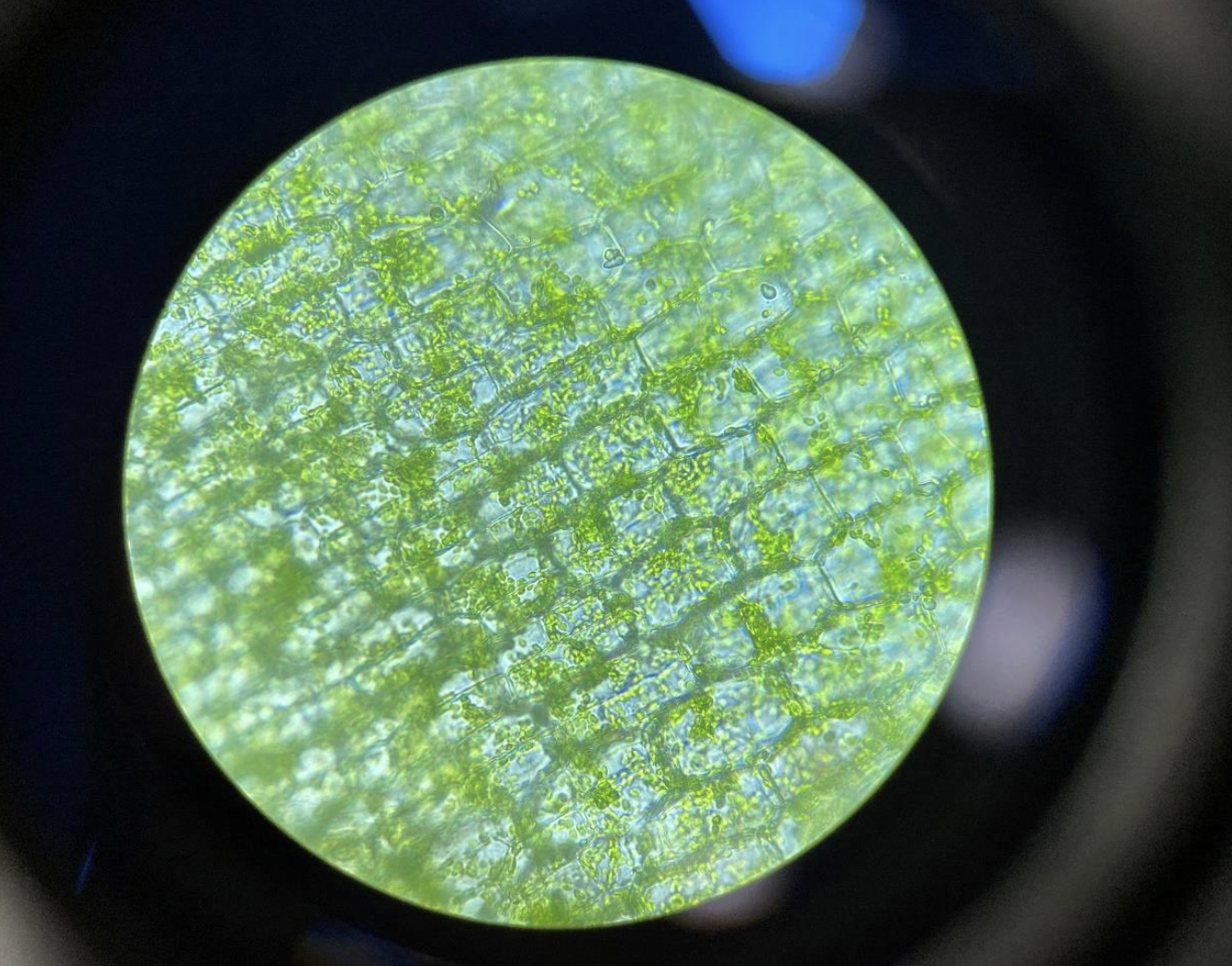
Elodea with chloroplasts 400x.
Elodea is a hydrophyte (plant that lives in water).
Chloroplasts are organelles that
perform photosynthesis in algae and in plants.Green dots (chloroplasts) inside plant cells.
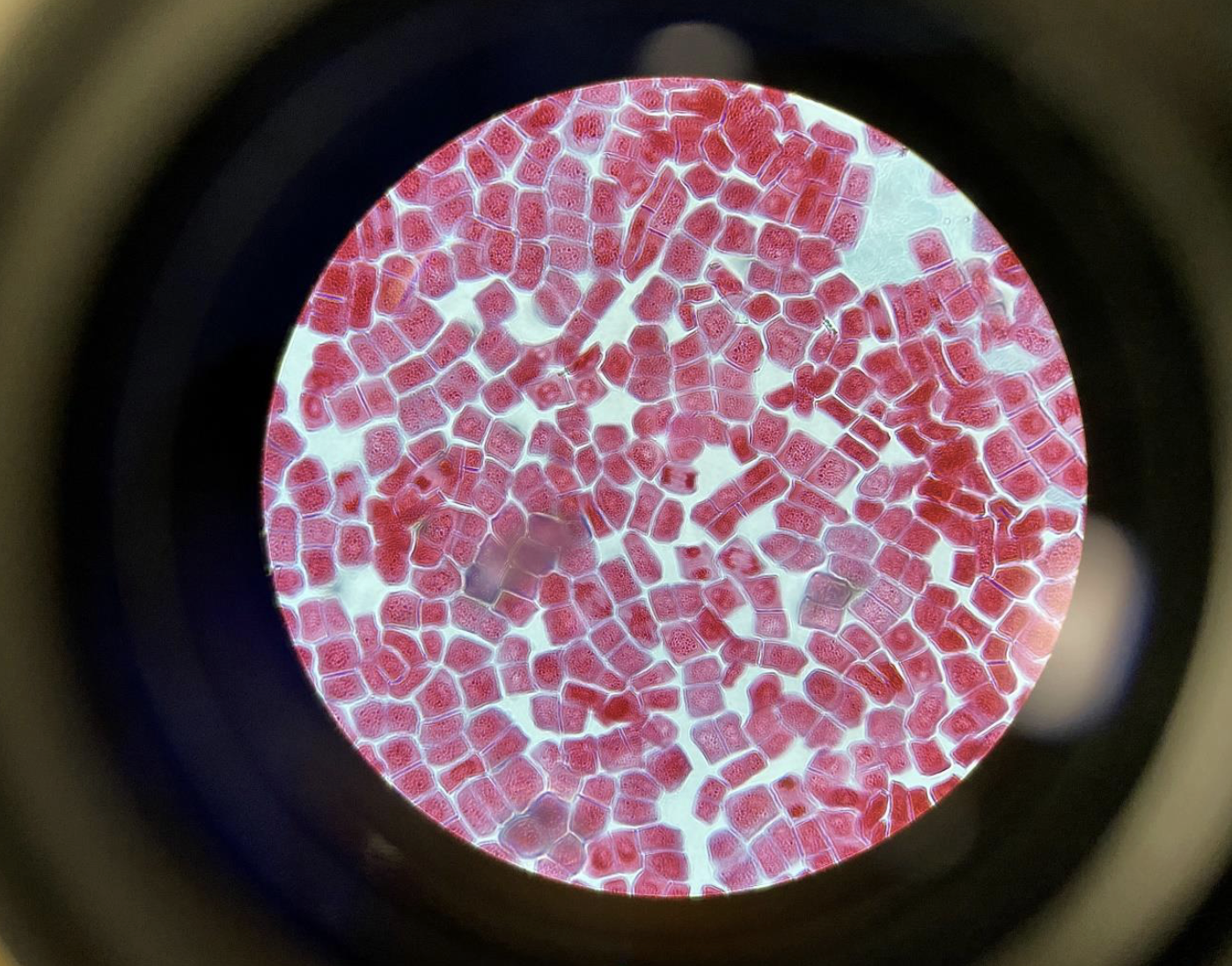
Plant Cell Mitosis 400x, cross section.
rows of square boxes with dark lines (chromosomes) inside, and sometimes a new wall growing between cells.
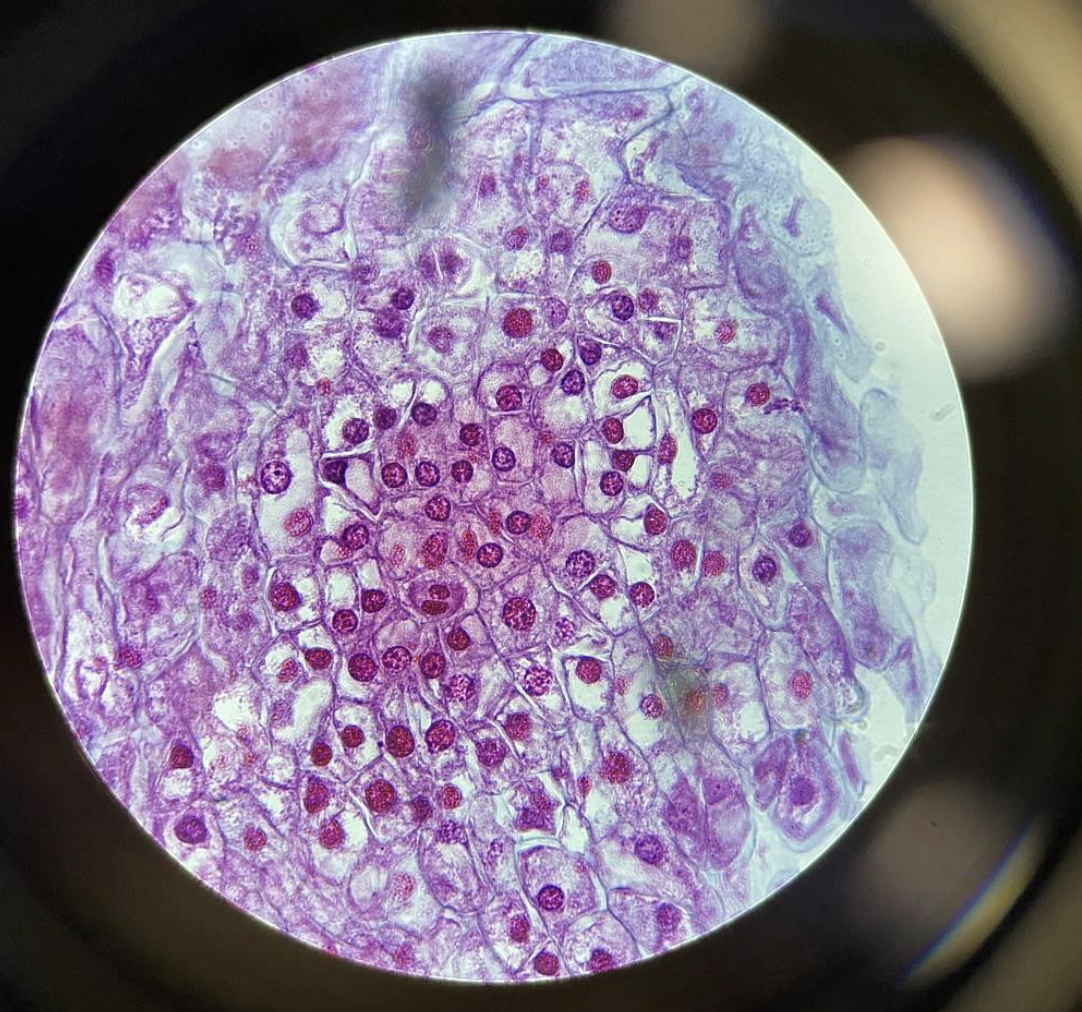
Nuclei in the Starfish Embryo 400x.
The nuclei can be seen in the center of the animal cells.
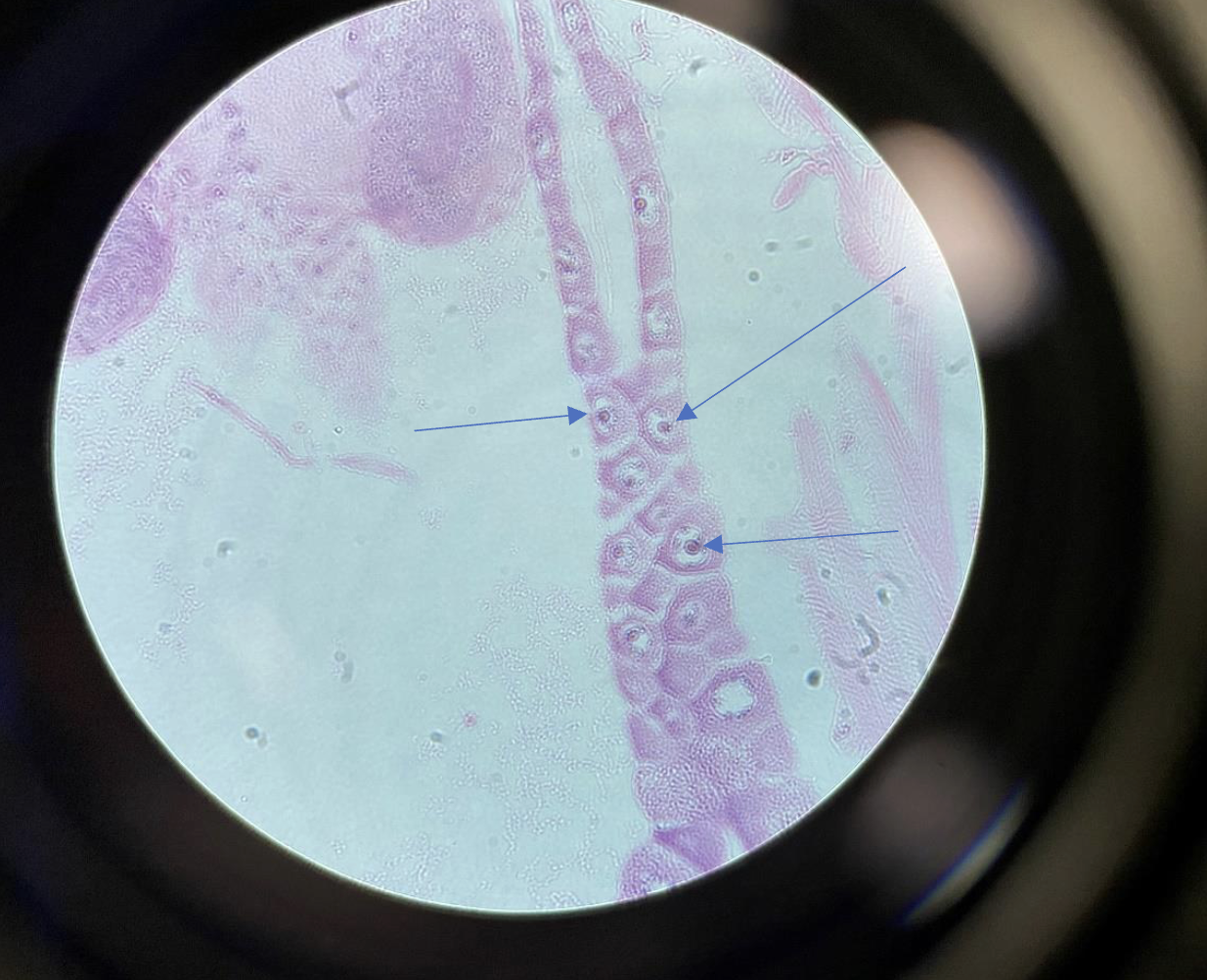
Drosophila Larvae Salivary Glands, 400x
They look like very thick, dark, banded rods inside the cell nuclei.
You can see clear stripes or bands running along the length of each chromosome.
looks kinda like a squid
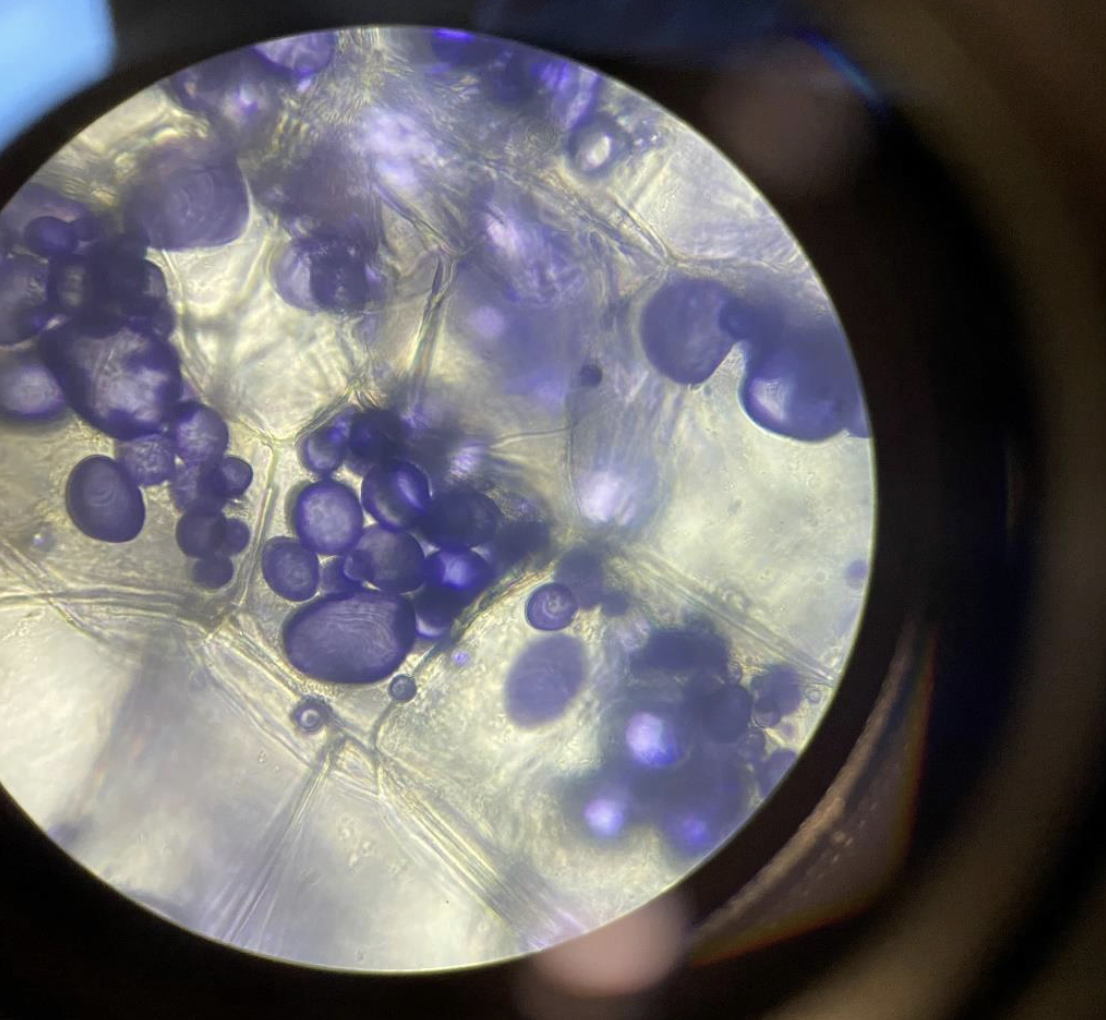
Storage Vesicles containing Starch in the Potato 400x.
The starch is stained purple in the storage vesicles. With iodine
potassium iodide.purple spots (starch) packed inside small sacs in the potato cells.
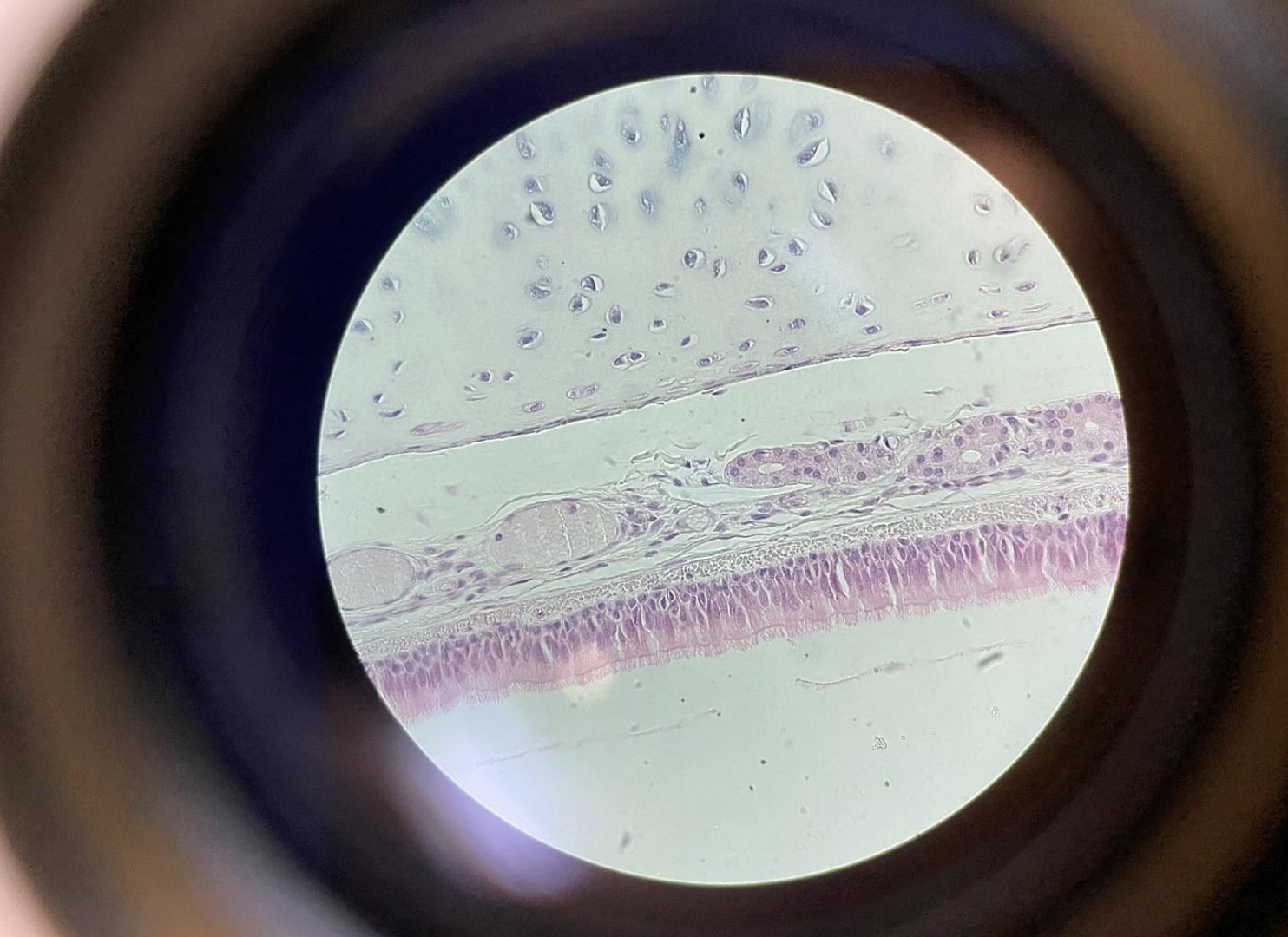
Trachea Epithelium, 400×
One layer of tall cells with tiny hairs (cilia) on top.
Nuclei are at different heights, so it looks like many layers but it’s just one.
Cilia move mucus up to be swallowed.
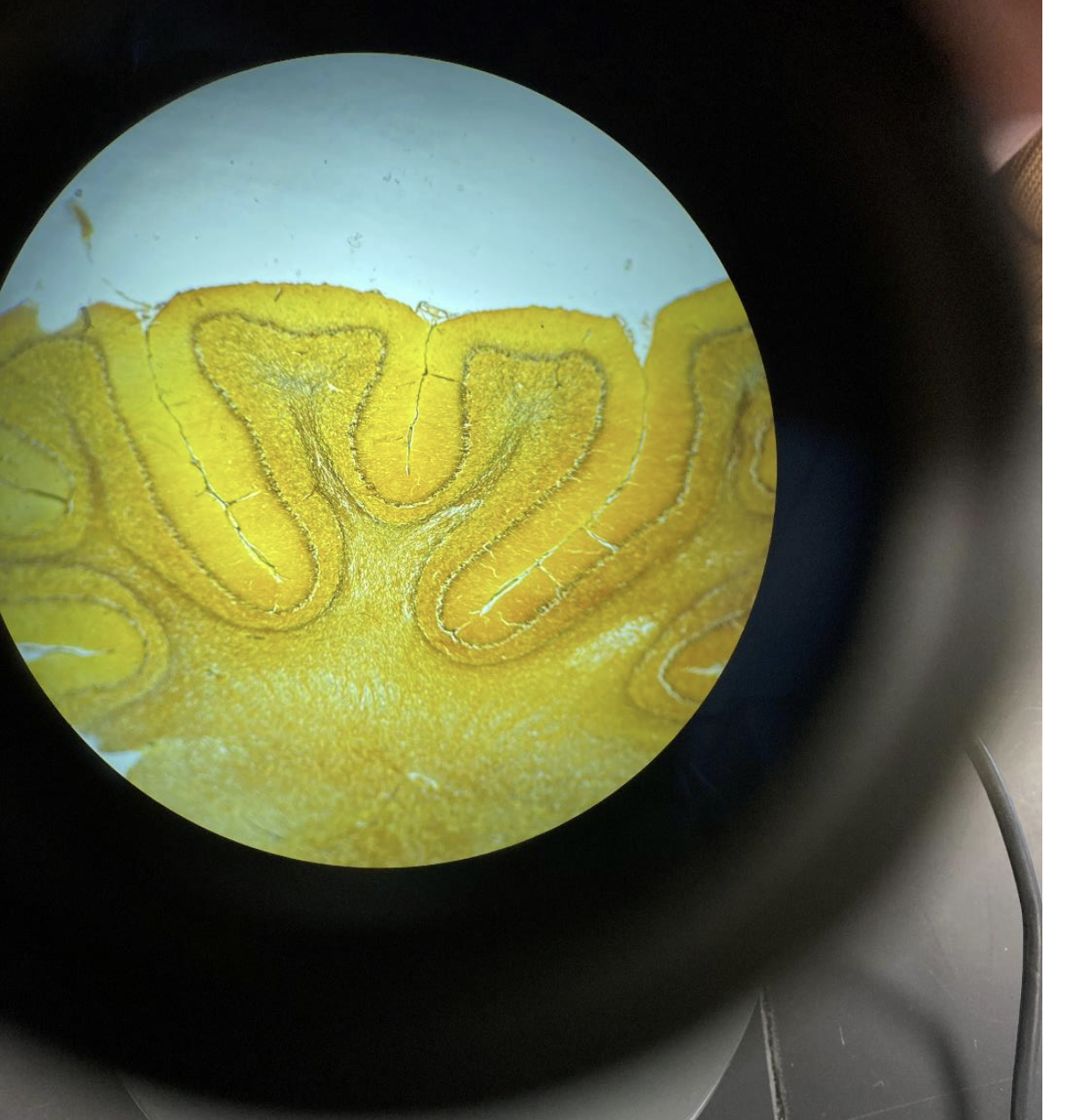
Cerebrum with gyri and sulci 40x
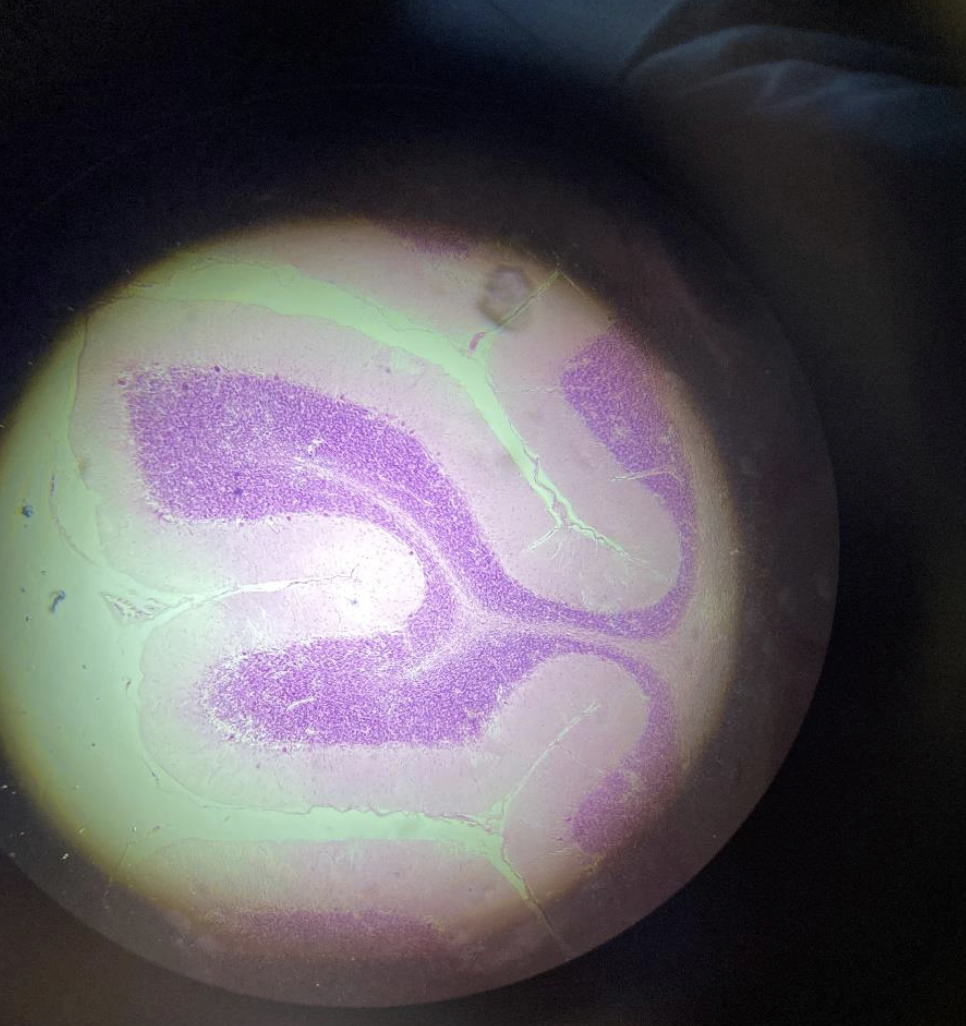
Cerebellum
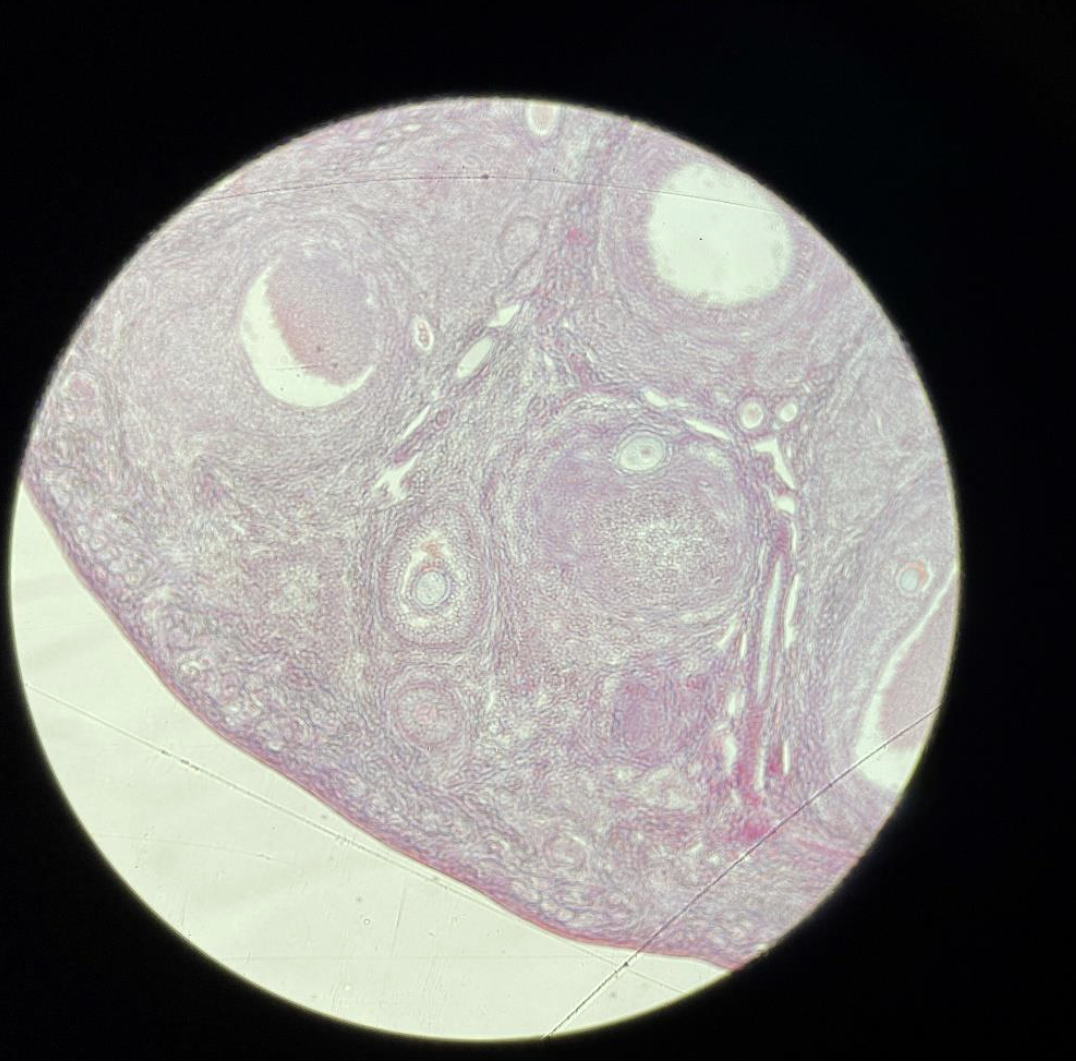
Cat Ovary
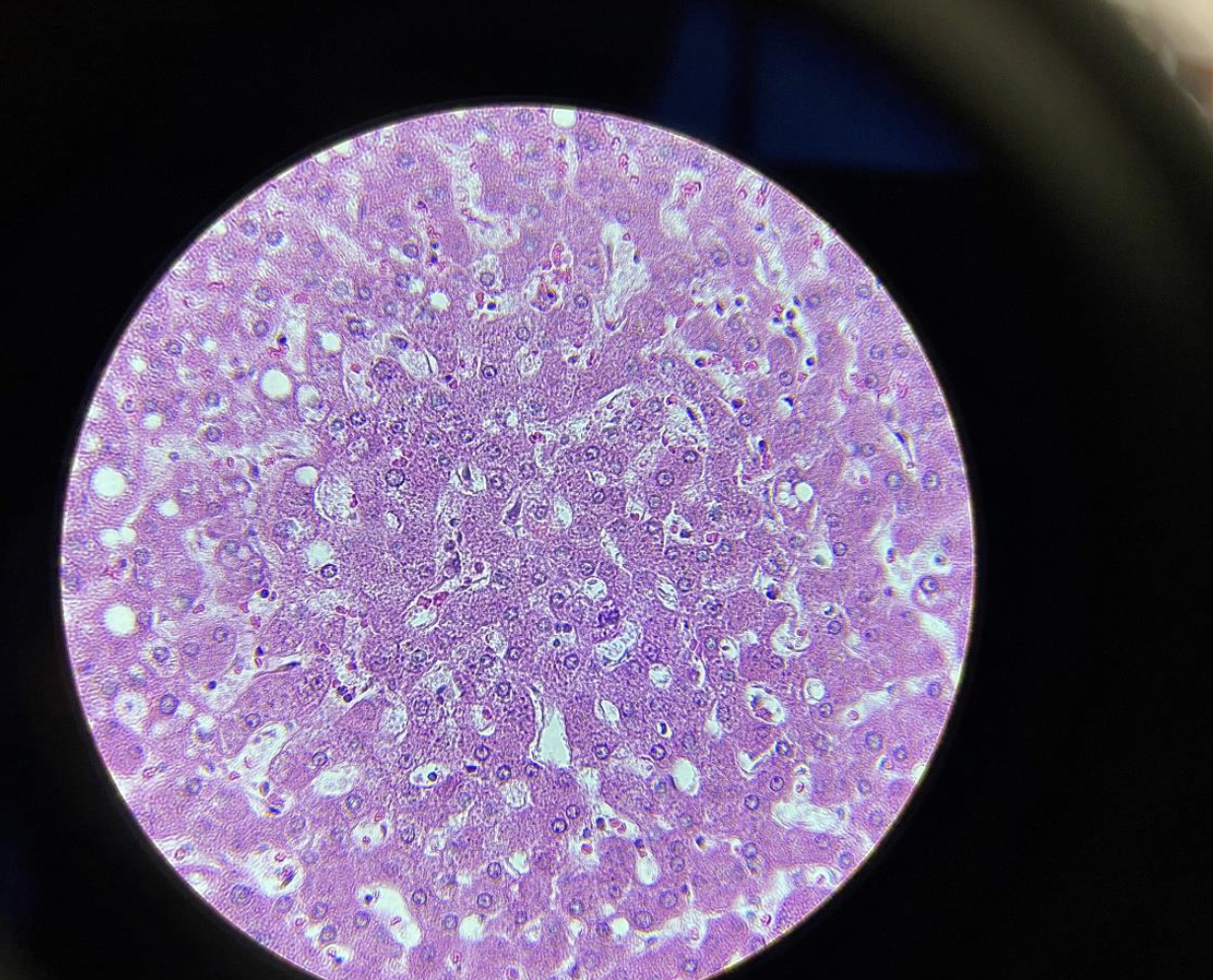
liver
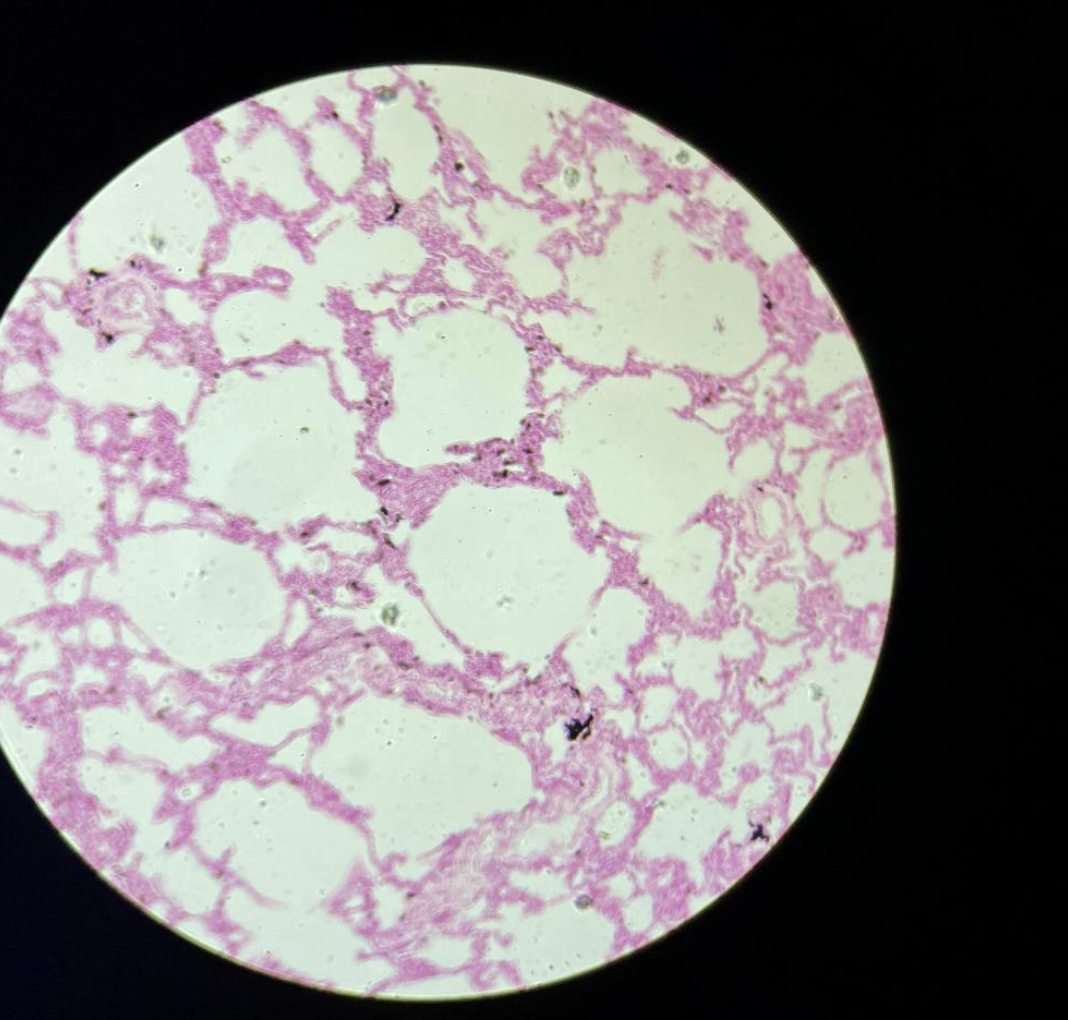
Lungs