4.1 International Economics
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Globalisation
Growing interdependence of countries and the rapid rate of change it brings about/increasing integration of the world’s local, regional and national economies into a single international market
Factors Contributing to Globalisation
Improvements in transport infrastructure and operations
Improvements in IT and communication
Trade liberalisation
International financial markets
TNCs - large companies operating around the world to take advantage of low labour costs
Impacts of Globalisation on consumers
More choice - wider range of markets
Lower prices - firms taking advantage of comparative advantages, eg/. Lower labour cost
Rise in prices - incomes are rising, and there is higher demand for goods and services
Loss of culture
Impact of globalisation on workers
Both losing and gaining jobs - eg/. Loss in the Western world’s manufacturing sector, as this is transferred to China or Poland
Increase migration - bringing skills and an increase in AD, which increases the number of jobs
International competition has led to a fall in wages or reduced growth for low-skilled workers in developed countries
Wages are up for high skilled workers; however, increasing inequality
Those in sweatshops will see poor conditions and low wages
Impact of globalisation on producers
Able to source from more countries
Risk reduction since of collapse of the market in one country will have a smaller impact on globalised businesses
Able to exploit comparative advantage and have larger markets, increasing profit
Impact of globalisation on government
May be able to receive higher taxes, however, higher levels of tax avoidance
Could lead to corruption by TNCs, bride and lobbying
Impact of globalisation on environment
Increased demand for raw materials, which is bad for the environment
Increased trade and production have led to higher emissions
However, the world can come together and tackle climate change and share ideas and tech
Impact of globalisation on economic growth
Increases investment within countries, investment of TNCs is an injection into the economy, which will have a larger impact due to the multiplier
May bring world class managements techniques and tech which can have a knock on effect to all industries
TNCs can cause political instability
Comparitive cost advantage will change over time
Comparative advantage
States that countries find specialisation mutually advantages if the opportunity costs of production are different
Absolute advantage
Producing more of a good using the same (or fewer) resources, or the same amount using fewer resources/lower cost.
Specialisation and trade advantages
Comparative advantage shows how the world output can be increased in countries that specialise in what they are best at producing
Different countries have different factors of production, and so trade allows countries to make use of factors of production
Trade enables consumers to have greater choice, greater consumer welfare
Trade means there is greater competition, which provides an incentive to innovate
Countries which isolate themselves for political reasons, like North Korea, have found that their economies tend to stagnate
Specialisation and trade disadvantages
Trade can lead to an overdependence
It can cause structural unemployment, as jobs are lost to foreign firms that are more efficient and competitive
The environment will suffer
May see a loss of sovereignty, eg/. With the EU
May result in a loss of culture
Factors influencing the pattern of trade
Comparative advantage
Countries will trade where there is a comparative advantage to trading
Emerging economies
Countries grow at different rates, and when they grow, they are likely to need to import more goods and services than before, as well as exporting more to pay for this
Trading blocs and bilateral trading agreements
Increases the level of trade between certain countries
Relative exchange rates
Prices are an important factor in determining whether consumers buy goods, and so a change in price will affect the pattern of trade
Reasons for restriction on free trade
Infant industry argument: Need to build up a reputation and customer base, and will have to cover a lot of sunk costs, meaning their AC will be higher
Job protection: Imports mean that domestic producers will lose out to international firms
Protection from potential dumping: When countries with surplus goods sell these goods off to other areas at a very low price, harming domestic producers in those countries
Protection from unfair competition: Domestic producers may be unable to compete with a firm that has very low labour costs
Terms of Trade: If a country buys a large amount of imports of a certain good, this will increase demand for that good and therefore the price, worsening the terms of trade
Danger of over-specialisation: No country should become totally reliant on another for important products or materials, so it is important to introduce protectionism on these goods to prevent firms and consumers from becoming reliant on them
Types of restrictions
Tariffs
Taxes placed on imported goods
Quotas
Limits are placed on the level of imports allowed into a country
Subsidies to domestic products
Payments to domestic producers which lower their costs, helping them become more competitive by enabling lower prices
Non-tariff barriers
Embargo: total ban on imported goods
Import licensing: Firms/countries need a license to be able to import
Impact of protectionist policies on consumers
Higher prices
Less choice
Impact of protectionist policies on producers
Domestic producers can sell goods at a higher price due to lower competition
However, there could be higher costs if the controls are on imports that are needed for production
Foreign producers will lose out as they are limited in where they can sell their goods
Impact of protectionist policies on workers
Little difference in employment figures
The market would reallocate resources and create new jobs, with greater security
Impact of protectionist policies on government
Gain tariff revenues in the short run, and they are politically popular
However, it can lead to an inefficient economy, which stifles growth
Impact of protectionist policies on living standards
Imports control results in deadweight welfare loss
It can also cause trade wars in retaliation
Impact of protectionist policies on equity
Regressive effect on the distribution of income as the rise in price affects the poorer members of society far more
Free Floating exchange rate system
where the value of the currency is determined purely by the market demand and supply of the currency
No need for reserves to buy pounds to keep at target
Able to partly autocorrect a trade deficit
Reduces the risk of currency speculation
Factors affecting free floating system
Determined by the interaction of demand and supply
Demand for pounds is determined by the amount of British goods foreigners want to buy and investment
Supply of pounds is determined by the amount of foreign goods people want to buy in the UK/invest
Therefore, currency is affected by the level of exports and imports,the level of investment and those going on holiday and speculation
Managed floating system
where the value of the currency is determined by demand and supply, but the central bank will try to prevent large changes in the exchange rate on a day-to-day basis
Fixed system
when the government sets their currency against another, and that exchange rate does not change
Avoids currency fluctuations, which encourages trade and investment
May reduce inflation
Trying to regulate the currency will decrease growth
It is easy to set an exchange rate wrong
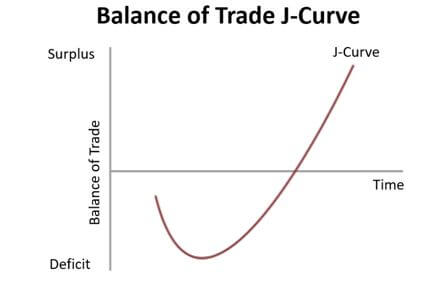
Marshall-Lerner condition and J-curve
States the sum of the price elasticities of imports and exports must be more than one if a currency devaluation is to have a positive impact on the trade balance. The J-curve shows how the current account will worsen before it improves
Impact of changes in exchange rates
Economic growth and unemployment: A weaker exchange rate is likely to increase exports, since they become cheaper, and decrease imports so lead to an increase in AD - increase employment and economic growth
Rate of inflation: Falls in the exchange rate will increase inflation as imports become more expensive, causing a rise in prices and a fall in SRAS. Also, the net exports section of AD will increase, and so inflation will rise further
FDI: A fall in the currency may increase FDI because it becomes cheaper to invest. However, if the currency continues to fall, then this is an indication that an economy has serious economic difficulties, which will discourage investment
Measures of international competitiveness
Relative unit labour costs: Unit labour costs are total wages divided by real output
Relative export prices: This is the price of the UK exports compared to the exports of the UK’s main trading partners