2.7 Alcohols and Carboxylic acids
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Reactions including industrial productions and different types of alcohols and carboxylic acids.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
General formula of an alcohol
CnH2n+1OH
How are the structures of alcohols classified?
Primary (1º), Secondary (2º), Tertiary (3º)
Primary Alcohol (1º)
The OH is joined to a carbon that has 1 R group and 2 H atoms
Secondary Alcohol (2º)
The OH is joined to a carbon that has 2 R groups and 1 H atom
Tertiary Alcohol (3º)
The OH is joined to a carbon that has 3 R groups and no H atoms.
Hydration of ethene conditions
steam and ethene
Conc phosphoric acid
300ºC
Pressure = 60-70 atm.
How is ethanol removed from the mixture of gasses?
Fractional distillation (close boiling points.)
Fermentation conditions
Yeast
Sugar
Anaerobic
Warm temperature
Boiling point of ethanol
Approximately 80ºC
Bioethanol
Obtained from sugars in plants by fermentation.
Biodiesel
Obtained from oils and fats present in the seeds of some plants.
Advantages of Biofuels
Renewable
Carbon neutral
Economic and political security
Disadvantages of Biofuels
Land use
Uses of resources
Lots of CO2 produced.
Uses of ethanol
Solvent
Alcoholic drinks
Fuel
Cleaning
Dehydration of alcohols to form alkenes conditions.
Concentrated sulphuric acid
170ºC
OR heated aluminium oxide at 360ºC
What type of reaction is the dehydration of alcohols?
Elimination reaction
Oxidising agent for oxidation of alcohols.
Potassium dichromate
Test for alcohols (1º and 2º)
acidified potassium dichromate (VI) → orange to green.
acidified potassium manganate (VII) → Purple to colourless.
What are primary alcohols oxidised to?
Aldehydes then, oxidise further to carboxylic acid.
Conditions for oxidation of primary alcohols.
heat (distillation)
heat under reflux for aldehyde → carboxylic acid.
What are secondary alcohols oxidised to?
Ketones (E.g. H3C-(C=O)-CH3)
Conditions for oxidation of secondary alcohols.
Heat under reflux
What do tertiary alcohols oxidise to?
Tertiary alcohols can’t oxidise.
Carboxylic acids general formula
CnH2n+1COOH
Why are carboxylic acids acidic?
They release H+ ions into water.
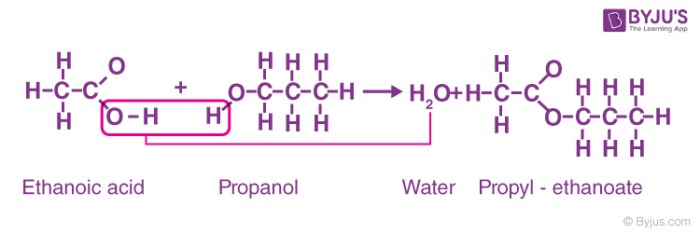
What is esterification?
Carboxylic acids react with alcohols to form esters.
Conditions for esterification?
Heat
Conc sulphuric acid
How to make a pure sample of an ester?
Simple distillation.

General equation for esterification
Carboxylic acid + Alcohol ⇌ Ester + Water