Biomechanics Final
1/352
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
353 Terms
Gait
The manner in which a person walks
Stride length
The distance you travel during the gait cycle; its between two heel strikes on the same foot (ex: starts at the first heel strike of the R leg and ends at the second heel strike of the R leg)
Gait cycle
Also called stride, the activity that happens between the time one foot touches the ground and the time the same foot touches the ground again
Step length
Distance between the first heel strikes on both feet ex: distance between the 1st heel strike of the R foot to the 1st heel strike of the L foot
Stance phase
The phase of gait when the foot is in contact with the ground
Swing phase
The phase of gait when the foot loses contact with the ground and the lower limb swings
Heel strike
A phase of the gait cycle when the heel comes into contact with the ground
Foot flat
A phase of the gait cycle when the entire foot is on the ground
Midstance
A phase of the gait cycle when your body passes over your weight-bearing foot; your COG is aligned with you stance leg
Heel-off
A phase of the gait cycle when the heel rises off the floor
Toe off
Signals the end of the propulsion and stance phases of the gait cycle
Acceleration
Speeding up in the forward direction
Deceleration
Slowing speed in the forward direction
Waddling gait
Shoulder behind the hips; arms back with the legs forward
Entire side of the body swings together
Minimal trunk/pelvis rotation and increased lordosis
Trendelenburg Gait
Atypical gait pattern due to dysfunction of hip abductors, the hip drops on the non-weight bearing side (the swing leg) and there is a lateral lean of the trunk
Genu recurvatum
Hyperextension of the knees; trunk leans anteriorly
Antalgic gait
Limping
Festinating gait
Shuffling gait that involves ‘freezing’ when a person stops or reaches a doorway; seen in Parkinson’s disease
Equinus gait
Atypical gait where the ankle is held in plantar flexion, preventing the heel from touching the ground normally
Foot slap gait
Atypical gait where the dorsiflexor muscles (Tibialis anterior) are unable to support a person’s body weight, leading to an uncontrolled descend of the foot; it creates a slapping noise
Foot drop
Atypical gait in with a person is unable to dorsi flex the ankle as the leg swings; involves hiking the hip to clear the foot
Dysfunction of the Tibialis anterior
Steppage gait
Atypical gait where an individual raises their knee higher than usual to ensure their foot clears the ground as it swings
Gluteus Maximus lurch
Hip flexes during heel strike, hyperextends at mid-stance; involves rocking of the trunk; moves COG over pelvis to keep balance
Dysfunction of the gluteus Maximus
Bell-clapper gait
Atypical gait due to a fused hip, the lumbar spine and pelvis compensates for this by being the prime movers of the swing phase on the affected side; results in decreased lumbar lordosis and a posterior pelvic tilt
Vaulting
Atypical gait due to decreased knee flexion and extension, it involves and individual rising up on their toes
Circumducted gait
Atypical gait where the leg begins at midline during toe off but it swings out during the swing phase before returning to midline for the heel-strike
Ataxic gait
Atypical gait due to damage to the cerebellum, it is uncoordinated, lacking balance, and causes jerking motions during gait; the individual also uses a wide base of support to compensate
Crouch gait
Hip and knees in chronic flexion; ankles in chronic dorsi flexion
Limited strength, ROM, high tone, extreme lateral arm swing
Hemiplegic gait
Hip extended, Adducted, and medially rotated; knee extended, ankle inverted
Flexion of affected arm with no arm swing
What does the PD gait look like during early stage PD?
Reduced arm swing
Reduced step length
Reduced axial rotation
Slower speed in general
What does PD gait look like during late stage PD?
Bilateral arm swing or no arm swing
Reduced step length
Slow movements
Shuffling gait
Reduced postural control
Fragmentation of movements
Freezing
Scissor gait
Knees and toes are turned inward; knees and thighs can touch and even cross
Flexion at waist, hips, and knees; excessive adduction due to tight adductors and weak abductors; internal rotation
What does gait require and involve?
Movement or stabilization of nearly every body joint
Body performing in the safest, most efficient manner
Repeated losing of and regaining of balance
Gait is a __________ progression of the whole body, produced by coordinated, _________ movements of body segments
Translatory, rotary
Gait involves alternating __________ and ___________ motions
Propulsive, retropulsive
What is the percentage of gait is the stance phase?
60%
What percentage of gait is the swing phase?
40%
What are the subdivisions of the stance phase?
Heelstrike
Foot flat
Midstance
Heel off
Toe off
What are subdivisions of the swing phase?
Acceleration
Mid swing
Deceleration
What are the sub phases of the stance phase?
Initial contact
Mid-stance
Push-off phase
What is the initial contact phase?
This is a component of the stance phases, it is begins when the foot first makes contact and ends with the foot flat; its the loading response/weight acceptance phase
What is the mid-stance phase?
It’s a component of the stance phase, it is begins at foot flat and ends with heel off; the terminal stance where COG moves from behind the stance leg to the front
What is the push-off phase?
A component of the stance phase, begins with heel off and ends with toe off; provides propulsion
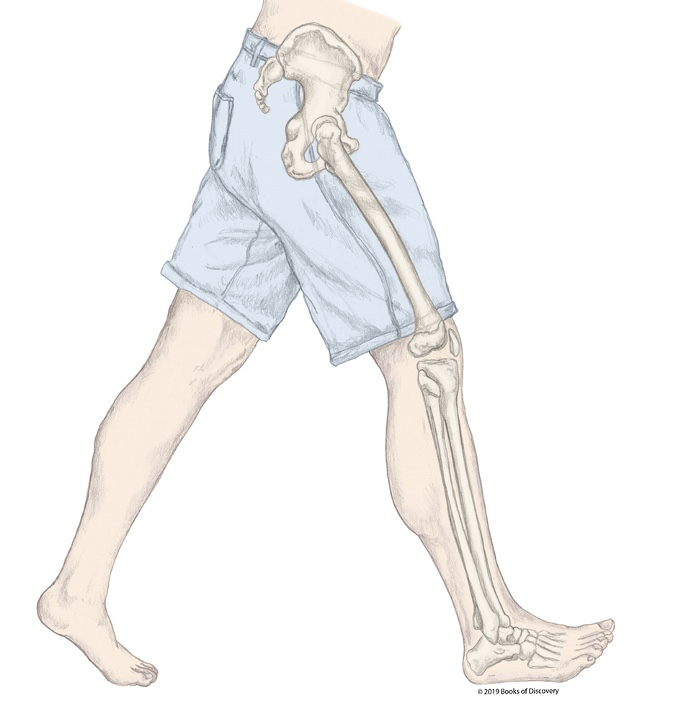
What phase of stance is the R LE in?
Heelstrike
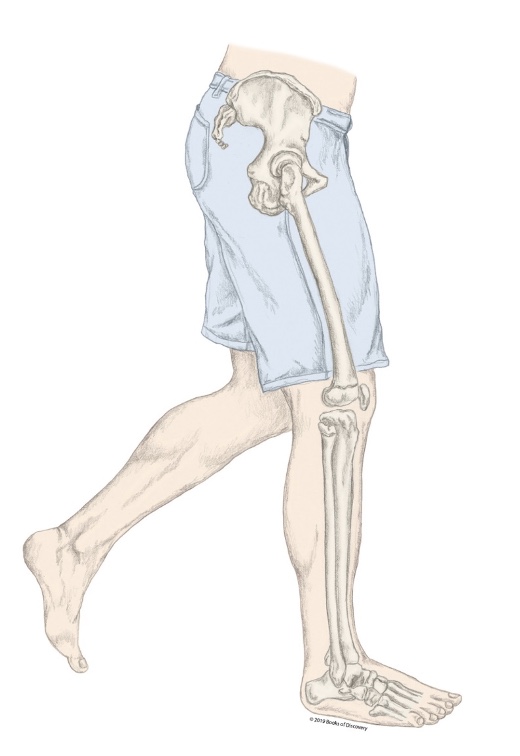
What part of the stance phases is the R LE in?
Foot flat
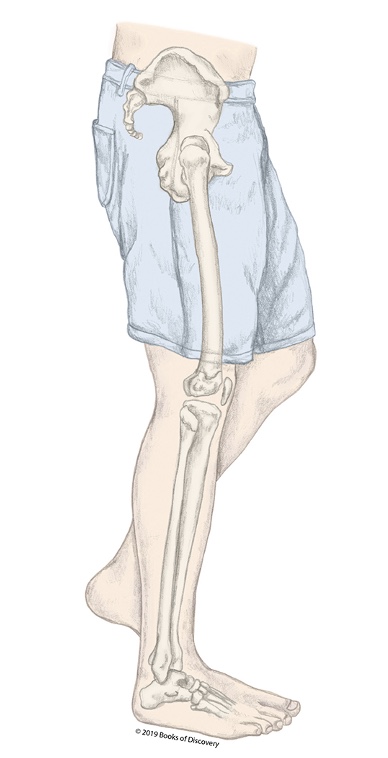
What stage of the stance phase is the R LE in?
Mid-stance
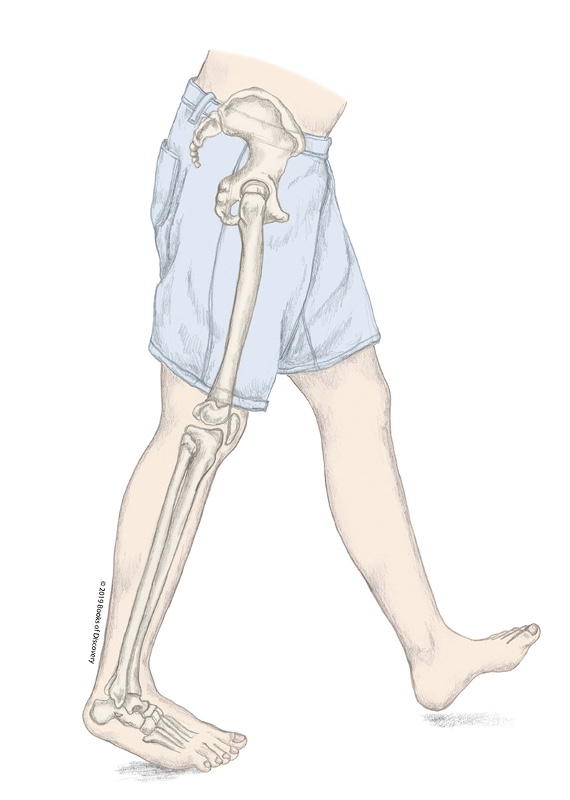
What stage of the stance phase is the R LE in?
Heel off
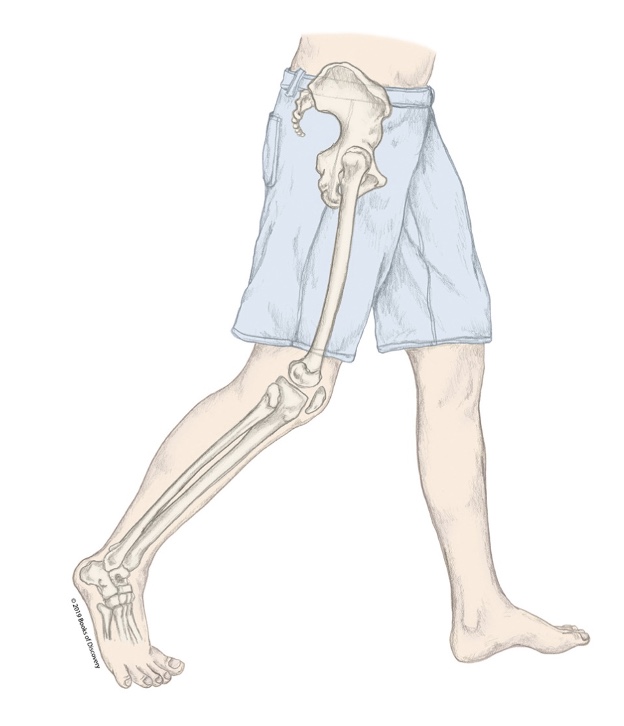
What stage of the stance phases is the R LE in?
Toe off
Early swing portion of the swing phase-
From toe off to mid-swing
Initial swing phase or acceleration phase
Mid-swing portion of the swing phase-
lower limb under the hip
Last swing portion of the swing phase-
Limb deceleration phase or terminal swing phase
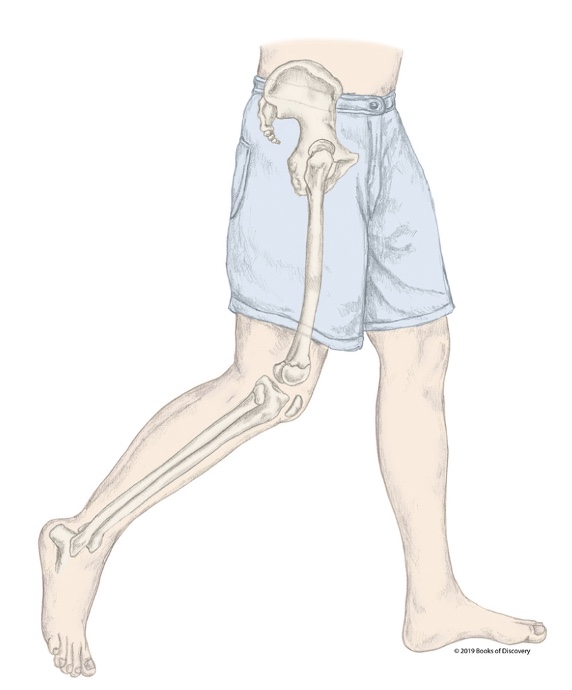
What stage of the swing phase is the R LE in?
Acceleration
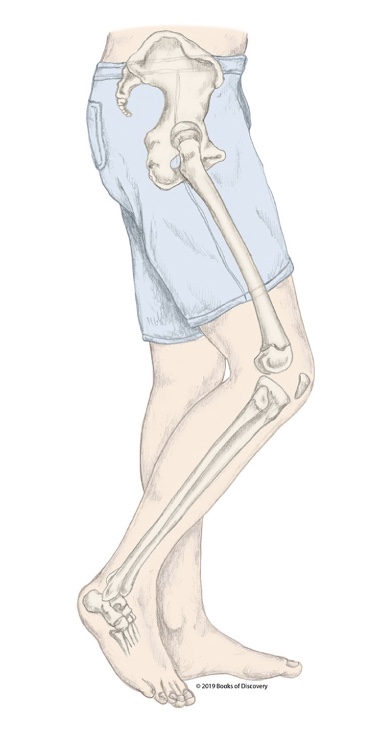
What stage of the swing phase is the R LE in?
Midswing
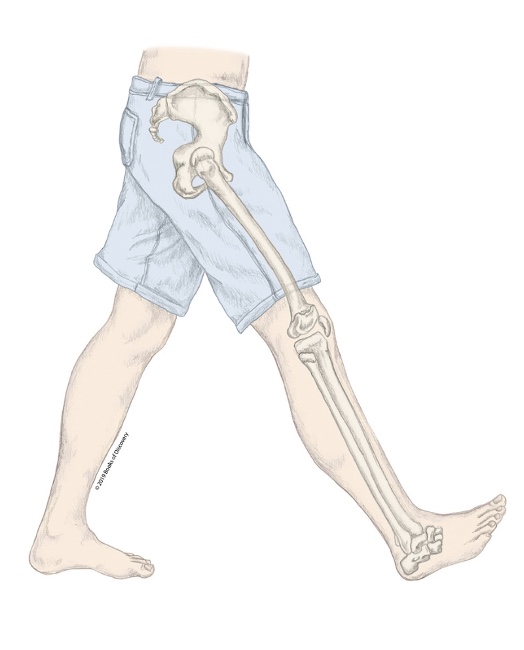
What stage of the swing phase is the R LE in?
Deceleration
Double limb support
Occurs at the initial contact and again at toe off
What represents 20% of the gait cycle?
Double limb support
Double limb support _________ as gait speed increases and often _________ as balance and stability decreases
Decreases, increases
Single limb support
Occurs during stance phases and throughout the swing phase
What makes up 40% of the gait cycle?
Single limb support
What is the average step length?
72 cm
Step width
Lateral measurement between two heels
Foot angle
Angle between body progression and long axis of the foot (are the toes point forward, in, or out?)
What possible conditions could result in an asymmetrical stride length?
Foot pain
What condition might result in an person increasing the step width?
Aging (Older or younger)
Being pregnant
What proximal bony alignment could contribute to a decrease in the foot angle or a “toeing- in”?
Tight hamstrings
Weakened glute muscles
Step time
Time to complete one right or left Stroop
Cadence
Step rate
Number of steps per minute
Stride time
Time to complete one full gait cycle
Walking or gait speed
Distance covered in a given amount of time
posture is influenced by…
Fitness levels, strength, balance, age, height, weight
Decreased gait speed is associated with increased risk for…
Falls
What is the COG displacement during gait?
Forward linear displacement
Vertical displacement- up and down
Lateral displacement- shifts to line up with the stance leg
Smooth sinusoidal curve
Peaks at double support
Low point at the heel strike
Joint kinematics during gait
Linear progression of the body with angular movements of the joints of the extremities
What limit is vertical rise of the COG?
Lateral pelvic tilt in the frontal plane
Knee flexion
Knee interactions
Ankle interactions
How do you limit vertical drop of the COG?
Pelvic rotation in the transverse plane
What limits lateral motion of the COG?
Valgus of the knee
When does posterior pelvic tilt occur?
During double limb support (assists with deceleration or breaking)
When does anterior pelvic tilt occur?
During single leg support (assists with propulsion)
When does the pelvis rotate in the frontal plane (laterally)?
During weight acceptance
To unload the weight the ASIS rotates forward in the horizontal plane
What degrees of flexion is the hip at when making initial contact?
30
What is the joint positioning the knee goes through?
Initial contact: 5 degrees of flexion that changes to about 10 - 15 degrees
Flexion of the knee serves as what (during initial contact)?
A shock absorber
How is the knee positioned during heel off and mid-swing?
35 degrees of flexion
60 degrees of flexion
How is the ankle positioned during initial contact, foot flat, and heel and toe off?
Talocrural joint- plantar flexion 0-5 degrees Dorsiflexors- eccentrically lower the foot
Tibia translates forward, 10 degrees of dorsi flexion
15 - 20 degrees of plantar flexion
How is the subtalar joint positioned during initial contact, mid-stance, and heel off?
2 - 3 degrees of inversion
Everts to about 2 degrees
Reverses to its neutral position
What is the role of the first tarsometatarsal (TMT) joint during gait?
Assist with flexibility of longitudinal arch
Has small degrees of plantar flexion and dorsi flexion
What is the role of the first metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint during gait?
Initial contact- slight extension to neutral
Push-off- extends to 45-55 degrees of closed-chain extension
What is the role of the upper extremities during gait?
Have rhythmic pattern opposite lower extremities
Balance rotation of the trunk
What is the role of the trunk during gait?
Rotates small amount in horizontal plane
Contributes to efficient gait pattern via arm swing and trunk rotation
What is the role of the hamstrings and gluteus maximus during gait?
Extend hip to prepare for weight acceptance
Prevent uncontrolled trunk flexion
What is the role of the hip flexors during gait?
Lift leg during initial swing phase
What is the role of the hip abductors during gait?
Stance leg eccentrically lowers contralateral pelvis
Concentrically control frontal plane alignment of femur
What is the role of the quadriceps during gait?
Assist with shock absorption at initial contact
Eccentrically control knee flexion on stance limb during weight transfer
Concentrically extend knee during stance phase
What is the role of the dorsiflexors during gait?
Eccentrically lower the foot during initial contact
During the swing phase it produces ankle dorsi flexion to clear the toes
What is the role of the plantar flexors during gait?
Eccentrically control forward movement of tibia and fibula over the ankle
Provide push-off during heel off with forward propulsion of body
What is the role of the Tibialis posterior during gait?
Acts as a supinator to decelerate pronation during initial contact and foot flat
Concentrically supinates foot from mid-stance to to off
What muscle is prone to an overuse injury?
Tibialis posterior
What are the roles of the fibularis longus and brevis during gait?
Act as pro actors
Anchors first ray
Stabilize the foot
Support medial longitudinal arch
What contractions occur during heel strike?
Isometric contraction during deceleration (hip extensors, knee flexors, plantarflexors)
Concentric contraction for positioning (hip flexors, knee extensors)