Midterm
A reminder that the Midterm will be on the chapters 1, 2, 8, 9, 10, and 11 as well as the introduction
I will add all the notes during the lectures that she did not specifically mention what was going to be on the test
I suggest studying even though we are taking the test at home because she said “most likely” so please study just in case for the sake of your grade.
Perceive and Process (Chapter 1)
How do we take in information in our perception-feelings and thinking
How do we think about the information we process-watching and doing
We deal with experiences to help us make sense of them (process)
We perceive through feeling and using our 5 senses to absorb information. Being directly involved in the new experience
Other people perceive by thinking and taking in information when the idea is separate from themselves. They like to analyze and make theories. Pretty much taking a scientific approach to problem-solving.
Some people process by doing active experimentation. They like to jump and start doing things as well as taking risks to make sense of things. They like to apply what they have learned in practical ways.
Learning Styles Page 42 (LSI section; Chapter 1)
==Feeling== (concrete experience) You like to learn things that make you feel important
==Watching== (reflective Observation) Like to plan things out and take time to make sure you fully understand a topic
==Thinking== (abstract conceptualization) Likes to absorb many concepts and gather lots of information on a new topic
==Doing== (Active Experimentation) enjoy hands-on activities that allow you to test out ideas and sees what works
Modes (LSI section; Chapter 1)
Mode 1 (feeling and watching) seeks a purpose for new information and wants to why a course matters and why it relates to your interests and goals.
==Mode 1 Why is it important?==
Mode 2 (watching and thinking) is interested in knowing what ideas or techniques are important. They seek a theory to explain events and enjoy learning and breaking a subject into key elements.
==Mode 2 what are the main points?==
Mode 3 (thinking and doing) loves an opportunity to try out what they are studying. Likes to get involved with new knowledge and investigate how ideas and techniques work.
==Mode 3 How does this work?==
Mode 4 (doing and feeling) gets excited about doing more than classroom assignments and like to get what they have practiced and find other uses for it. Always seeking ways to use gained skills for a workplace.
==Mode 4 What if questions?==
Mode Strengths
==Balancing your preferences Mode 1== \n •Strengths \n • Imaginative ability \n • Recognizing problems \n •Too much of this can lead to \n • Feeling paralyzed by alternatives \n • Inability to make decisions \n •Too little of this can lead to \n • Lack of ideas \n • Not recognizing problems and opportunities \n •You can develop this mode by \n • Being aware of other peoples' feelings \n • Listening with an open mind
==Balancing your preferences Mode 2== \n •Strengths \n • Planning \n • Developing theories \n •Too much of this \n • Vague ideals \n • Lack of practical application \n •Too little of this \n • Inability to learn from mistakes \n • No systematic approach \n •You can develop this mode by \n • Organizing information \n • Designing experiments
==Balancing your preferences Mode 3== \n •Strengths \n • Problem-solving \n • Decision making \n •Too much of this \n • Solving the wrong problems \n • Hasty decision making \n •Too little of this \n • Lack of focus \n • Scattered thoughts \n •You can develop this mode by \n • Experimenting with fresh ideas \n • Setting goals
==Balancing your preferences Mode 4== \n •Strengths \n • Getting things done \n • Leadership \n •Too much of this mode can lead to \n • Meaningless activity \n •Too little of this can lead to \n • Work not completed \n • Lack of motivation \n •You can develop this mode \n • Making a commitment to objectives \n • Being personally involved
Money (Chapter 10)
Student loans
Subsided - the bank or government is paying the interest for you while you’re in school ( a minimum of half time ) during your post-graduation grace period, and if you need a loan deferment.
Unsubsidized - you are responsible for the interest from the moment the loan is disbursed from your account. It doesn’t apply until 6 months after you finish school
If you take out loans \n Choose loans with low-interest rates \n Borrow only what you need for that semester
Make More Money
- focus on your education
- consider financial aid
- increase your income while you’re in school
- do your best at every job
- give yourself a raise before you start work
spend less money
- Look at big-ticket items
- Look to small-ticket items
- be aware of the quality
- save money on eating and drinking
- lower your phone bills
- Go green
- pay cash
- postpone purchases
- notice what you spend on fun
- use the envelope system
- don’t compete with big spenders
- use the money you save to prepare for emergencies and reduce debt
- spend less and feel the power
Take charge of your credit
- Balance the benefits with real costs
- pay off the balance each month
- scrutinize credit card offers
- avoid cash advances
- check statements against records
- use just one card
- get a copy of your credit card
- protect your credit score
Pay all your bills on time
hold on to credit card that youve have for awhile
avoid applying for new credit cards
pay your card balance every month
pay as much as you can above the minimum
never charge more than your limit
avoid using a credit card as a soruce f cash
avoid ay actions that lead a credit card company to reduce your credit limit
- choose schools with costs in mind
- avoid debt when possible
- shop carefully for loans
- repay your loans
Values and Goals (Chapter 2)
- Discover what you want
- Know how to get what you want
3. Follow up by doing what you intend to do
5 types of procrastination
- dreams
- worries
- Defiers
- Overdoers
- perfectionists
Quadrants
- ==Important+Urgent (need to learn how to manage)==
- crisis, deadlines
- pressing problems
- emergencies
- ==Important+not Urgent (need to learn how to focus)==
- preparation and planning
- relationship and building
- recognizing
- opportunities/ learning
- ==Urgent+not Important ( avoid this area )==
- interruptions/distractions
- some calls and emails
- dealing with other’s requests
- ==Not important+ Not Urgent ( Limit )==
- busywork, trivia
- surfing social media/ internet
- time wasters
Communication (Chapter 8)
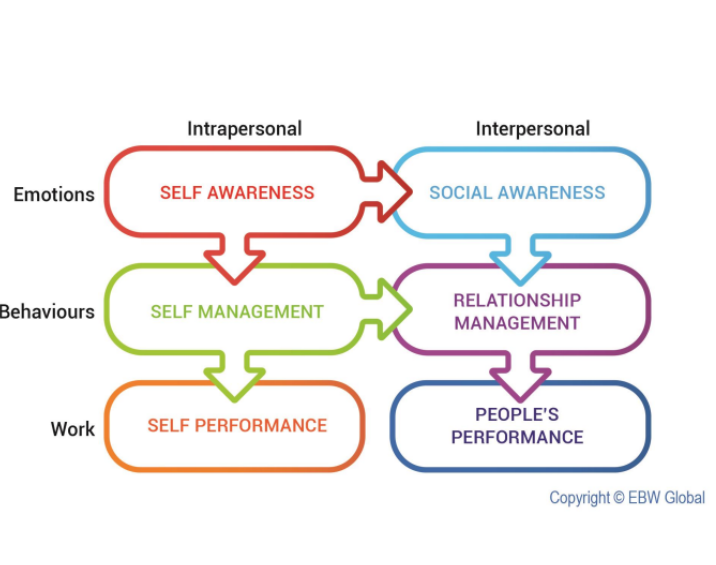
Developing emotional intelligence
Recognize three elements \n of emotions \n •Physical sensations \n •Thoughts \n •Actions \n •Name, accept and express \n your emotions \n •Respond rather than \n React
Communicating in Teams
What is the difference between sympathy and empathy? @@“Sympathy involves understanding from your perspective. Empathy involves putting yourself in the other person's shoes and understanding WHY they may have these particular feelings. In becoming aware of the root cause of why a person feels the way they do, we can better understand and provide healthier options.”@@
@@Verbal@@ \n •Tone of voice \n •Small percentage is \n verbal
@@Nonverbal@@ \n •Body language
Choosing to listen
Nonverbal listening \n Maintain eye-contact \n Verbal listening \n Stay open to the adventure of listening
be quiet
maintain eye contact
display openness
send acknowledgments
release distractions
Suspend Judgements
Verbal Listening
- choose when to speak
- feedback meaning
- notice verbal and nonverbal messages
- listen for requests and intentions
- allow emotion
- ask for more
- be careful with questions and advice
- take care of yourself
- stay open to the adventure of listening
Choosing to speak
• Replace “you” messages with “I” messages \n • Questions \n • Nonverbal messages \n • Barriers \n • Speak candidly \n • Speak up
• take these ideas to work
• offer feedforward
Managing Conflict

Assertiveness

Sections where she didn’t specify what was on the test.
Student Mastery (Chapter introduction)
Discover What you Want?
- What do you want from your education?
- Have well-defined goals that align with your behaviors and thoughts
Mastery
- attaining a level of skill that goes beyond technique
- the work is effortless
- you experience a flow or being in the moment
- you let go of control and work seems to be self-propelled
- Mastery is not taught, it is learned through experience
Master Student Discovery (Chapter 1)
- [ ] Discovery
- [ ] Intention
- [ ] Action
Discovery Statements
- Record the specifics about your thoughts, feelings, and behavior
- use discomfort as a signal
- suspend judgment
- tell the truth
Intention Statements
Keep these guidelines in mind when writing Intention statements \n • Make intentions observable \n • Small and achievable \n • Anticipate self-sabotage \n • Don’t have them depend on others \n • Set timelines and reward yourself
Action Statements
• This is where the magic happens \n • Your life starts to take on meaningful results \n • Keep these in mind when things get tough \n • Baby steps- change does not occur overnight \n • Make sure intention statements include behaviors to do this will ensure you are on the right track \n • If you get stuck tell the truth, you cannot expect new results from old behaviors
•Look for prompts to action throughout this book
•Remember that it’s not about self-improvement
Keep the process alive
- Think about the process as flying a plane
- work smarter not harder
- take a path to self-actualization
- see the process as a lifelong adventure
Transition to Higher Education
• Some stuff you may notice \n • New academic standards \n • A new level of independence \n • Difference in teaching styles \n • To aid in the transition \n • Be sure to tackle the unknowns \n • Admit your feelings-whatever they \n maybe \n • Find and use resources, get to know \n people \n • Be a self-regulated learner
Respect in the Classroom
✓Arrive on time \n ✓Show interest in being in the \n classroom \n ✓Enter a classroom with civility \n ✓Attend class regularly \n ✓Participate fully \n ✓Communicate respectfully
Motivation
•Develop motivation with practice \n ✓Make a promise \n ✓Befriend your discomfort \n ✓Change your mind and body \n ✓Sweeten the task \n ✓Ask for support \n ✓Payoffs to the costs
Attitudes, Affrimations, and visulations
You can change your attitude through affirmations and visualizations, you don’t have to live with your bad attitude
| Present tense | Detailed | Positive |
|---|
Create a visualization based on your affirmations
Habits
Look at your behaviors, are they aligned with your goals and dreams? \n ✓if you want an “A” are you working hard, are you studying \n To create a new habit \n ✓Start small, an achievable goal that will give you results \n ✓Get feedback and support \n ✓Monitor your behavior
Student Master Qualities
Inquisitive- Curious about everything, likes asking questions, wants to know how to get the value of the lecture even when found boring
Able to focus- has the energy and capacity for amazement to keep the attention and is 100% focused. A master student has attention like a child wanting to learn new things.
Willing to change- unknown does not scare the master student, they invite it. We all have pictures of who we are as people and as they can be useful, they can also harm us. Must embrace new ideas and try new things.
Able to organize and sort- able to take a large body of information and discover the relationships between them. Able to organize hundreds of different categories and has the guts to set big goals. Has the precision to plan carefully so that those goals can be achieved.'
Competent- Studies and practices until the skill become second nature. Able to apply what they learn to different situations.
Joyful- Able to smile and smile at the amazement of the world and their experience with it.
Able to suspend Judgement- Open to opinions and able to let go of their own opinions when needed. Listens to opposite povs and doesn't let judgment get in the way of learning.
Energetic- Enthusiastic and involved
Well- Takes care of themselves mentally and physically
Self aware- Willing to be honest about themselves and tells the truth about their strengths and things that they can improve on
Responsible- Takes responsibility for things that happen in their life, especially events that most would blame on others
Willing to take risks- often does projects with no guarantee of success and participates in class discussions.
A generalist- Interested in everything that the classroom presents to them and actively wants to deepen his learning through socializing with others as well as going to different events that involve studying.
Willing to accept a paradox- They are willing to commit to something that may seem absurd like managing money and reaching their financial goals.
Courageous-admits his fear and fully experiences it.
Self-directed- their goals come themselves and within themselves and no one else.
Spontaneous- They are truly here and now. Capable of responding to fresh and unplanned ways.
Relaxed about grades- Isn’t too depressed nor euphoric grades, does not let grades prove their self worth
Tech Savy- Defines technology as a tool to help with a human purpose
Intuitive- Has an inner sense that cannot be explained by logic, trusts their gut instincts
Creative- Where they make dull details into something they can create.
Willing to be uncomfortable- if the master student has a goal that is necessary for them to be uncomfortable they are willing to accept it.
Optimistic- sees setbacks as temporary and islolated
Willing to laugh- Able to laugh at themselves and celebrate learning
Hungry- has a hunger for knowledge and It gives him the desire to learn
Willing to Work- Once inspired they follow through with persistence
Caring- Cares about knowledge just as much as people. Also wants to learn from others just as they learn from themselves
Health (Chapter 11)
Health Habits
- Success in school is directly tied to your health
- Adopt habits that sustain your well being
- Become aware of the habits that affect your health
- Health is a continuum - Death too early, or a life filled with joy
- Health changes - By Choice or Chance
- We have choices for our Health - Attitudes and Habits
Choose your Fuel
| Emphasize | Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, fat-free/low-fat milk, and milk products |
|---|---|
| Include | Lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, eggs, and nuts |
| Choose | Food low in saturated fats, trans fat, cholesterol, salt, sugars |
Choose to Exercise
- stay active throughout the day
- Adapt to Campus Environment
- Do what you enjoy
- Vary your Routine
- Get active early
- exercise with other people
- join a gym without fear
- look for gradual results
Choose Freedom from Distress
- Accept physical sensations
- change your thinking
- meditate
- solve problems
- take care of your body
- find alternatives to chemicals
- reach out for help
Stress Management
- Monitor your stress
- Think about strategies
- Think about how well the strategies work for you
- Do you feel the need to make any changes in the way you manage stress
- resolve to work on health de-stress activities
Develop a strong self-image
- [ ] set up winning situations
- [ ] set goals with care
- [ ] adopt a model
- [ ] change the convo about yourself
- [ ] compare yourself to you
- [ ] surround yourself with support
Ask For Help
ask with - Clarity, sincerity, an open mind, opening for more ideas, ask again.
Choose to stay safe
- Always lock doors when away from home
- avoid walking home alone
- Be prepared
- get familiar with the campus layout
- Inquire about the school escort system
- learn self-defense and rape prevention
Prevent Unwanted Pregnancy
• Abstinence \n • Barrier methods \n • Natural family planning \n • Hormonal methods \n • Implants \n • Emergency contraceptives \n • Permanent methods \n • Withdrawal does not work \n • Evaluate birth control methods \n • Know where to get birth control
Prevent Injection
• Abstain from sex \n • Talk to your partner \n • Use condoms \n • Take action soon after sex \n • Get vaccinated \n • Get screened for STIs \n • Recognize the symptoms of STIs \n • Get treated right away
The Truth About Drugs
• Society uses drugs to solve problems \n • Instant comfort comes from the use of drugs \n • The pay-off is instant and will provide immediate comfort, but then the cost is much greater than the pay-off \n • The cost of using will affect work, school, family, your finances, and any other thing you find important \n • These addictions can lead to self-defeating behaviors, and you will likely lose everything \n • Addiction can lead to death \n • Abstain from substance abuse because it causes more pain than pleasure in the long run
Time (Chapter 2)
Managing Time
•Calendar \n • To-do lists \n •Next actions list
Schedule time in a weekly plan
- Finish all the big tasks first so you can complete the smaller tasks later on
7-step procrastination plan
Monday: Make it meaningful. \n Tuesday: Take it apart. \n Wednesday: Write an intention \n statement. \n Thursday: Tell everyone. \n Friday: Find a reward. \n Saturday: Settle it now. \n Sunday: Say no.
Ways to get the most out of your time.
• Choose time \n • Choose place \n • Get focused \n • Questions to ask \n • Health
• Study boring or difficult \n subjects first \n • Use waiting time \n • 2 hours of studying for \n • every hour in class
• monitor how much time you spend online
• use a regular study area
• Pay attention to your attention
• agree with living mates about study time
• get off the phone
• learn to say no
• hang a do not disturb on your door
• get ready the night before
• call ahead
• avoid noise distractions
•Manage interupptions
Questions to keep you focused
ask what is the one task that will move me toward his goal
ask if you are being too hard on youself
ask is this a piano
ask can I do one more thing
ask can I delegate this
ask how did I waste time
ask could I find the time if I really wanted to
ask am I willing to promise it
Questions to keep focused
•What is one task I can accomplish toward achieving my \n goal? \n • Am I being too hard on myself? \n • Does this need to be perfect? \n • Can I do just one more thing? \n • Can I delegate this? \n • How did I waste time? \n • Would I pay myself for what I am doing now? \n • Could I find the time if I really wanted? \n • Am I willing to promise it?
Multi-Tasking
- Unplug from technology
- Capture fast-breaking ideas with minimal interruptions
- Handle interruptions with care
- multitask with care
- align your activities with your passions
Values
- Focus your attention
- self-responsibility
- integrity
- Risk-Taking
- Contributing
- Translate your values into visible behaviors
Goals
- Write down your goals
- write specific goals
- write goals in several time frames
Long term goals
midterm goals
short term goals
- Write goals in several areas of life
Education
Career
Finacial Life
Family Life or Relationship
Social Life
Contribution
Spiritual life
level of health
- Reflect on your goals
Check in with your feelings
Check for alignment
Check for obstacles
Check for next steps
- Move into action immediately
Planning Sets You Free
- Schedule for Flexibility and Fun
- Back up to a bigger picture
- Look boldly for things to change
- look for what’s missing and what to maintain
- think even further into the future
- return to the present
- schedule fixed blocks of time first
- set clear starting and stopping times
- plan for changes in your workload
- involve others when appropriate
- Start the day with your most important task
- Plan in a way that works for you
Stop Procrastination
- Discover the costs
- Discover your procrastination style
- trick yourself into getting started
- let feelings follow the action
- choose to work under pressure
- think ahead
- play with antiprocastination apps
- create goals that draw you forward
Diversity
Building relationships across cultures
- Start with self-discovery
- look for differences between individualist and collectivist cultures
Remember that someone from acollectivist culture may place a high value on saving face
respet titles and last names
put messages in context
- Look for common ground
- speak and listen with cultural sensitivity
speak slowly, distinctly and pateintly
to clarify a statement don’t repeat individual words over and over again. Be simple and Direct
Avoid slang and figures of speech
use gestures to accompany your words
English courses for nonnative speaks often emphasize written english.
stay calm and avoid sending nonverbal messages that you’re frustrated
- Look for individuals, not group representatives
- find a translator, mediator, or model
- develop support systems
- be willing to accept feedback
- Speak up against discrimination
thats a sterotype, and we don’t have to fall for it
other people are going ot take offense at that. lets not tell jokes to put others down
I realize to know that you don’t mean to offend anybody but I feel hurt about what you said
I still think that story is racist and creates and atmosphere that I don’t want to be in
- Change the institution
stereotypes are errors in thinking
Prejudice refers to postiive or negative feeligns about others that are based on sterotypes
Discrimination takes place wen sterotypes or prejudice gets expressed in policies and laws that undermine equal opportunies for all cultures
- Take these ideas to work
Overcome Stereotypes
- Look for errors in thinking
Selective perception
Self-fufilling prophecy
Self-Justification
- Create categories in a more flexible way
- test your generalizations about people through action
- be willing to see your own stereotypes
Harassment
- point out sexist language and behavior
- observe your own language and behavior
- encourage support for women
- take action