2. Fetal Development, Timelines, Critical Periods, and Sensitive Times (via joseph_na4)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is the standard Estimated Date of Delivery (EDD) when calculated from the time of fertilization versus the Last Normal Menstrual Period (LNMP)?
From Fertilization: 266 days or 38 weeks.
From LNMP: 280 days or 40 weeks.
In pregnancy calculations, what is the difference between a Lunar month and a Calendar month?
Lunar Month: Exactly 28 days; a full pregnancy is considered 10 lunar months.
Calendar Month: 28/30/31 days; a full pregnancy is considered roughly 9.5 calendar months.
What are the three clinical stages of prenatal growth and their specific timelines in weeks or months?
Germinal Period: 0–2 weeks.
Embryonic Period: 3–8 weeks.
Fetal Period: 9 weeks to birth (Early: 3–6 months; Later: 7–9 months).
On a written exam, how would you correlate the clinical stages of prenatal growth with the common lay terms used by patients?
Clinical stages (Germinal, Embryonic, Fetal) correspond to the patient-friendly terms of 1st, 2nd, and 3rd "trimesters".
Define a Critical Period in development and describe its typical beginning and end.
A specific time when an event has its greatest consequences and proper stimuli must occur for normal development; it begins and ends abruptly.
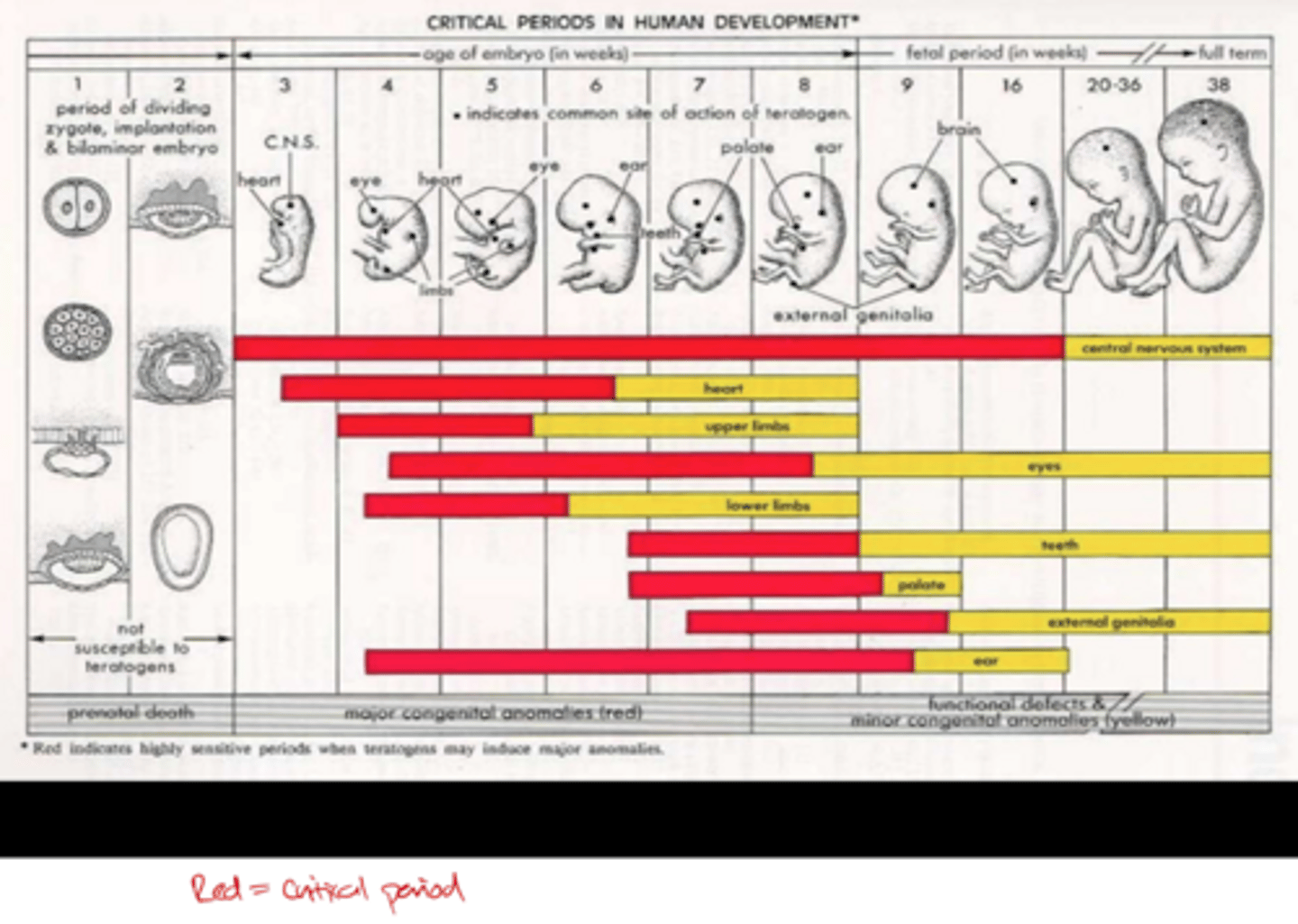
Define a Sensitive Period and explain how it differs from a Critical Period regarding learning efficiency.
A window of maximal sensitivity that begins and ends gradually; while learning or development can still occur after this period, it is not as efficient.
From a clinical perspective, what is the developmental outcome if the necessary stimuli are missing during a Critical Period?
The trajectory of development is altered or permanently impaired (often described as "the bad thing at the right bad time").
What are the two primary biological hallmarks of the Germinal Period?
At what specific time point after conception does implantation into the uterus typically occur?
1. Rapid cell division. 2. Implantation into the uterus.
Day 8–9.
Name the three primary germ layers of tissue that form during the embryonic period.
Describe the developmental progression of the Central Nervous System (CNS) during weeks 2-8.
Endoderm, Mesoderm, and Ectoderm.
It progresses from the Primitive streak to the Neural Plate, ending with Tube fusion.
At what specific time point after conception does Neural Tube fusion typically occur?
28 days.
In the general order of embryonic development, what major structural milestones occur between Day 28 and Day 35?
Day 28: Neural tube fusion.
Day 28–30: Limbs, ears, and optic pits appear.
Day 35: Tubular heartbeat begins, tactile sense develops, and head-on-body righting begins
Describe the timeline for the development of the heart and vestibular structures during the embryonic period.
Day 35: Heart is tubular.
Day 44: Semicircular canals form.
Day 54–55: Heart develops 4 chambers.
What observable physical features are present by the end of the 8th week of gestation?
Fingers and toes, eyelids, ears, a rounding head, and nasal structures.
Fetal period week 8-40 (know general order)
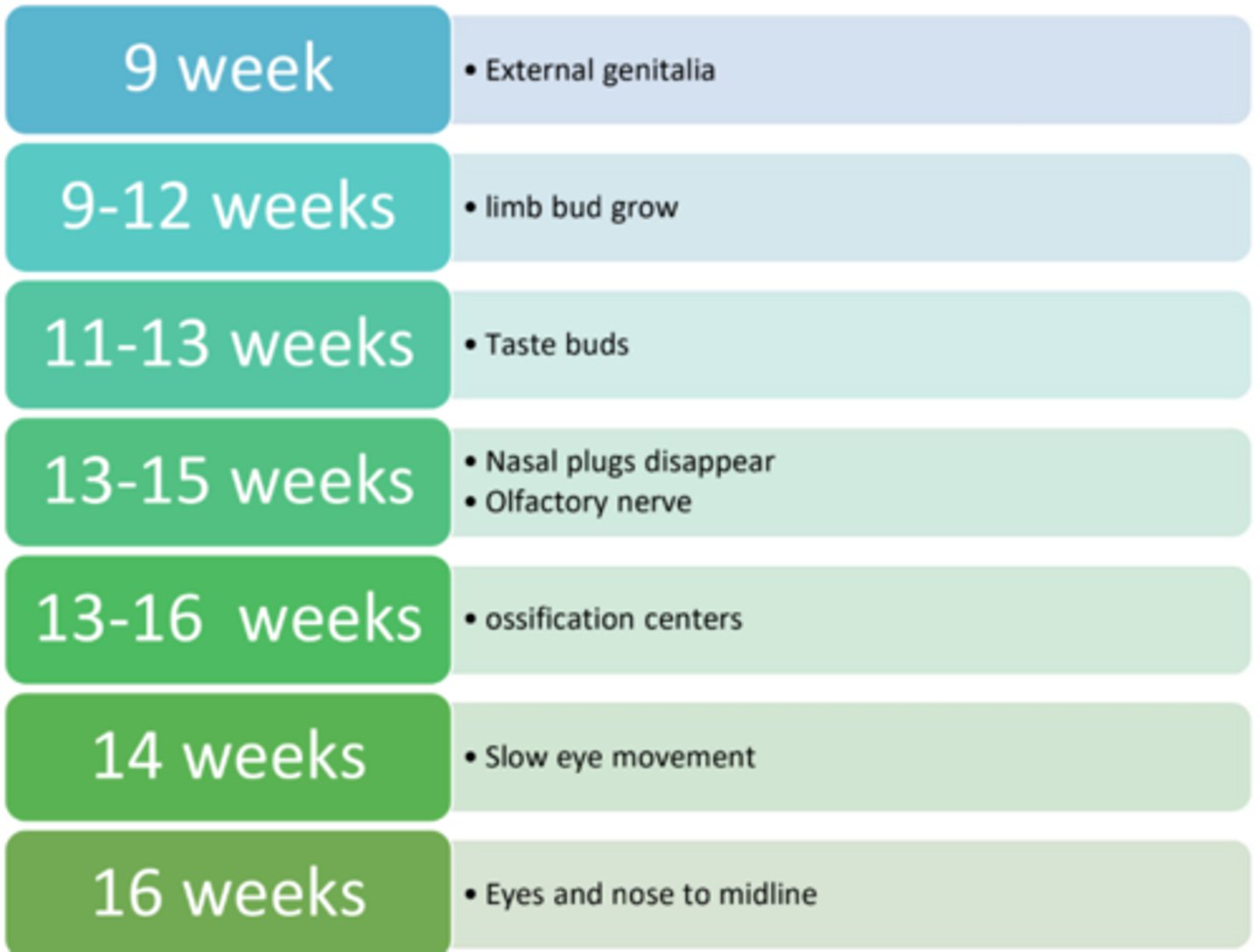
Fetal period 2-9 months/20-26 weeks
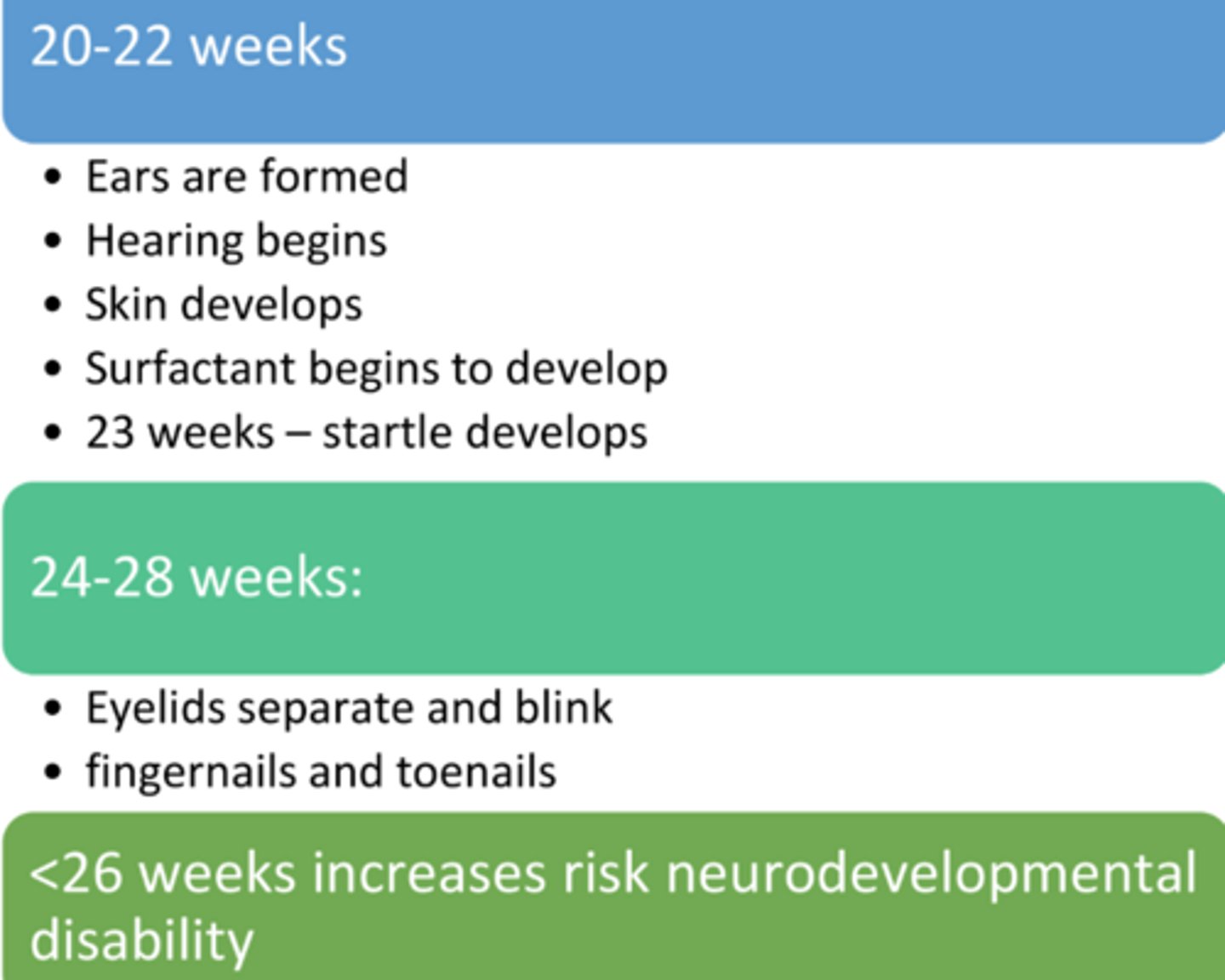
<__ weeks increases risk of neurodevelopmental disability
<26 weeks
At what point does a clinician stop correcting for prematurity in an infant's age, and what is the standard "normal" gestation window?
Correct for prematurity if the infant is born < 37 weeks; stop correcting once the infant reaches 38 weeks. The standard "normal" birth window is 37–40 weeks.
Fetal period 2-9 months/26+ weeks
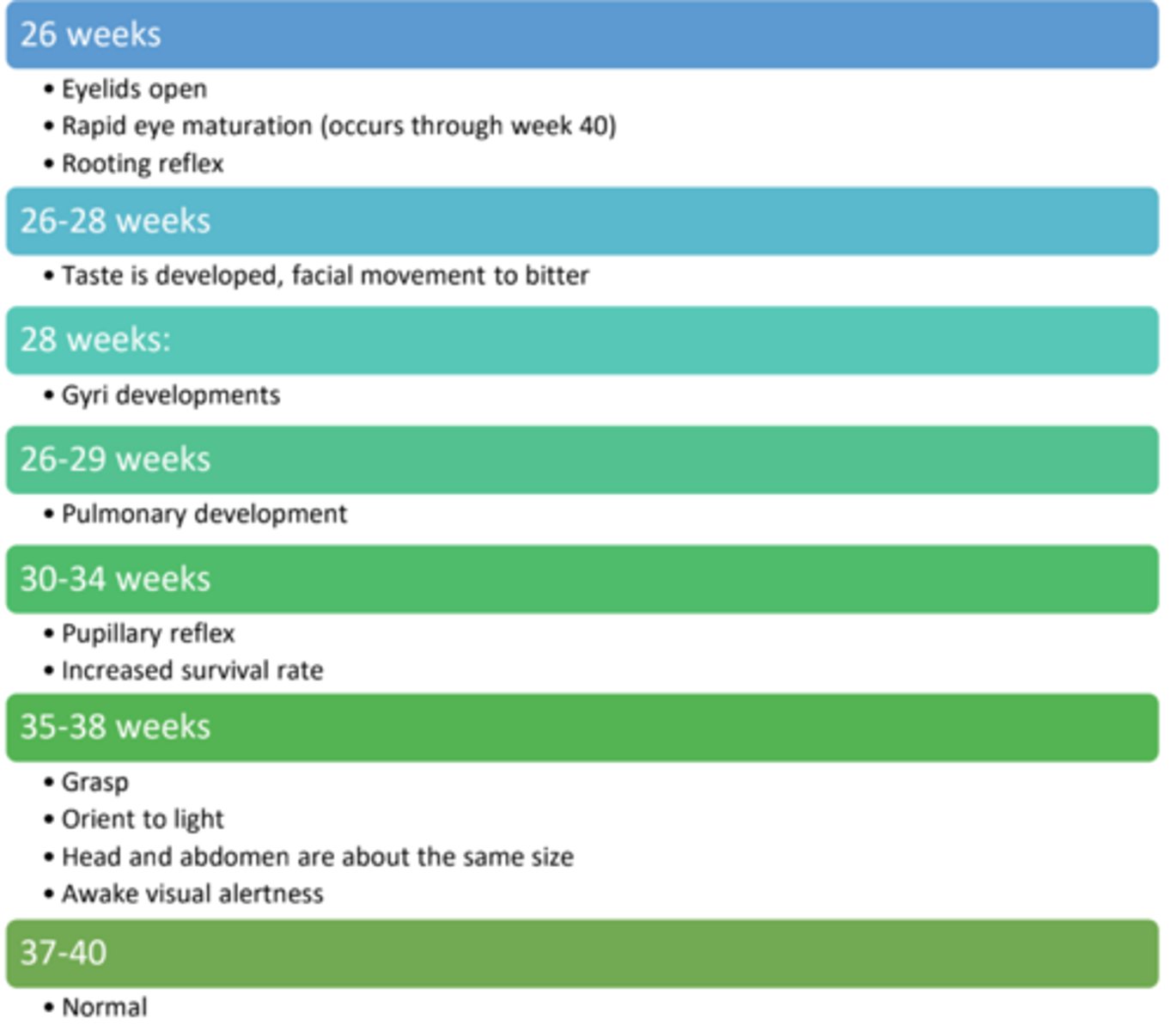
What is the first functioning organ to develop in an embryo, and what are its primary milestones at Week 5?
The Heart is the first functioning organ. By Week 5 (from conception), it exists in tubular form and begins to have a heartbeat.
Describe the developmental timeline of the lungs, specifically focusing on surfactant and breathing capability. (what weeks)
Week 21: Surfactant production begins.
Weeks 26–29: Lungs are developed enough to support breathing.
Week 32: Alveoli are developed for improved gas exchange.
Identify the major neural structures that emerge during weeks 3 and 4 of development.
Week 3: Primitive streak and primitive node (migration to fibroblasts, chondroblasts, and osteoblasts).
Week 4: Neural plate and neural tube fusion. (28 days)
Describe the timeline for the development of brain gyri (ridges) during the prenatal period.
Gyri begin forming and continue to develop through Week 28.
In the timeline of skeletal development, when do limb buds first appear?
Day 28–30.
At what point in fetal development do distinct fingers and toes emerge?
When does the process of ossification (bone formation) begin in the developing fetus?
Day 54–55 (or between Weeks 9–12).
Weeks 13–16.
List the order of the development of senses
Touch
Vestibular
Smell
Taste
Hearing
Sight
During the 1st trimester, what movements are established, and when does the mother typically first feel them?
Movements: Hands to face, jaw movements, bend/stretch, breathing, and upper extremity (UE) reaching.
Maternal Sensation: Typically between 16–18 weeks.
Compare the typical movement patterns seen in the 2nd trimester versus the 3rd trimester.
2nd Trimester: Hiccups, startles, and active stretches of the UE, lower extremity (LE), mouth, and trunk.
3rd Trimester: Decreased overall movement; however, facial movements increase and sleep cycles begin around 26–28 weeks.
When do most primitive reflexes begin, and what is their primary clinical purpose?
Most begin in utero and are used clinically to evaluate the integrity of the neural system.
What is the clinical significance of primitive reflex findings regarding peripheral vs. central nervous system (CNS) injuries?
Absent reflex: Suggests a peripheral injury.
Too strong or persistent reflex: Suggests a CNS problem (e.g., spasticity or cerebral palsy).
Asymmetrical reflex: Warrant further workup for localized issues
Describe the stimulus and response for the Palmar Grasp reflex.
Stimulus: Stroking the infant's palm.
Response: The infant's hands close tightly.
What external and biological factors can negatively impact fetal development during gestation?
Name the three birth-related weight and timing factors that can impact a child's developmental trajectory.
Pharmaceuticals and Viruses.
Heredity.
Maternal factors (Nutrition, health/care, and exercise).
Oxygen deprivation.
1. Low birth weight. 2. Preterm birth. 3. Post-term birth.
Is physiological extension or flexion typical posturing in infants?
physiological flexion
What are the three hallmark motor and postural characteristics of a full-term infant?
1. General activity: Good, with spontaneous kicking and flailing.
2. Reflexes: Developed and brisk.
3. Posture: Assumes physiological flexion.
How does the general activity and reflex profile of a preterm infant differ from a full-term infant?
Activity: Poor or diminished.
Reflexes: Sluggish or incomplete (e.g., Moro, sucking, swallowing).
They often assume an extended posture (rather than flexion) due to low muscle tone.
What are the three clinical classifications for low birth weight and their corresponding weight thresholds?
LBW (Low Birth Weight): < 5 lbs (2500 g)
VLBW (Very Low Birth Weight): < 3.3 lbs (1500 g)
ELBW (Extremely Low Birth Weight): < 2.2 lbs (1000 g)
Define SGA and LGA in the context of neonatal assessment.
SGA: Small for gestational age
LGA: Large for gestational age
What does IUGR stand for, and what is its primary characteristic/cause?
Intra-uterine growth retardation/restriction; it is typically due to a space issue within the uterus that prevents the fetus from growing.