2.8 Miscibility gaps & twins
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Exsolution
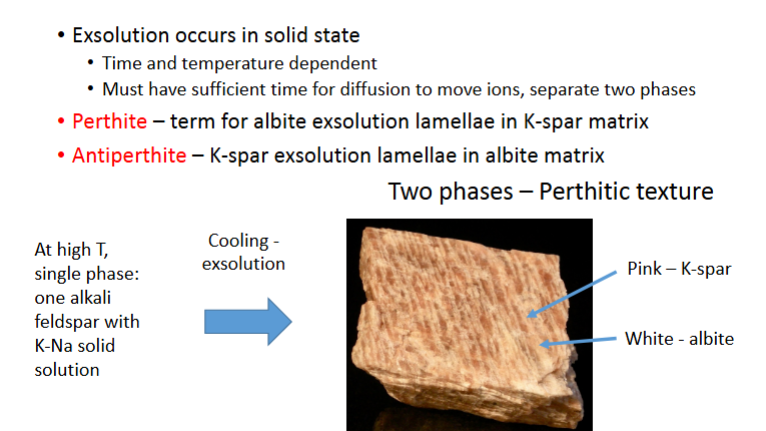
Exsolution occurs in solid state
• Time and temperature dependent
• Must have sufficient time for diffusion to move ions, separate two phases
Perthite – term for albite exsolution lamellae in K-spar matrix
Antiperthite – K-spar exsolution lamellae in albite matrix
Twinning
• Intergrowth of two or more crystals
• Related by symmetry element not present in original single mineral
• Several twin operations (i.e. symmetry element):
Reflection
Rotation
Inversion (rare)
• “Twin Law” – describes twin operation and axis or plane of symmetry
Reflection
• Two or more segments of crystal
• Related by mirror that is along a common crystallographic plane
• Can not be a mirror in the original mineral
Rotation
• Two or more segments of crystal
• Related by rotation of crystallographic axis common to all
• Usually 2-fold
• Can not duplicate rotation in original mineral
Twin terminology
• Composition surface – plane joining twins, may be irregular or planar
• Composition plane – if composition surface is planar; referred to by
miller index
• Contact twin – no intergrowth across composition plane
Penetration twin
Penetration twin – inter-grown twins, typically irregular composition surfaces
twins
• Simple twins – two twin segments
• Multiple twins – three or more segments repeated by same twin law
• Polysynthetic twins – succession of parallel composition planes
(plagioclase)
• Cyclic twins – succession of composition planes that are not parallel
Mechanism forming twins
• Growth – occur during growth of minerals
• Transformation – displacive polymorphs
Occurs during cooling of minerals
E.g. leucite, transforms from cubic to tetragonal system - @ 665º C
Space change accommodated by twins
Deformation twinning
• Result from application of shear stress
• Lattice obtains new orientation by displacement along successive planes