Ch. 26 Urinary system: urine formation by kidneys
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
The kidney’s main function is to maintain homeostasis. What are the 6 ways this occurs?
Excretion of metabolic waste (urea, uric acid, creatinine (from muscle creatine), bilirubin, hormones, “foreign “stuff”: drugs, toxins, food additives”)
Water and electrolyte balance
pH balance by eliminating acids
Regulation of calcitriol - essential for normal calcium deposition and reabsorption in the GI tract
Gluconeogenesis - after prolonged fasting
RBC production regulation - stimulated by hypoxia
The kidneys maintain homeostasis with water and electrolyte balance. What is the goal or result of this?
a. regulate arterial pressure
b. regulate venous pressure
c. regulate filration rate
d. all of the above
a. regulate arterial pressure
with sodium and renin to angiotensin II
T/F: Gluconeogensis can occur at the kidney but only after prolonged fasting or starvation
true - processes faster than the liver too
Explain the regulation of erythrocyte production
O2 will be delivered to the kidneys
where it stimulates the secretion of erythropoietin (EPO). EPO then promotes the production of red blood cells in the bone marrow, increasing oxygen transport in the blood.
cycle repeats
*stimulated by hypoxia because EPO creates RBC when oxygen carrying hemoglobin levels are low
How does kidney disease affect the regulation of EPO production?
patient will become anemic because of inability to create RBC because O2 delivery is needed to the kidneys to start EPO production
How does urine travel to the ureter?
a. Major calyx, minor calyx, renal pelvis
b. Minor calyx, renal pelvis, major calyx
c. renal pelvis, minor calyx, major calyx
d. minor calyx, major calyx, renal pelvis
d. minor calyx, major calyx, renal pelvis
________ filters blood by removing metabolic wastes while extracting much of its water content
renal system
functional unit of the kidney
tiny sac-like structure where blood is delivered and INITIALLY FILTERED
nephron
renal corpuscle
Afferent arteriole vs efferent arteriole
afferent a - carries blood toward the corpuscle to be filtered
efferent a - carries non-filtered portion of blood away from the corpuscle
Define the following
Glomerulus
Bowman’s (glomerular capsule)
Podocyte
Glomerulus - specialized capillary that filters blood
Bowman’s (glomerular capsule) - outer layer of the corpuscle and site of filtration
Podocyte - specialized cells that prevent large molecules such as proteins from exiting filtrate
T/F: the glomerulus is a capillary
true
What is the site of filtration?
a. Glomerulus
b. Bowman’s capsule
c. Nephron
d. Podocyte
b. Bowman’s capsule
Why is there no venous system in the renal system?
blood does not go back to the heart
no gas diffusion occurs so O2 is still present in the blood
What 4 actions is the nephron responsible for?
filtration - to create filtrate
reabsorption - back into the blood
secretion
excretion - elimination of urine
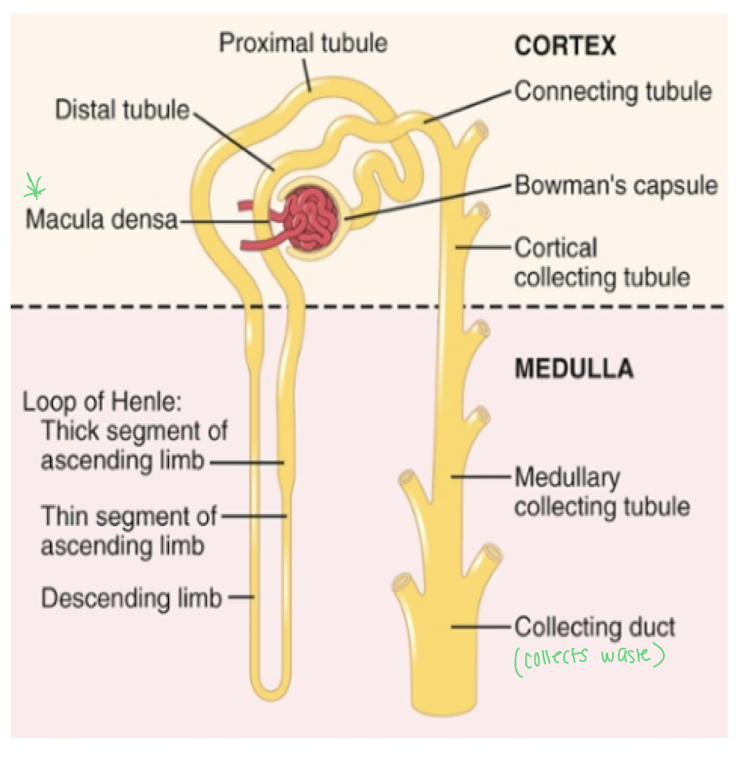
Give the steps of the filtration pathway
renal corpuscle (glomerulus and bowman’s capsule (site of filtration))
Proximal convoluted tubule - for reabsorption and secretion
loop of henle - reabsorption alllowing urine to be concentrated here
macula densa cells - touch the glomerulus and sense Na+ levels
Distal convulated tubule - reabsorption and secretion
collection duct - some reabsorption
renal pelvis
ureter
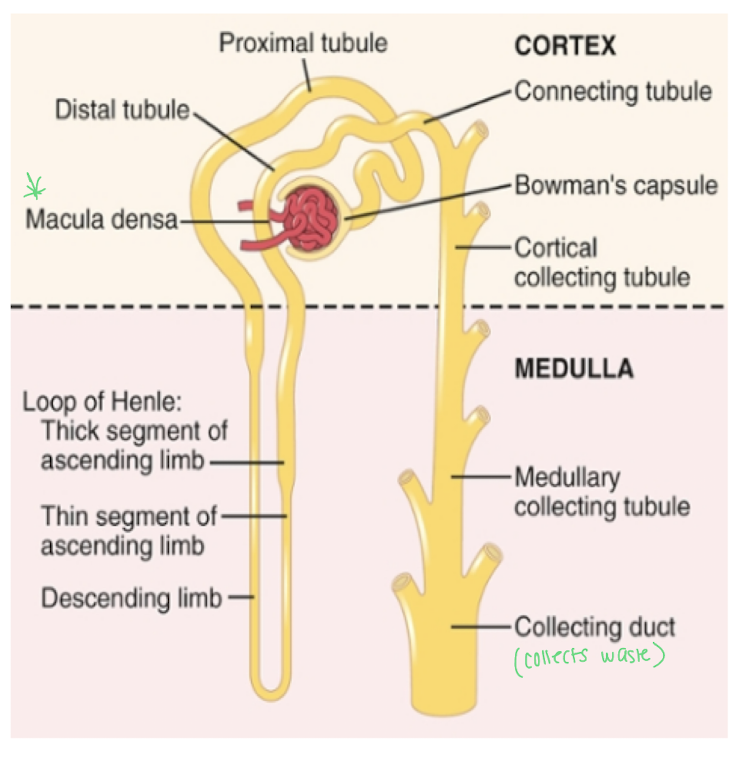
_____ is the portion of the tubules that loops back very close to the corpuscle
distal convoluted tubule
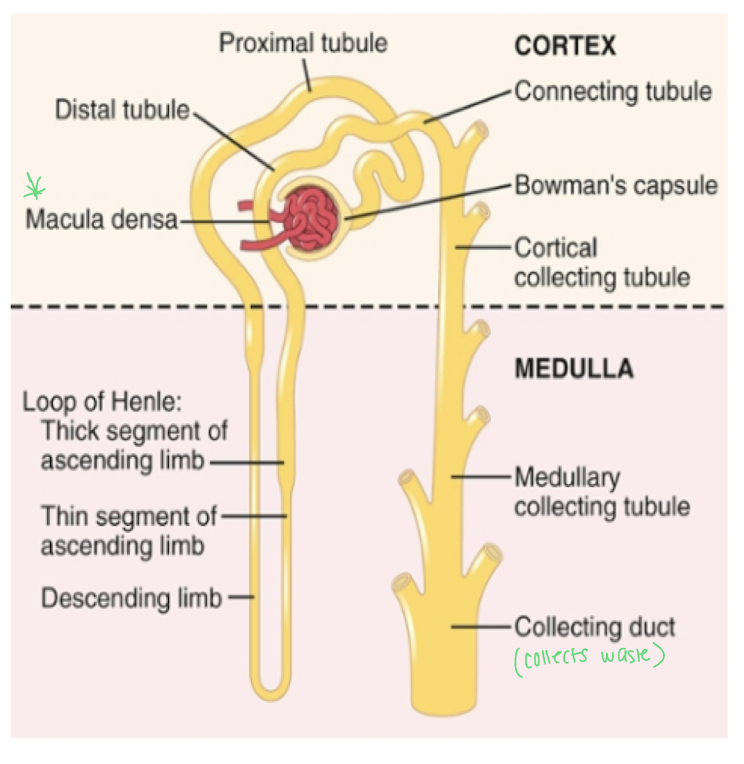
Describe the loop of henle
has a descending limb and an ascending limb
together these segments concentrate urine by extracting water from filtrate
What are the two types of nephrons in the kidneys and what differentiates them?
Cortical nephron
located deep in the cortex
short loop of henle
Juxtamedullary nephron
near the medulla
long loop of henle and concentrates urine
The Kidneys are delicate organs that filter blood and produce urine.
How many nephrons are in each kidney?
How many glomerulus are designated to each nephron?
How do nephrons hold up with age?
Are they (kidneys) able to regenerate?
about 800,000 to 1,200,000 nephrons
1 glomerulus per nephron
10% decrease in nephron function every 10 years after 40 y/0
by age 80, 40% fewer functioning nephrons that at 40 y/o
unable to regenerate but the nephrons are able to adjust
Smooth muscle chamber with a body (rugae) and a neck is known as the _____
bladder
Why are the rugae in the bladder important?
allow the bladder to expand as it fills with urine
Which of the following are false about the bladder?
a. Lower part of the neck of the bladder is called the posterior urethra
b. the smooth muscle of the bladder is known as the detrussor muscle
c. the bladder’s trigone consists of rugae to aide in expanding as it fills with urine
d. electrical pathways are responsible for the bladder to contract as a unit or all at once with gap junctions
c. the bladder’s trigone consists of rugae to aide in expanding as it fills with urine
no rugae in trigone
Why are the ureters in the trigone angled and not entering the trigone directly superiorly?
To prevent backflow of urine into the ureters when the bladder contracts.
T/F: Micturition is not a reflex
false - it is a reflex because brain integration is not required
Explain how the bladder empties with the input of spinal reflexes
The bladder will continue to fill until the spinal reflex is initiated but can be overrided by the cortex and brain stem
the internal sphincter which is smooth muscle will hold the urine in the bladder
involuntary action
the external sphincter is made of skeletal muscle and is under voluntary control
innervated by the pudendal nerve
Autonomic spinal reflex
sympathetic stimuli will inhibit contraction (fight/flight)
parasympathetic stimulation (S2-S4) causes contraction because the body has relaxed
stretch sensation in the bladder will allow sensory and motor nerve fibers on the bladder to release urine as the muscle contracts
Give a quick step by step overview of how the micturition reflex occurs at the parasympathetic level
the reflex is controlled by the PNS at S2-S4
stretch receptors in the bladder wall detect filling
sigals are sent to the spinal cord causing:
detrusor muscle to contract
internal urethral sphincter to relax, allowing urine to flow from the bladder and the external sphincter will release the urine voluntarily when appropriate
What can occur with extreme bladder filling or overdistention?
The afferent signals from the bladder stretch receptors become so strong they:
overrride the voluntary control of the brain
engage spinal reflex without brain input
causes reflex inhibition of the external sphincter, relaxing it involuntarily ad urination occurs
Explain the relationship between volume in the bladder and pressure in the bladder
The pressure in the bladder will not change from 150 to 300 ml because the bladder is expanding. At 300 ml the bladder will begin to contract as urine enters the bladder and as contractions increase, pressure increases because the urge to urinate will increase.
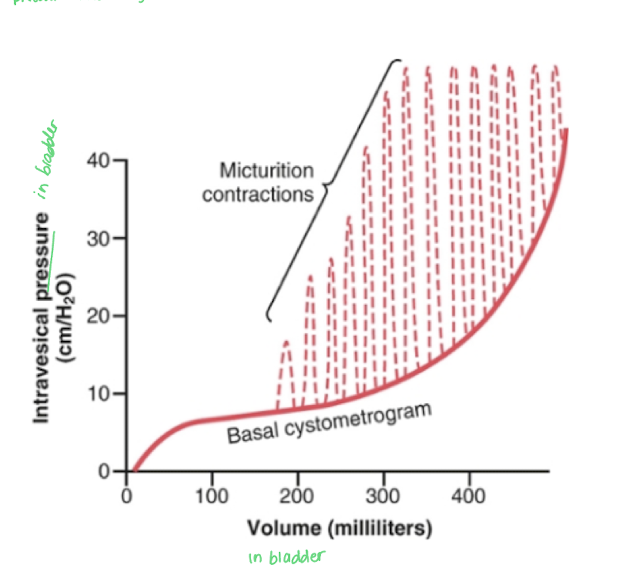
Bladder smooth muscle tone keeps pressure steady up to ______ ml
a. 500 ml
b. 300 ml
c. 150 ml
a. 100 ml
b. 300 ml
How does damage to sensory nerve fibers affect micturition?
atonic bladder occurs where pressure in the bladder does not change
therefore, stretch can’t be detected, reflex can’t be initiated, bladder fills to capacity and then overflows known as overflow incontinence
occurs in T2D with damage to the nerves = no sensation
how does damage to the sacral region of the spine affect micturition?
causes an “automatic bladder”
reflex is intact but is exaggerated and spastic = frequent urination
how does damage to the brain above the pons affect micturition?
individual loses ability of voluntary control of bladder leading to involuntary and frequent urination
urge to urinate is present but unable to supress it because the brain can no longer inhibit the reflex
The kidneys are not supposed to filter protein. How can it be detected and what does it signify?
found by detecting protein in the urine
signifies kidney damage
How can you control the volume of GFR?
Pressure
pressure added to the efferent arteriole will increase filtrate
pressure added to the afferent arteriole will decrease filtrate
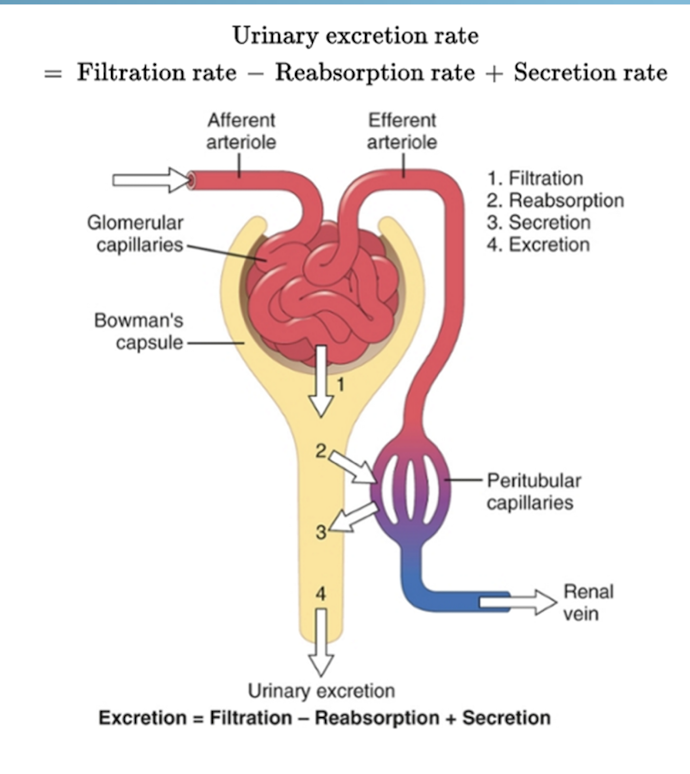
Absorption and Secretion
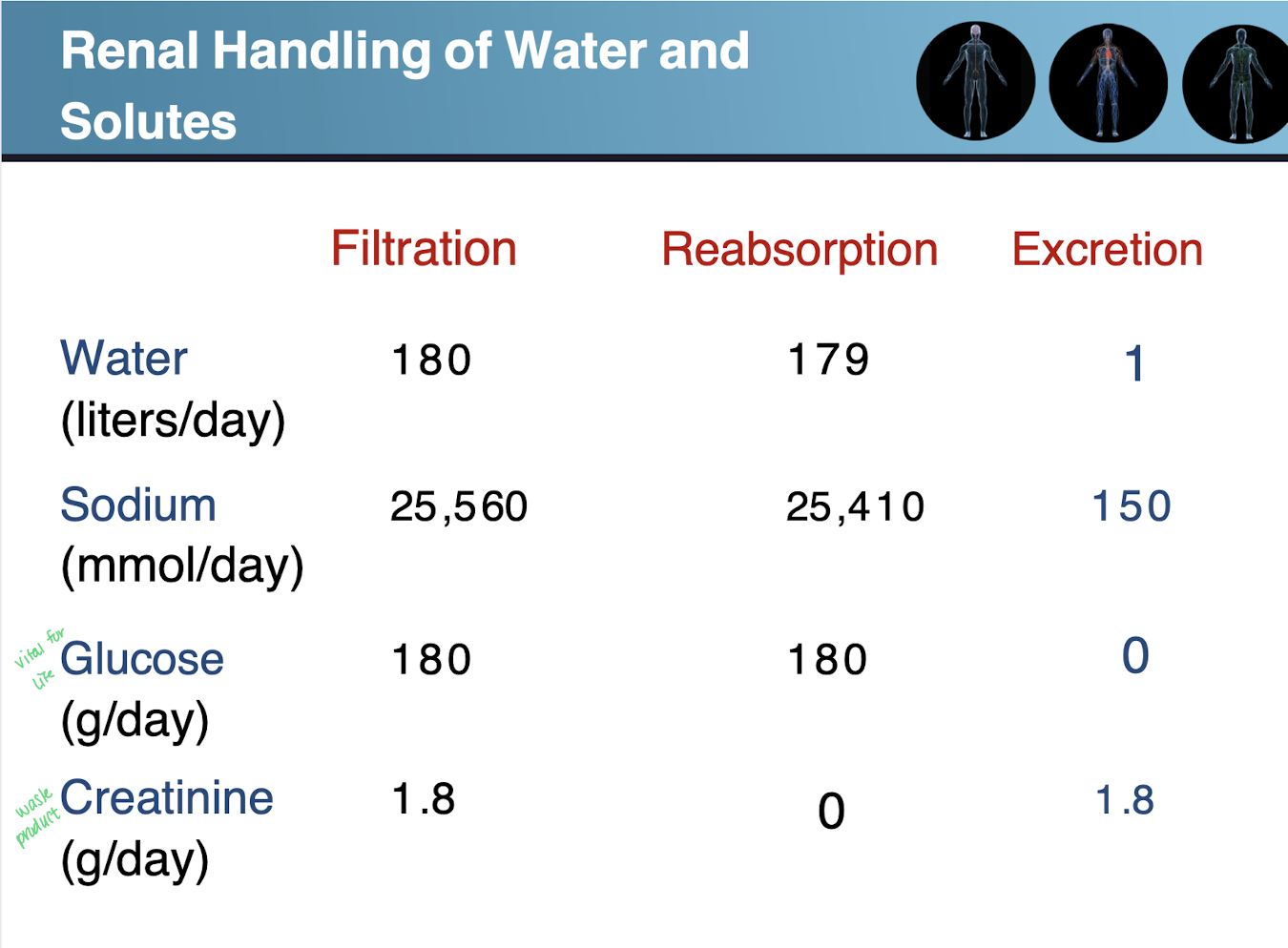
If entered into the kidneys, what can we expected to be filtered and excreted?
When do we see excretion < filtration?
What elements do we see to not be excreted?
Only excretion occurs with which elements?
inulin and creatinine
Na, Cl, water - partial reabsorption from the tubules into the blood
Amino acids (building blocks) and glucose (energy) - body needs these to function so we don’t want them to be removed
organic acids and bases are not reabsorbed
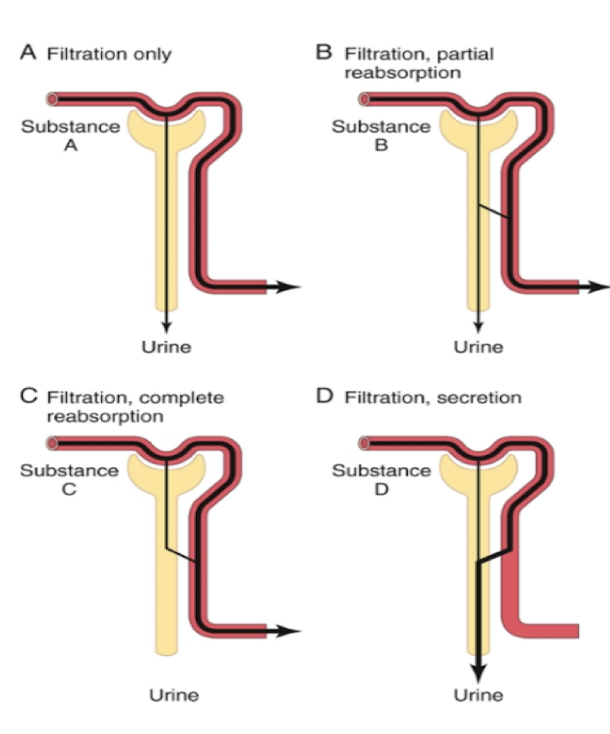
What elements do we commonly see being secreted after filtration?
drugs
potassium
toxins
H+ ions (acidity)
penicillin
T/F: reabsorption is more important than secretion
true
Which nutrients are greatly absorbed? (Hint: 5 answers)
a. K+
b. Na+
c. Cl-
d. proteins
e. glucose
f. amino acids
g. bicarbonate
h. hydrogen
Na+, Cl-, glucose, amino acids, and bicarbonate
K and H are secreted
Review chart