skeletal muscles
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
muscle mechanism
move in antagonistic pairs against incompressible skeleton

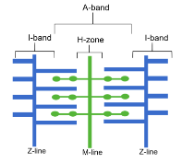
ultrastructure of myofibril
Z-line: boundary between sarcomeres
I-band: only actin
appears light under optical microscope
not visible when myofibril contracts
A-band: overlapping region between actin and myosin
appears dark under optical microscope
H-zone: only myosin
not visible when myofibril contracts
role of glycogen in skeletal muscle
a store of glucose
to be hydrolysed to glucose during respiration to provide ATP
role of ATP in myofibril contraction
ATP allows binding of myosin to actin, forming actinomyosin bridges
provides energy to move myosin head
importance of ATPase during muscle contraction
breaks down ATP to release energy
energy used to form actinomyosin bridges
role of tropomyosin in myofibril contraction
moves out of the way when calcium ions bind, allowing myosin to bind to actin
role of actin in myofibril contraction
actin are thin filaments involved in myofibril contraction
provide myosin binding sites for myosin heads to bind, which enables the formation of actinomyosin cross bridges
role of myosin in myofibril contraction
myosin are thick filaments with moveable heads
myosin heads attach to binding sites on actin
this enables the formation of actinomyosin cross bridges
myosin heads move, pulling actin along
detaches from binding site and moves to original position
explain how calcium ions cause myofibril to start contracting
Ca2+ binds to actin and uncovers myosin binding site on actin filament
process muscle contraction
action potential arrives at neuromuscular junction
calcium ions diffuse into myofibrils from sarcoplasmic reticulum
Calcium ions bind to tropomyosin and cause the movement of tropomyosin
this movement causes the exposure of the myosin-binding site on actin filament
this uncovers of binding sites on actin
myosin heads to binds/attaches to the exposed sites on actin filament
myosin head binds to actin
actinomyosin cross bridge formed
hydrolysis of ATP causes myosin head to bend
bending pulls the actin filament
attachment of a new ATP molecule to each myosin head causes the myosin head to detach from actin
how can a fall in pH lead to a reduction in the ability of calcium ions to stimulate muscle contraction
low pH changes shape of calcium ion receptors
fewer calcium ions bind to tropomyosin
fewer tropomyosin molecules move away from binding site
so fewer binding sites on actin revealed
so fewer myosin heads can bind and fewer actinomyosin cross bridges can form
so the myosin head doesnt move and pull actin filament
4 pieces of evidence that support sliding filament theory
H-zone narrows
I-band narrows
Z-lines get closer
sarcomere shortens
A-zone remains same width
proves that myosin filaments do not shorten
muscle relaxation
Ca2+ is actively transported back into sarcoplasmic reticulum
Tropomyosin blocks binding site on actin
role of phosphocreatine in muscle contraction
phosphorylates ADP directly to ATP when oxygen for aerobic respiration is limited
how to calculate length of one sarcomere
view thin slice of muscle under optical microscope
calibrate eyepiece graticule
measure distance from middle on one light band to another
where are slow and fast-twitch muscle fibres found
slow-twitch: sites of sustained contraction (e.g. calf muscle)
fast-twitch: sites of short-term, rapid, powerful contractions (e.g. biceps)
role of slow and fast-twitch muscle fibres
slow-twitch: long-duration contraction
well-adapted to aerobic respiration to prevent lactate build-up
fast-twitch: powerful short-term contraction
well-adapted to anaerobic respiration
adaptations of slow-twitch muscle fibres
glycogen store: many terminal ends that can be hydrolysed to release glucose for respiration
contain myoglobin: higher affinity for oxygen than haemoglobin at lower partial pressures
many mitochondria: aerobic respiration produces more ATP
surrounded by many blood vessels: high supply of oxygen and glucose
structure and properties of fast-twitch muscle fibres
large stores of phosphocreatine
more myosin filaments
thicker myosin filaments
high concentration of enzymes involved in anaerobic respiration
extensive sarcoplasmic reticulum: rapid uptake and release of Ca2+
why do both slow and fast muscle fibres contain ATPase?
ATPase causes hydrolysis of ATP
muscle contraction requires ATP