Comprehensive Microanatomy and Histology of Skin, Circulatory, and Lymphatic Systems
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What type of epithelium lines the oral cavity?
Stratified squamous epithelium.
What specialized modification do simple columnar epithelium have?
Microvilli.
What is the shape of the lining of the pancreatic duct?
Cuboidal.
Which parts of the kidney can be seen microscopically?
Cortex and medulla.
After blood is filtered through the glomerulus, where does the resulting fluid enter?
Bowman space.
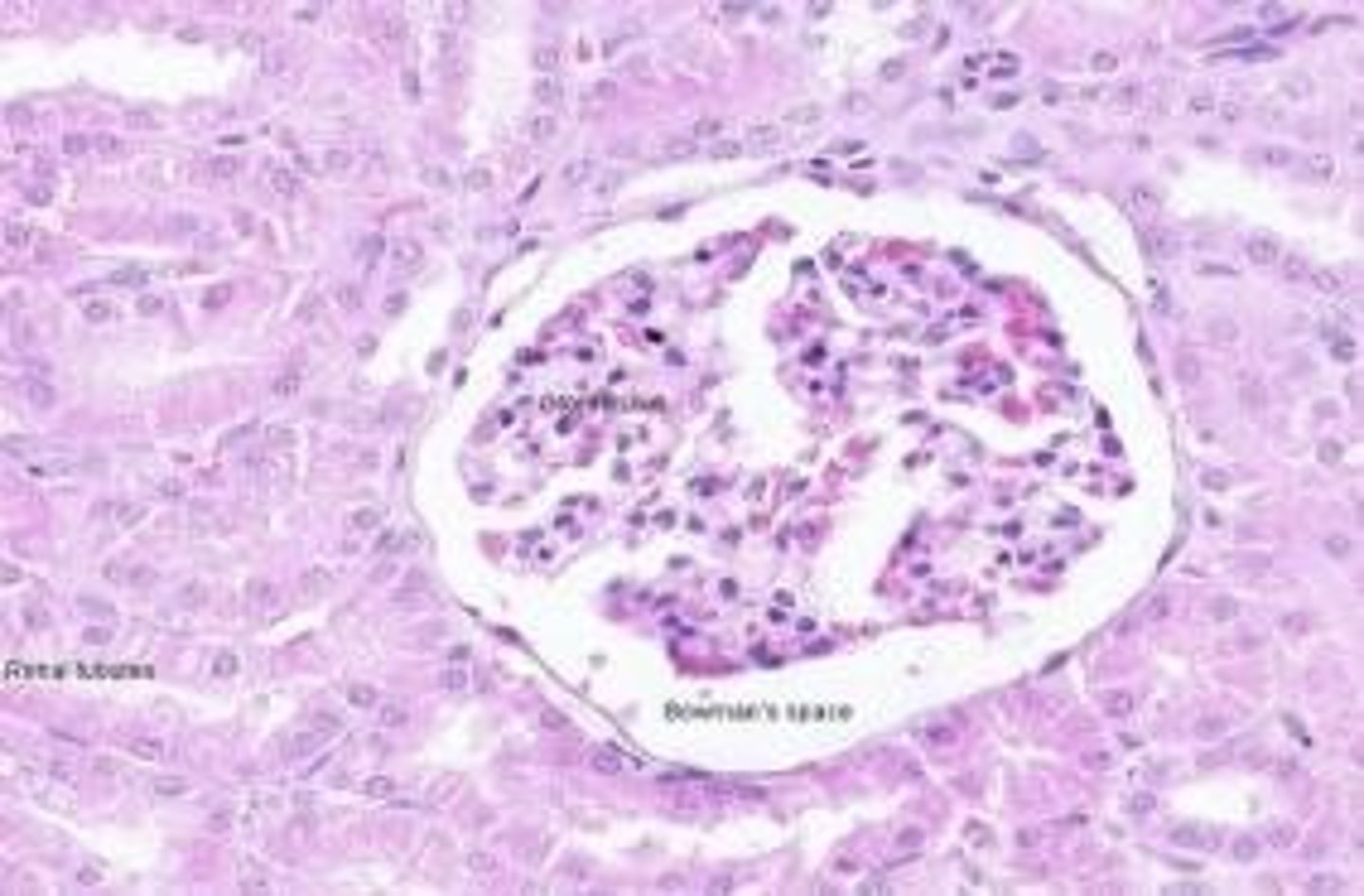
What is the primary function of the proximal convoluted tubule in the kidneys?
To reabsorb useful substances and concentrate waste.
Where would you expect to find keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium?
Skin over the dorsal aspect of the head.
What type of gland is a nasal secretory gland?
Acinar.
How are cells attached to the basement membrane?
Hemidesmosomes.
What type of secretion do sebaceous glands undergo?
Holocrine.
What type of muscle are arrector pili muscles?
Smooth muscle.
Which two cell types live in the epidermis but cannot be identified on light microscopy?
Merkel cells and Langerhans cells.
What is the primary composition of the primary dermal lamina?
Collagen.
What is the primary composition of the primary and secondary epidermal lamina?
Keratin.
What are the layers of the epidermis from top to bottom?
Stratum corneum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, stratum basale.
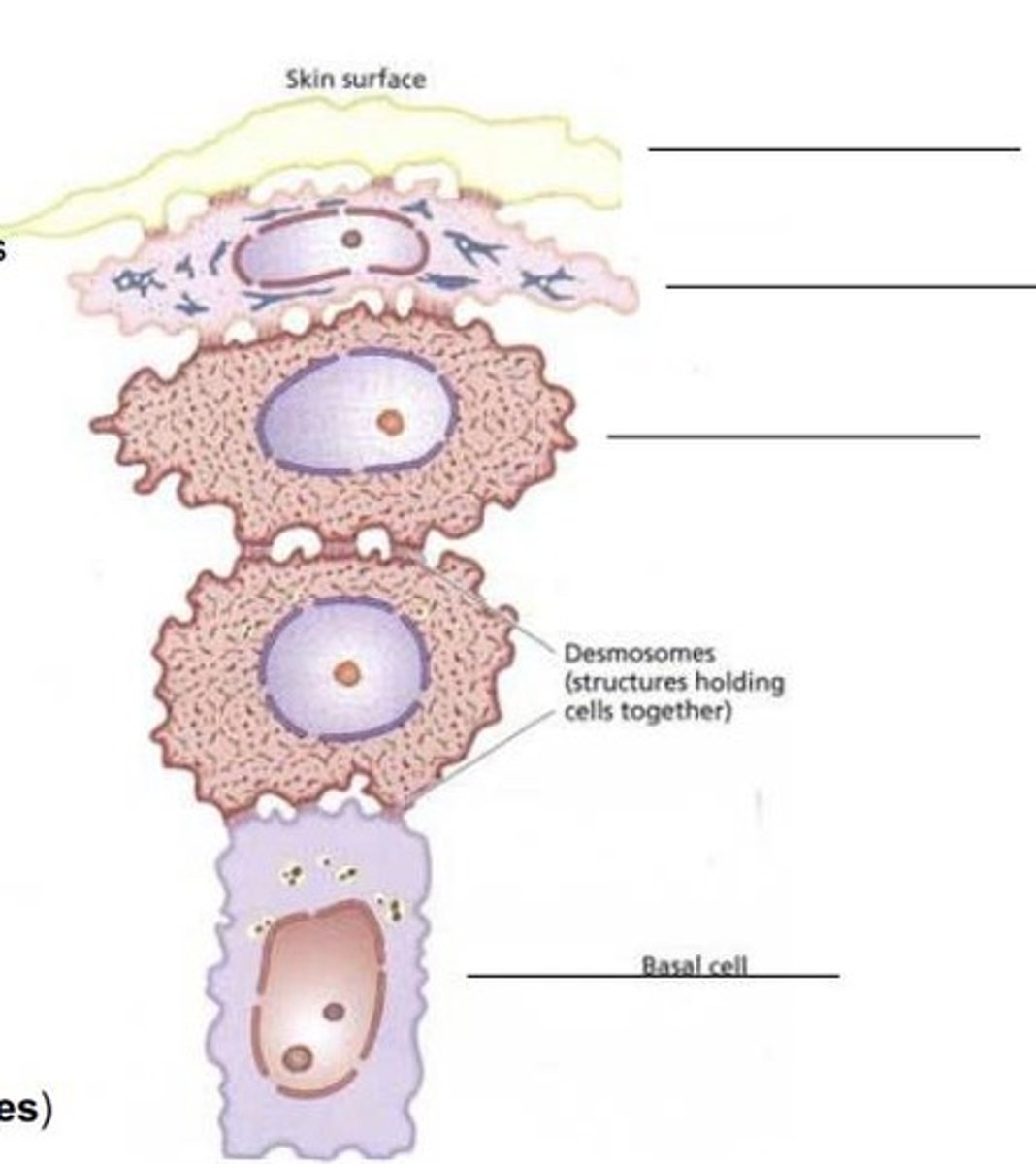
What is the function of melanocytes in the stratum basale?
To make melanin and pass it onto adjacent keratinocytes.
What is the role of Langerhans cells in the epidermis?
Similar to macrophages, involved in immune response.
What does the epidermis lack?
Blood vessels and lymphatics.
What is the function of the subcutaneous tissue?
Energy storage, thermoregulation, protective padding, and maintaining surface contours.
What type of secretion do ceruminous glands produce?
Cerumen, an important part of ear wax.
What is the function of the thoracic duct in the lymphatic system?
To empty lymph into large veins near the heart.
What are the primary lymphoid organs?
Bone marrow and thymus.
What are the secondary lymphoid organs?
Lymph nodes, spleen, and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT).
What is the difference between primary and secondary lymphoid follicles?
Primary follicles are immunologically inactive, while secondary follicles are immunologically active with a germinal center.
What is the structure of lymph nodes?
Organized into a cortex and medulla, with lymphoid nodules surrounded by diffuse lymphoid tissue.
What is the composition of the spleen?
White pulp (dense aggregates of T lymphocytes) and red pulp (highly vascular with red blood cells).
What is the function of the thymus?
Production of T cells.
What is the structure of the heart's endocardium?
Simple squamous epithelium, similar to blood vessels.
What type of arteries are the aorta and its largest branches?
Elastic arteries.
What type of arteries are medium-sized arteries with muscular tunica media?
Muscular arteries.
What is the function of capillaries in the circulatory system?
Where oxygen, nutrients, and carbon dioxide diffuse.
What is the primary function of veins?
To carry blood back to the heart, often with valves for one-way flow.