Economics: market equilibrium & price mechanism
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Markets
The interaction of consumers (demand) and sellers (supply).
Competitive market equilibrium
The amount supplied is equal to the amount demanded.
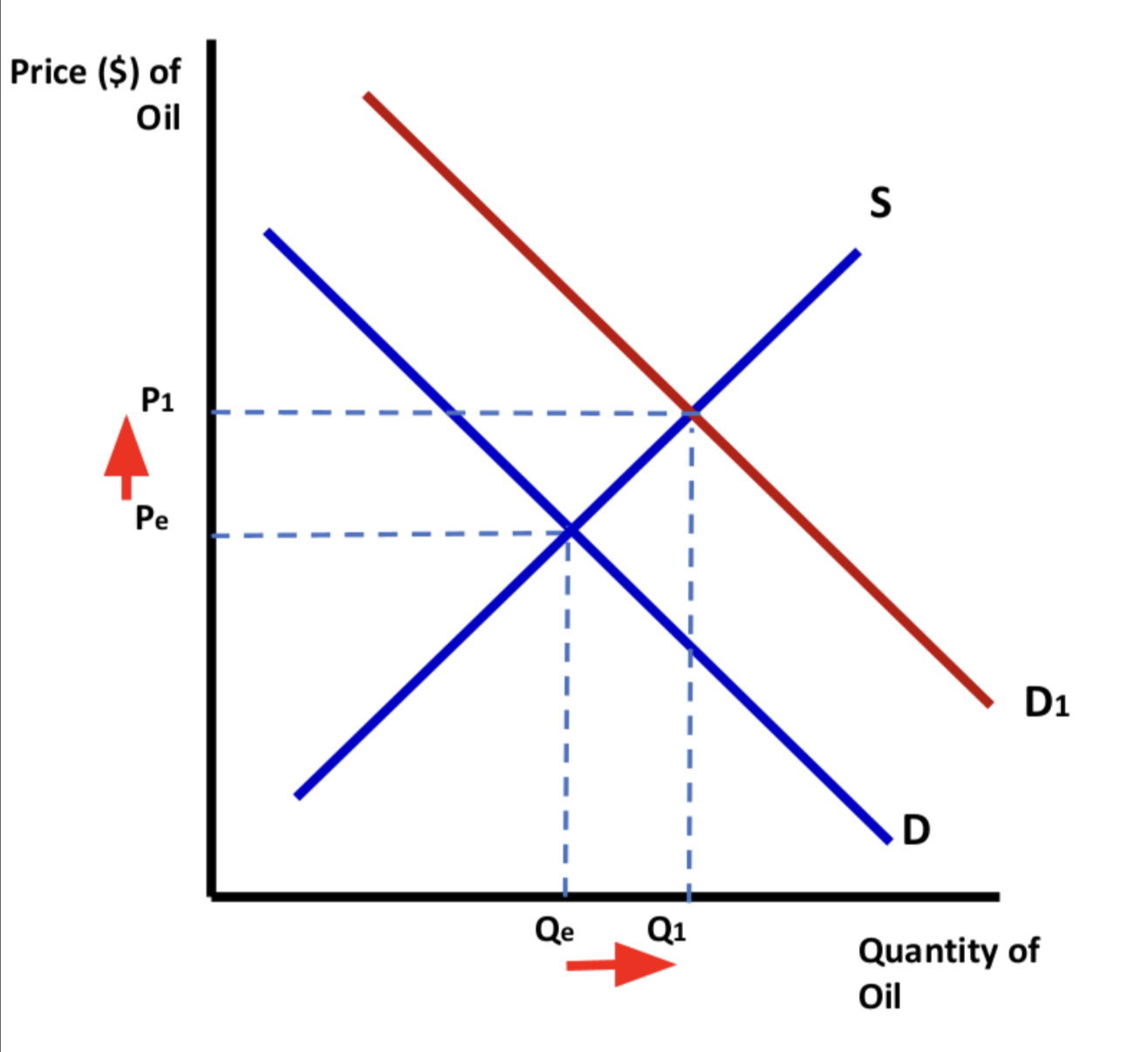
Graph: What will the graph look like with an increase in demand for reasons other than price?
The demand curve will shift to the right. A new market equilibrium price and quantity is formed.
Graph: What will the graph look like with an increase in supply for reasons other than price?
The supply curve will shift to the right. A new market equilibrium price and quantity is formed.
Disequilibrium in the market
The quantity buyers want (demand) doesn’t match the quantity sellers offer (supply) at the current price, creating either a shortage (excess demand) if the price is too low, or a surplus (excess supply) if the price is too high. It prevents the market from reaching equilibrium, where demand and supply are equal.
Functions of prices in a market
Signalling function - to determine how resources should be allocated
Rationing function - to reduce the demand for scarce resources
Incentive function - to change the behaviour of consumers and producers
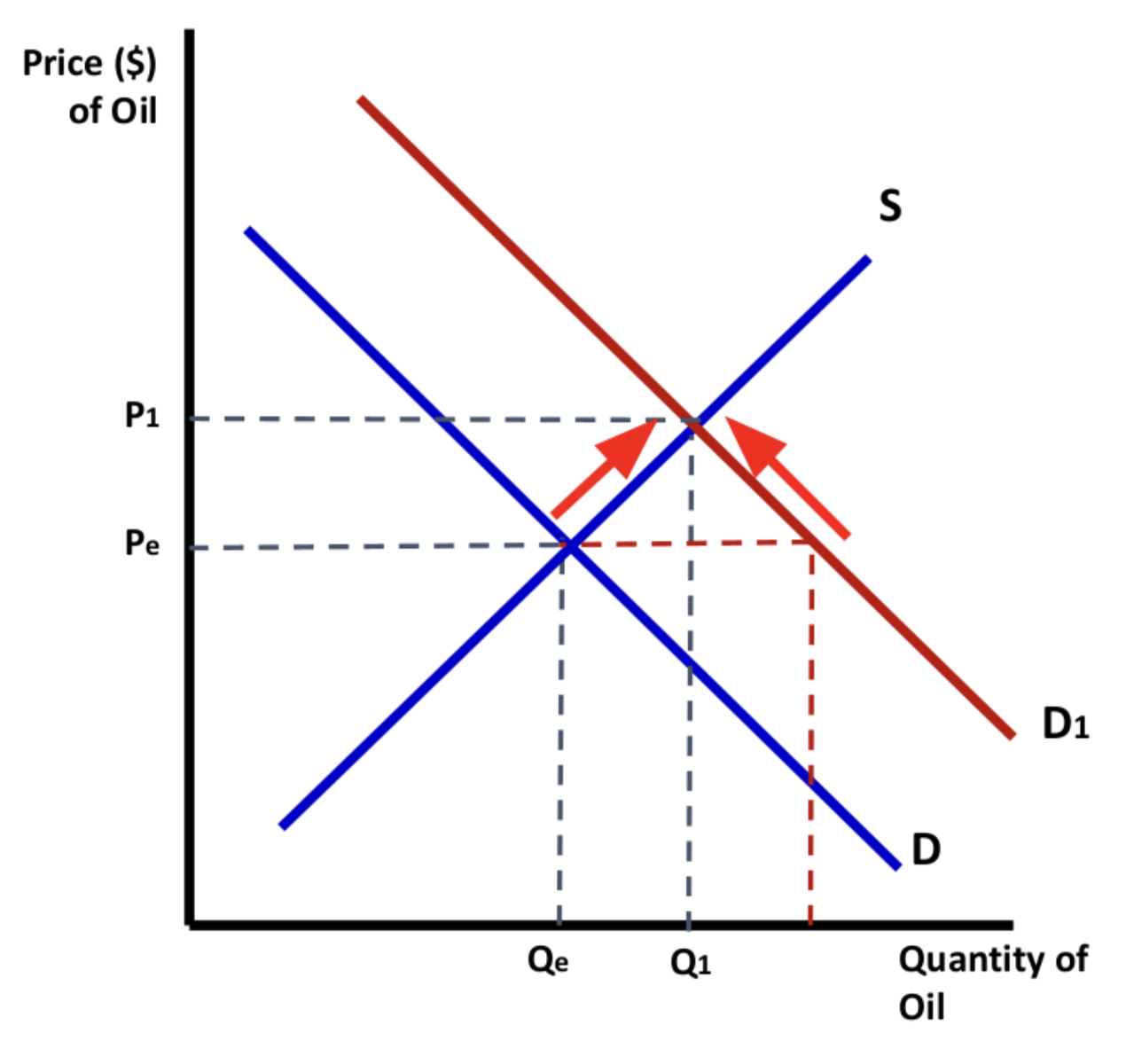
Graph: EXPLAIN what happens when theres an increase in demand for reasons other than price (market equilibrium).
An increase in demand —> shift the demand curve to the right —> causing disequilibrium and excess demand at Pe —> excess demand signals suppliers to increase the price —> increased prices reduce quantity demanded, through the rationing function of prices. New market equilibrium price and quantity formed.
Price gouging
The practise of increasing the prices of goods, services, or commodities to a level much higher than is considered reasonable after a demand or supply shock.
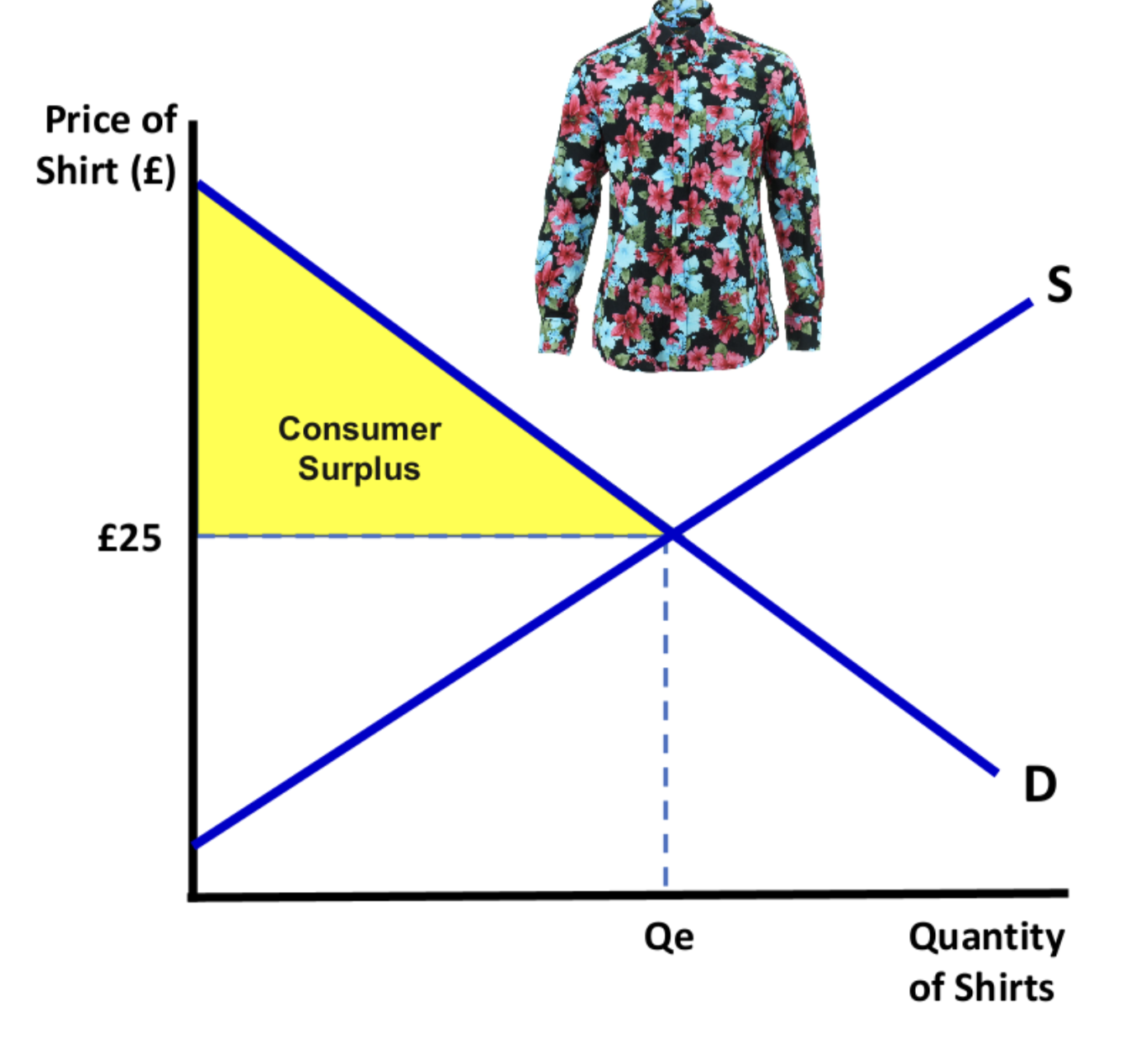
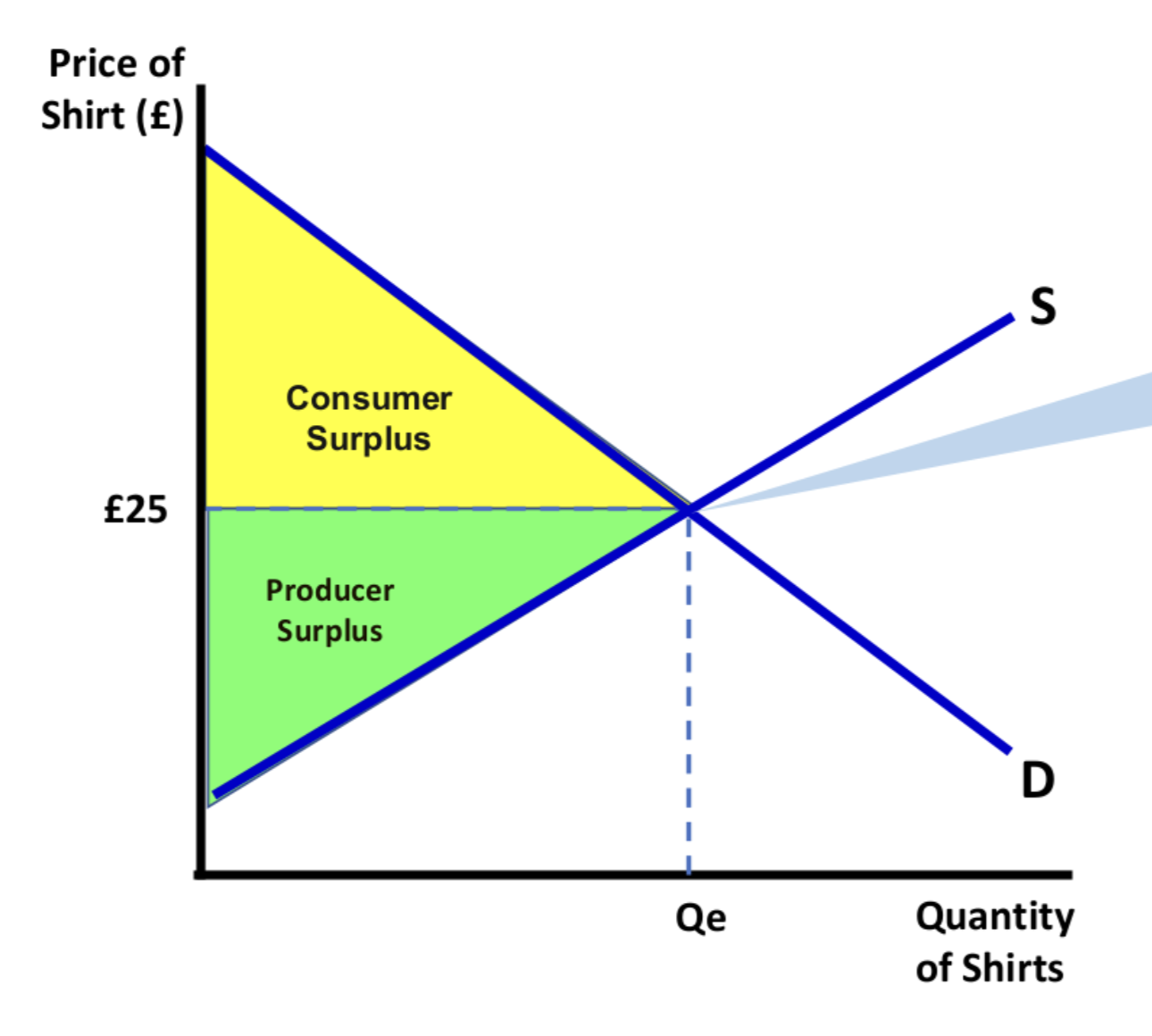
Consumer surplus
The difference between what a consumer is willing to pay for a good and the price they actually pay.
Economic welfare
Measured using the concepts of consumer and producer surplus.
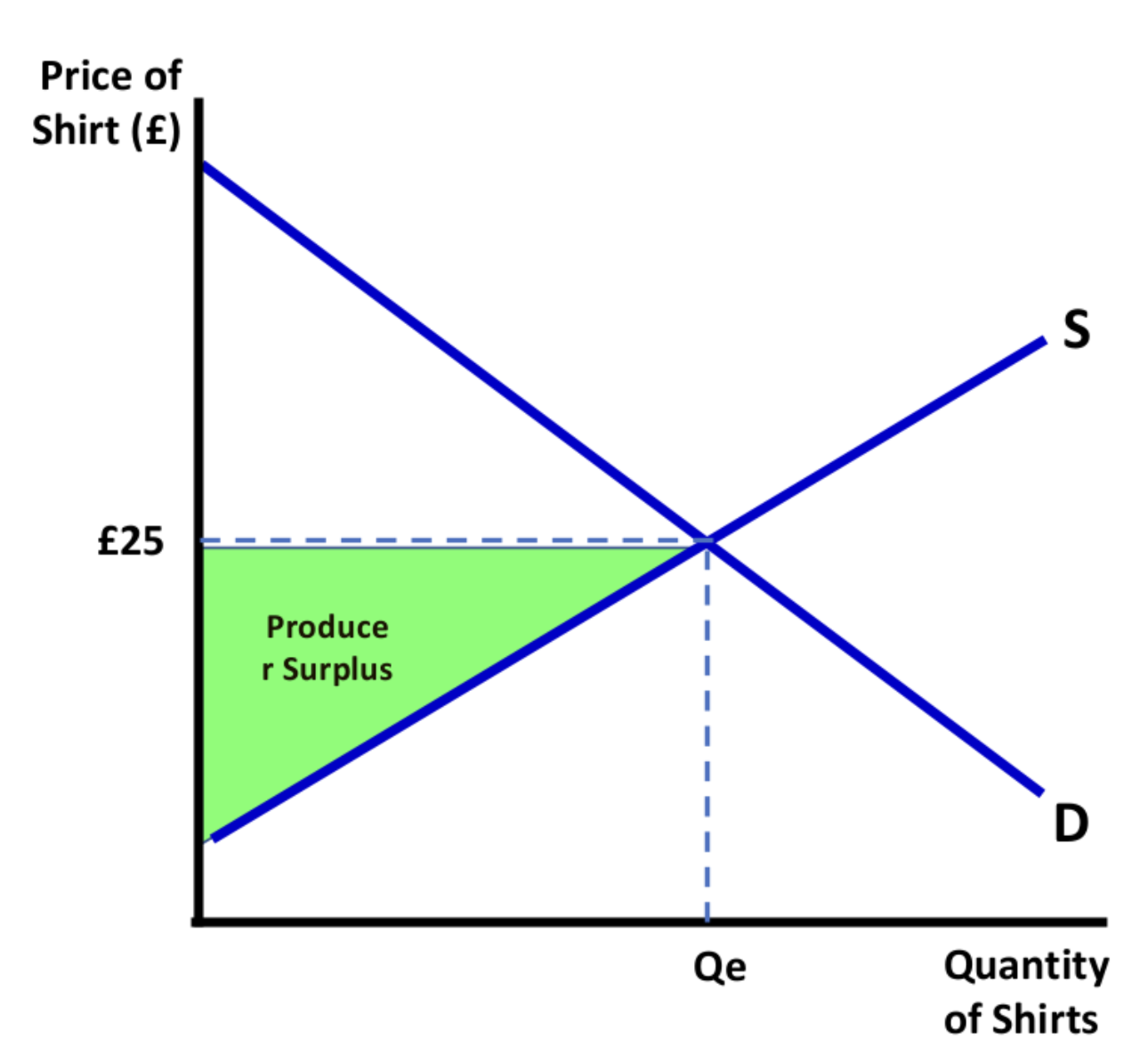
Producer surplus
The difference between the price a firm would be willing to receive for a good and the actual price they receive.
Graph: Where is producer surplus?
Graph: Where is consumer surplus?
Graph: Where is the community surplus?
Stakeholders
An individual, group, or organisation that can affect or be affected by economic activity.