Genetics - Lecture 21: Evolutionary & Population Genetics
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
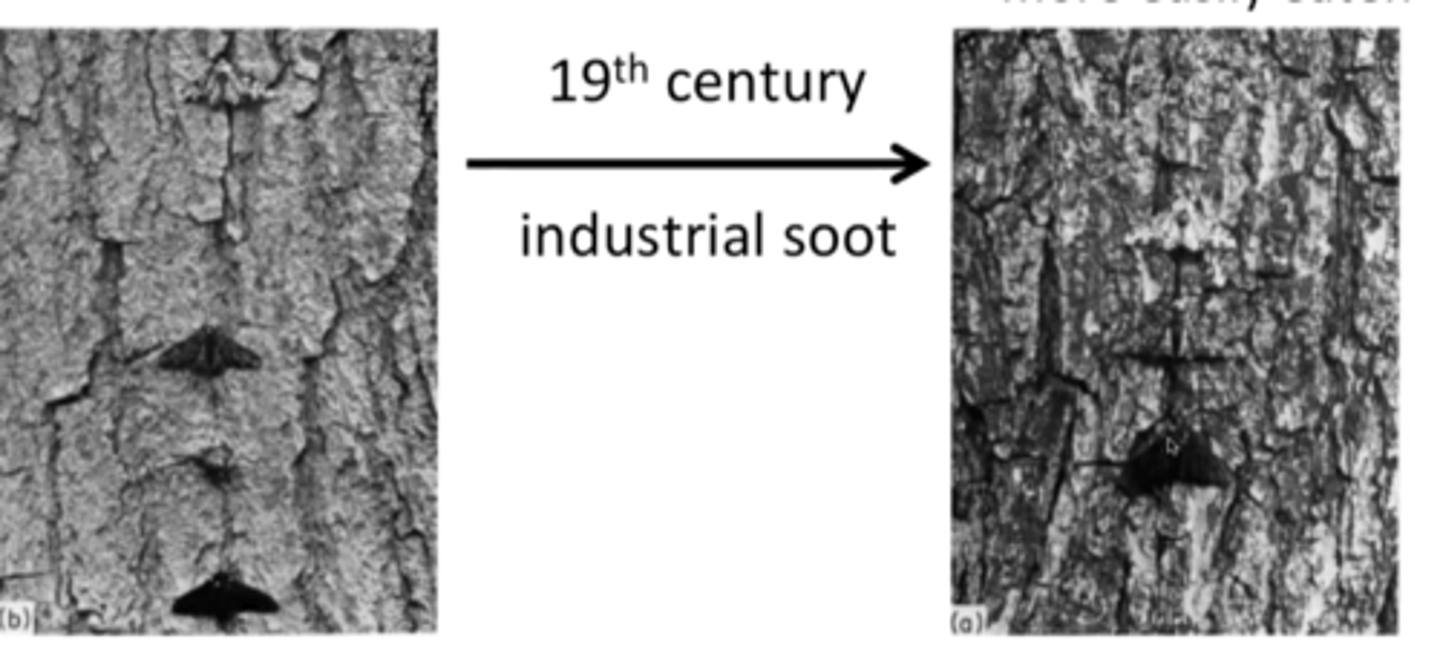
Industrial melanization
before industrial revolution, light colored moths were better suited for their environment - after industrial revolution, dark colored moths were favored
p frequency
frequency of dominant allele in a population
q frequency
frequency of recessive allele in a population
q^2
frequency of homozygous recessive
p^2
frequency of homozygous dominant
2pq
frequency of heterozygous genotype
For what traits is the Hardy-Weinberg Law invalid?
traits that affect reproductive fitness
Positive selection
natural selection that increases the frequency of a favorable allele
Negative selection
natural selection that decreases the frequency of a harmful allele
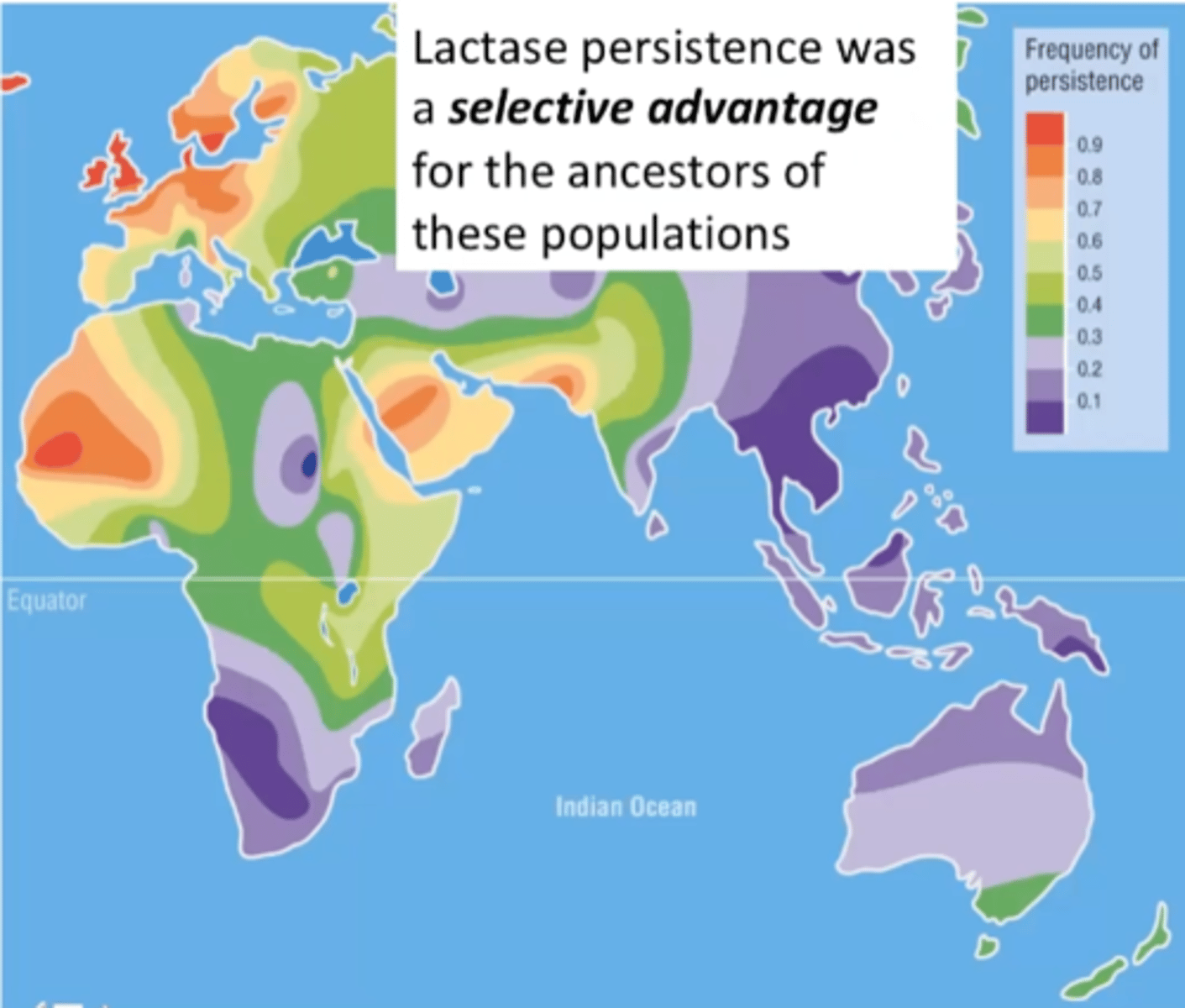
Example of selection in evolution
lactase persistence
Balancing selection
heterozygote has the advantage
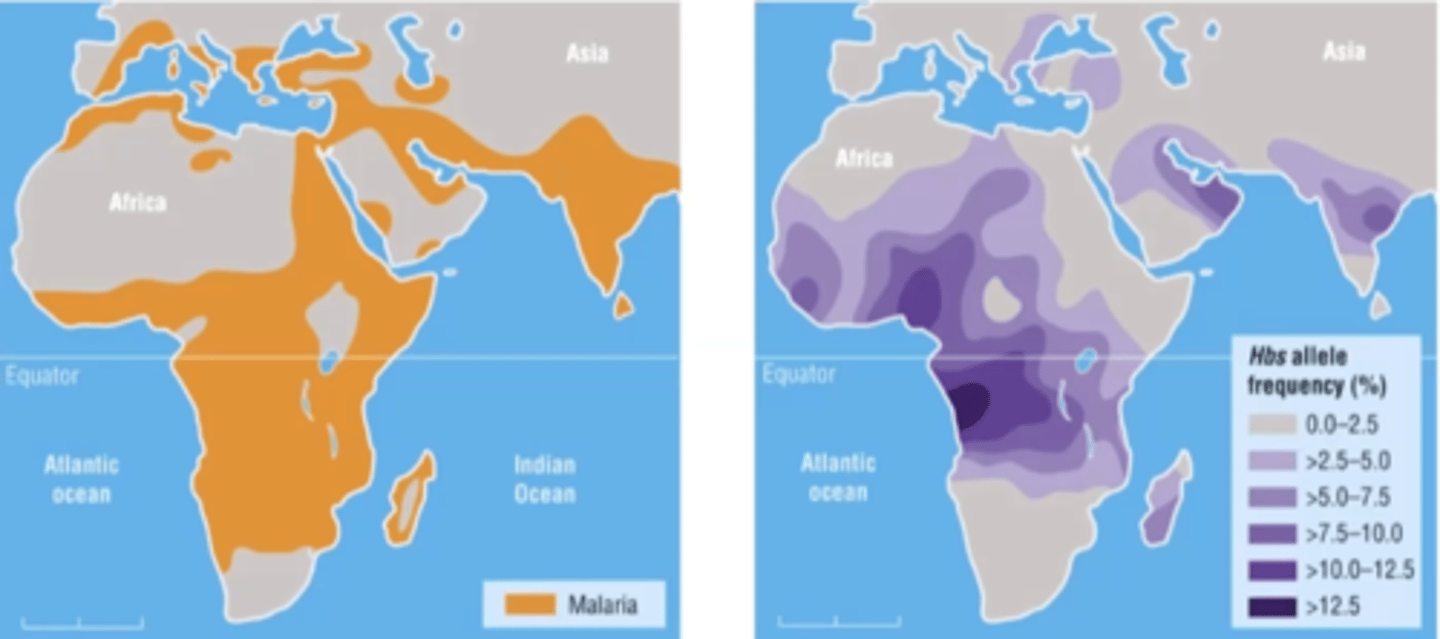
Example of balancing selection
sickle cell anemia
Alleles that do not affect fitness
allele frequencies will stay the same from generation to generation
Genetic drift
A change in the allele frequency of a population as a result of chance events rather than natural selection.
Bottlenecks
the effective population becomes smaller, increasing the chances of skewing allelic frequencies from their "natural" values
Causes of bottlenecks
- migration
- catastrophe
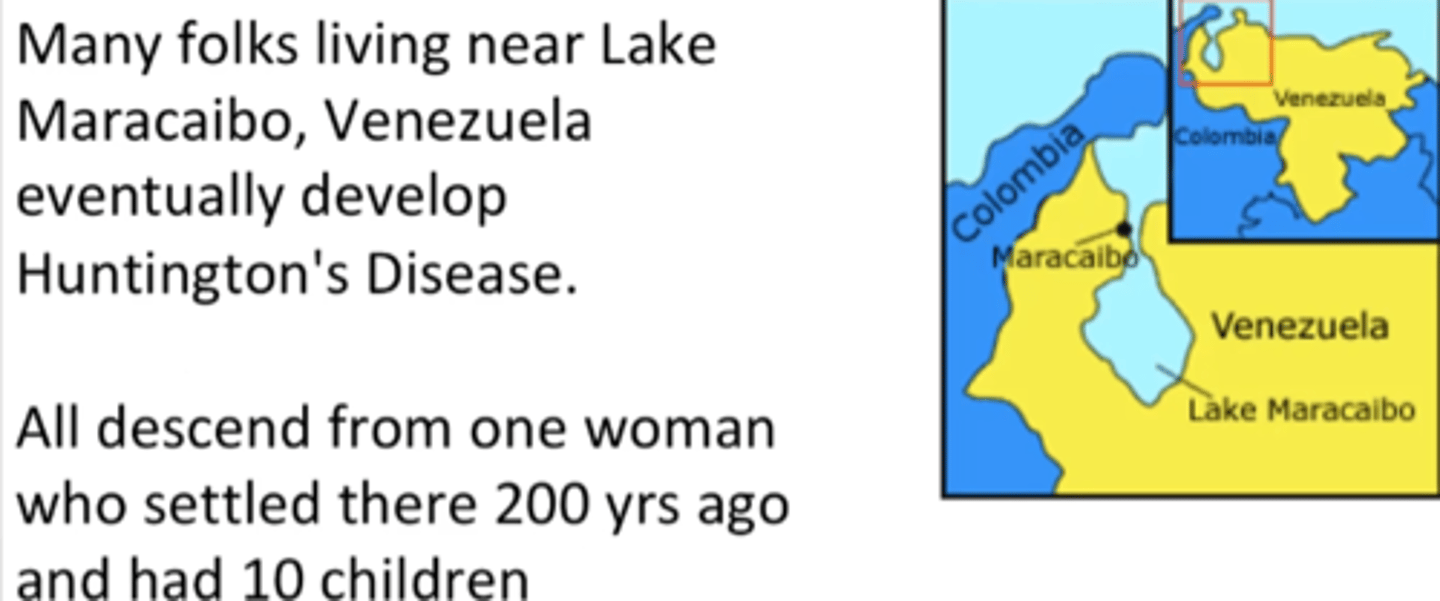
Founder effect
A genetic bottleneck caused when a small group arrives in a new place
Disease that the Founder effect was useful in studying:
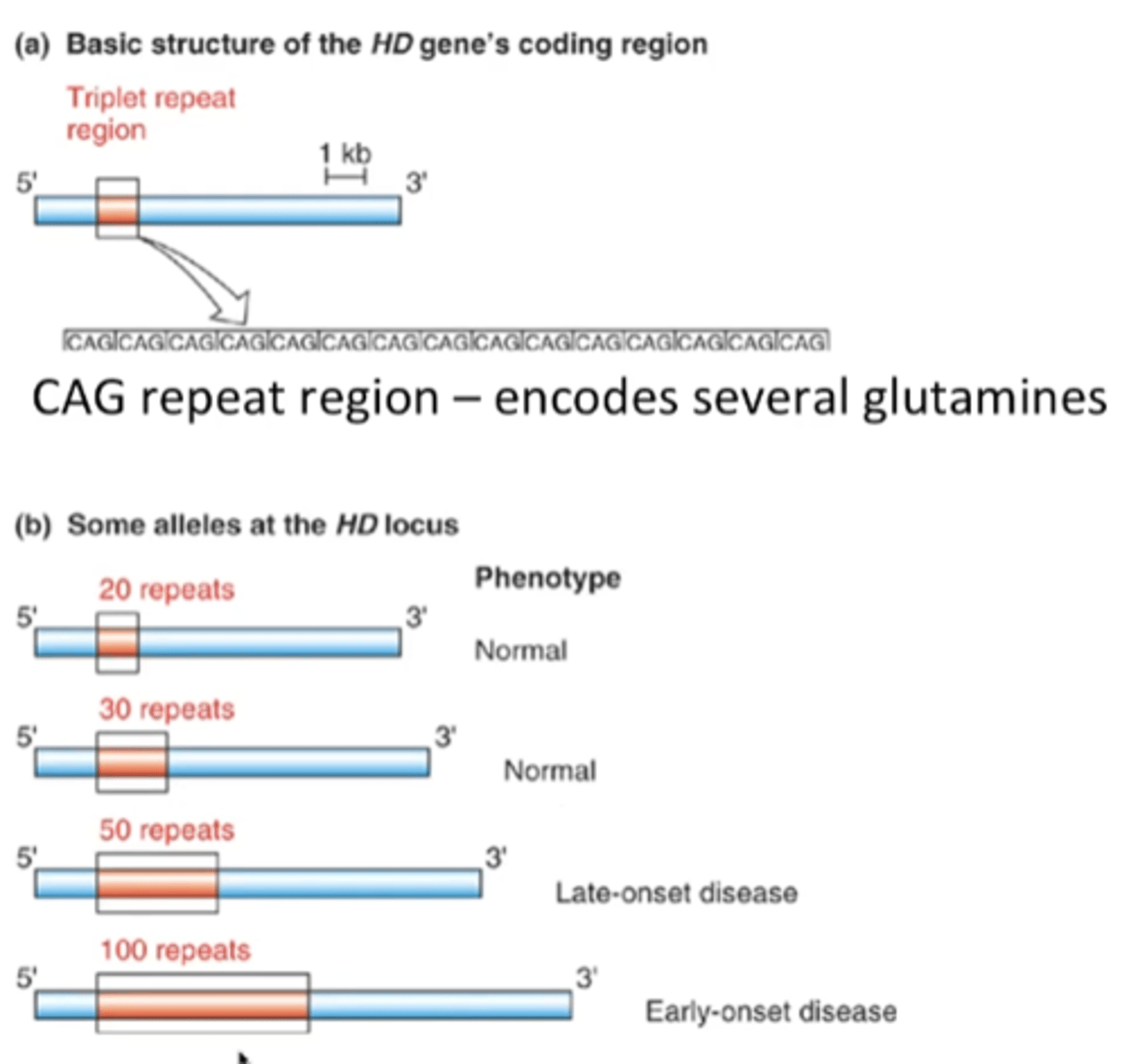
Huntington's disease
Repeat region disease
(Huntington's) variable repeated segments in the protein coding region of a gene - different number of repeats determines phenotype and time of onset
ALX1 gene
Gene for a transcription factor that affects the beak development associated with beak shape in Darwin's finches
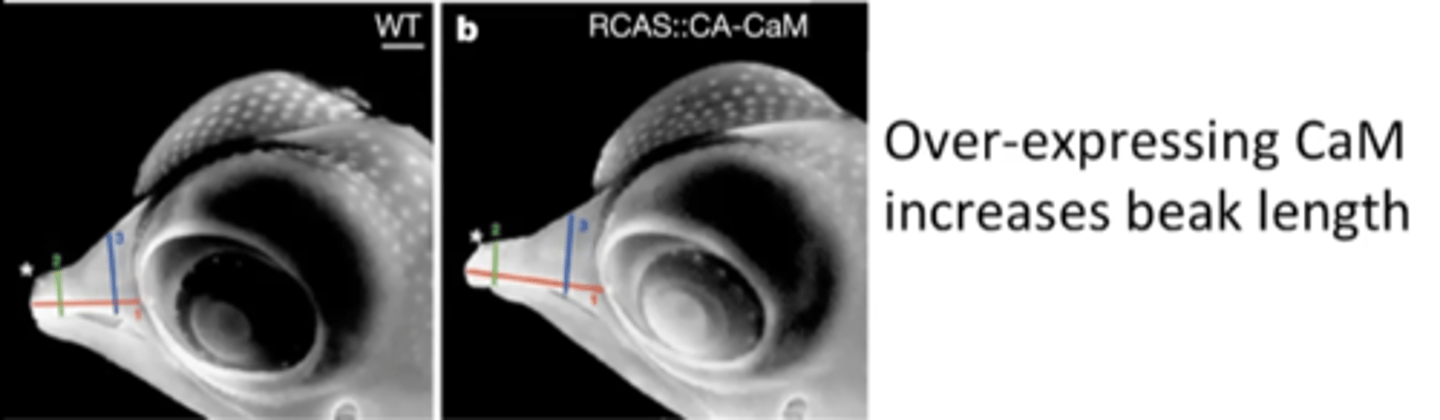
CaM
protein that affects beak length
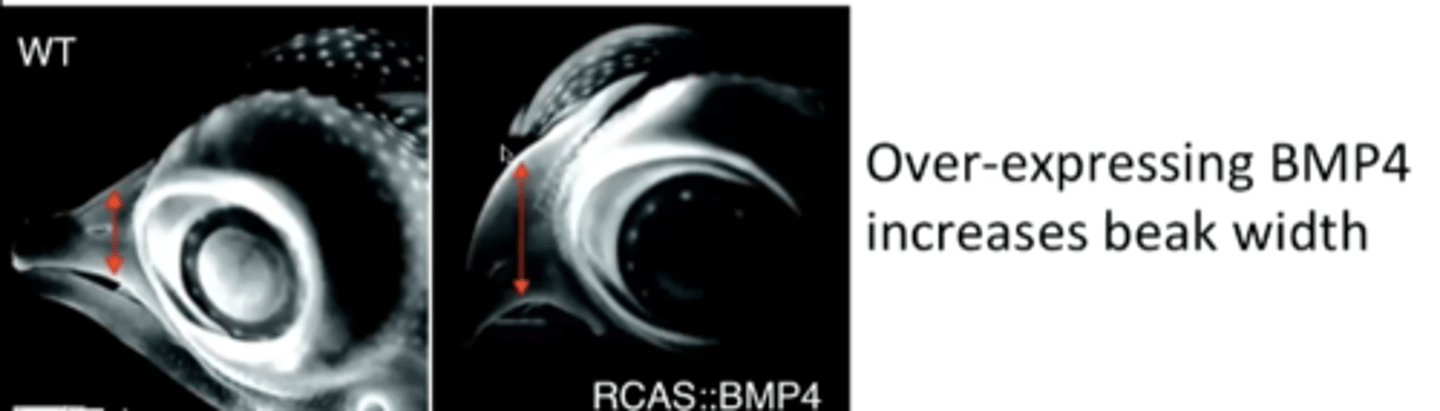
BMP4
protein that affects beak width
Genetic algorithms
represent solutions to complex problems as chromosomes
Start of a genetic algorithm
begin with a population of random solutions and allow them to recombine with each other based on fitness
Brute force solution
Consider all potential solutions and select the correct one - too many combinations
Steps of a genetic algorithm
- create a population of different combinations
- score the fitness for each combination
- mate combinations with each other
- repeat until no more improvements occur
Convergence
no more improvements by mutation