Lecture 2 | Neuroanatomy | Silk
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
what is the somatic system in charge of?
voluntary muscles
what is the autonomic system in charge of?
organs and glands
-sympathetic division & parasympathetic division
what is typical of sympathetic division?
dominates during time of stress
fast heart rate, elevated blood pressure, adrenaline, increased blood flow to skeletal muscles
what is typical of the parasympathetic division?
dominates when energy needs to be conserved and stored
increased salivation, digestion, slows heart rate and decreased respiration
what are the layers of the meninges?
outer: Dura mater < arachnoid mater < pia mater
what is important about the BBB when it comes to pharmacological implications?
need lipophilic small molecules
t/f all areas of the brain are supplied by the same arteries
false
different areas of the brain are supplied by different arteries
Structure of the neuron
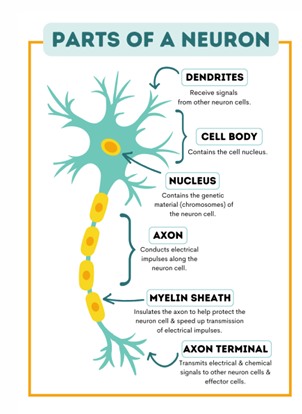
what are the amino acid neurotransmitter?
GABA, glutamate, glycine
what are the monoamine neurotransmitter?
dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin
what are the neuropeptide neurotransmitter?
substance P, endorphins
what does UP, DOWN, and AROUND
UP: sensory neurons
DOWN: motor neurons
AROUND: interneurons
what do sensory neurons do?
convert physical stimuli into electrical signals
what do motor neurons do?
direct biobehavioral response appropriate for the situation
what do interneurons do?
form interacting neural circuits
responsible for conscious sensations, recognition, memory, decision-making, cognition
what makes up the brainstem?
Midbrain
Pons: relay of signals, involvement in sleep and respiration
Medulla Oblongata: regulation of cardiovascular and respiratory systems, reflex centers
what is the reticular formation?
modulates consciousness
what is substantia nigra
key in dopamine synthesis
what is the cerebellum?
the back brain
receives input from proprioceptive pathways and the motor cortex
important in balance, coordinationof limb position and movment
what is the thalamus responsible for?
major relay center for sensory and motor signals
what is the hypothalamus responsible for?
key regulator of autonomic and endocrine functions such as temperature, hunger, thirst, and circadian rhythms
what is the epithalamus (pineal gland) responsible for?
secretes melatonin
what is the role of basal ganglia?
regulation of voluntary movement, habit formation, and reward pathways
what are the major structures in the limbic system?
hippocampus
amygdala
cingulate cortex
septal nuclei
what are the functions of the limbic system?
emotion, memory, motivation and olfaction, also the reward pathways
what are the lobes of the cortex?
Frontal
Parietal
Temporal
Occipital
Insular
what are the cholinergic system pathways?
Nucleus Basalis of Meynert → cortex
helps in cognition and memory; relevant to alzheimers
what are the dopaminergic systems?
nigrostriatal : relevant to movement control
mesolimbic/mesocortical: relevant to reward, cognition
tuberoinfundibular : relevant to pituitary hormone regulation
what are the noradrenergic pathways?
Locus Coeruleus → widespread cortical projections
relevant to vigilance and arousal
what are serotonergic pathways?
Raphe Nuclei in the brainstem
relevant to depression, migraines, hallucinogens
What are GABAergic pathways?
major inhibitory neurotransmitter
what are Glutamatergic pathways?
major excitatory neurotransmitter
target of NMDA antagonists