Plant reproduction
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What helps plants attract insects
Bright petals
Contain nectar
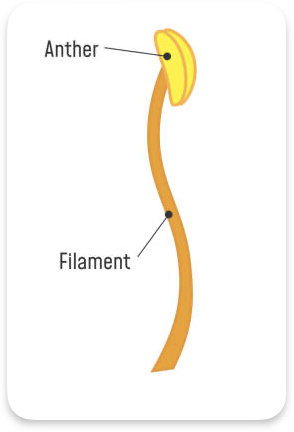
Stamen
Male part
Anther - Produce pollen
Fillament
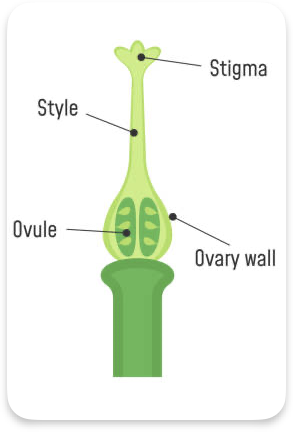
Carpel
Female part
Stigma - pollen attaches
Ovary - Produces female gametes
Ovule - contains female gamete
Style - connect stigma to ovary
Pollination
Transfer of pollen fro anther to stigma
2 types of pollination and how
Self-pollination - Own pollen lands on own stigma
Cross-pollination - receive pollen from different plant of same species
What contain the male and female gametes
Male - pollen grain
Female - Ovules
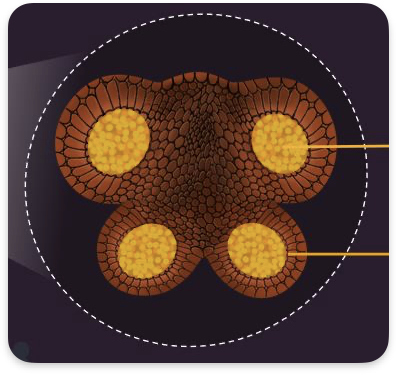
What are the orange bits + describe pollen grain formation
Pollen sacs - Mother cells undergo meiosis to produce 4
Each one then mitoses to form pollen grain with generative and tube nucleus
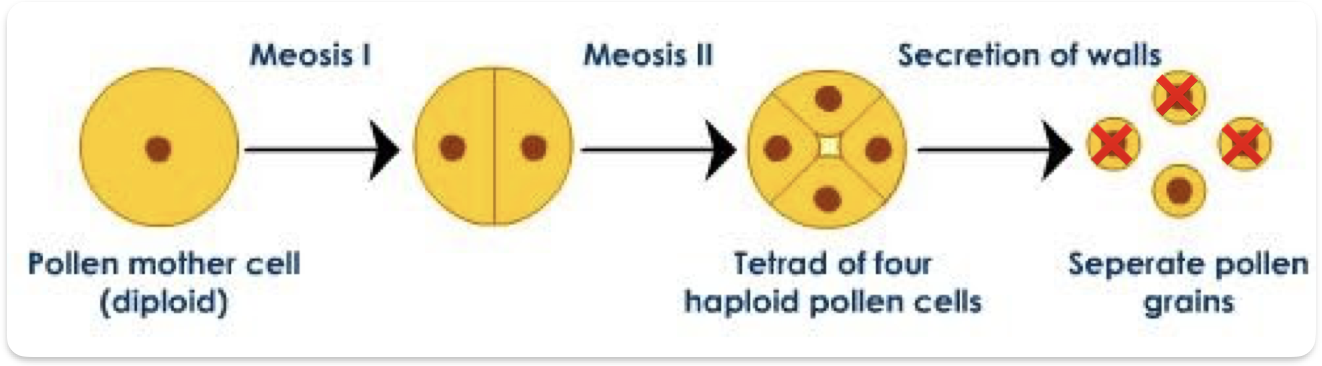
How are female gametes produced
Mother diploid cell (megaspore) undergoes meiosis to produce 4 haploid cells from inside ovule
3 degenerate leaving 1 remaining
Mitoses 3 times to produce Embryo sac with 8 nuclei
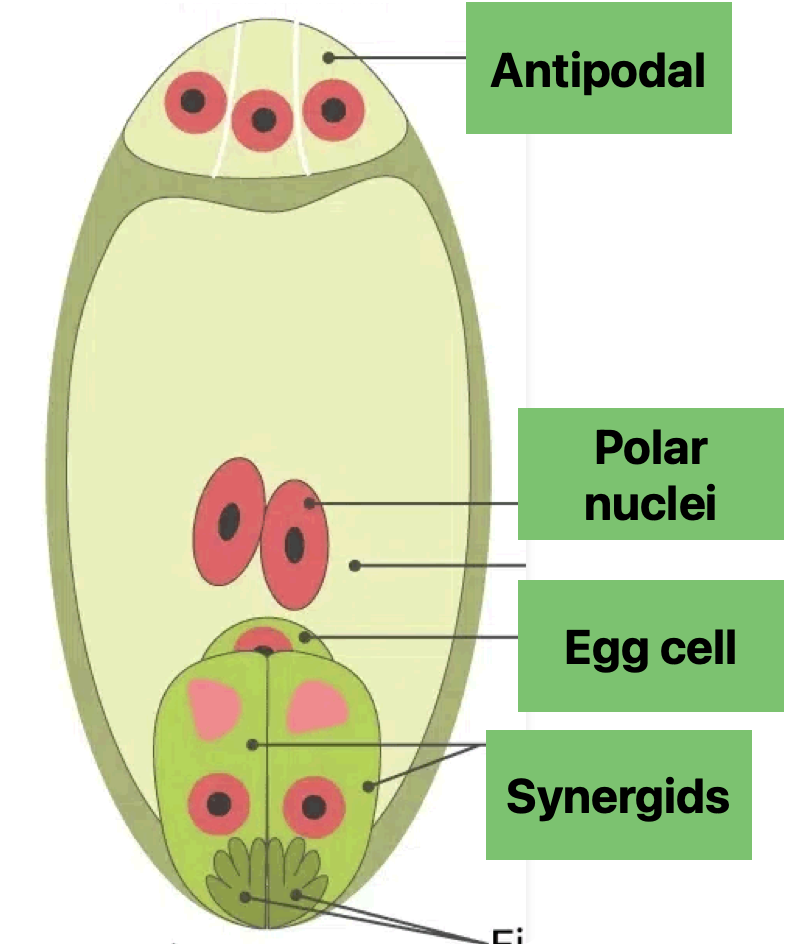
What do the 8 nuclei become in the female embyro sac
2 synergids
1 Ovule
3 antipodal cells
2 free polar nuclei
Describe pollination
When pollen lands on the stigma - pollen tube nucleus controls growth of pollen tube
Generative nucleus undergoes mitosis to produce 2 sperm nuclei
Pollen tube make way to micropyle - tube nucleus degenerates
Micropyle
Entrance to ovule (bottom)
Describe fertilisation once sperm nucleus enter the micropyle
First one Fuses with egg cell to form zygote
Other one fuses with 2 free polar nuclei to make triploid endosperm
Zygote eventually develops into an embryo and grows into new plant
How does germination happen in monocotyledon
Water absorbed through micropyle
Gibberellin stimulates growth of aleurone layer
This causes amylase and maltase to be synthesised
these break down starch from endosperm to use glucose for respiration
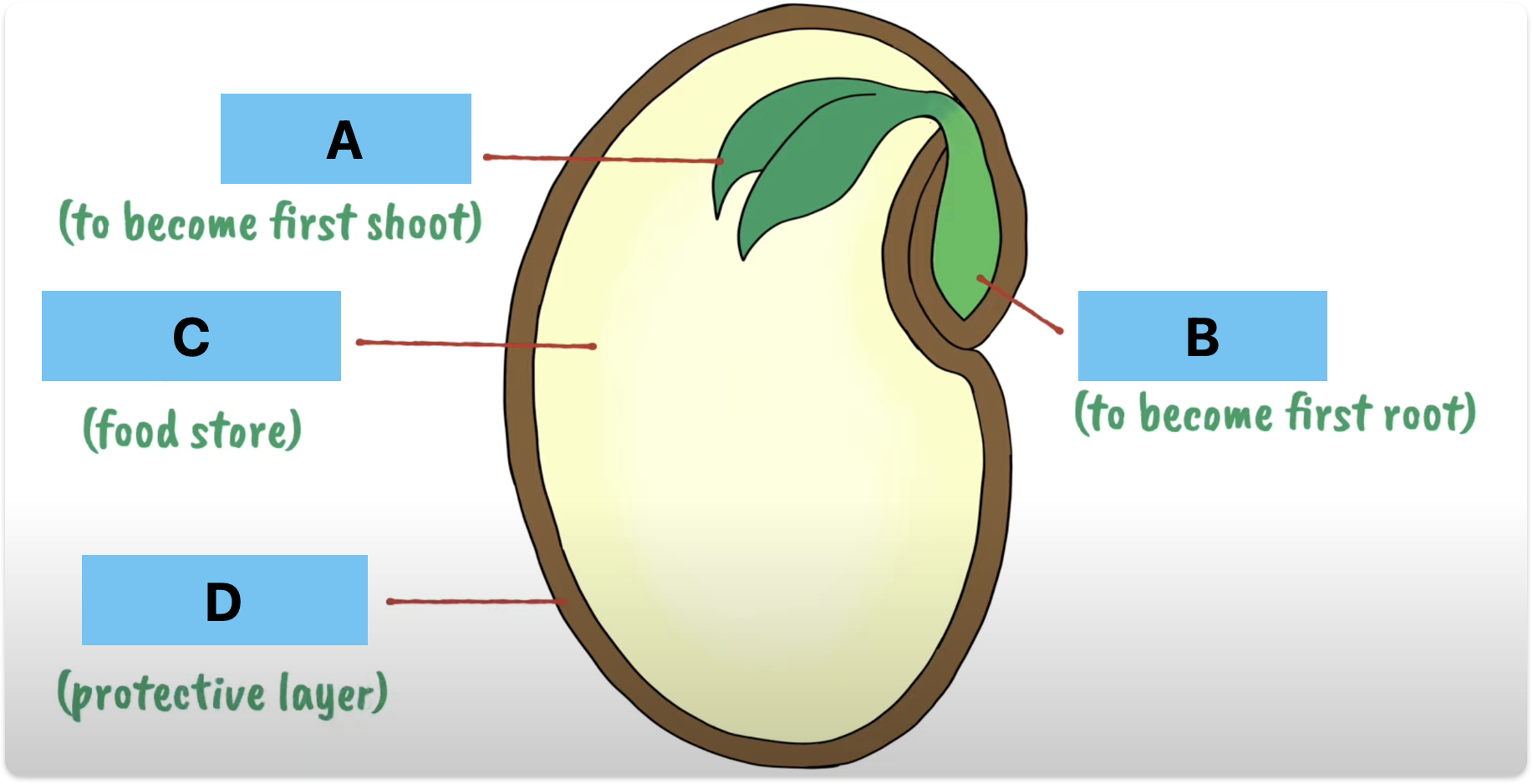
Label A-D + function
Plumule - become first shoot
Radicle - become first root
Cotyledon - Food store
Seed coat
What 3 thing do you need for germination
O2
optimum temperature
water
Ovary
Contains ovules and develops into fruit
Ovule
Eventually form seeds
fucking
unnecessary
Parts of a seed (5)
Embryo - living part
Radicle - grows root
Plumule - grows young root
Food store - Reserve of food which supplies embryo
Testa - seed coat
Types of seeds (2)
Monocotyledon - maize
Dicotyledon - broad beans
Conditions needed for growth of seeds
Water
Oxygen
Warmth
Cotyledons
Starch stores
Describe seed germination
Seeds absorb water through micropyle
cotyledon swell and testa split allowing for entry of oxygen
Gibberellin produced and diffuses into aleurone layer
Induces synthesis of amylase
which breaks down starch form endosperm into maltose
maltose then used for aerobic respiration and grow
Radicle
grows down from cotyledon to form roots
Plumule
Grows up from cotyledon
What is the meristem
Growing point of a plant