Psychology Lecture 7: Visual Acuity & VEP Terms Study Set
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Infants prefer to fixate on ...
faces or complex patterns
Forced choice preferential looking
- acuity is the spatial frequency that produced ...
75% correct by the observer
Forced choice preferential looking
- strengths
- infant views a large number of trials of short duration
- little observer bias--only child can see grating
- allow acuity estimate for individual infant
Forced choice preferential looking
- Limitations
- limited usefulness in clinic setting b/c need at least 60 trials to determine acuity
Operant Forced preferential looking explain
every time child looked at grating, they were rewarded somehow
Humans vs monkeys Forced preferential looking acuity values at birth?
they show similar acuity values
From Snellen degree, cyc/deg, how to get Acuity in 20/x format?
600/Snellen Degree
For humans with FPL, acuity in cyc/deg is roughly numerically equal to ...
age in months for human infants
For monkey infants with FPL, acuity in cyc/deg is roughly numerically equal to ...
age in weeks for these infants
Method of constant stimuli def
same size in random order
(FPL) Preferential looking 3 procedures
- method of constant stimuli
- staircase procedures
- acuity card procedure
1 octave= what?
doubling cyc/deg by 2 (like going from 3-->6 cyc/deg which is equivalent to going from 20/200 to 20/100)
Inter-ocular difference is what?
<1 octave
how can monocular PFL measurements be useful?
determine if baby has amblyopia or not
Preferential looking development in premature infants -- explain
predictable from post term rather than postnatal
post term # months after birthdate minus # months premature
(example if infant born 1 month premature, 3 months postnatal; post-term = 2 months)
Preferential Looking Testing
- strengths
- non-invasive
- inexpensive
- applicable to several clinic populations (accessible)
Preferential looking limitations
- variability of PL results (accurate to only plus or minus 1 octave (3 lines in acuity)
- potential for observer bias
- grating acuity not the same as snellen acuity
Visual evoked potential (VEP)
- what is this?
- electrical signal generated in the occipital region of the cortex are measured in response to watching gratings change on screen
VEP waveforms vary according to ...
characteristics of the stimulus -- know that different patterns generate different signals
VEP amplitude difference in amblyopia to gratings vs luminance flashes
- gratings -- VEP amplitudes reduced in amblyopic eye compared to normal eye
- luminance flashes -- VEP amplitudes are the same in amblyopic and fellow eyes
VEP amplitudes trend as gratings get smaller?
amplitudes get smaller and smaller
With increasing spatial frequency, what happens to the VEP amplitude?
decreases
Adult like VEP waveform by when?
6 months
VA adult like by what age?
6 months
Spatial Frequency Sweep VEP
- explain how to do it
present 19 different spatial frequencies 10 sec each and then it's the linear extrapolation of VEP amplitude to zero uV for acuity estimate
Spatial Frequency Sweep VEP
- advantages
- increased sampling of VEP amplitude versus spatial frequency function
- repeated measures
- clinical applicability
Sweep VEP
- normal VA development -- what is it?
- VA improves rom 4.5 c/d (20/130) at birth to 20 c/d (20/30) by 8 months
Sweep Visual Evoked Potential
- clinical applications
- amblyopia
- media opacities
- cortical visual impairment
Pre term vs post term infants for VEP grating acuity difference and significance?
- pre term infants show much higher acuity than the post term infants during the first few months of life (goes away by 6-8 months of age) -- visual experience influences this
VEP testing
- strengths
- rapid test
- inter-ocular differences and confidence intervals are better than preferential looking
- grating acuity norms are higher than preferential looking
VEP testing limitations
- expensive
- need to train people how to use it
- grating acuity underestimates vision loss compared to snellen acuity
VEP, PL, and OKN acuity estimate differences -- why?
- they tap different visual mechanisms
VEPs measure what mechanisms in vision?
visual responses in early cortical processing
FPL techniques rely on ...
the whole infant's vision system
expect adult level VEP by what age? same with FPL?
12 months, and no, not with FPL
normal
what pattern of VA development
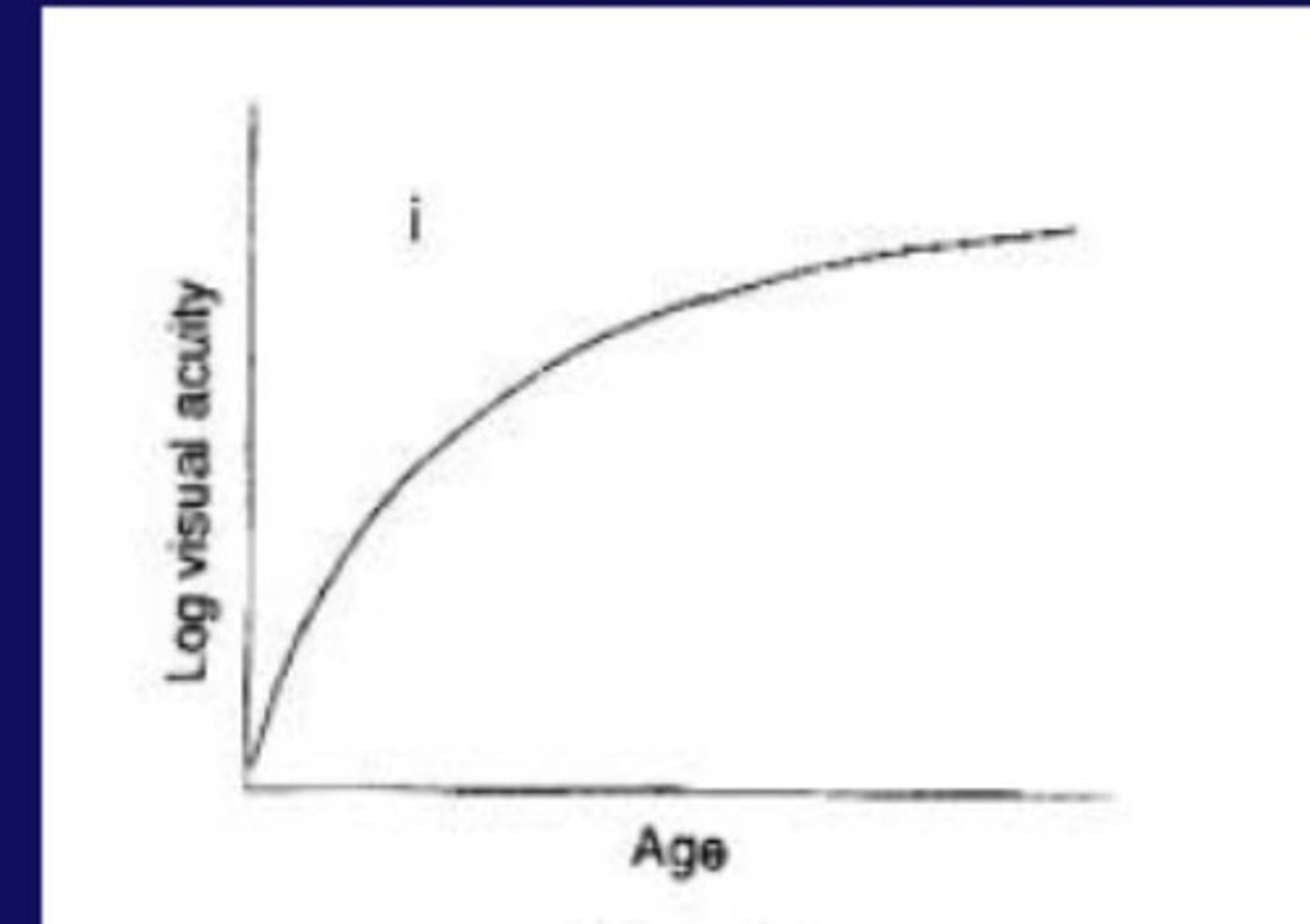
Do adult OKN acuity estimates agree with psychophysical estimates?
no