Neurobiology Exam 1
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
resting membrane potential
constant, negative voltage occurring when a neuron is at rest
receptor potential
graded change in membrane potential due to a sensory stimulus
synaptic potential
graded change in membrane potential due to a synaptic stimulus
action potential
activation of axons due to sensory or synaptic stimulus; frequency of firing reflects strength of stimulus
passive responses
graded changes in polarization that do NOT result in an action potential
passive conduction
signal decays as it travels along the axon
active conduction
signal remains constant as it travels along the axon
active transporters
move ions across the cell membrane against their natural gradient to maintain disequilibrium
ion channels
allow certain ions to move freely across the cell membrane towards equilibrium
resting membrane potential is determined by _____
K+ concentration
resting membrane is nearly impermeable to _____, so its concentration doesn’t really affect resting potential
Na+
electrochemical equilobrium
when electrical force across the membrane exactly balances the concentration gradient, causing ions to stay put
equilibrium potential
voltage at which a specific ion is at electrochemical equilibrium
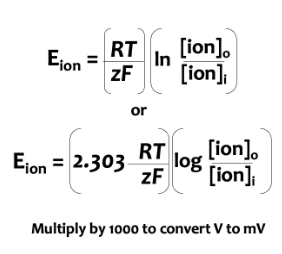
Nernst equation
used to predict an ion’s equilibrium potential
Goldman’s equation
used to predict an ion’s membrane potential when it is permeable to multiple ions
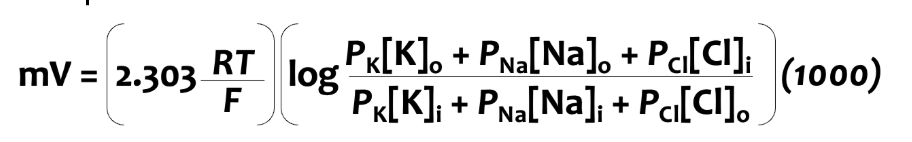
endoderm
interior germ layer; turns into digestive tract
mesoderm
middle germ layer; turns into skeleton & organs
ectoderm
exterior germ layer; turns into epidermis & nervous system
prosencephalon
forerunner subdivision that becomes the forebrain
mesencephalon
forerunner subdivision that becomes the midbrain; conserved areas include tectum & tegmentum; associated with cerebral aquaduct
rhombencephalon
forerunner subdivision that becomes the hindbrain
telencephalon
major subdivision formed from prosencephalon; conserved areas include olfactory bulb, pallium, & subpallium; associated with lateral ventricles & 3rd ventricle
diencephalon
major subdivision formed from prosencephalon; conserved areas include thalamus & hypothalamus; associated with 3rd ventricle
metencephalon
major subdivision formed from rhombencephalon; conserved areas include isthmus, cerebellum, & pons; associated with anterior 4th ventricle
myelencephalon
major subdivision formed from rhombencephalon; conserved areas include medulla; associated with posterior 4th ventricle
notochord
cylinder of mesodermal cells underneath the neural plate/tube responsible for inductive signals during neural development
neuroectoderm
section of ectoderm on neural plate above the notochord that will turn into the nervous system
neuromeres
segments of neural crest/tube that differentiate into distinct regions, determined by hox genes
endomembrane system
group of organelles (nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, ribosomes) that work together to modify, package, & transport lipids & proteins
glial cells
promote synaptogenesis and maintain neuronal signaling
astrocytes
form blood-brain-barrier on capillaries and maintain ionic environment
radial glia
guides migration of new cells, later differentiate into astrocytes
microglia
macrophages of the nervous system: phagocytic & cytotoxic
oligodendrocytes
form myelin sheaths around multiple axons in CNS & can impede injury recovery
ependymal cells
line the ventricles to produce & circulate CSF
schwann cells
form myelin sheath around single axons in PNS & aid in injury recovery
satellite cells
promotes cell survival in PNS & may maintain neuronal environment
subventricular zone astrocytes
type of glial stem cell that can form more stem cells, neurons, astrocytes, or oligodendrocytes
oligodendrocyte precursor cell
type of glial stem cell that mainly forms oligodendrocytes
Ohm’s law
I=V/R; I= current in amperes (coulombs per second), V= voltage in volts, R= resistance in ohms
V0
point of stimulus
λ (lambda)
where V0 decays to 37% of its value
V∞
steady state
T (tau)
time it takes to reach 63% of V∞