ANATOMY: Bones, Joints and Muscles
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Functions of Bones (5)
Supports body weight, stores minerals/lipids, protects organs, produces blood cells, provides leverage.
Periosteum
A dense outer membrane that protects bones, allows muscle and tendon attachment, and contains blood vessels and nerves for bone health.
Cortical bone
Dense outer bone providing strength and support.
Trabecular bone
Spongey bone at the ends of long bones and in vertebrae, allowing for shock absorption and housing bone marrow.
Medullary Cavity
The medullary cavity is the central cavity of bones that contains bone marrow for blood cell production and is used for fat storage.
Red bone marrow
Soft tissue found in certain bones that produces red and white blood cells and platelets, essential for oxygen transport, immune defense, and blood clotting.
Yellow bone marrow
Stores fat and produces bone, cartilage, and fat cells. It can also convert to red marrow to boost blood cell production when needed.
Joints
The connection between two or more bones that allows for movement and provides structural support. Joints can be classified by their motion (synarthrosis, amphiarthrosis, diarthrosis) or by their structure (bony, fibrous, cartilaginous, synovial).
Synarthrosis
No motion
Amphiarthrosis
Little movement
Diarthrosis
Most movement
Synovial
Moveable joints
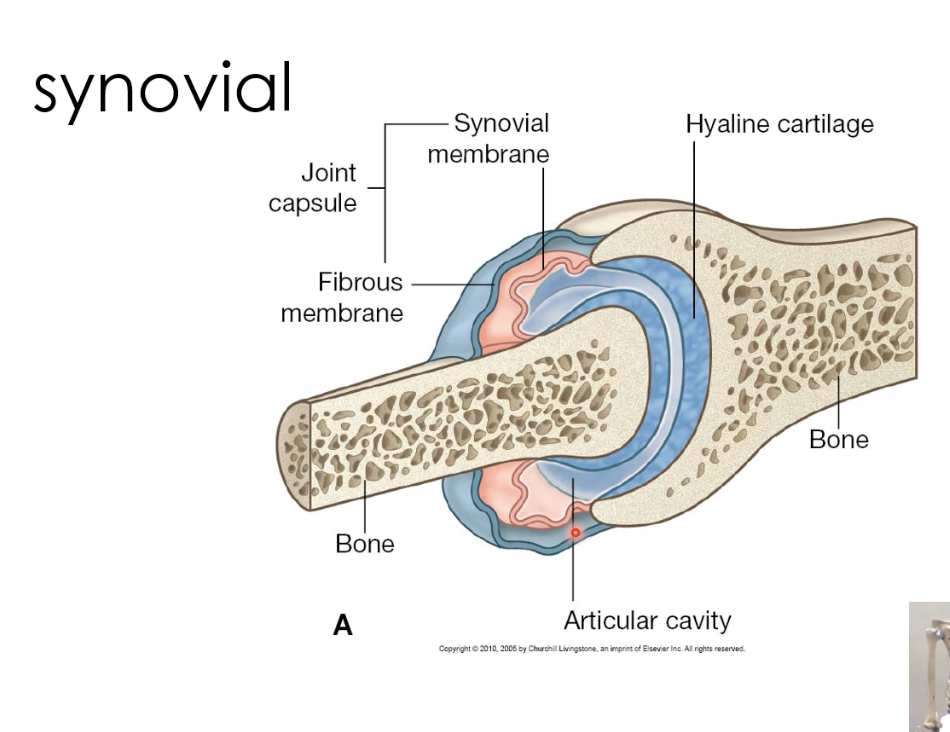
Fibrous joint capsual
The outer protective layer that encloses the ends of bones in a synovial joint, providing stability while allowing movement.
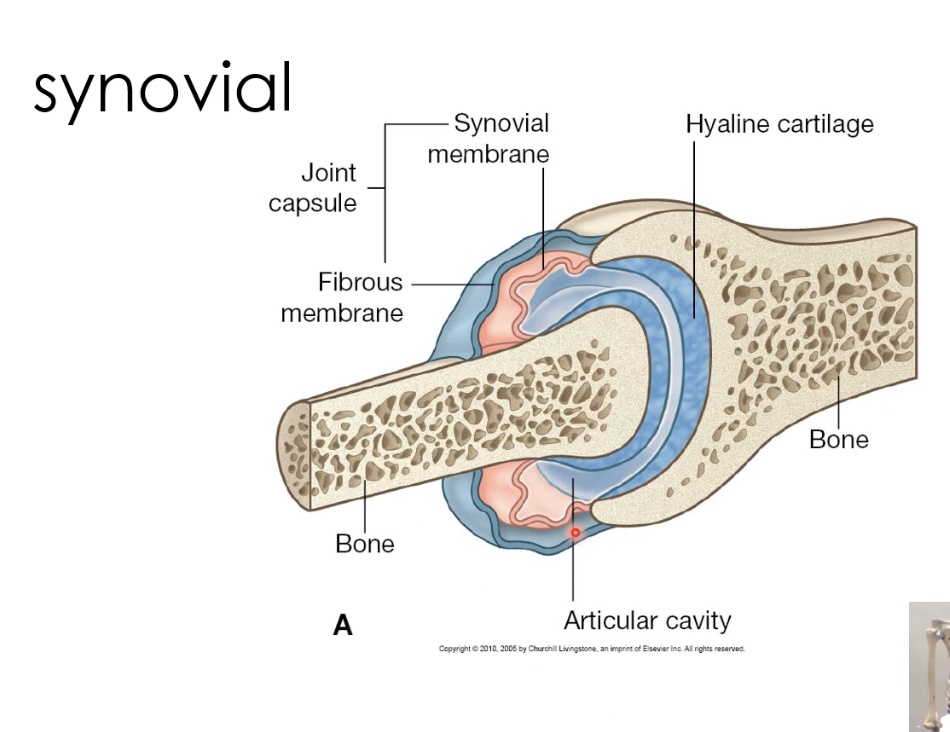
Synovial membrane
A soft, red membrane with a rich blood supply that produces synovial fluid, which lubricates the joint and nourishes cartilage.
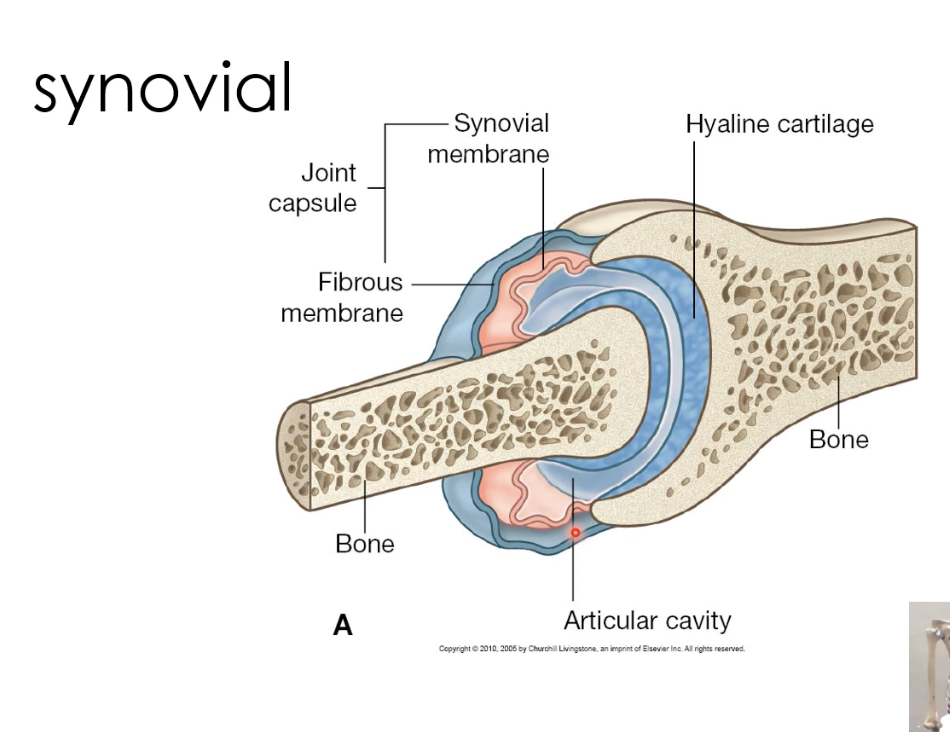
Articular cavity
The space between bones in a synovial joint, lined with strong, smooth cartilage that supports weight-bearing and movement while receiving nutrients from synovial fluid.
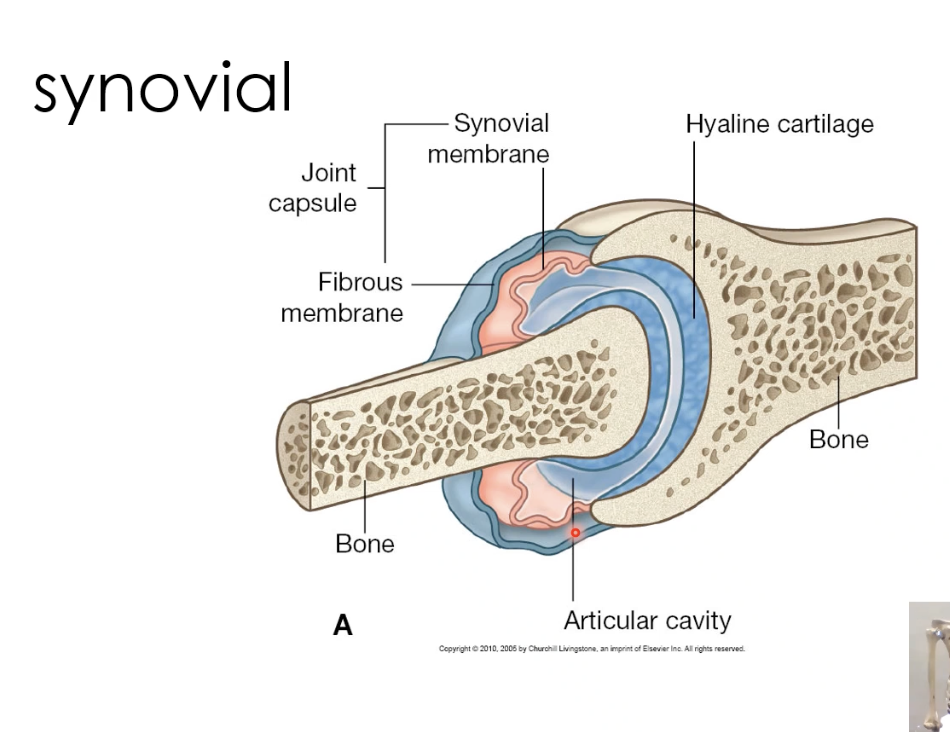
Hyaline cartilage (found in most synovial joints)
A smooth, glassy cartilage that covers the ends of bones in synovial joints, reducing friction and absorbing shock. It provides a low-friction surface for movement and is also found in the nose, trachea, and ribs.
Cardiac muscle
Involuntary muscle regulated by the heart's pacemaker.
Smooth muscle
Involuntary muscle found in arteries, digestive, and urinary tracts.
Skeletal muscle
Controls posture and movement, stores protein/energy, regulates body temp, and guards entrances/exits. Voluntary and involuntary (reflexes).
Muscle origin
The fixed attachment point of a muscle, usually on a bone that remains stable during contraction. The muscle fibers extend from the origin, cross a joint, and pull the insertion toward it when contracting.
Muscle Insertion
The attachment point of a muscle on a bone that moves when the muscle contracts, pulling toward the origin.
Muscle action
The movement that occurs when a muscle contracts, pulling its insertion toward its origin.
Muscle innervation
The specific nerve that sends motor signals to a muscle, enabling contraction and movement.
Agonist (prime move)
The muscle responsible for producing the main movement in an action.
Antagonist
The muscle that performs the opposite movement of the agonist, helping to control or slow down the action.
Concentric contraction
A type of muscle contraction where the muscle shortens as it generates force.
Eccentric contraction
A type of muscle contraction where the muscle lengthens while still generating force, often to control movement.
Isometric contraction
A type of muscle contraction where the muscle remains the same length, producing force without movement.
Fibrocartilage
The strongest type of cartilage, dense with collagen fibers, designed to absorb shock and resist compression. Found in intervertebral discs, knee menisci, and the pubic symphysis.
Elastic cartilage
The most flexible cartilage, containing elastic fibers for stretch and resilience. Found in the ear, epiglottis, and parts of the larynx.
CNS
The brain and spinal cord, responsible for processing and interpreting information.
PNS
All nerves outside the CNS, carrying sensory and motor signals between the body and the CNS.
Afferent Neurons
Sensory neurons that send impulses to the CNS from the body.
Efferent neurons
Motor neurons that send signals from the CNS to organs, glands, and muscles.
Somatic nervous system
Controls voluntary movements like walking and writing. (PNS)
Autonomic nervous system
Regulates involuntary bodily functions like digestion, heart rate, and breathing. (PNS)
Spinal nerves
Mixed nerves (both motor and sensory) that connect the spinal cord to the body.
There are 31 pairs, named by:
Letter = Spine region (Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral)
Number = Adjacent vertebra
Nerve Plexus
A network where spinal nerves mix and share axons before reaching muscles and organs.
Sympathetic Nervous System
Activates the "fight or flight" response, increasing heart rate and alertness in stressful situations. (Autonomic NS)
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Controls the "rest and digest" response, slowing the heart rate and promoting digestion. (Autonomic NS)