Geology exam 3 minerals igneous sedimentary adn metamorphic
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:51 AM on 3/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
1
New cards
**contact metamorphism**
heat being the main source for creating change in a rock to created a new rock contact with magma speckled non folate no mineral alignment
2 factors the size of the magma intrusion and types of chemical present
2 factors the size of the magma intrusion and types of chemical present
2
New cards
Regional metamorphisism
pressure being the main source for creating change in a rock to created a new rock foliations pressure from convergingnjn plates
3
New cards
Dynamic metamorphisism
results from differential pressures most often found near faults contains Mylonites hard dense fine grained rock
4
New cards
**metamorphic precursors**
The type of rock that is a precursor to the metaphorically changed rock like shale id the precursor to slate
5
New cards
Slate
is a foliated metamorphic rock with the finest grains that forms at relatively low temperatures and pressures. shale is its prolith / precurssor typically has 1 cleavage plane
6
New cards
Crusts main minerals
oxygen silicon aluminum iron calcium
7
New cards
sedimentary
rock that forms at or near the surface by cementing together of loose fragments or grains of rock weathered away from previous rock or by chemically cementing pieces of matter together EX sandstone, coal, halite, limestone
8
New cards
detrial
rocks that form from cemented-together solid fragments and grains broken off of pre-existing rocks EX. sandstone
steps for this rock to form (Weathering, Erosion, Transportation, deposition, lithification)
steps for this rock to form (Weathering, Erosion, Transportation, deposition, lithification)
9
New cards
law of superposition
younger rocks are on top of older rocks
10
New cards
Viscocity
a fluids resistance to flow
11
New cards
sedimentary rock is classified by
Clastic/detrial and chemical how the rock is weathered to be created is what causes this. texture and grain size and composition.
12
New cards
the order of rock particles
smallest-largest
clay, silt ,sand (fine, medium, coarse) granules, pebbles, cobbles, boulders
clay, silt ,sand (fine, medium, coarse) granules, pebbles, cobbles, boulders
13
New cards
breccia
sharp angular rocks in the composition of sedimentary rocks
14
New cards
conglomerate
rounded smooth particles composed in a sedimentary rock
15
New cards
Foliated
have elongated materials that are clearly aligned in parallel lines or wavy bands similar to miese lines
16
New cards
Non folate
there is no obvious alignment of the minerals very small and few if any lines
17
New cards
metamorphism of limestone
originally created from organic debris of calcium from sea animals it later becomes marble under metamorphism of heat and pressure
18
New cards
Metamorphism of sandstone
originally created by the cementation and compaction od sand when exposed to metamorphic pressure the sedimentary rock minerals become aligned and create quartzite
19
New cards
Classifications of igneous rocks
textures/Grain size and silica content
felsic intermediate mafic and ultramafic
Aphanitic Phaneritic Porphyritic glassy vesicular pyroclastic
felsic intermediate mafic and ultramafic
Aphanitic Phaneritic Porphyritic glassy vesicular pyroclastic
20
New cards
Plutonic rock
crystallization of a rock within the earths crust aka intrusive igneous rock
21
New cards
**Aphanitic**
fine grained rapid cooling
22
New cards
**Phaneritic**
coarse grained slow cooling
23
New cards
Porphyritic
2 stage cooling history looks like a chocolate chip cookie with big and small particles
24
New cards
Glassy
rocks made of a solid mass glass or tiny crystals surrounded by glass typically fracture conchoidally
25
New cards
**Pyroclastic**
consist of chunks or shards that are backed welded or cemented together after they have solidified
26
New cards
**Vesicular**
gas cavities formed by expansion of a bubble of gas or steam during solidification of the rock
27
New cards
rock textures occurring in igneous rocks
Vesicular pyroclastic glassy porphyritic
Phaneritic Aphanitic
Phaneritic Aphanitic
28
New cards
most common and effective agent for transporting sediment
water flow
29
New cards
**In marine environment the largest sediments are found where?**
close to shore nearest to the currents end
Streams stop carrying bigger particles when the current slows usually in the middle of lakes are small particles
Streams stop carrying bigger particles when the current slows usually in the middle of lakes are small particles
30
New cards
**Sedimentary structures**
stratification, cross bedding, ripple marks, fossil tracks and trails, and mud cracks
31
New cards
stratification
when different agents of deposition deposite different materials at different times on top of eachother creating lines / striations in the terrain
32
New cards
cross bedding
wind and water deposit sediment along sloping surfaces leaving behind marks on a large structure
33
New cards
Ripple marks
like mini sand dunes are produced when water flows over fine sediments they are created in shallow environments can be caused by waves
34
New cards
Mud cracks
when fine grain sediment dries out and shrinks cracking and pulling apart from each other
35
New cards
Types of metamorphisism
regional Dynamic and contact metamorphism pressure and heat
36
New cards
Country rock
rock native to the area the rock that magma intrudes into and forms plutonic rock in and rock that breaks off into magma giving it impurities
37
New cards
bowens reaction
the order of crystal formation as magma cooling occurs
continuous calcium booted out by sodium
discontinuous olivine first formed OPAB
based upon the chemical structure other minerals that are cooling
continuous calcium booted out by sodium
discontinuous olivine first formed OPAB
based upon the chemical structure other minerals that are cooling
38
New cards
Continuous and discontinuous branches are
based off of their mineral composition
continuous goes from calcium roch to sodium rich leaving behind many metal minerals
continuous goes from calcium roch to sodium rich leaving behind many metal minerals
39
New cards
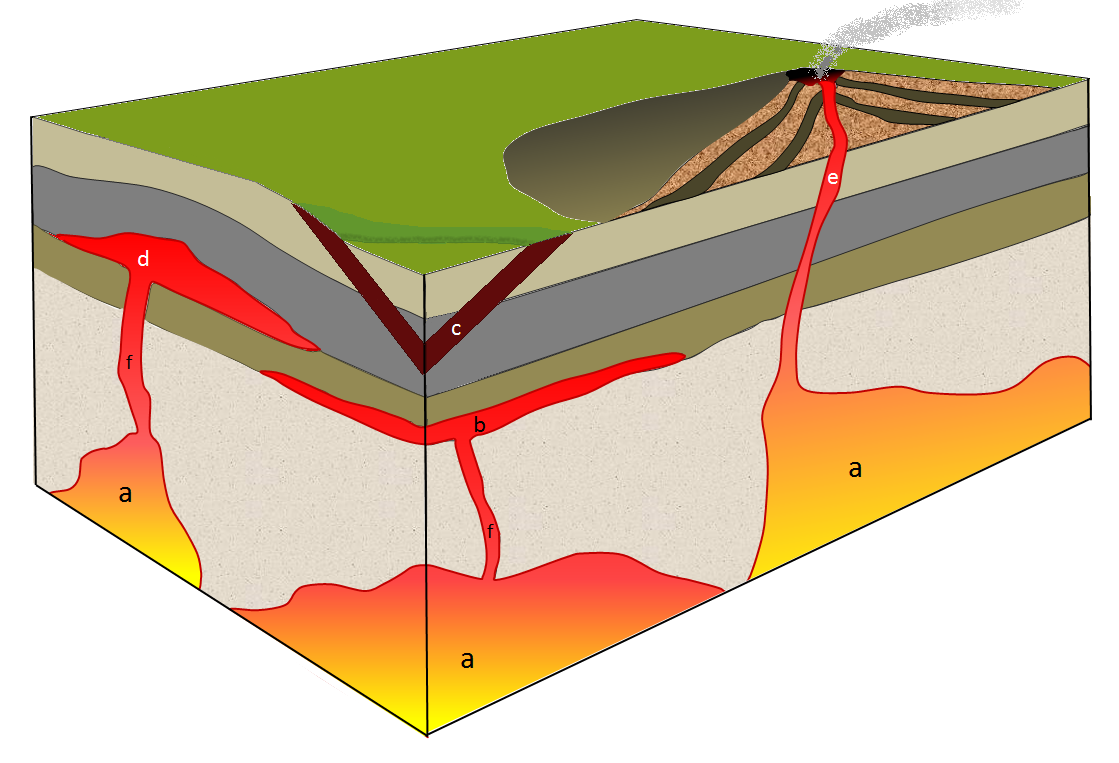
fill in the terms to the photo
A stocks/batholiths
B sill
C dyke
D Laccolith
E pipe
B sill
C dyke
D Laccolith
E pipe
40
New cards
sill
concordant turbular intrusions horizontal pushes crust up sill like window sill
41
New cards
dyke
discordant tabular intrusions vertical stretches crust out
42
New cards
**Laccolith**
blister shaped intrusions
43
New cards
Batholith
a chamber with lots of igneous rock
44
New cards
**coal formation**
when dead plant matter submerged in swamp environments deprived of air (anaerobic) then subjected to years of heat and pressure the longer it is formed the more energy it holds
45
New cards
How can hydrocarbons get trapped in reservoir rock?
(Fault, Salt or stratigraphic traps) when organic matter gets covered with rock and through the years heat and pressure build up to a point where they can break down the organic material into hydro carbons which become trapped underground because of the rock above and around it that created the pressure for the hydrocarbon to be formed
46
New cards
**metamorphic rocks/age of the Earth**
created through metamorphisms of pressure and heat the oldest metamorphic rock is 4 billion years old the earth is 4.6 billion years old
47
New cards
lithostatic pressure
results from the weight of overlying rocks minerals and grains are more closely packed
48
New cards
differential pressure
pressure that results from unequal forces applied to a rock
49
New cards
minerals
These are pieces that cannot be split anymore are the smallest piece we can get that still retains the properties (Naturally occurring, inorganic, distinct chemical composition, crystalline solids, with physical properties)
50
New cards
cleavage
Cleavage forms in directions where the bonds holding atoms are weakest (One plane is like pages in a book 2 planes can be 90 and 60 degrees 3 planes is cube 4 planes is crazy looking)
51
New cards
sulfide
Galena metal cation bonded with sulfide anion (sulfides),
bacterial break- consist of both discovered and undiscovered materials that can be currently or potentially extracted.
* Metals, sand, stone, sulfur, salt, and others
* Nonmetals and energy resourcesdown of organic materials and human and animal wastes
bacterial break- consist of both discovered and undiscovered materials that can be currently or potentially extracted.
* Metals, sand, stone, sulfur, salt, and others
* Nonmetals and energy resourcesdown of organic materials and human and animal wastes
52
New cards
sulfate
Gypsum (sulfate) Many sulfates form by precipitation out of water at or near the Earth’s surface
53
New cards
**Resources**
consist of both discovered and undiscovered materials that can be currently or potentially extracted.
* Metals, sand, stone, sulfur, salt, and others
* Nonmetals and energy resources
* Metals, sand, stone, sulfur, salt, and others
* Nonmetals and energy resources
54
New cards
Reserves
are the part of the environment base that can
be economically extracted.
be economically extracted.
55
New cards
placer deposites
a type of mineral deposit in which grains of a valuable mineral like gold or the rare earths are mixed with sand deposited by a river or glacier
56
New cards
Atoms
the smallest particle that still retains the properties of elements. Neutrons protons electrons
57
New cards
protons
Positively charged particles in the nucleus are called
58
New cards
neutrons
Neutrally charged particles
59
New cards
electrons
Negatively charged particles orbit the shell of the atom
60
New cards
isotitopes
have a different number of neutrons basically the same element different font
61
New cards
ionic bonds
transference of electrons between atoms
62
New cards
covalent bonds
not transferred but shared and both use (we share a brain cell) Strong bongs but sheets bonding is weak mineral will always break along a weak sheath line