DSA29 - Delirium
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
•Widespread disturbance of neural networks (Linked to REDUCED CHOLINERGIC function + EXCESS of DOPAMINE activity)
•Reflects complex interactions among brain insults, aberrant stress responses, and neuro-inflammatory mechanisms (ex. IL-1, IL-6, Cortisol)
What is the basis for the pathophysiology of Delirium?
•Delirium BEFORE?
•OLDER
•DEMENTIA
•Functional DISABILITIES
•MALE Gender
•Poor VISION AND HEARING
•MCI
•ETOH use disorder
•LAB ABNS
What are some PREDISPOSING Risk Factors for Delirium?
•Medication S/Es
•Surgery
•Anesthesia
•Untreated pain
•Hypoxia
•Acute illness
•Acute exacerbation of chronic illness
What are some PRECIPITATING Risk Factors for Delirium?
Often w/n older adults (many after HIGH RISK Surgery)
While the causes behind Delirium are multifactorial, what is a common cause for it and age group it is seen?
" I WATCH DEATH":
-INFEX (Enceph, Mening, Sepsis, Mumps, HIV, Typhoid) OR INTOX (Op, BZD, EtOH, Anti-Ch, Sed-Hypno)
-W/D (EtOH, BZD, Barb, Op)
-ACUTE METABOLIC (Acidosis, Alkalosis, Renal/Hepatic)
-TRAUMA (Stroke, burn, CHI, post-op)
-CNS PATHOLOGY (ICH, stroke, TUMOR, NPH, Grand Mal Seizure, Aneurysm)
-HYPOXIA (Anemia, CO, Cardiopulmonary)
-DEFICIENCIES (B12, folate, thiamine --> Wernicke's, niacin) OR Degenerative (HD, CJD, Wilsons)
-ENDOCRINOPATHIES (Pituitary, glucose/hypoglycemia, thyroid, adrenal)
-ACUTE VASCULAR (Shock = Hyper/Hypothermia OR Hypoperfusion, HTN urgency, MI, SLE, Sarcoidosis)
-TOXIC DRUGS (Medications, solvents, pesticides)
-HEAVY METALS (Lead, Manganese, mercury)
List the Acronym for the potential causes of Delirium
-Perioperative --> 7-10 % increased risk of 30-day mortality
-Delirium + Dementia --> 70% inc risk of death at 6 mo
-Delirium in ICU = x2-4 increase in overall mortality
List some potential prognoses for Delirium
Disturbance in attention and awareness
According to the DSM-5 Criteria A, how is Delirium defined?
The disturbance develops over a short period of time, represents a CHANGE FROM BASELINE ATTENTION AND AWARENESS, and tends to FLUCTUATE in SEVERITY during the COURSE of a day
According to the DSM-5 Criteria B, what is the time frame and S/S for Delirium?
An additional disturbance in cognition
According to the DSM-5 Criteria C, what also needs to be occurring along with disturbance in attention and awareness, for this condition to be considered Delirium?
-Preexisting, established, or evolving neurocognitive disorder
-Not occur in the context of a severely reduced level of arousal, such as coma
According to the DSM-5 Criteria D, what are qualifiers for Delirium (aka what needs to be R/O)?
Evidence from the history, physical exam, or laboratory findings that the disturbance is a direct physiological consequence of...
> Substance Intoxication
> Substance Withdrawal
> Medication (Medication-Induced)
> Another medical condition
> Multiple Etiologies
According to the DSM-5 Criteria E, what needs to be presented to officially diagnose Delirium (aka to FIND THE CAUSE)?
Lasting hours to days
Timing wise, what is considered ACUTE Delirium?
Lasting weeks to months
Timing wise, what is considered PERSISTENT Delirium?
-Mood Lability
-Agitation
-Increased Psychomotor Activity
What are S/S of HYPERACTIVE Delirium (often more recognized)?
-Sluggishness
-Lethargy
What are S/S of HYPOACTIVE Delirium (often MISSED)?
-Normal activity BUT attention/awareness disturbed
-Rapidly fluctuating level of activity
What are S/S of MIXED Delirium?
•SUDDEN/ACUTE Onset
•WAXING and WANING of symptoms
•Must be CAUSED BY PHYSIOLOGICAL CONSEQUENCES of some other process
•Symptoms CAN'T BE CAUSED by a NEUROCOGNITIVE DISORDER or a COMA
•Must SPECIFY CAUSE
What are the main differentiators of Delirium from Dementia?
Struggles differentiating dementia from delirium or with mental health disorders
While the Confusion Assessment Method is up to 99% effective at screening for Delirium (when used by experts), what is a drawback of this test?
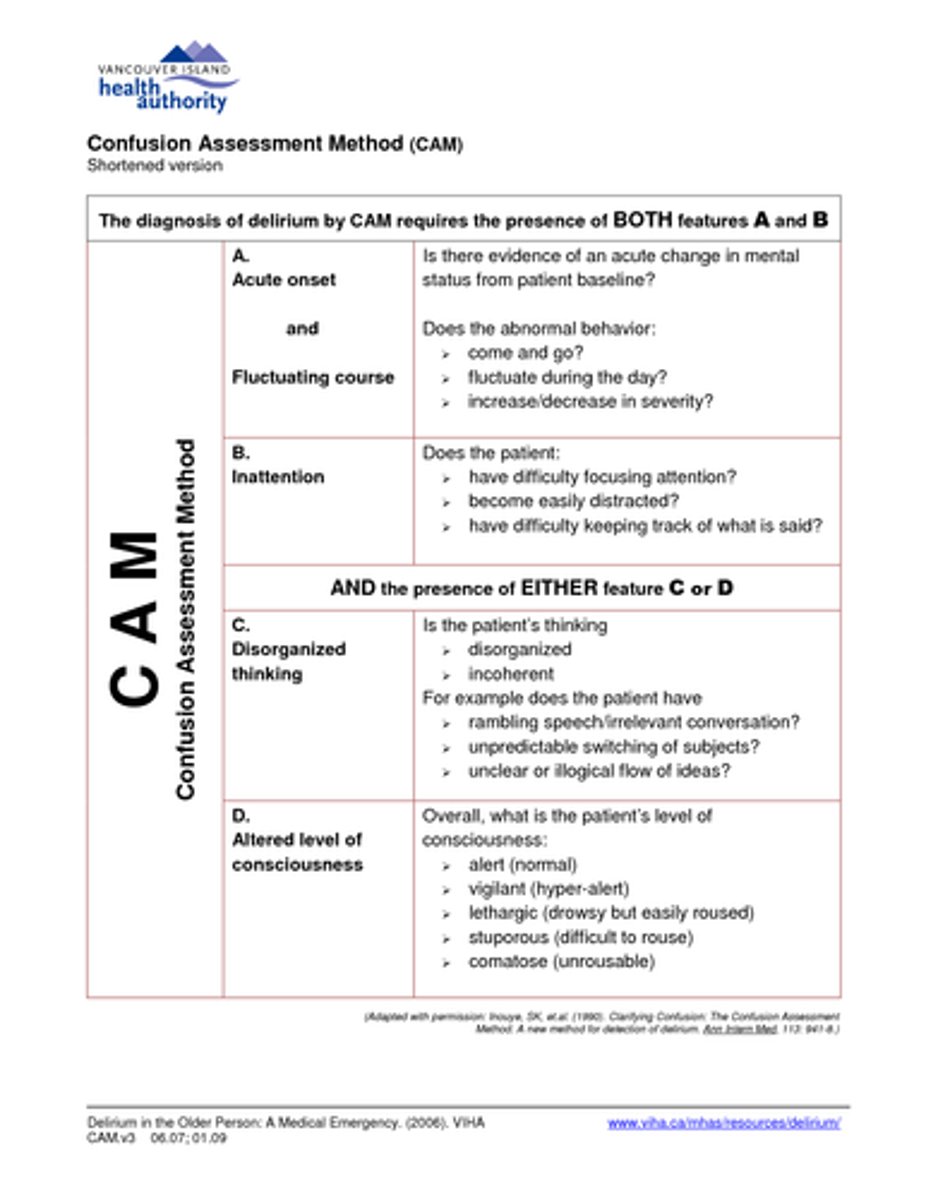
-Test to quickly assess for Delirium & Cognitive Impairment (1-2 min)
-89% sensitive, 84% specific
-Scoring:
> 0 = Delirium or severe cognitive impairment unlikely
> 1–3 = Possible cognitive impairment
> 4 or more = Possible delirium (+/- cognitive impairment)
Describe the 4AT Test
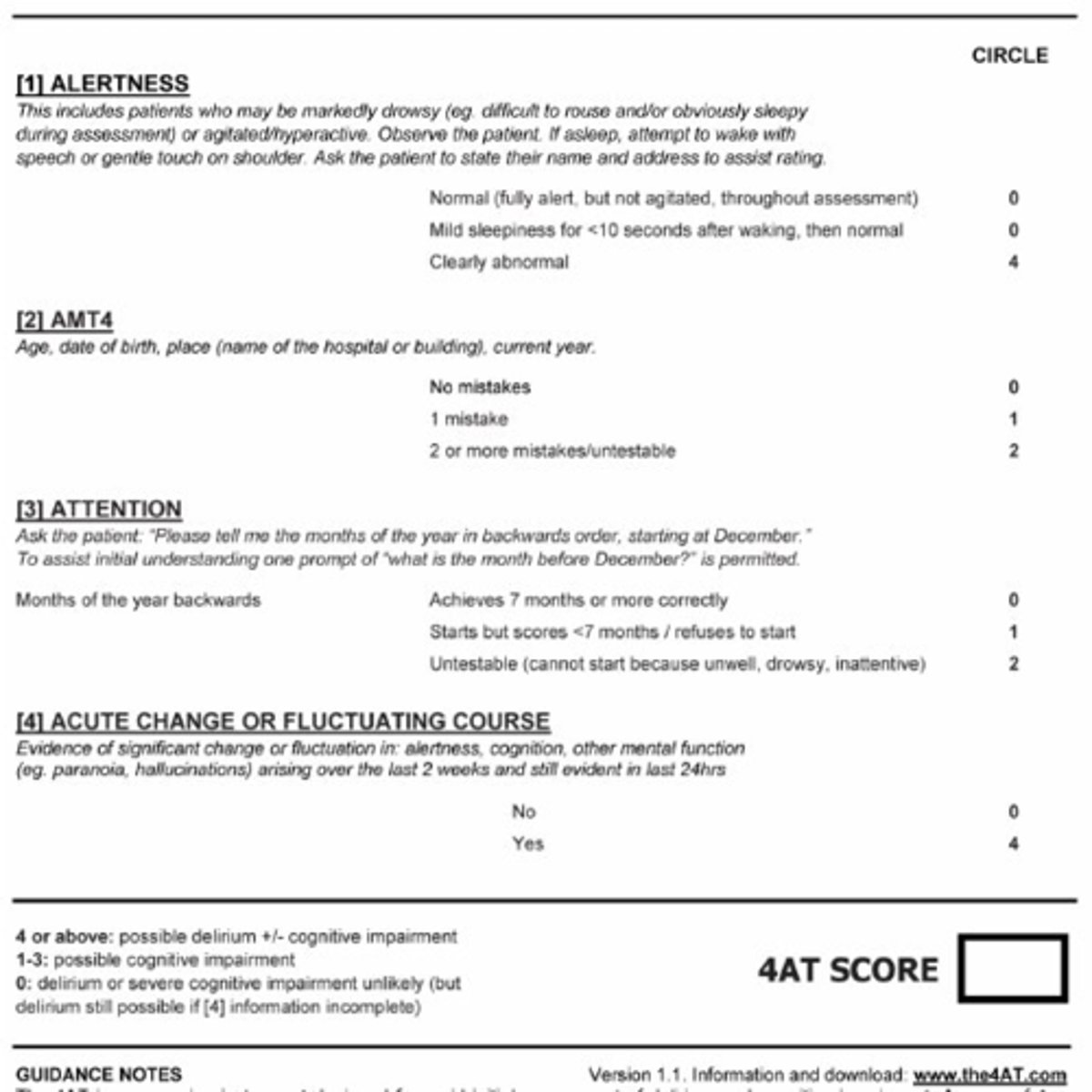
-Tx underlying cause!
-Educate family (current care, post care + Help them understand there may be irreparable damage)
-Call Psych (Meds to control sx OR Nonpharm)
How exactly is Delirium treated?
Reserved for patients experiencing AGITATION or OTHER DISTRESSING SX, or in DANGER OF HARM (SELF/OTHERS):
•ANTIPSYCHOTICS typically used
> HALOPERIDOL = MC due to lower anticholinergic effects and multiple routes of administration
> 2nd generation antipsychotics are accepted
•Melatonin
•Dexmedetomide (alpha-2 agonists)
•Benzodiazepines avoided (UNLESS it is due to alcohol or benzodiazepine withdrawal)
List the Pharmacological Tx for Delirium
•Lights in room turned on/blinds open during the day and closed off at night
•Glasses and hearing aid w/in reach
•Date and clock visible
•Frequent reorientation, reassurance
•Early mobilization out of bed
•Ensuring oxygen saturation
•Review medications
•Treat pain
•Provide nutrition
•Minimize restraints
•Maintain staff continuity
List the Nonpharmacological Tx for Delirium