chromatin, epigenetics, and rna processing (22-24)
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lectures 22-24
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
how do saccharomyces cerevisae control mating type?
they have HMLalpha and HMRa loci that are silenced
when time for mating, the MAT locus takes on either a or alpha configuration by non-reciprocally combing HMLalpha or HMRa
mating type only expressed when in MAT locus
a sign that told us histones impact repression?
histone mutations resulted in expression from regions that should be silent
proteins essential for silencing the silent mating type loci
RAP1
SIR1, 2, 3,4
RAP1
binds to silencer region near HMLalpha or HMRa
also binds to repeptive sequence in telomere
recognized by SIR proteins
SIR1
silent info regulator
works with RAP1
acetylation of histones tails
reduces the interaction between histone and DNA(PO4 backbone specifically)
neutralizes lysine(positive) residues
SIR3 and 4
bind to hypocacetylated histone tails
SIR 2 (4)
recognize SIR3,4 and join complex
makes histone bind tighter to DNA
forms large complex with telomeric dna
histone deacetylase
hypoacetylation of histone tails
due to feedback loop of SIR proteins
SIRs will recognize deacetlyaed regions and come join, spreads deacetlyation
Ume6
critical dna binding protein
has Rpd3/Sin3 corepressor complex that changes chromatin near URS
URS
dna binding transcription repressor
Rpd3
histone deactylase
subunit of Ume6
HATs
histone acetyl transferases
open up chromatin and make it more accesible
can activation domains trigger chromatin condensation?
yes
VP-16
transcription activation domain that results in dedcondensation when added to cell
pioneer transcription factors
can only interact with exposed dna on the outside of the nucleosome
cause dna to unwind
recruit enzymes that change the shape of histone tails
which histones are most important/unimportant?
H1 unimportant
H3, H2, H4 very important
exampels of epigenetic traits that get passed on within the body
inactive x chromosones
developmental restrictions
imprints
epigenetic readers and writers
can sometimes be the same protein
readers recognize marks of histone tail modifications and recruit writers after cell divison
writers write in the same marks into new dna
CTD of rna pol II
very extended and unstructured with weird conformations
has YSPTSPS repeated sequence
when is ser 5 of CTD phosphorylated? by who?
after intiation but before elongation
cdk7
why does the rna pol II pause after intiation?
to give time for ser5 phosphorylation and for factors needed for later to associate
what post transcriptional processing does mRNA go through
5’ 7-methylguanylate cap
protects from exonucleases
methylation
stabilizes and faciliattes nuclear transport
recognized dby translational factors
polyadenylation
what happens to the CTD during the pause after intiation?
first, ser5 phosphorylated by cdk7
capping enzyme uses phosphorylated ser5 as a scaffold and caps 5’ end
cdk9 phosphorylates ser2, DSIF, NELF and other enzymes
cdk9
phosphorylates ser2 and other enzymes associated with rna pol II
recruits splicing factors, polyadenylation factors, aexport factors
phosphorylates NELF and DSIF
NELF (3)
negative elongation factor
protein that actively blocks elongation and causes stalling
phosphoruylation by cdk9 causes it to dissociate
once gone elongation factors can come
DSIF
contributes to stalling
phosphorylation by cdk9 causes it to put pressure on rna pol II’s clamp domain
when does mrna splicing occur?
co transcriptionally
splice donor and splice aceptor
donor → GU
acceptor → AG
branch point
conserved A near the 3’ end of the mRNA
slightly upstream of pyrimidine rich region
whats the spliceosome made of?
5 snRNPs
snRNP
a snRNA (U1-U6) associtated with 6-10 proteins
U1 snRNA
binds near spice donor site
guided by SR proteins
U2 snRNA
partially compliment to area near branch point A
A is unbound and bulges out
Lariat structure
2’-5’ linkage forms a loop of intron
occurs from A attacking 5’ phosphate of the intron to be removed
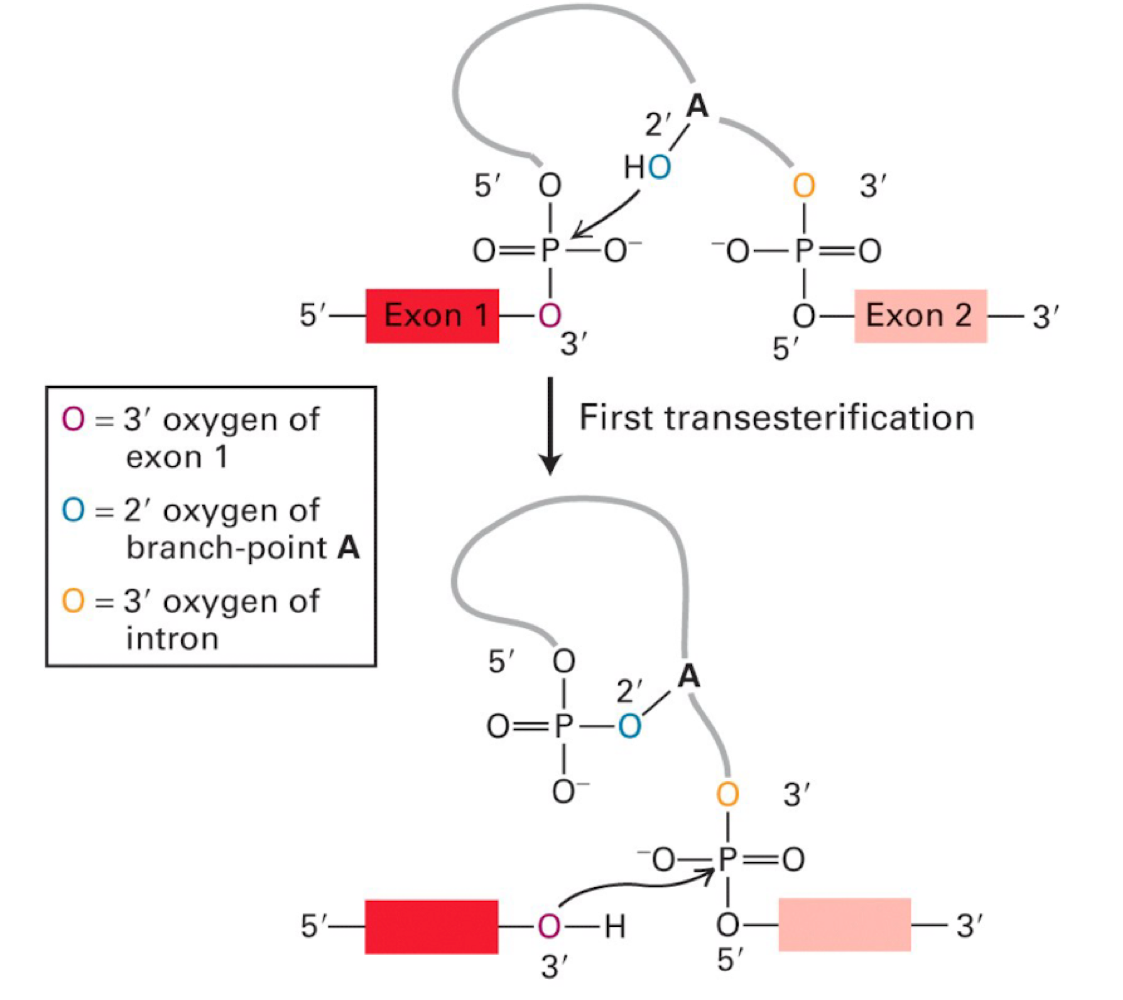
trans-esterification reactions
the reactions involved with forming and resolving Lariat structures
nucleophilic attack by A on 5’PO4 of intron
OH on exon attacks PO4 on other exon
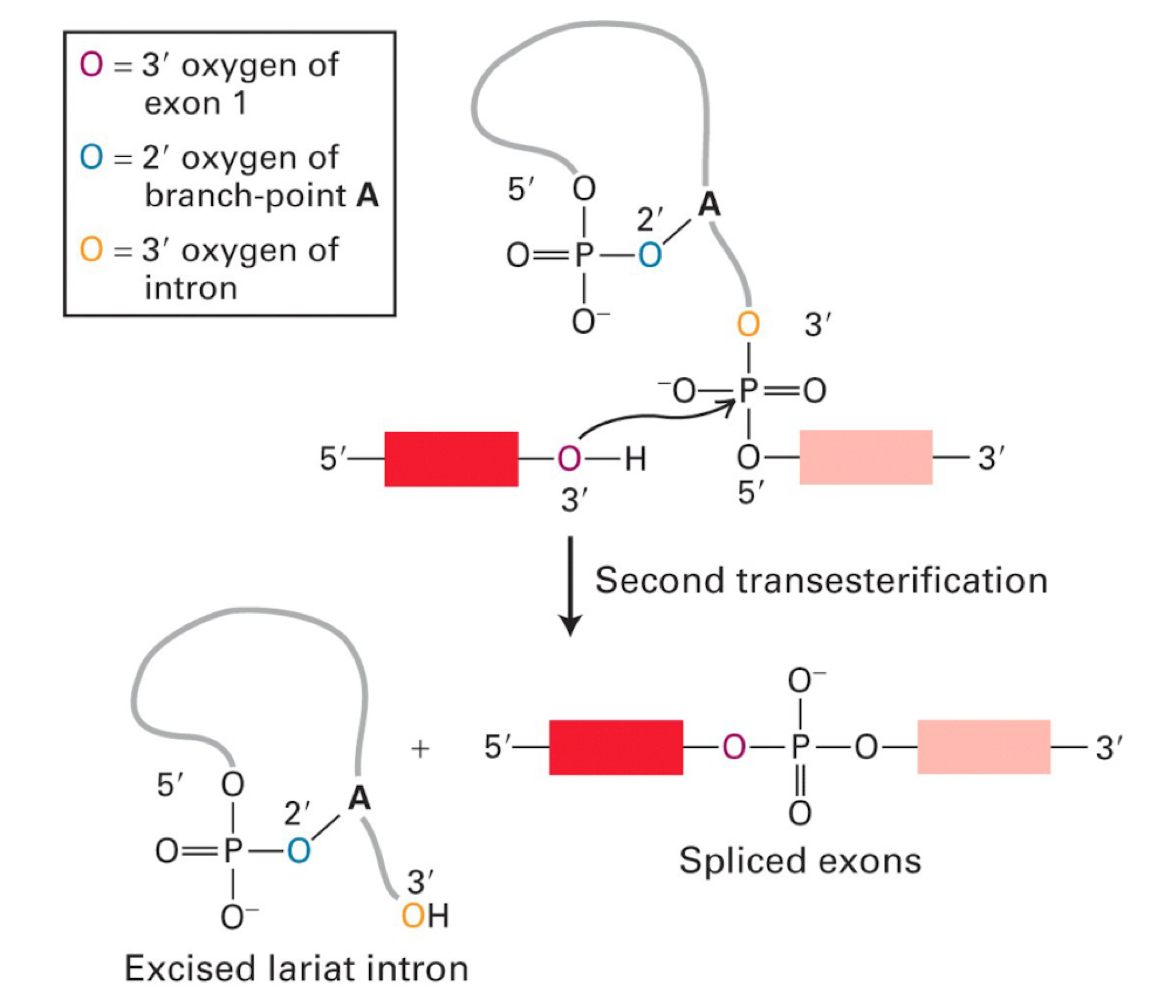
how are lariat strcutres resolved?
debranching enzyme cuts the 2’-5’ linkage
normal riboexonucleases come in and degrade it
self splicing introns
group 1
group 2
fold into crazy structures
only in mt and cp

exceptions to GU AG rule
sometimes A or C replaces the G i GU
sometimes AG → AC
how is rRNA transcribed
in tandem rerpeats
large 48S product made
cut into 18S, 5.8D, 28S in humans
spacer regions removed by special cleavage reactions using snoRNAs
snoRNAs in rRNA cleavage
snorna bp with pre rrna to make U bulge out
U is vulnerable to modifications
pseudoU
stabilizes rna
seen in rrna and trna
4 steps of tRNA processing
5’ end sequence removed
short segment of second loop sometimes removed
add 5’ CCA 3’ to 3’ end
modify internal bases

RNA binding protein
largely mediates deciding where an intron/exon boundary is
RRM domain bindin protein
RNA recognition motif
one of most common RNA binding proteins that help determine exon/intron boundaries
U2AF
binds to 3’ end of intron and says THIS IS THE INTRON BOUNDARY
has subunits that interact with small residues near AG
exon splicing enhancers
decorate entire exon
promote exon joining
help U2AF recognize the boundary
recognized by SR proteins
SR proteins (3)
bind to exon splicing enhancers
helps U1snRNP recognize the 5’ end of the intron
have RRM domains
semi detailed explanation of how sex determination in drospophilia works
females express early sxl protein during early embryogenesis
later in development sxl specifies splicing differences in females
males never express sxl and as a result never express tra either
tra specifies dsx splicing, so males and females have different dsx proteins
cellular deaminases
turn A→I and C→U
aka rna editing
rna editing
results in mature mRNA not matching gene sequences
more rare in highe rorder eukaryotes
widespread in mt and plasmids of protozoa and plants
polyadenylation of mrna
final step of post trancriptional processing
does not hapen to histones
how does mrna polyadenylation work?
AAUAA and GU sequence recognized by cleavage and polyA factors
PAP comes in, then cleavage occurs
PAP adds ~8nt poly A tail
PABPN1 rapidly adds ~200A residues