Science 6th grade finale
4.0(3)Studied by 1 person
Card Sorting
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 9:08 PM on 5/19/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
1
New cards
\
Larry was told that a certain muscle cream was the newest best thing on the market and claims to double a person’s muscle power when used as part of a muscle-building workout. Interested in this product, he buys the special muscle cream and recruits Patrick and SpongeBob to help him with an experiment. Larry develops a special marshmallow weight-lifting program for Patrick and SpongeBob. He meets with them once every day for a period of 2 weeks and keeps track of how many marshmallows they can lift. Before each session Patrick’s arms and back are lathered in the muscle cream, while Spongebob’s arms and back are lathered with the regular lotion.
WRITE A HYPOTHESIS (use if… then format)
Larry was told that a certain muscle cream was the newest best thing on the market and claims to double a person’s muscle power when used as part of a muscle-building workout. Interested in this product, he buys the special muscle cream and recruits Patrick and SpongeBob to help him with an experiment. Larry develops a special marshmallow weight-lifting program for Patrick and SpongeBob. He meets with them once every day for a period of 2 weeks and keeps track of how many marshmallows they can lift. Before each session Patrick’s arms and back are lathered in the muscle cream, while Spongebob’s arms and back are lathered with the regular lotion.
WRITE A HYPOTHESIS (use if… then format)
\
If Larry’s muscle cream is used before a workout, then a person’s muscle power will double.
If Larry’s muscle cream is used before a workout, then a person’s muscle power will double.
2
New cards
Larry was told that a certain muscle cream was the newest best thing on the market and claims to double a person’s muscle power when used as part of a muscle-building workout. Interested in this product, he buys the special muscle cream and recruits Patrick and SpongeBob to help him with an experiment. Larry develops a special marshmallow weight-lifting program for Patrick and SpongeBob. He meets with them once every day for a period of 2 weeks and keeps track of how many marshmallows they can lift. Before each session Patrick’s arms and back are lathered in the muscle cream, while Spongebob’s arms and back are lathered with the regular lotion.
WHICH PERSON IS IN THE CONTROL GROUP?
WHICH PERSON IS IN THE CONTROL GROUP?
SpongeBob
3
New cards
Larry was told that a certain muscle cream was the newest best thing on the market and claims to double a person’s muscle power when used as part of a muscle-building workout. Interested in this product, he buys the special muscle cream and recruits Patrick and SpongeBob to help him with an experiment. Larry develops a special marshmallow weight-lifting program for Patrick and SpongeBob. He meets with them once every day for a period of 2 weeks and keeps track of how many marshmallows they can lift. Before each session Patrick’s arms and back are lathered in the muscle cream, while Spongebob’s arms and back are lathered with the regular lotion.
WHAT IS THE INDEPENDENT VARIABLE?
WHAT IS THE INDEPENDENT VARIABLE?
The muscle cream
4
New cards
Larry was told that a certain muscle cream was the newest best thing on the market and claims to double a person’s muscle power when used as part of a muscle-building workout. Interested in this product, he buys the special muscle cream and recruits Patrick and SpongeBob to help him with an experiment. Larry develops a special marshmallow weight-lifting program for Patrick and SpongeBob. He meets with them once every day for a period of 2 weeks and keeps track of how many marshmallows they can lift. Before each session Patrick’s arms and back are lathered in the muscle cream, while Spongebob’s arms and back are lathered with the regular lotion.
WHAT IS THE INDEPENDENT VARIABLE?
WHAT IS THE INDEPENDENT VARIABLE?
The difference between the amount of marshmallows Patrick can lift and SpongeBob
5
New cards
Larry was told that a certain muscle cream was the newest best thing on the market and claims to double a person’s muscle power when used as part of a muscle-building workout. Interested in this product, he buys the special muscle cream and recruits Patrick and SpongeBob to help him with an experiment. Larry develops a special marshmallow weight-lifting program for Patrick and SpongeBob. He meets with them once every day for a period of 2 weeks and keeps track of how many marshmallows they can lift. Before each session Patrick’s arms and back are lathered in the muscle cream, while Spongebob’s arms and back are lathered with the regular lotion.
WHAT ARE CONTROLLED VARIABLES? WHY ARE THEY IMPORTANT TO MAINTAIN?
WHAT ARE CONTROLLED VARIABLES? WHY ARE THEY IMPORTANT TO MAINTAIN?
The weightlifting program. The purpose of a controlled variable is to keep all conditions as similar as possible between two subjects except for the independent variable.
6
New cards
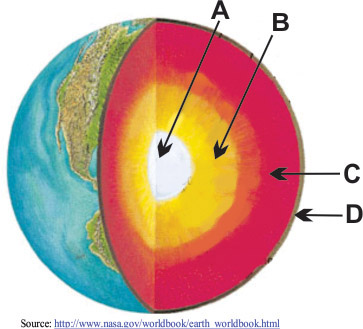
Match the layer of the Earth to the appropriate letter in the diagram.
What layer is letter A?
What layer is letter A?
Inner Core
7
New cards
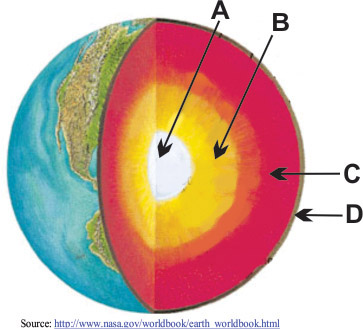
Match the layer of the Earth to the appropriate letter in the diagram.
What layer is letter B?
What layer is letter B?
Outer Core
8
New cards
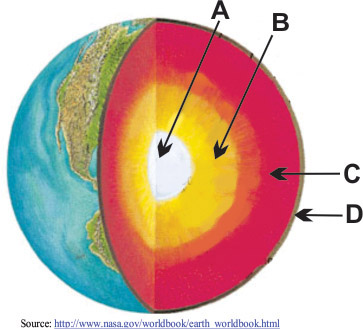
Match the layer of the Earth to the appropriate letter in the diagram.
What layer is letter C?
What layer is letter C?
Mantle
9
New cards
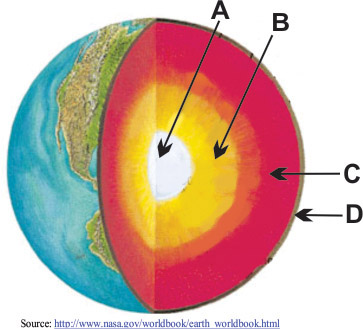
Match the layer of the Earth to the appropriate letter in the diagram.
What layer is letter D?
What layer is letter D?
Crust
10
New cards
Fill in the blanks
Two plates collide and one goes beneath the other. The plate that subducts under the other is probably a(n) ________ plate (oceanic or continental) and it gets pushed under because it is ____ (more or less) dense than the other.
Two plates collide and one goes beneath the other. The plate that subducts under the other is probably a(n) ________ plate (oceanic or continental) and it gets pushed under because it is ____ (more or less) dense than the other.
Oceanic, more
11
New cards
Fill in the blank
1. The __ states that Earth's crust and rigid upper mantle are broken into plates that move at different rates and in different directions.
1. Hypothesis of continental movement
2. Hypothesis of continental drift
3. Theory of plate tectonics
4. Theory of seafloor spreading
1. The __ states that Earth's crust and rigid upper mantle are broken into plates that move at different rates and in different directions.
1. Hypothesis of continental movement
2. Hypothesis of continental drift
3. Theory of plate tectonics
4. Theory of seafloor spreading
answer- C
12
New cards
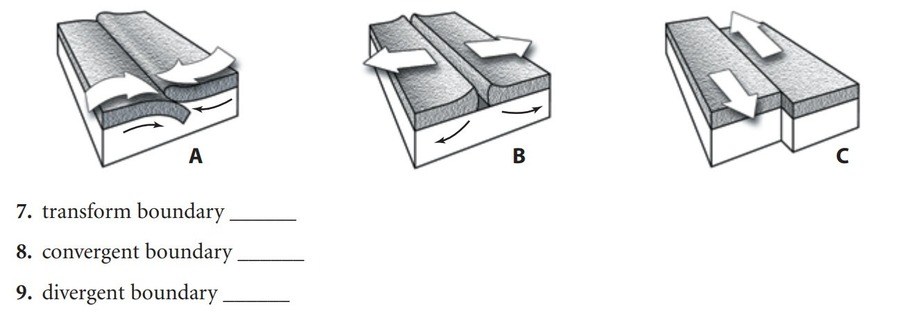
Match the boundary type to the appropriate diagram to the side.
What letter represents a transform boundary?
What letter represents a transform boundary?
answer- C
13
New cards
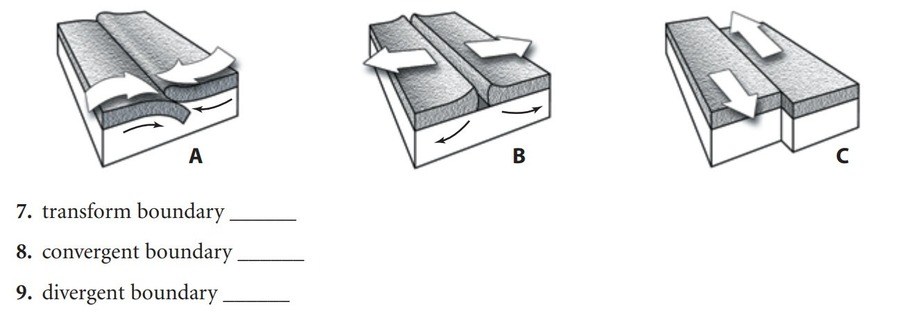
Match the boundary type to the appropriate diagram to the side.
What letter represents a convergent boundary?
What letter represents a convergent boundary?
answer- A
14
New cards
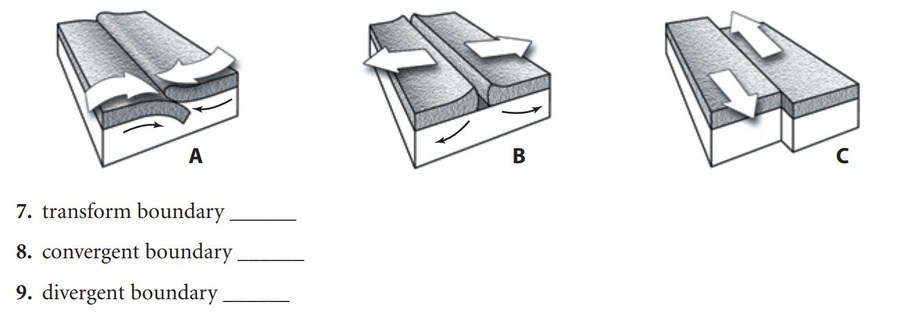
Match the boundary type to the appropriate diagram to the side.
What letter represents a divergent boundary?
What letter represents a divergent boundary?
answer- B
15
New cards
Where do most volcanoes form?
Plate boundaries
16
New cards
True or False – If the statement is true, mark it with a T. If it is false, change the underlined word to make it true.
__Secondary (S) waves__ are the type of seismic wave that are the last to be recorded on a seismograph and cause the most damage in an earthquake.
__Secondary (S) waves__ are the type of seismic wave that are the last to be recorded on a seismograph and cause the most damage in an earthquake.
False- Surface Waves
17
New cards
True or False – If the statement is true, mark it with a T. If it is false, change the underlined word to make it true.
The __crust__ is the thickest layer of the Earth.
The __crust__ is the thickest layer of the Earth.
False- mantle
18
New cards
True or False – If the statement is true, mark it with a T. If it is false, change the underlined word to make it true.
Movement in the __inner core__ moves the plates of the Earth.
Movement in the __inner core__ moves the plates of the Earth.
False- convection currents in the mantle
19
New cards
True or False – If the statement is true, mark it with a T. If it is false, change the underlined word to make it true.
When magma reaches Earth’s surface it is called __lava__.
When magma reaches Earth’s surface it is called __lava__.
True
20
New cards
True or False – If the statement is true, mark it with a T. If it is false, change the underlined word to make it true.
Oceanic plates are made of more dense __basalt__ rock.
Oceanic plates are made of more dense __basalt__ rock.
True
21
New cards
True or False – If the statement is true, mark it with a T. If it is false, change the underlined word to make it true.
The __focus__ is where an earthquake originates, usually deep underground.
The __focus__ is where an earthquake originates, usually deep underground.
True
22
New cards
What are the five physical properties of a mineral?
Inorganic, naturally occurring, solid, definite chemical composition, orderly arrangement of atoms
23
New cards
What is the difference between a rock and a mineral?
Minerals are inorganic, multicolored, and made from elements through chemical compositions. Minerals have a definite crystalline structure and can contain nutritional value. Rocks, usually made from minerals, have no definite shape and can come in many colors.
24
New cards
What is chemical weathering? Give an example.
Chemical weathering is the breaking down of rock which changes the chemical composition. Acid rain, carbon dioxide
25
New cards
What is physical weathering? Give an example.
Mechanical or physical weathering is when the rocks and minerals are broken down but the Chemical composition remains the same. Mechanical weathering physically breaks up rock. Wind, Ice, Temp.
26
New cards
Fill in the blanks
Roots growing into a rock is an example of _________ weathering.
Roots growing into a rock is an example of _________ weathering.
Physical
27
New cards
Which activity demonstrates chemical weathering?
1. Freezing of water in the cracks of a granite boulder.
2. Abrasion of a streambed by tumbling rocks.
3. Dissolving of limestone by carbonic acid.
4. Boulders falling from a cliff and shattering on the rocks below.
1. Freezing of water in the cracks of a granite boulder.
2. Abrasion of a streambed by tumbling rocks.
3. Dissolving of limestone by carbonic acid.
4. Boulders falling from a cliff and shattering on the rocks below.
answer- C
28
New cards
Fill in the blank
The movement of weathered material by wind or water is known as ___________
The movement of weathered material by wind or water is known as ___________
Erosion
29
New cards
Fill in the blank
Eroded materials that are transported are finally dropped off in a process called ____________
Eroded materials that are transported are finally dropped off in a process called ____________
deposition
30
New cards
What is igneous rock? What are the two types of igneous rock? How are they different?
Created when magma or lava cools and crystallizes. Extrusive - form outside of the Earth’s surface. Crystals are small because they cool quickly. Intrusive - form inside the Earth. Crystals are large because they cool slowly.
31
New cards
What is sedimentary rock? How is it formed?
Forms where rocks are broken down into smaller pieces or dissolved in water as rocks erode or the remains of plants and animals are pressed and cemented together.
32
New cards
What is metamorphic rock? How is it formed?
Forms when existing rock is changed by heat, pressure or chemical reactions
33
New cards
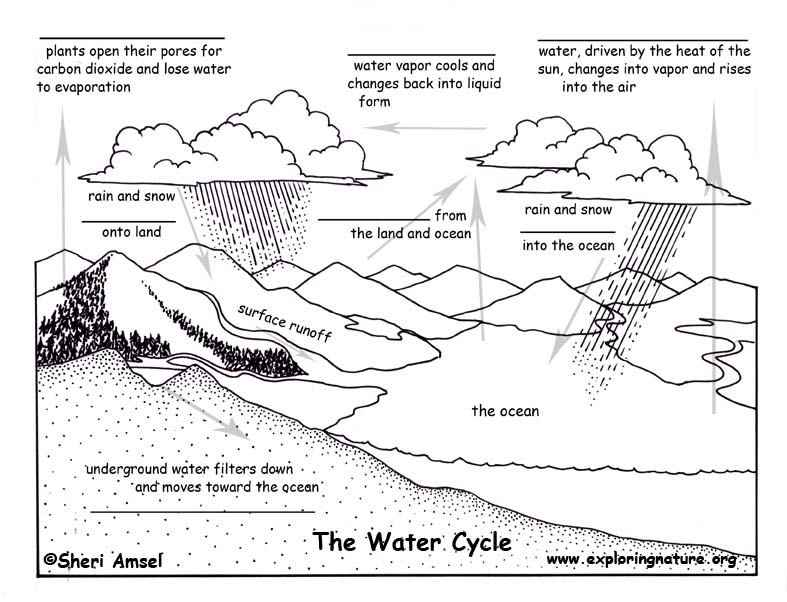
Label the picture below with the following terms: infiltration, precipitation, evaporation, condensation, transpiration and runoff.
click on the photo to see the answer
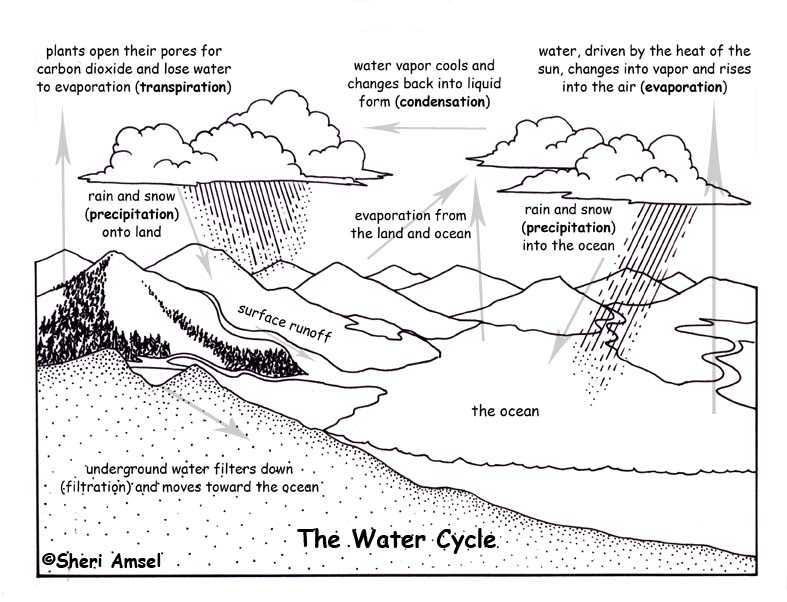
34
New cards
Fill in the blank with one of the words from the blank
__Cold Nutrients Offshore Trade-Wind Upwelling Vertically__
In addition to moving horizontally, ocean water moves _________.
__Cold Nutrients Offshore Trade-Wind Upwelling Vertically__
In addition to moving horizontally, ocean water moves _________.
Vertically
35
New cards
Fill in the blank with one of the words from the blank
__Cold Nutrients Offshore Trade-Wind Upwelling Vertically__
The upward motion of ocean water is called _________.
__Cold Nutrients Offshore Trade-Wind Upwelling Vertically__
The upward motion of ocean water is called _________.
Upwelling
36
New cards
Fill in the blank with one of the words from the blank
__Cold Nutrients Offshore Trade-Wind Upwelling Vertically__
Upwelling waters originate from the bottom of the ocean and are ______.
__Cold Nutrients Offshore Trade-Wind Upwelling Vertically__
Upwelling waters originate from the bottom of the ocean and are ______.
Cold
37
New cards
Fill in the blank with one of the words from the blank
__Cold, Nutrients, Offshore, Trade-Wind, Upwelling, Vertically__
Areas of upwelling exist mainly off the western coasts of continents in the _______________ belts.
__Cold, Nutrients, Offshore, Trade-Wind, Upwelling, Vertically__
Areas of upwelling exist mainly off the western coasts of continents in the _______________ belts.
Trade-Wind
38
New cards
Fill in the blank with one of the words from the blank
__Cold Nutrients Offshore Trade-Wind Upwelling Vertically__
The trade winds blow surface water offshore, and the surface water is replaced by _________ deep water.
__Cold Nutrients Offshore Trade-Wind Upwelling Vertically__
The trade winds blow surface water offshore, and the surface water is replaced by _________ deep water.
Upwelling
39
New cards
Fill in the blank with one of the words from the blank
__Cold Nutrients Offshore Trade-Wind Upwelling Vertically__
Upwelling waters are rich in __________ which support an abundant marine life population.
__Cold Nutrients Offshore Trade-Wind Upwelling Vertically__
Upwelling waters are rich in __________ which support an abundant marine life population.
Nutrients
40
New cards
What happens to most of the rain that falls in urban areas? Why?
Some of it evaporates, returning to the atmosphere, some seeps into the ground, and the remainder becomes surface water, traveling to oceans and lakes by way of rivers and streams. This is referred to as urban runoff. It is due to impervious cover (parking lots, pavement, buildings) that prevents water from soaking into the ground.
41
New cards
What is a watershed?
A land area that channels rainfall and snowmelt to creeks, streams, and rivers, and eventually to outflow points such as reservoirs, bays, and the ocean.
42
New cards
Rank these gases in order from highest to lowest concentration of Earth's atmosphere (highest concentration means that it makes up the biggest part of the atmosphere): carbon dioxide, water vapor, oxygen, nitrogen
highest concentration-nitrogen, oxygen, water vapor, dioxide-lowest concentration
43
New cards
Fill in the blanks
Molecules in a substance with a high temperature move ______ (fast/slowly), while molecules in a substance with a low temperature move ______(fast/slowly).
Molecules in a substance with a high temperature move ______ (fast/slowly), while molecules in a substance with a low temperature move ______(fast/slowly).
fast, slowly
44
New cards
What are the three types of heat transfer? Give an example of each.
Conduction - touching a hot pan, Convection - warm air rise and cool air sinks, Radiation - sun heats pavement
45
New cards
What molecule is important because it blocks harmful ultraviolet rays from the Sun?
Ozone
46
New cards
Describe what happens to temperature as you travel higher into the troposphere.
It gets colder
47
New cards
Describe what happens to air pressure as you travel higher into the troposphere.
The pressure goes down as you travel higher
48
New cards
In which layer of the atmosphere is the ozone layer found?
The stratosphere
49
New cards
What would be the long-term effect if the ozone layer was destroyed?
Without the ozone layer, too much harmful UVB radiation would have reached the Earth's surface. Increased exposure to ultraviolet radiation can cause skin cancer and eye cataracts, and damage crops, plants and microorganisms, affecting ecosystems and food chains.
50
New cards
Which is more dense, warm air or cold air?
Cold air is more dense
51
New cards
Why does warm air rise at a front and cold air stays close to the ground?
Convection currents
52
New cards
**Fill in the first blank using the following word bank, each option is a different color:**
==Water Vapor== %%Dew Point%% Temperature @@Convection@@ ^^Fahrenheit^^ %%Evaporation%% Latent @@Heat@@ ^^Condensation^^
Heat and temperature are not the same. _______ is a measure of how rapidly or slowly molecules move. In contrast, _____ is the transfer of energy that takes place because of temperature differences. Temperature can be measured in degrees Fahrenheit degrees Celsius, or Kelvins. The most commonly used temperature scale in the United States is _______. The atmosphere’s temperature plays a role in the formation of rain. The first step in cloud formation is when liquid water on the earth’s surface undergoes ________ and turns into a gas. Now in the atmosphere, ______ turns from a gas back into liquid cloud droplets through ___________. This process releases _____ heat. Those cloud droplets coalesce together and eventually form drops big enough to fall from the sky as precipitation. The heat released goes on to fuel more _______ __cells.__ \*\*\*Air must be saturated before condensation can occur. Saturation is the point at which the air holds as much water vapor as it possibly can. The __________ is the temperature to which air must be cooled at constant pressure to reach saturation. Until this temperature is reached, condensation cannot occur and rain cannot fall.
==Water Vapor== %%Dew Point%% Temperature @@Convection@@ ^^Fahrenheit^^ %%Evaporation%% Latent @@Heat@@ ^^Condensation^^
Heat and temperature are not the same. _______ is a measure of how rapidly or slowly molecules move. In contrast, _____ is the transfer of energy that takes place because of temperature differences. Temperature can be measured in degrees Fahrenheit degrees Celsius, or Kelvins. The most commonly used temperature scale in the United States is _______. The atmosphere’s temperature plays a role in the formation of rain. The first step in cloud formation is when liquid water on the earth’s surface undergoes ________ and turns into a gas. Now in the atmosphere, ______ turns from a gas back into liquid cloud droplets through ___________. This process releases _____ heat. Those cloud droplets coalesce together and eventually form drops big enough to fall from the sky as precipitation. The heat released goes on to fuel more _______ __cells.__ \*\*\*Air must be saturated before condensation can occur. Saturation is the point at which the air holds as much water vapor as it possibly can. The __________ is the temperature to which air must be cooled at constant pressure to reach saturation. Until this temperature is reached, condensation cannot occur and rain cannot fall.
Temperature
53
New cards
**Fill in the second blank using the following word bank, each option is a different color:**
==Water Vapor== %%Dew Point%% Temperature @@Convection@@ ^^Fahrenheit^^ %%Evaporation%% Latent @@Heat@@ ^^Condensation^^
Heat and temperature are not the same. _______ is a measure of how rapidly or slowly molecules move. In contrast, _____ is the transfer of energy that takes place because of temperature differences. Temperature can be measured in degrees Fahrenheit degrees Celsius, or Kelvins. The most commonly used temperature scale in the United States is _______. The atmosphere’s temperature plays a role in the formation of rain. The first step in cloud formation is when liquid water on the earth’s surface undergoes ________ and turns into a gas. Now in the atmosphere, ______ turns from a gas back into liquid cloud droplets through ___________. This process releases _____ heat. Those cloud droplets coalesce together and eventually form drops big enough to fall from the sky as precipitation. The heat released goes on to fuel more _______ __cells.__ \*\*\*Air must be saturated before condensation can occur. Saturation is the point at which the air holds as much water vapor as it possibly can. The __________ is the temperature to which air must be cooled at constant pressure to reach saturation. Until this temperature is reached, condensation cannot occur and rain cannot fall.
==Water Vapor== %%Dew Point%% Temperature @@Convection@@ ^^Fahrenheit^^ %%Evaporation%% Latent @@Heat@@ ^^Condensation^^
Heat and temperature are not the same. _______ is a measure of how rapidly or slowly molecules move. In contrast, _____ is the transfer of energy that takes place because of temperature differences. Temperature can be measured in degrees Fahrenheit degrees Celsius, or Kelvins. The most commonly used temperature scale in the United States is _______. The atmosphere’s temperature plays a role in the formation of rain. The first step in cloud formation is when liquid water on the earth’s surface undergoes ________ and turns into a gas. Now in the atmosphere, ______ turns from a gas back into liquid cloud droplets through ___________. This process releases _____ heat. Those cloud droplets coalesce together and eventually form drops big enough to fall from the sky as precipitation. The heat released goes on to fuel more _______ __cells.__ \*\*\*Air must be saturated before condensation can occur. Saturation is the point at which the air holds as much water vapor as it possibly can. The __________ is the temperature to which air must be cooled at constant pressure to reach saturation. Until this temperature is reached, condensation cannot occur and rain cannot fall.
Heat
54
New cards
**Fill in the third blank using the following word bank, each option is a different color:**
==Water Vapor== %%Dew Point%% Temperature @@Convection@@ ^^Fahrenheit^^ %%Evaporation%% Latent @@Heat@@ ^^Condensation^^
Heat and temperature are not the same. _______ is a measure of how rapidly or slowly molecules move. In contrast, _____ is the transfer of energy that takes place because of temperature differences. Temperature can be measured in degrees Fahrenheit degrees Celsius, or Kelvins. The most commonly used temperature scale in the United States is _______. The atmosphere’s temperature plays a role in the formation of rain. The first step in cloud formation is when liquid water on the earth’s surface undergoes ________ and turns into a gas. Now in the atmosphere, ______ turns from a gas back into liquid cloud droplets through ___________. This process releases _____ heat. Those cloud droplets coalesce together and eventually form drops big enough to fall from the sky as precipitation. The heat released goes on to fuel more _______ __cells.__ \*\*\*Air must be saturated before condensation can occur. Saturation is the point at which the air holds as much water vapor as it possibly can. The __________ is the temperature to which air must be cooled at constant pressure to reach saturation. Until this temperature is reached, condensation cannot occur and rain cannot fall.
==Water Vapor== %%Dew Point%% Temperature @@Convection@@ ^^Fahrenheit^^ %%Evaporation%% Latent @@Heat@@ ^^Condensation^^
Heat and temperature are not the same. _______ is a measure of how rapidly or slowly molecules move. In contrast, _____ is the transfer of energy that takes place because of temperature differences. Temperature can be measured in degrees Fahrenheit degrees Celsius, or Kelvins. The most commonly used temperature scale in the United States is _______. The atmosphere’s temperature plays a role in the formation of rain. The first step in cloud formation is when liquid water on the earth’s surface undergoes ________ and turns into a gas. Now in the atmosphere, ______ turns from a gas back into liquid cloud droplets through ___________. This process releases _____ heat. Those cloud droplets coalesce together and eventually form drops big enough to fall from the sky as precipitation. The heat released goes on to fuel more _______ __cells.__ \*\*\*Air must be saturated before condensation can occur. Saturation is the point at which the air holds as much water vapor as it possibly can. The __________ is the temperature to which air must be cooled at constant pressure to reach saturation. Until this temperature is reached, condensation cannot occur and rain cannot fall.
Farenheit
55
New cards
**Fill in the fourth blank using the following word bank, each option is a different color:**
==Water Vapor== %%Dew Point%% Temperature @@Convection@@ ^^Fahrenheit^^ %%Evaporation%% Latent @@Heat@@ ^^Condensation^^
Heat and temperature are not the same. _______ is a measure of how rapidly or slowly molecules move. In contrast, _____ is the transfer of energy that takes place because of temperature differences. Temperature can be measured in degrees Fahrenheit degrees Celsius, or Kelvins. The most commonly used temperature scale in the United States is _______. The atmosphere’s temperature plays a role in the formation of rain. The first step in cloud formation is when liquid water on the earth’s surface undergoes ________ and turns into a gas. Now in the atmosphere, ______ turns from a gas back into liquid cloud droplets through ___________. This process releases _____ heat. Those cloud droplets coalesce together and eventually form drops big enough to fall from the sky as precipitation. The heat released goes on to fuel more _______ __cells.__ \*\*\*Air must be saturated before condensation can occur. Saturation is the point at which the air holds as much water vapor as it possibly can. The __________ is the temperature to which air must be cooled at constant pressure to reach saturation. Until this temperature is reached, condensation cannot occur and rain cannot fall.
==Water Vapor== %%Dew Point%% Temperature @@Convection@@ ^^Fahrenheit^^ %%Evaporation%% Latent @@Heat@@ ^^Condensation^^
Heat and temperature are not the same. _______ is a measure of how rapidly or slowly molecules move. In contrast, _____ is the transfer of energy that takes place because of temperature differences. Temperature can be measured in degrees Fahrenheit degrees Celsius, or Kelvins. The most commonly used temperature scale in the United States is _______. The atmosphere’s temperature plays a role in the formation of rain. The first step in cloud formation is when liquid water on the earth’s surface undergoes ________ and turns into a gas. Now in the atmosphere, ______ turns from a gas back into liquid cloud droplets through ___________. This process releases _____ heat. Those cloud droplets coalesce together and eventually form drops big enough to fall from the sky as precipitation. The heat released goes on to fuel more _______ __cells.__ \*\*\*Air must be saturated before condensation can occur. Saturation is the point at which the air holds as much water vapor as it possibly can. The __________ is the temperature to which air must be cooled at constant pressure to reach saturation. Until this temperature is reached, condensation cannot occur and rain cannot fall.
Evaporation
56
New cards
**Fill in the fifth blank using the following word bank, each option is a different color:**
==Water Vapor== %%Dew Point%% Temperature @@Convection@@ ^^Fahrenheit^^ %%Evaporation%% Latent @@Heat@@ ^^Condensation^^
Heat and temperature are not the same. _______ is a measure of how rapidly or slowly molecules move. In contrast, _____ is the transfer of energy that takes place because of temperature differences. Temperature can be measured in degrees Fahrenheit degrees Celsius, or Kelvins. The most commonly used temperature scale in the United States is _______. The atmosphere’s temperature plays a role in the formation of rain. The first step in cloud formation is when liquid water on the earth’s surface undergoes ________ and turns into a gas. Now in the atmosphere, ______ turns from a gas back into liquid cloud droplets through ___________. This process releases _____ heat. Those cloud droplets coalesce together and eventually form drops big enough to fall from the sky as precipitation. The heat released goes on to fuel more _______ __cells.__ \*\*\*Air must be saturated before condensation can occur. Saturation is the point at which the air holds as much water vapor as it possibly can. The __________ is the temperature to which air must be cooled at constant pressure to reach saturation. Until this temperature is reached, condensation cannot occur and rain cannot fall.
==Water Vapor== %%Dew Point%% Temperature @@Convection@@ ^^Fahrenheit^^ %%Evaporation%% Latent @@Heat@@ ^^Condensation^^
Heat and temperature are not the same. _______ is a measure of how rapidly or slowly molecules move. In contrast, _____ is the transfer of energy that takes place because of temperature differences. Temperature can be measured in degrees Fahrenheit degrees Celsius, or Kelvins. The most commonly used temperature scale in the United States is _______. The atmosphere’s temperature plays a role in the formation of rain. The first step in cloud formation is when liquid water on the earth’s surface undergoes ________ and turns into a gas. Now in the atmosphere, ______ turns from a gas back into liquid cloud droplets through ___________. This process releases _____ heat. Those cloud droplets coalesce together and eventually form drops big enough to fall from the sky as precipitation. The heat released goes on to fuel more _______ __cells.__ \*\*\*Air must be saturated before condensation can occur. Saturation is the point at which the air holds as much water vapor as it possibly can. The __________ is the temperature to which air must be cooled at constant pressure to reach saturation. Until this temperature is reached, condensation cannot occur and rain cannot fall.
Water Vapor
57
New cards
**Fill in the sixth blank using the following word bank:**
==Water Vapor== %%Dew Point%% Temperature @@Convection@@ ^^Fahrenheit^^ %%Evaporation%% Latent @@Heat@@ ^^Condensation^^
Heat and temperature are not the same. _______ is a measure of how rapidly or slowly molecules move. In contrast, _____ is the transfer of energy that takes place because of temperature differences. Temperature can be measured in degrees Fahrenheit degrees Celsius, or Kelvins. The most commonly used temperature scale in the United States is _______. The atmosphere’s temperature plays a role in the formation of rain. The first step in cloud formation is when liquid water on the earth’s surface undergoes ________ and turns into a gas. Now in the atmosphere, ______ turns from a gas back into liquid cloud droplets through ___________. This process releases _____ heat. Those cloud droplets coalesce together and eventually form drops big enough to fall from the sky as precipitation. The heat released goes on to fuel more _______ __cells.__ \*\*\*Air must be saturated before condensation can occur. Saturation is the point at which the air holds as much water vapor as it possibly can. The __________ is the temperature to which air must be cooled at constant pressure to reach saturation. Until this temperature is reached, condensation cannot occur and rain cannot fall.
==Water Vapor== %%Dew Point%% Temperature @@Convection@@ ^^Fahrenheit^^ %%Evaporation%% Latent @@Heat@@ ^^Condensation^^
Heat and temperature are not the same. _______ is a measure of how rapidly or slowly molecules move. In contrast, _____ is the transfer of energy that takes place because of temperature differences. Temperature can be measured in degrees Fahrenheit degrees Celsius, or Kelvins. The most commonly used temperature scale in the United States is _______. The atmosphere’s temperature plays a role in the formation of rain. The first step in cloud formation is when liquid water on the earth’s surface undergoes ________ and turns into a gas. Now in the atmosphere, ______ turns from a gas back into liquid cloud droplets through ___________. This process releases _____ heat. Those cloud droplets coalesce together and eventually form drops big enough to fall from the sky as precipitation. The heat released goes on to fuel more _______ __cells.__ \*\*\*Air must be saturated before condensation can occur. Saturation is the point at which the air holds as much water vapor as it possibly can. The __________ is the temperature to which air must be cooled at constant pressure to reach saturation. Until this temperature is reached, condensation cannot occur and rain cannot fall.
Condensation
58
New cards
**Fill in the seventh blank using the following word bank, each option is a different color:**
==Water Vapor== %%Dew Point%% Temperature @@Convection@@ ^^Fahrenheit^^ %%Evaporation%% Latent @@Heat@@ ^^Condensation^^
Heat and temperature are not the same. _______ is a measure of how rapidly or slowly molecules move. In contrast, _____ is the transfer of energy that takes place because of temperature differences. Temperature can be measured in degrees Fahrenheit degrees Celsius, or Kelvins. The most commonly used temperature scale in the United States is _______. The atmosphere’s temperature plays a role in the formation of rain. The first step in cloud formation is when liquid water on the earth’s surface undergoes ________ and turns into a gas. Now in the atmosphere, ______ turns from a gas back into liquid cloud droplets through ___________. This process releases _____ heat. Those cloud droplets coalesce together and eventually form drops big enough to fall from the sky as precipitation. The heat released goes on to fuel more _______ __cells.__ \*\*\*Air must be saturated before condensation can occur. Saturation is the point at which the air holds as much water vapor as it possibly can. The __________ is the temperature to which air must be cooled at constant pressure to reach saturation. Until this temperature is reached, condensation cannot occur and rain cannot fall.
==Water Vapor== %%Dew Point%% Temperature @@Convection@@ ^^Fahrenheit^^ %%Evaporation%% Latent @@Heat@@ ^^Condensation^^
Heat and temperature are not the same. _______ is a measure of how rapidly or slowly molecules move. In contrast, _____ is the transfer of energy that takes place because of temperature differences. Temperature can be measured in degrees Fahrenheit degrees Celsius, or Kelvins. The most commonly used temperature scale in the United States is _______. The atmosphere’s temperature plays a role in the formation of rain. The first step in cloud formation is when liquid water on the earth’s surface undergoes ________ and turns into a gas. Now in the atmosphere, ______ turns from a gas back into liquid cloud droplets through ___________. This process releases _____ heat. Those cloud droplets coalesce together and eventually form drops big enough to fall from the sky as precipitation. The heat released goes on to fuel more _______ __cells.__ \*\*\*Air must be saturated before condensation can occur. Saturation is the point at which the air holds as much water vapor as it possibly can. The __________ is the temperature to which air must be cooled at constant pressure to reach saturation. Until this temperature is reached, condensation cannot occur and rain cannot fall.
Laten
59
New cards
Fill in the eighth blank using the following word bank, each option is a different color:
==Water Vapor== %%Dew Point%% Temperature @@Convection@@ ^^Fahrenheit^^ %%Evaporation%% Latent @@Heat@@ ^^Condensation^^
Heat and temperature are not the same. _______ is a measure of how rapidly or slowly molecules move. In contrast, _____ is the transfer of energy that takes place because of temperature differences. Temperature can be measured in degrees Fahrenheit degrees Celsius, or Kelvins. The most commonly used temperature scale in the United States is _______. The atmosphere’s temperature plays a role in the formation of rain. The first step in cloud formation is when liquid water on the earth’s surface undergoes ________ and turns into a gas. Now in the atmosphere, ______ turns from a gas back into liquid cloud droplets through ___________. This process releases _____ heat. Those cloud droplets coalesce together and eventually form drops big enough to fall from the sky as precipitation. The heat released goes on to fuel more _______ __cells.__ \*\*\*Air must be saturated before condensation can occur. Saturation is the point at which the air holds as much water vapor as it possibly can. The __________ is the temperature to which air must be cooled at constant pressure to reach saturation. Until this temperature is reached, condensation cannot occur and rain cannot fall.
==Water Vapor== %%Dew Point%% Temperature @@Convection@@ ^^Fahrenheit^^ %%Evaporation%% Latent @@Heat@@ ^^Condensation^^
Heat and temperature are not the same. _______ is a measure of how rapidly or slowly molecules move. In contrast, _____ is the transfer of energy that takes place because of temperature differences. Temperature can be measured in degrees Fahrenheit degrees Celsius, or Kelvins. The most commonly used temperature scale in the United States is _______. The atmosphere’s temperature plays a role in the formation of rain. The first step in cloud formation is when liquid water on the earth’s surface undergoes ________ and turns into a gas. Now in the atmosphere, ______ turns from a gas back into liquid cloud droplets through ___________. This process releases _____ heat. Those cloud droplets coalesce together and eventually form drops big enough to fall from the sky as precipitation. The heat released goes on to fuel more _______ __cells.__ \*\*\*Air must be saturated before condensation can occur. Saturation is the point at which the air holds as much water vapor as it possibly can. The __________ is the temperature to which air must be cooled at constant pressure to reach saturation. Until this temperature is reached, condensation cannot occur and rain cannot fall.
Convection
60
New cards
Fill in the ninth blank using the following word bank:
==Water Vapor== %%Dew Point%% Temperature @@Convection@@ ^^Fahrenheit^^ %%Evaporation%% Latent @@Heat@@ ^^Condensation^^
Heat and temperature are not the same. _______ is a measure of how rapidly or slowly molecules move. In contrast, _____ is the transfer of energy that takes place because of temperature differences. Temperature can be measured in degrees Fahrenheit degrees Celsius, or Kelvins. The most commonly used temperature scale in the United States is _______. The atmosphere’s temperature plays a role in the formation of rain. The first step in cloud formation is when liquid water on the earth’s surface undergoes ________ and turns into a gas. Now in the atmosphere, ______ turns from a gas back into liquid cloud droplets through ___________. This process releases _____ heat. Those cloud droplets coalesce together and eventually form drops big enough to fall from the sky as precipitation. The heat released goes on to fuel more _______ __cells.__ \*\*\*Air must be saturated before condensation can occur. Saturation is the point at which the air holds as much water vapor as it possibly can. The __________ is the temperature to which air must be cooled at constant pressure to reach saturation. Until this temperature is reached, condensation cannot occur and rain cannot fall.
==Water Vapor== %%Dew Point%% Temperature @@Convection@@ ^^Fahrenheit^^ %%Evaporation%% Latent @@Heat@@ ^^Condensation^^
Heat and temperature are not the same. _______ is a measure of how rapidly or slowly molecules move. In contrast, _____ is the transfer of energy that takes place because of temperature differences. Temperature can be measured in degrees Fahrenheit degrees Celsius, or Kelvins. The most commonly used temperature scale in the United States is _______. The atmosphere’s temperature plays a role in the formation of rain. The first step in cloud formation is when liquid water on the earth’s surface undergoes ________ and turns into a gas. Now in the atmosphere, ______ turns from a gas back into liquid cloud droplets through ___________. This process releases _____ heat. Those cloud droplets coalesce together and eventually form drops big enough to fall from the sky as precipitation. The heat released goes on to fuel more _______ __cells.__ \*\*\*Air must be saturated before condensation can occur. Saturation is the point at which the air holds as much water vapor as it possibly can. The __________ is the temperature to which air must be cooled at constant pressure to reach saturation. Until this temperature is reached, condensation cannot occur and rain cannot fall.
Dew Point
61
New cards
Fill in the blank
The area of the globe that receives the most solar radiation year round is called the ________.
The area of the globe that receives the most solar radiation year round is called the ________.
Equator
62
New cards
Fill in the blank
Climates are classified based on average monthly __________ and __________.
Climates are classified based on average monthly __________ and __________.
Temperature, Precipitation
63
New cards
Fill in the first two blanks
Different paths of the Earth receive more or less solar radiation. Fill in the latitudes for each of the following climate zones on the Earth.
1. Tropics = latitudes __° and __° °N and °S
2. Temperate = latitudes __° and __° °N and °S
3. Polar = latitudes __° and __° °N and °S
Different paths of the Earth receive more or less solar radiation. Fill in the latitudes for each of the following climate zones on the Earth.
1. Tropics = latitudes __° and __° °N and °S
2. Temperate = latitudes __° and __° °N and °S
3. Polar = latitudes __° and __° °N and °S
0°, 30°
64
New cards
Fill in the third and fourth blanks
Different paths of the Earth receive more or less solar radiation. Fill in the latitudes for each of the following climate zones on the Earth.
1. Tropics = latitudes __° and __° °N and °S
2. Temperate = latitudes __° and __° °N and °S
3. Polar = latitudes __° and __° °N and °S
Different paths of the Earth receive more or less solar radiation. Fill in the latitudes for each of the following climate zones on the Earth.
1. Tropics = latitudes __° and __° °N and °S
2. Temperate = latitudes __° and __° °N and °S
3. Polar = latitudes __° and __° °N and °S
30°, 60°
65
New cards
Fill in the fifth and sixth blanks
Different paths of the Earth receive more or less solar radiation. Fill in the latitudes for each of the following climate zones on the Earth.
1. Tropics = latitudes __° and __° °N and °S
2. Temperate = latitudes __° and __° °N and °S
3. Polar = latitudes __° and __° °N and °S
Different paths of the Earth receive more or less solar radiation. Fill in the latitudes for each of the following climate zones on the Earth.
1. Tropics = latitudes __° and __° °N and °S
2. Temperate = latitudes __° and __° °N and °S
3. Polar = latitudes __° and __° °N and °S
60°, 90°
66
New cards
What is the difference between weather and climate?
Weather changes from day to day and climate is over a long period of time.
67
New cards
Earth’s tropical regions receive more of the Sun’s energy than polar regions because they
1. Contain a greater percentage of dry land.
2. Have more vegetation to absorb the Sun’s energy.
3. Have a thinner atmosphere than the polar regions.
4. Receive a greater concentration of the Sun’s rays.
1. Contain a greater percentage of dry land.
2. Have more vegetation to absorb the Sun’s energy.
3. Have a thinner atmosphere than the polar regions.
4. Receive a greater concentration of the Sun’s rays.
answer- d
68
New cards
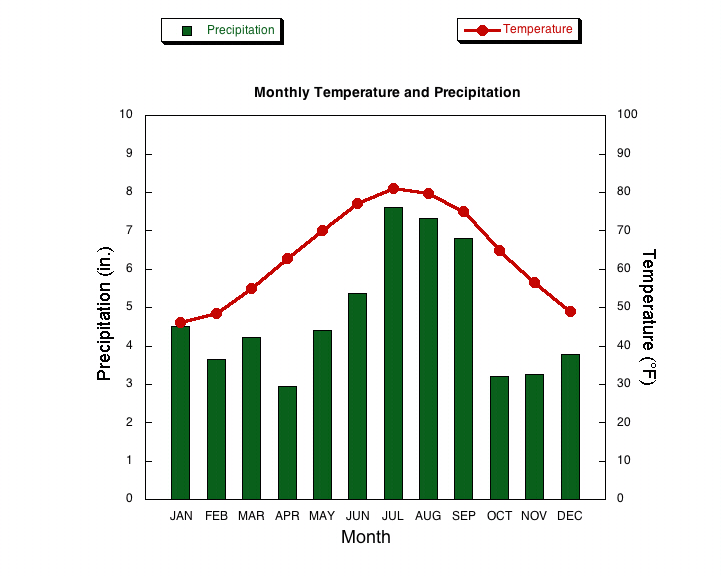
Using the climagram on the left, which month has the lowest precipitation in Wilmington, NC?
April
69
New cards
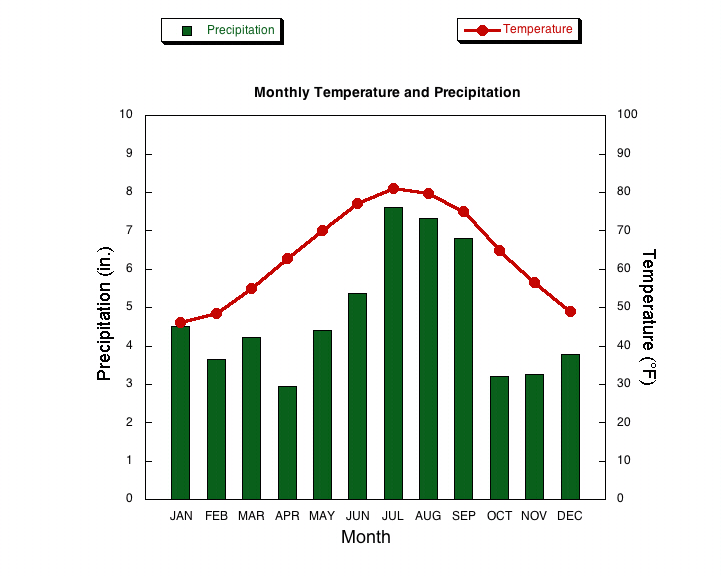
Approximately what temperature °F is the warmest average shown for this location?
July, 80°
70
New cards
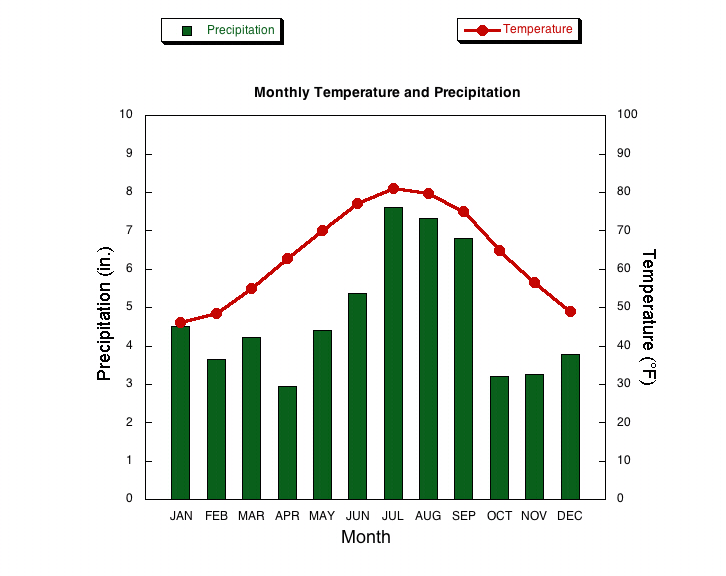
Which is the independent variable in this climagram?
The month
71
New cards
What is Global Warming? What causes it?
Global warming is the term used to describe the rising of the average temperature on Earth. It has to do with the overall climate of the Earth rather than the weather on any given day. It is caused by increased concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, mainly from human activities such as burning fossil fuels, and farming.
72
New cards
How could planting trees help reduce global warming?
As trees grow, they help stop climate change by removing carbon dioxide from the air, storing carbon in the trees and soil, and releasing oxygen into the atmosphere.
73
New cards
What is a renewable resource? List Examples.
Water, wind, geothermal, biomass, solar. A renewable resource is a natural resource which will replenish to replace the portion depleted by usage and consumption, either through natural reproduction or other recurring processes in a finite amount of time in a human time scale.
74
New cards
What is a nonrenewable resource? List examples.
Oil, natural gas, coal, nuclear, A non-renewable resource is a natural resource that cannot be readily replaced by natural means at a pace quick enough to keep up with consumption.
75
New cards
Define the terms rotation and revolution. Know how to draw a diagram for each
Rotation = Earth’s spinning on its axis. This takes 24 hours.
Revolution = Earth’s circling around the Sun. This takes 365 days.
Revolution = Earth’s circling around the Sun. This takes 365 days.
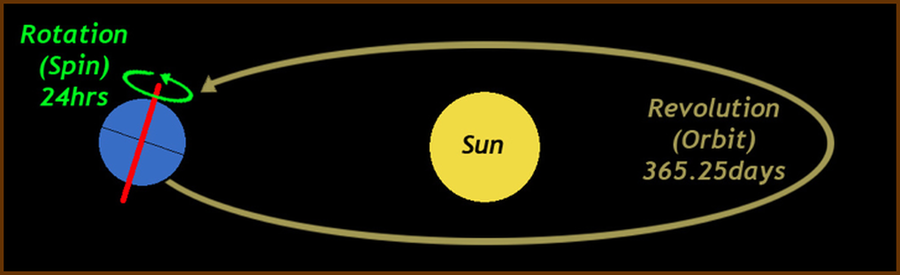
76
New cards
What is a Neap Tide? know how to draw a diagram of a neap tide, showing the locations of the earth, sun, and moon.
Neap tides occur when the sun, moon, and Earth form a right angle, and this causes the regular high tides and low tides to become much lower than usual. This happens during the first and 3rd quarter moon phases.
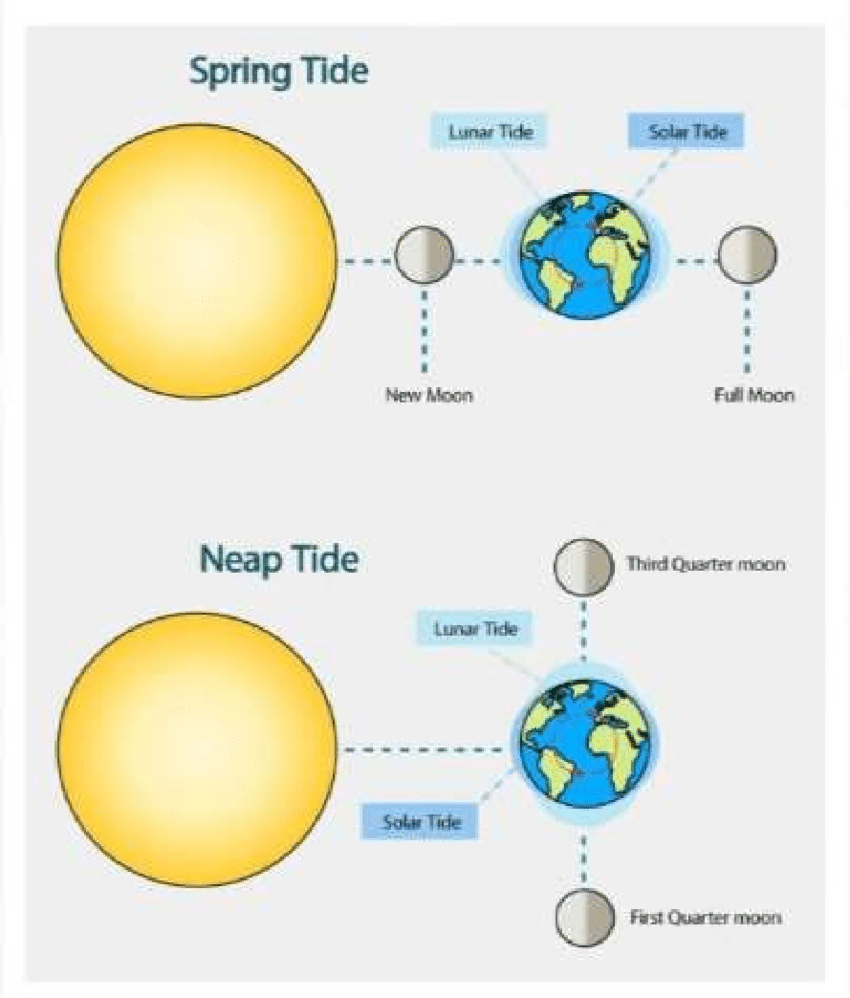
77
New cards
What is a spring tide? Know to draw a diagram of the two phases of the moon that correspond with a spring tide, and show the location of the sun, moon, and the Earth
Spring tides occur when the sun, moon, and Earth are lined up, and this causes regular high tides and low tides to be much higher. This occurs during full and new moon phases.
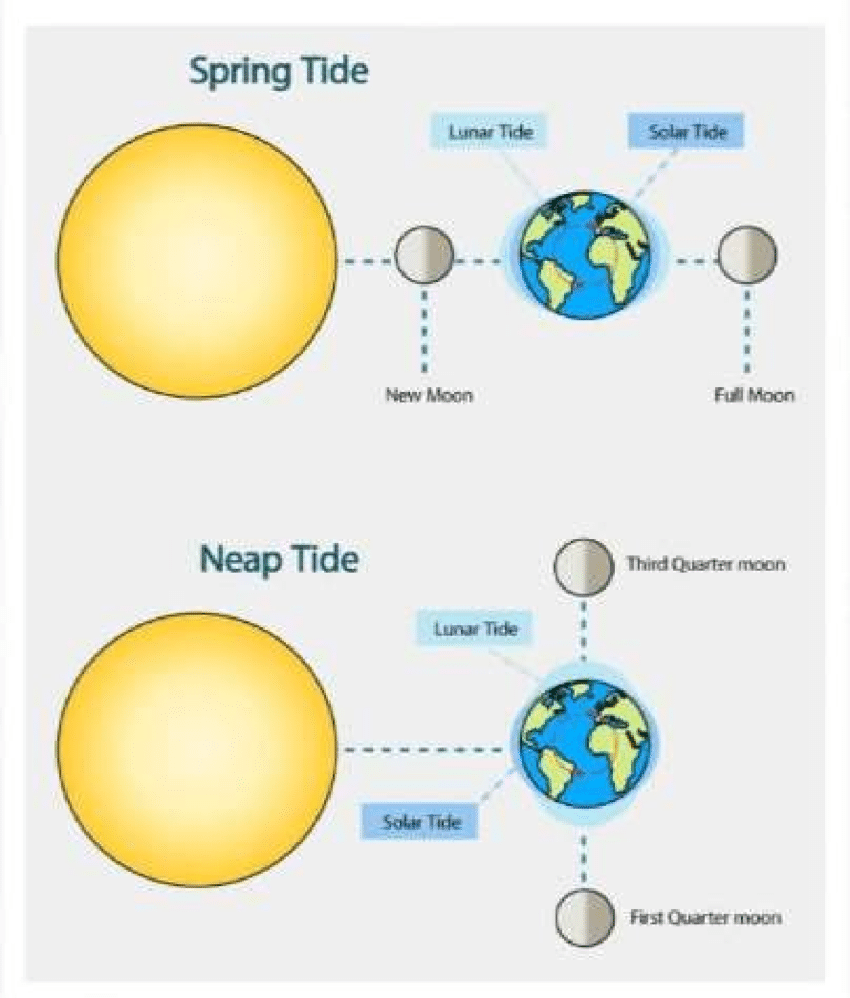
78
New cards
What is a solstice?
Time of the year when the sun is farthest from the equatorial plane resulting in long nights and short days.
79
New cards
How do the lengths of day contrast from summer solstice and winter solstice?
The summer solstice is the longest day of the year, meaning it experiences the maximum intensity of the sun's rays and has the most hours of sunlight. The winter solstice is the shortest day of the year and has the fewest hours of daylight.
80
New cards
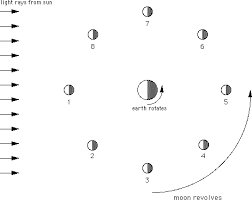
In which position would a person on Earth see a full moon?
5
81
New cards
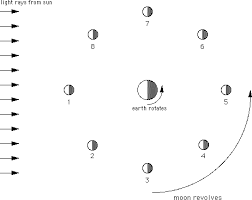
In which position(s) would a person on Earth see a moon in the waxing phases?
2, and 4
82
New cards
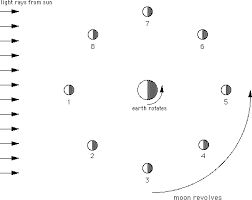
In which position(s) would a person on Earth see a moon in the waning phases?
6, and 8
83
New cards
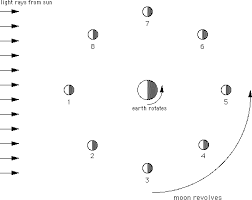
In which position would a person on Earth see a third quarter moon?
7