Cerebral Cortex I
1/85
Earn XP
Description and Tags
LSU KIN 4571 Exam 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
lobe
a well-defined portion of an organ
sulcus/fissure
a groove or slit
gyrus
a convoluted surface of the brain
Broca’s area
Damage to this area causes a hard time producing speech. You know what you want to say but cannot physically say it.
Wernicke’s Area
Damage to this area causes “word salad” where your speech sounds perfect but it’s comprised of random words and you have difficulty understanding what someone is saying to you.
Broca’s speech production
What is in blue?
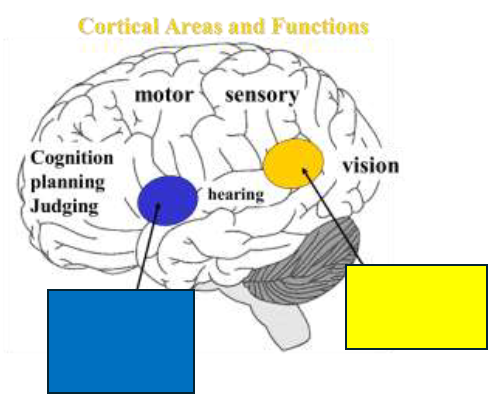
Wernicke’s language comprehension
What is in yellow?
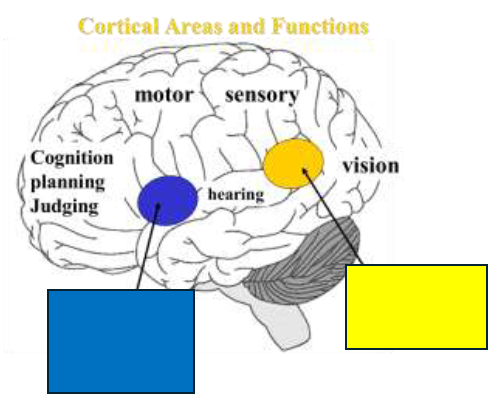
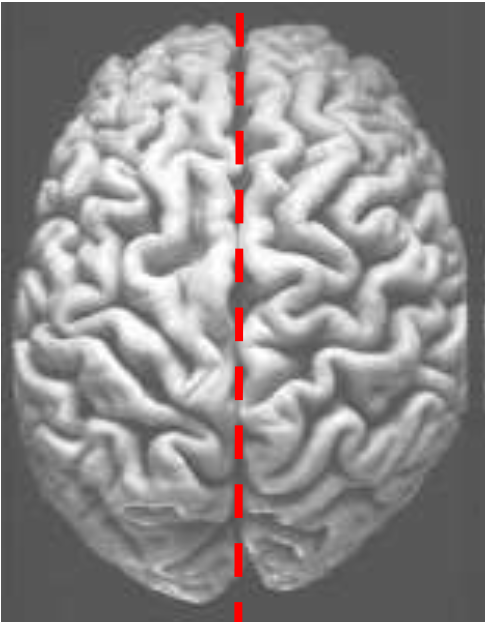
Interhemispheric Fissure
What does the dotted red line represent?
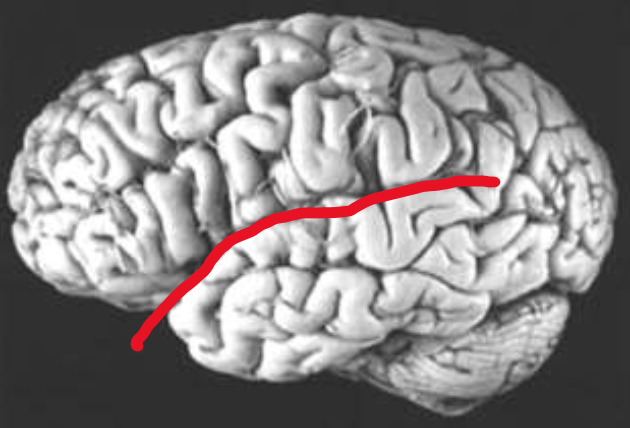
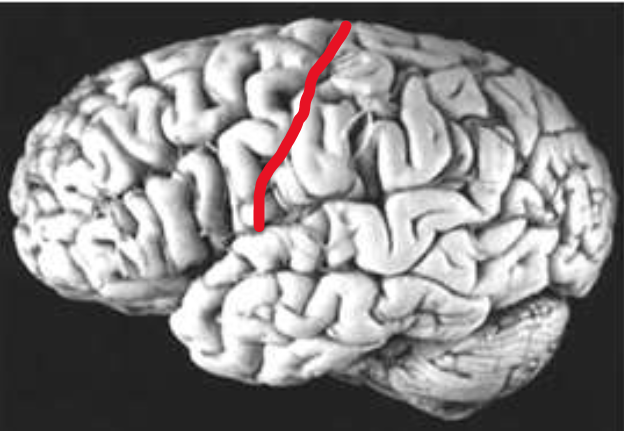
Lateral Fissure
What does the red line represent?
Parieto-occipital Fissure
What does the red line represent?
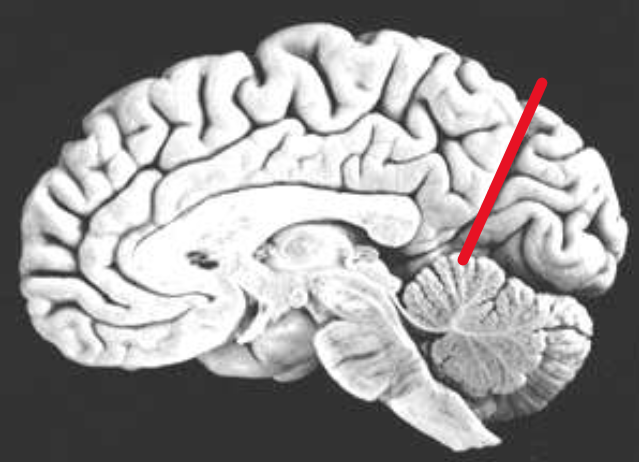
Central Sulcus
What does the red line represent?
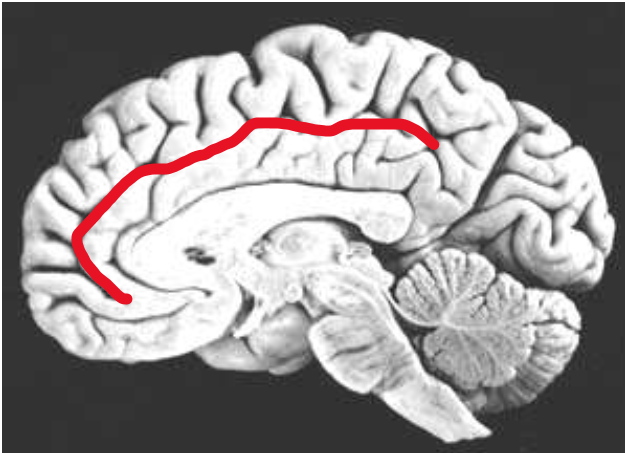
Cingulate Sulcus
What does the red line represent?
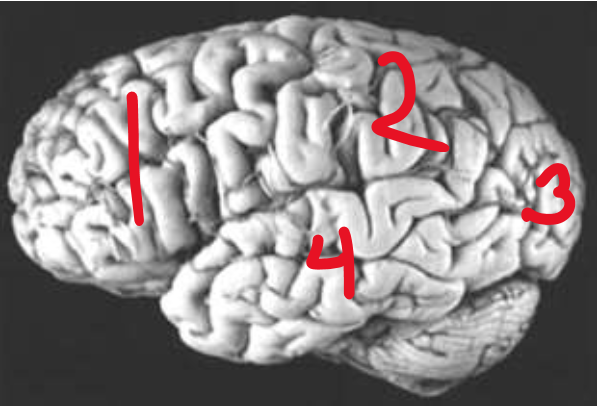
Frontal Lobe
What is number 1?
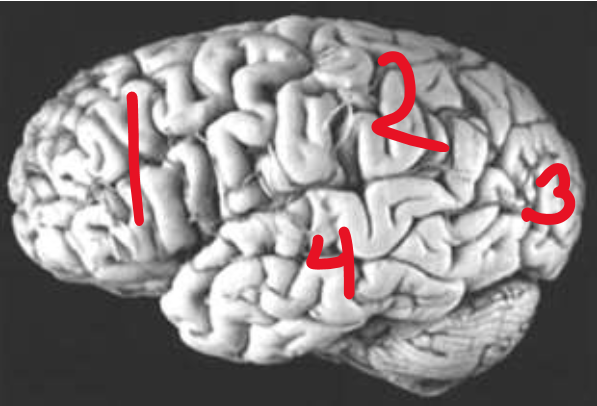
Parietal Lobe
What is number 2?
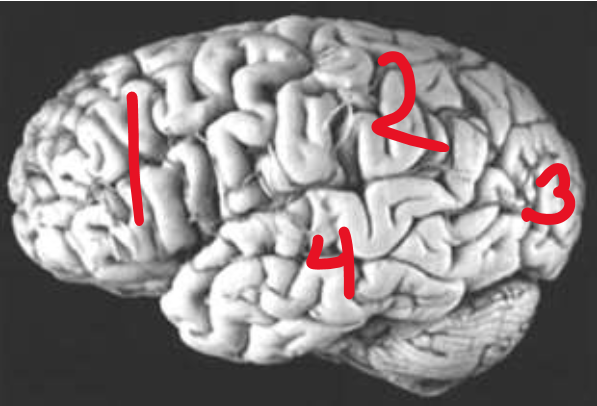
Occipital Lobe
What is number 3?
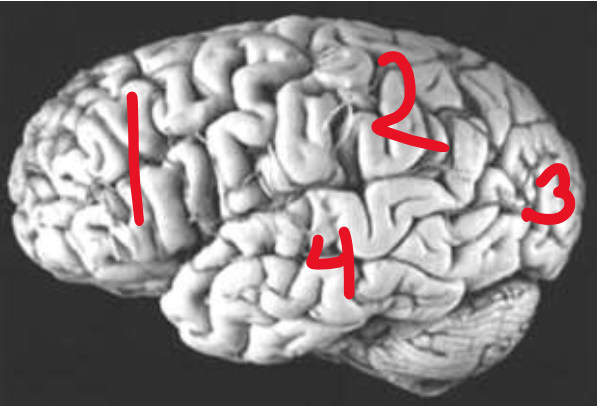
Temporal Lobe
What is number 4?
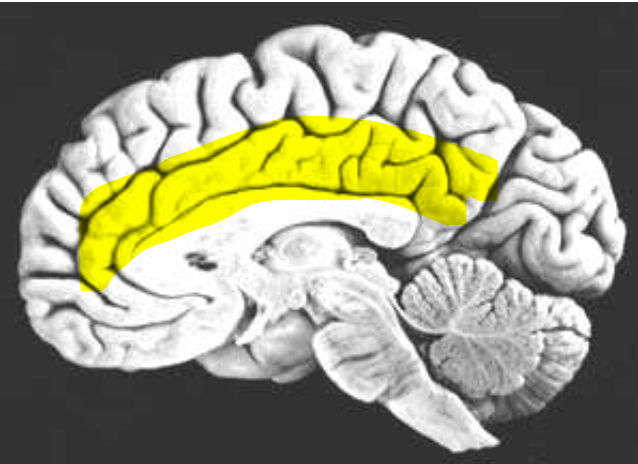
Limbic Lobe
What is the name of the highlighted region?
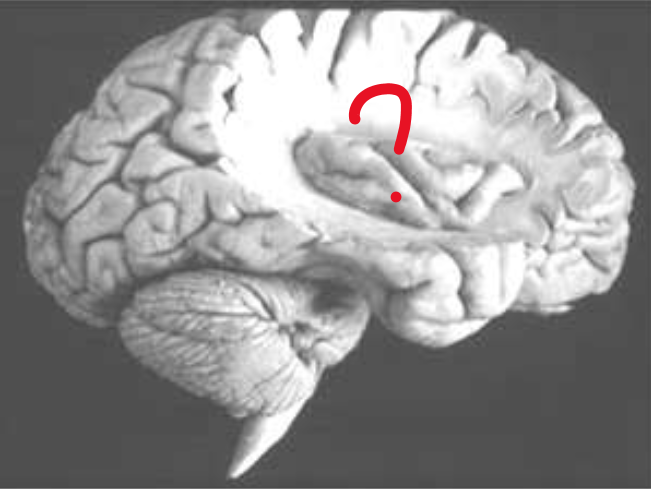
Insular Lobe
What does the red question mark represent?
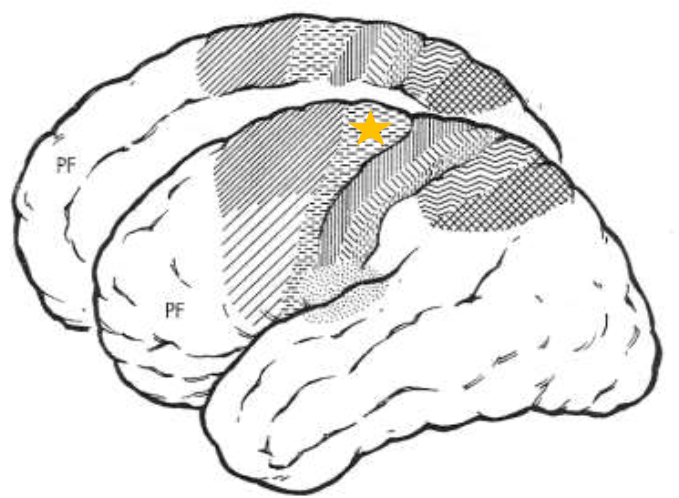
Primary Motor Cortex (MI)
What does the star represent?
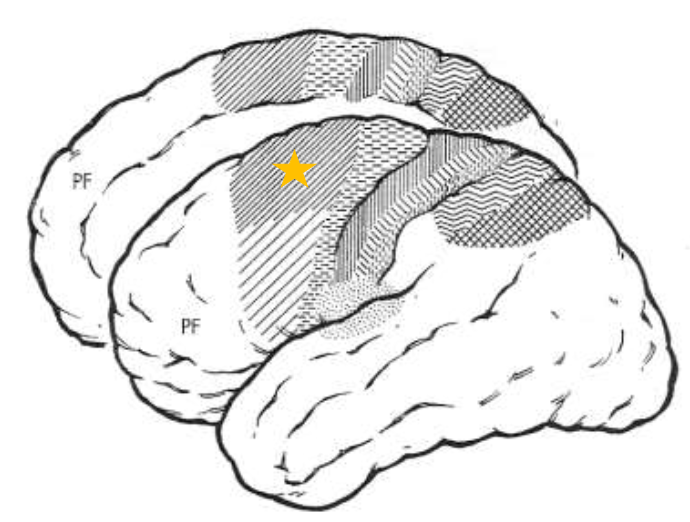
Supplementary Motor Area (SMA)
What does the star represent?
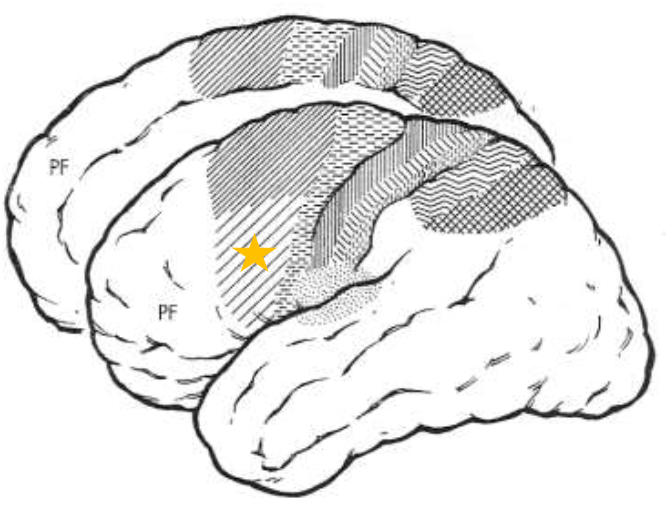
Premotor Cortex (PM)
What does the star represent?
Primary Somatosensory Area 3 (SI3)
What does the star represent?
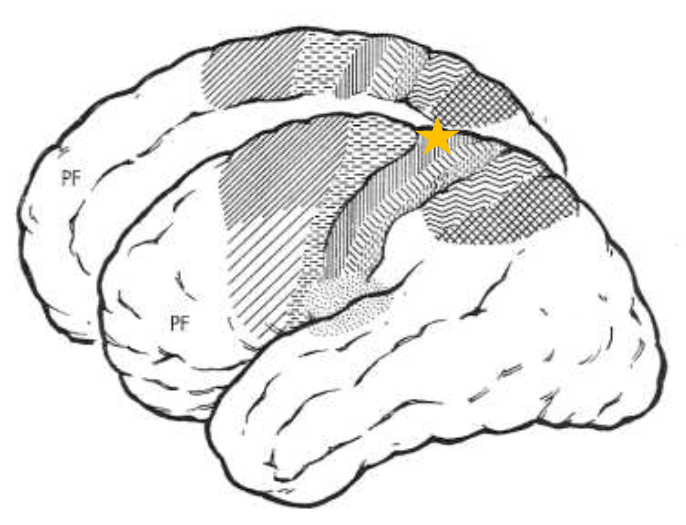
Primary Somatosensory Area 1 (SI1)
What does the star represent?
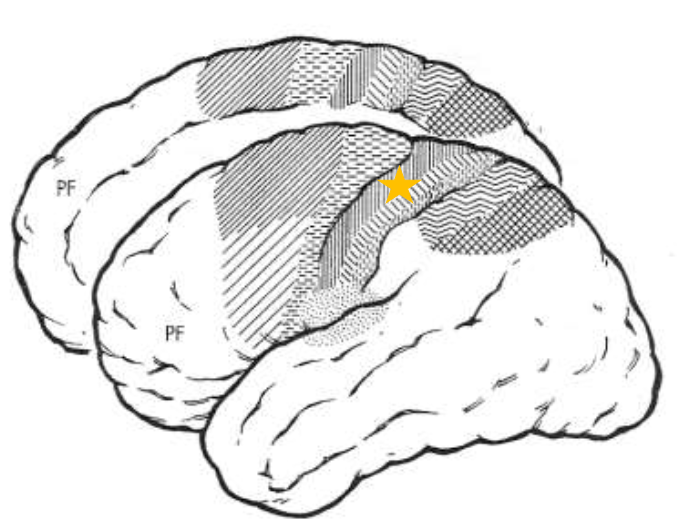
Primary Somatosensory Area 2 (SI2)
What does the star represent?
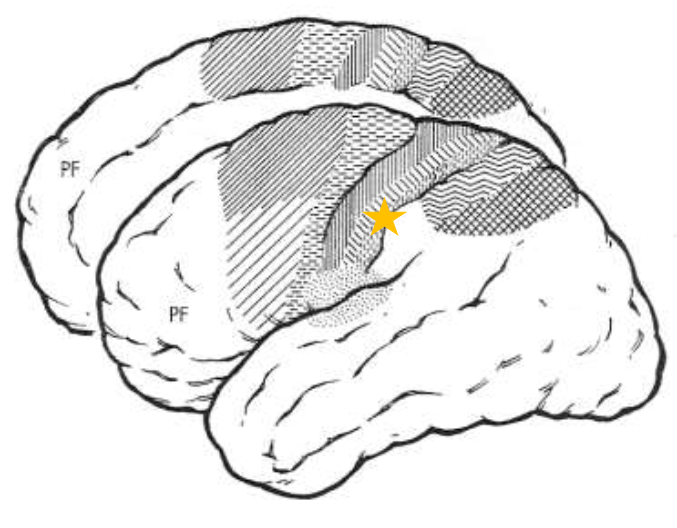
Secondary Somatosensory Area (SII)
What does the star represent?
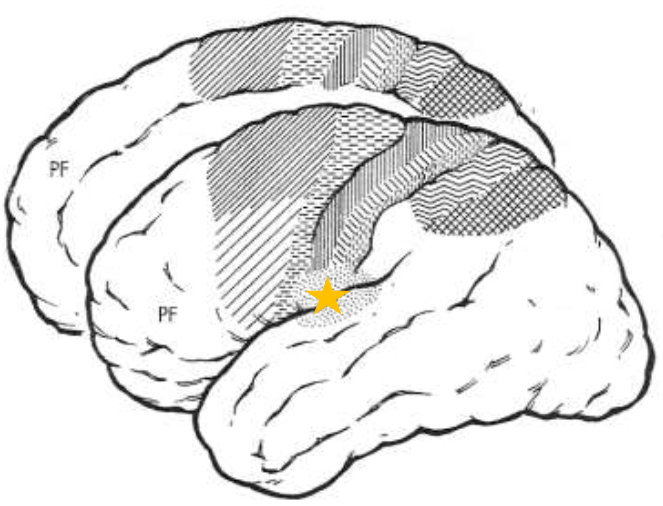
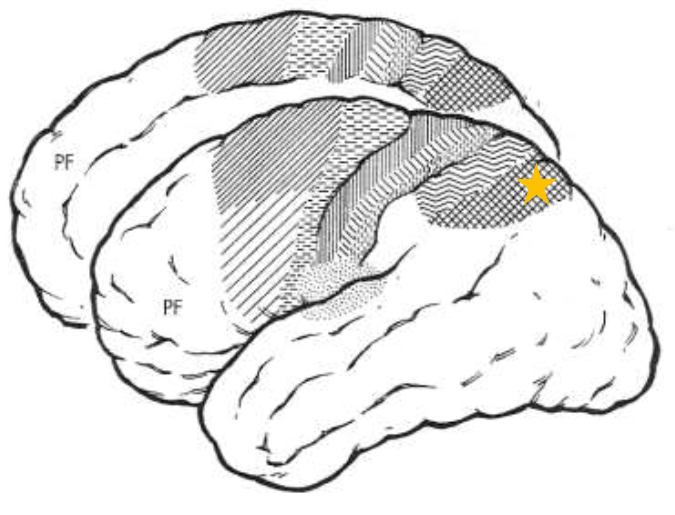
Posterior Parietal Cortex Area 5
What does the star represent?
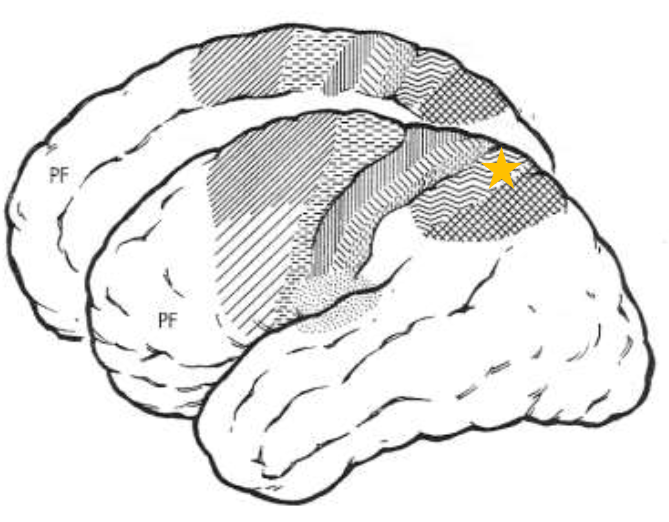
Posterior Parietal Cortex Area 7
What does the star represent?
Lower Limb
What part of the body does the most medial homunculus represent?
Upper limb
What part of the body does the middle homunculus represent (between most medial and most lateral)?
Face
What part of the body does the most lateral homunculus represent?
MI (movement) and SI (sensory)
What cortical areas have homunculi?
4
How many Brodmann Area(s) does the Primary Motor Cortex (MI) have?
lowest
What is the stimulation threshold of the Primary Motor Cortex (MI)?
“Individual” joints muscle contraction (simple movement)
What stimulation activates the Primary Motor Cortex (MI)?
Descending; Contralateral
What projections does the Primary Motor Cortex (MI) have? What is it mostly?
Bilateral
The descending projections of the Primary Motor Cortex (MI) that control the face are sometimes ____________.
6
How many Brodmann Area(s) does the Premotor Cortex (PM) have?
Higher
What is the stimulation threshold of the Premotor Cortex?
Multi-joint movement, coordination, visual and tactile cues (complex movements)
What stimulation activates the Premotor Cortex (PM)?
Descending and Corticocortical
What projections does the Premotor Cortex (PM) have?
axial and proximal muscles
What does the descending projections of the Premotor Cortex (PM) control?
visual and tactile
What type of information does the Corticocortical Projections of the Premotor Cortex (PM) send to the MI to carry out actions?
6-medial
How many Brodmann Area(s) does the Supplementary Motor Area (SMA) have?
higher
What is the stimulation threshold of the Supplementary Motor Area (SMA)?
Thinking, planning, sequences (complex movements)
What stimulation activates the Supplementary Motor Area (SMA)?
Descending; Corticocortical
The Supplementary Motor Area (SMA) has some _________ projections but it’s mostly __________.
Contralateral and Bilateral
The descending and corticocortical projections of the Supplementary Motor Area (SMA) are _________.
Primary Motor Cortex (MI)
The Supplementary Motor Area (SMA) mostly projects information to the _____________.
Coordinated movements
________________ are orchestrated by projections to the Primary Motor Cortex (MI).
movement modulation
The Basal Ganglia controls ___________.
Coordination
The Cerebellum controls _____________.
paresis of the affected area (homunculus)
What is the damage if there are lesions on the Primary Motor Cortex (MI)?
axial and proximal; digits
Recovery for damage to the Primary Motor Cortex (MI): slow, beginning in _____________, gradual improvement toward _______.
trunks and arms; learn/remember
If the Primary Motor Cortex (MI) is damaged, the movement of the __________ (premotor cortex) and the ability to ___________ motor sequences (SMA) will be maintained.
manual dexterity
If the Primary Motor Cortex (MI) is damaged, ___________ is lost.
paresis of axial and proximal muscles
What is the damage if there are lesions on the Premotor Cortex (PM)?
perform slow complex motor sequences
What is the recovery for a damaged Premotor Cortex (PM)?
afferent; visual or tactile
If the Premotor Cortex (PM) is damaged, there will be a loss of performing complex movements depending on ________ and any movement using ___________ sense.
motor apraxia
What is the damage if there are lesions on the Supplementary Motor Area (SMA)?
independent use of each hand
What is maintained after damage to the Supplementary Motor Area (SMA)?
sequenced movements and cooperation with both hands
What is lost if the Supplementary Motor Area (SMA) is damaged?
Thalamus; Parietal Fields and PM
The Primary Somatosensory Area (SI) gets most of its info from the ___________ and sends most of its info to the ___________.
T10
What dermatome is by the belly button?
T4
What dermatome is by the nipple?
below
If there is a spinal cord transection, the loss of sensation will be _______ the injury.
cervical
dermatomes of the head, shoulders, outer part of arm (back of hand side), hands
thoracic
dermatomes of thoracic cavity and inner part of arm (palm side)
lumbar
dermatomes of lumbar area and anterior portion of legs and feet (top of foot/leg)
sacral
dermatomes of backside and posterior portion of legs and feet (bottom of foot/leg)
SI; Insular
The Secondary Somatosensory Area (SII) gets and sends most of its info from and to ______. It also sends a lot of info to the __________.
Prefrontal
Composed of: Decision making, goal setting, cognitive skills, visual motor tasks, motor planning
exploratory movements
The Secondary Somatosensory Area (SII) is very active during __________.
somatic sensory
Posterior Parietal Cortex Area 5 (PP5) is ___________.
visual input
Posterior Parietal Cortex Area 7 (PP7) is ___________.
prefrontal cortex
The two Posterior Parietal Cortex Areas (5 and 7) mostly communicate through the __________ but can communicate with each other.
active learning
The Posterior Parietal Cortex (PP) Areas 5 and 7 produce a strong response during __________.
contralateral sensory loss
What is lost if the Primary Somatosensory Area has lesions?
Primary Somatosensory Area (SI)
Lesions on this area causes: no accurate feedback, decreased sharp dull sensations, proprioception, object location, tactile stereognosis (perceiving object properties via touch)
grip load/force; ataxia; fine
If the Primary Somatosensory Area is damaged, then __________ will be affected, ______ will occur and you will have a hard time with ______ motor skills.
Secondary Somatosensory Area (SII)
Lesions on this area causes: decreased association between object size and movements
texture/shape; grip force
If the Secondary Somatosensory Area (SII) is damaged, then there will be an effect on object _________ and _________.
contralateral; visual/tactile
What is lost if there are lesions on the Posterior Parietal Cortex Areas 5 and 7 (PP)?
reach/grasp
What relies on visual/tactile information?
Posterior Parietal Cortex Area 5 (PP5)
Lesions on this area causes: decreased tactile agnosia where other sensations can be perceived, but touch cannot be interpreted.
Posterior Parietal Cortex Area 7 (PP7)
Lesions on this area causes: decreased visually guided movements
contralateral neglect syndrome
Damage to the Posterior Parietal Cortex Areas (5 and 7) causes ___________, where half of the body and its visual field are ignored.