Infection and Immunology SUMMATIVE REVIEW NOT FOR I&I COURSE
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Review for Summatives; this is not as comprehensive as my other decks.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome is a set of criteria to screen for sepsis. What levels are considered abnormal for each of the following criteria?
HR
T
RR
WBC
HR >90 bpm abnormal
T >100.4 F or <96.8 F
RR >20 bpm
WBC >12,000 cells/microliter or <4000 cells/uL
Mycobacterium avium complex is more common in patients with _____ and is treated with __________.
more common in patients with AIDS (CD4 <50 cells/uL)
Tx: Macrolide (Azithromycin OR clarithromycin) PLUS ethambutol and rifabutin
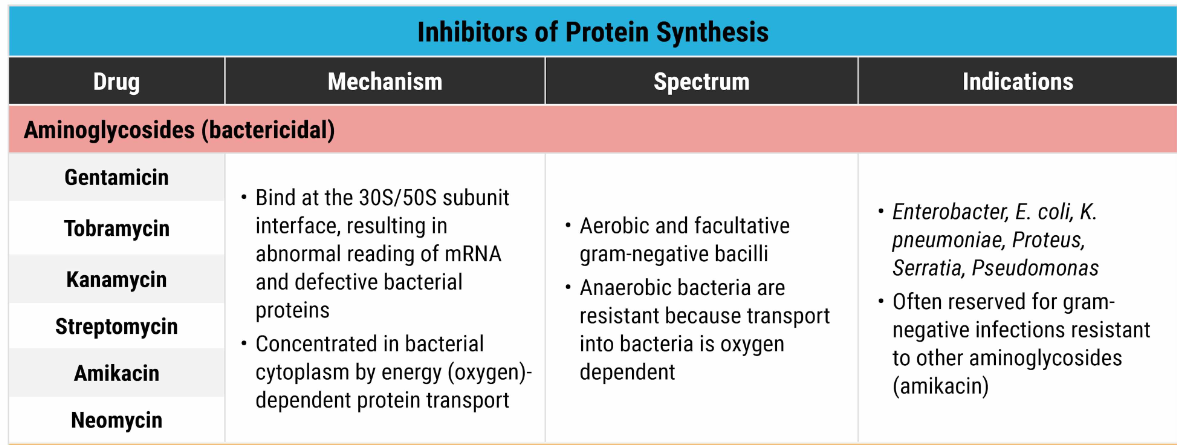
The following antibiotics are examples of _________, and their MOA is ______:
Gentamicin, Kanamycin, Streptomycin, Neomycin
aminoglycosides (batericidal); inhibit protein synthesis
Which of the following agents are NOT recommended against MRSA?
a. doxycycline
b. Piperacillin-tazobactam
c. clindamycin
d. Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole
B. Piperacillin-tazobactam
the other three agents are indicated against MRSA (doxy, bactrim, clindamycin)
Co-infection of HIV and __________ can lead to the development of Kaposi Sarcoma, which can present in oral mucosa or skin.
Human herpesvirus 8 infection
How is Epstein-Barr virus mononucleosis different from (clinically) cytomegalovirus mononucleosis?
Tonsillitis, enlarged cervical lymph nodes, and splenomegaly are more common in Epstein-Barr virus mononucleosis. Fever and systemic symptoms are more common in cytomegalovirus mononucleosis.
Patients with HIV who are on prophylactic Bactrim (TMP-SMX) may develop _____ anemia as a complication due to …
macrocytic anemia due to folate deficiency
(Bactrim (TMP-SMX) interferes with folate synthesis; folate is needed for DNA synthesis, and erythropoiesis is disturbed when DNA synthesis is disrupted)
Q fever (Coxiella burnetti) can be treated with…
doxycycline (first line for acute Q fever)
___________ is associated with hot tub folliculitis
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
most common cause of cellulitis
Streptococcus pyogenes
What is the most common cause of babesiosis in the USA? What are some symptoms?
Babesia microti which is spread by tick bites
Ssx include gradual onset of flu like symptoms
What is the route of administration for Bacitracin, and what is the coverage (gram neg or gram positive)
route: topical
covg: gram positive
What is the treatment for lymphogranuloma venereum (hint: it’s the same as for granuloma inguinale)?
give the medicine plus the timing
doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for 21 days
Diphyllobothriasis (fish tapeworm) is the largest human tapeworm. ___ deficiency supports the diagnosis.
B12 deficiency - associated w fish tapeworm
True or False: Penicillin is effective against gram positive bacteria, but not gram negative or beta lactamase producing organisms
true
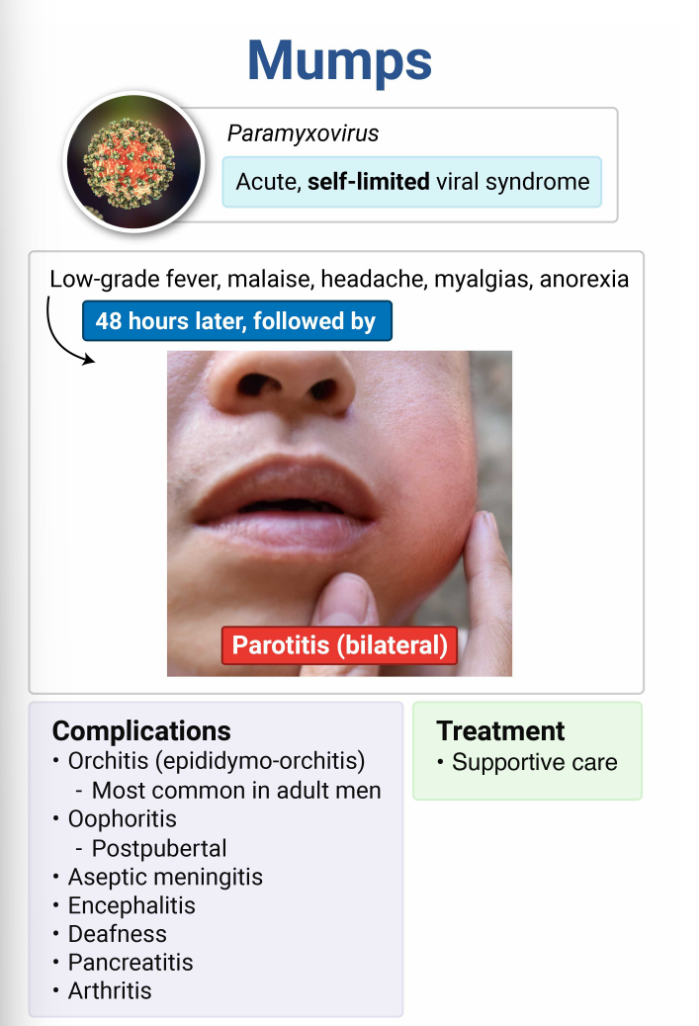
What virus causes mumps?
paramyxovirus (remember… it causes PAROtitis)
True or False - Cirprofloxacin is the treatment of choice in severe cases of Salmonellosis
true
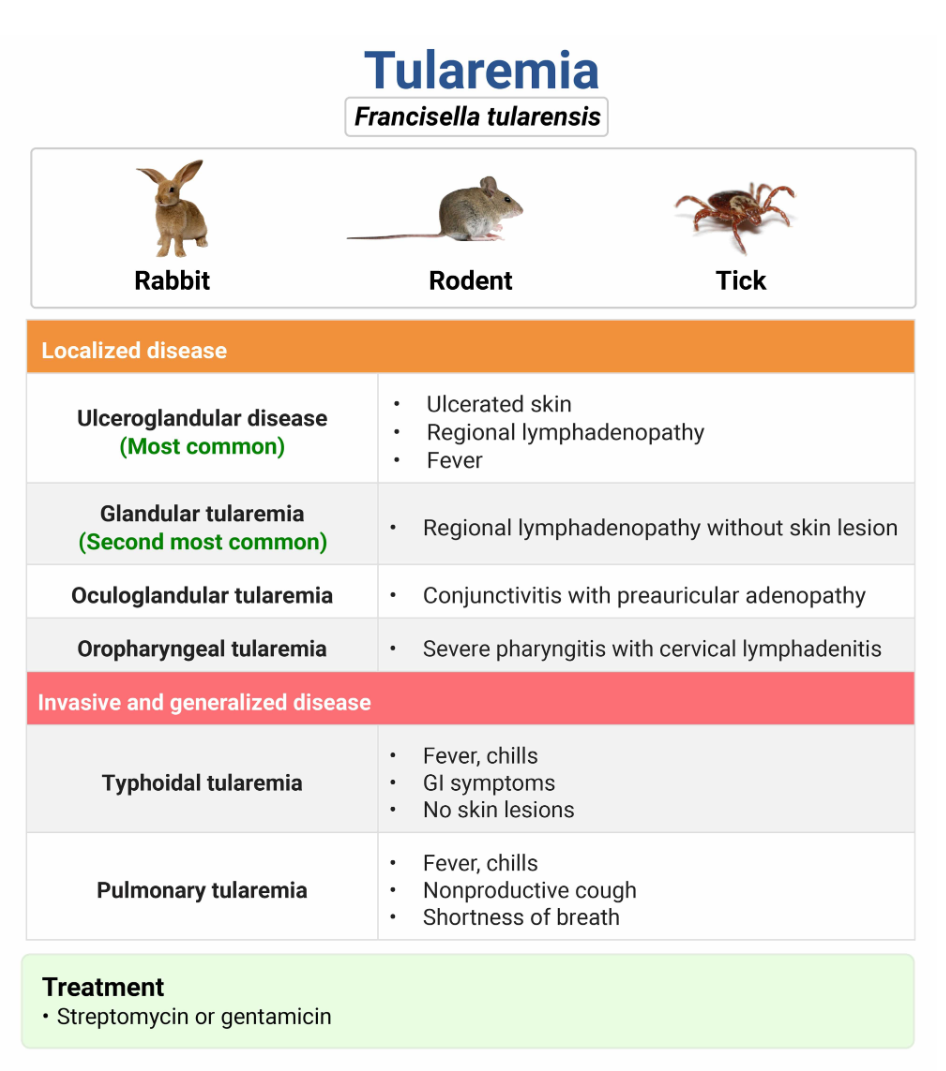
Francisella tularensis causes what disease?
Tularemia
True or False - First generation Cephalosporin antibiotics, such as Cephalexin, cefadroxil, and cefazolin have poor activity against most gram positive organisms, but good activity against most gram-negative organisms.
FALSE; the opposite is true
first gen cephalosporins are good against most gram positive organisms, but don’t work well against gram negative organisms.
First gen cephalosporins, such as cephalexin, can therefore be used for skin infections
What is the empiric treatment for chlamydia in pregnancy?
Azithromycin 1000 mg given as a single dose
true or false - Doxycycline is contraindicated in pregnancy
true - doxycycline shouldn’t be used in pregnancy because it can lead to bone growth problems and permanent discoloration of the fetus’s teeth
How can you differentiate between Rubella and Varicella (clinical presentation)
Rubella - pink or light red spotty rash that starts on face and spreads downwards; usually minimal systemic ssx
Varicella - usually has a prodrome (fever, pharyngitis, malaise, myalgias) followed by an itchy vesicular rash (fluid filled blisters that can scab)
What population are we most concerned about with Rubella, and why?
pregnant persons (esp in first 16 weeks of pregnancy), because Rubella can cause fetal abnormalities (congenital rubella syndrome); this can lead to SNHL, cardiac defects, and congenital cataracts
What tick-borne illness has an abrupt onset of systemic symptoms, which can include severe headache, photophobia, vomiting, diarrhea, and myalgias- with a blanching maculopapular eruption on palms and soles spreading centrally (that begins within 3-5 days of symptom onset)?
What is the treatment?
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
Treatment: always doxycycline, even in children

What causes oral hairy leukoplakia? In what population is this more common?
caused by epstein-barr virus, more common in HIV
What agent do you use to treat pneumocystis jirovecci pneumonia?
Bactrim (TMP-SMX)
this can also be used prophylactically in HIV+, but can lead to macrocytic anemia due to impaired folic acid synthesis
The presence of merozoites arranged in tetrads (known as a Maltese Cross) is an uncommon but pathognomonic finding for ___________; this is a tick-borne disease similar to malaria that lyses red blood cells.
babesiosis (which is caused by Babesia microti)
True or False - Primaquine + Clindamycin is alternative treatment to Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in patients with a severe sulfa allergy
True
name 4 side effects of macrolides (Azithromycin, clarithromycin, erythromycin, telithromycin)
GI disturbance, ototoxicity, QTc prolongation, cholestatic jaundice
True or False - Nitrofurantoin (Macrobid) is the antibiotic of choice for acute pyelonephritis
False; while Macrobid is often used for urinary tract infections, it doesn’t reach therapeutic doses in the upper urinary tract and should NOT be administered as treatment for pyelonephritis
A preferred option for pyelonephritis include Ciprofloxacin, Levaquin, and Bactrim
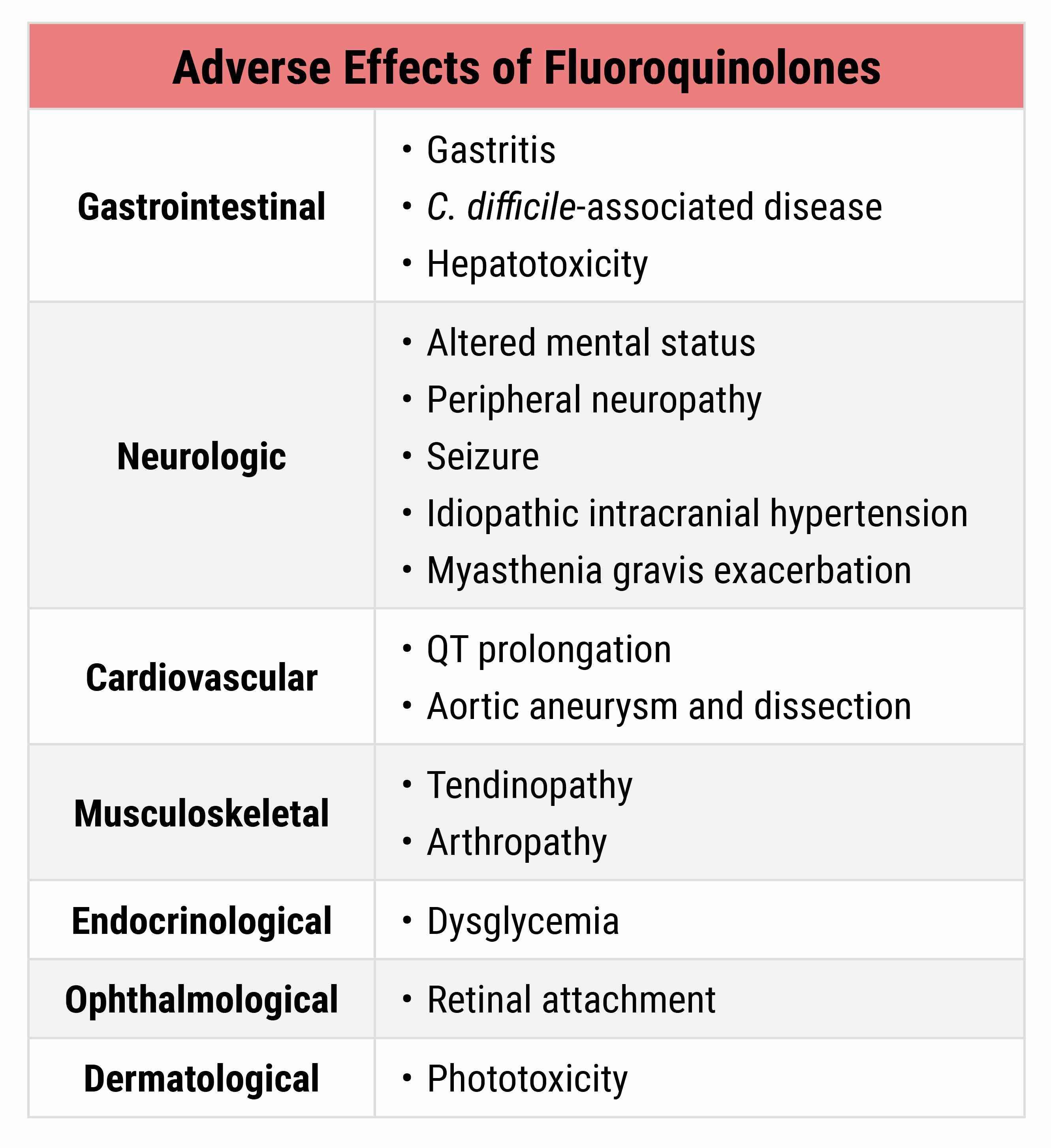
Fluoroquinolones, such as levofloxacin and ciprofloxacin, carry a black box warning of increased risk of tendinitis and tendon rupture, and worsening of what neurological condition?
worsening of myasthenia gravis
see chart for list of complications
Three cephalosporins with activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa include ceftazidime, cefoperazone, and __________.
Cefepime
NOTE: In neutropenic patients with severe illness, two agents should be used to provide coverage against P aeruginosa- often a beta-lactam and an aminoglycoside or fluoroquinolone.