Ferrante - biomedical decision making
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What are the three main phases of diagnostic process?
Make a priori hypothesis
Gather information to reduce uncertainty
Update the initial hypothesis
What is prior probability and posterior probability?
Prior probability is the initial hypothesis of the physician.
Posterior probability is conditional probability, the probability that event A will occur given that event B is known to occur p[A|B]
How to estimate pre-test probability?
Subjective estimate: “What was the frequency of disease in similar patients whom I have seen?”
Objective estimate: prevalence: the frequency of an event in a population; It is normally available in literature
clinical prediction rules: they define how clinicians can use combinations of clinical findings to estimate probability. It is a set of clinical findings and corresponding diagnostic weights developed from systematic study of patients who have a particular diagnostic problem
How can you measure test performance?
Sensitivity: true positive rate
Specificity: true negative rate
False negative rate
False positive rate
What is the Receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve?
The best way to characterize a test is by the range of values of sensitivity and specificity
Any given point along an ROC curve for a test corresponds to the test sensitivity and specificity for a given threshold of “abnormality” (Cut-off)
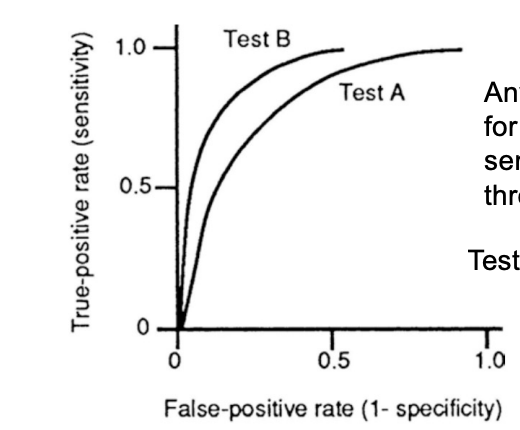
What is spectrum bias, test referral bias, interpretation bias?
Spectrum bias: it happens when study population include only very sick patients and healthy subjects (low FN → overestimation of sensitivity)
Test referral bias: it happens when only the resulted positive cases undergo the gold standard (low TN and FN overestimation of TPR, underestimation of TNR)
Test interpretation bias: it happens when the knowledge of the gold standard results affect the interpretation of the test results (TN and TP are overestimated)
What is Baye’s theorem for post-test probability?
update the probability of a disease after a diagnostic test result, based on how accurate the test is and how likely the disease was before testing.
What is predictive value for post-test probability?
It is an alternative approach to estimate of the probability of disease in a person who has a positive or negative test.
PV gives the probability of true disease state once the patients test result is known.
Which method is better, baye’s or PV?
Baye’s is preferred - it computes the post-test probability of a disease for any prior probability.
PV suffers of generalizability.
How large effect does different test results have on post-test probability?
If the clinician is almost certain about a diagnosis, then a negative test result has a big effect on the post test probability whilst a positive result has a little effect.
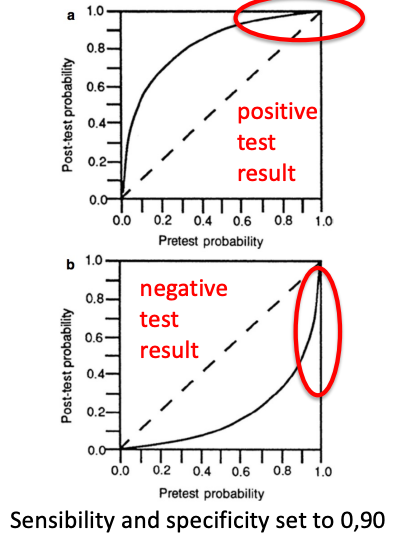
When to choose a test with high sensitivity vs high specificity?
Test specificity (TNR) affects primarily the interpretation of a positive test. Thus, if you are trying to rule in a diagnosis, you should choose a test with high specificity
Test sensitivity (TPR) affects primarily the interpretation of a negative test. Thus, if you are trying to exclude a disease, choose a test with a high sensitivity
What are common problems with probabilistic reasoning?
1. inaccurate estimation of pre-test probability
2. faulty application of test-performance measures
3. violation of the assumptions of conditional independence between 2 different tests applied one after the other
4. mutual exclusivity of diseases
What is expected-value decision making?
The probabilities times the corresponding years of survival are summed to obtain the total expected value (utility) in this case the expected survival
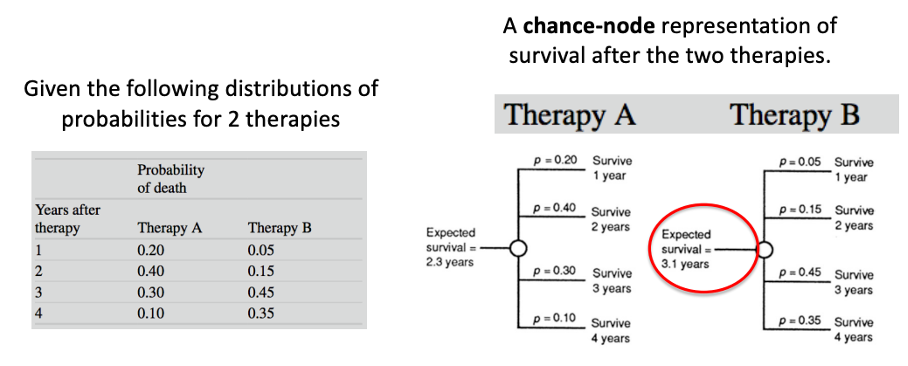
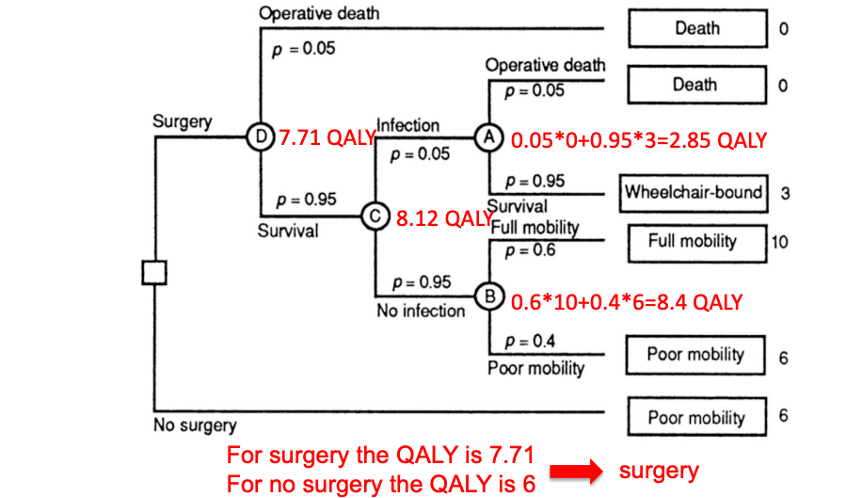
What is the process of expected-value decision making?
Create a decision tree (most difficult); formulate the problem, assign probabilities, measure outcome.
calculate the expected value of each decision alternative
Choose the decision alternative with the highest expected value
Probabilistic sensitivity analysis
What are some other modeling approaches?
Influence diagrams
Belief networks
Markov models
Why is probability and decision analysis important in medicine?
It is applied to the many decisions that must be based on imperfect data, and they will have outcome that cannot be known with certainty at the time the decision is made.
Sensitivity analysis is very useful to understand whether uncertainty on specific variable should concern or not
Decision making is also applied in the control of costs and in the development of guidelines
Computers tools can help in the process of decision making clinical decision support systems (CDSS)