Hartman's Nursing Assistant Care: The Basics 6th Edition
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
PPE
equipment that helps protect employees from serious workplace injuries or illnesses resulting from contact with workplace hazards
Sterilization
cleaning measure that destroys all microorganisms, including pathogens
Disinfection
a process that destroys most, but not all, pathogens; it reduces the pathogen count to a level that is considered not infectious
Blood borne pathogens
microorganisms found in human blood, body fluid, draining wounds, and mucous membranes that cause infection and disease in humans
MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus)
bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus) that have developed resistance to the antibiotic methicillin
myocardial infarction (MI)
a condition that occurs when the heart muscle does not receive enough oxygen because blood vessels are blocked; also called a heart attack
Cyanotic
pertaining to a blue or purple discoloration due to deoxygenated blood
emesis
the act of vomiting
Dyspnea
difficulty breathing
causative agent
a pathogenic microorganism that causes disease
susceptible host
an uninfected person who could get sick
reservoir
a place where a pathogen lives and multiplies
portal of entry
any body opening on an uninfected person that allows pathogens to enter
portal of exit
any body opening on an infected person that allows pathogens to leave
mode of transmission
how a pathogen travels
long term care
care given in long-term care facilities for people who need 24-hour, skilled care
skilled care
medically necessary care given by a skilled nurse or therapist
chronic conditions
any disease or condition that lasts a long time (usually longer than six months). It usually can't be cured and therefore requires ongoing treatment and management. Examples include arthritis and asthma.
diagnosis
medical conditions determined by a doctor
Adult day services
care for people who need some help during certain hours, but who do not live in the facility where care is given
Medicare
the federal health insurance program for people who are 65 or older, have certain disabilities or permanent kidney failure, or are ill and cannot work.
Medicaid
a medical assistance program for people who have a low income, as well as for people with disabilities
Registered Nurse (RN)
a licensed nurse who assesses residents, creates the care plan, monitors progress, provides skilled nursing care, gives treatments and medications, and supervises the care given by nursing assistants and other members of the care team
Licensed Practical Nurse (LPN)
-Works under supervision of the RN
-Collaborate with other team members
-Possess technical knowledge and skills
-Participate in the delivery of nursing care, using the nursing process as a framework
- takes about 1 to 2 years to complete license
Physical Therapist (PT)
administers therapy to increase movement, promote healing, reduce pain, and prevent disability
Occupational Therapist (OT)
Helps residents learn to adapt to disabilities by training residents to perform ADLs and other activities
What is ageism?
Discrimination against older persons / elderly.
What are developmental disabilities?
A type of disability present at birth or emerge during childhood.
What are physical needs?
Food, water, sleep, activity.
What are psycho-social needs?
Love, acceptance by others, safety.
What is cognitive?
Ability to learn, think clearly and understand.
What is apathy?
Lack of interest, lack of care.
What are hallucinations?
False sensory perception; seeing things that are not there.
What is anxiety?
Worry, fear, uneasiness about a situation or condition.
What is phobia?
Intense, irrational fear of or anxiety about a situation, place or object.
What is delusion?
Persistent false belief; a person believing someone is controlling their mind.
What are advanced directives?
Legal document that allows people to decide what kind of medical care they want if they are unable to make the decisions themselves.
What is a living will?
Outlines the medical care a person wants; takes affect while a person is alive.
What is durable power of attorney for healthcare?
Appoints someone to make healthcare decisions.
What is DNR?
Do not perform CPR if a person's heart stops beating.
Who defined the five stages of grief?
Elizabeth Kubler-Ross.
What is Cheyne-Stokes?
Type of respiration's usually seen when a person is dying. Slow, rapid, irregular and apnea periods of breathing.
What are standard precautions?
Using PPE with every individual you will have contact with any body fluids or mucus membranes.
What is hearing?
Usually last sense to leave a person's body.
What is postmortem care?
Care given to a body after death has occurred.
What is palliative care?
Focusing on pain relief, comfort and managing symptoms.
What is the nervous system?
CNS, PNS; control and message center for the body.
What is the circulatory system?
Provides food, oxygen, hormones to cells; Hypertension, Congestive Heart Failure, ANGINA (chest pain).
What is the musculoskeletal system?
Works together to move the body, gives the body its shape, 206 bones.
What is the gastrointestinal system?
Starts in the mouth and ends in the anus; digestion, absorption, elimination.
What is the integumentary system?
Largest organ, protective covering, made up of layers; skin.
What is Type 1 Diabetes?
Insulin dependent diabetes diagnosed in children and young adults.
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Most common form of diabetes that can be modified with diet, exercise and weight loss.
What is pre-diabetes?
Elevated glucose levels not high enough for type 2 diabetes diagnosis.
What is gestational diabetes?
Diabetes that occurs during pregnancy.
What is diabetes?
Pancreas produces too little insulin or does not properly use insulin.
What is gait?
To walk.
What is dysphagia?
Difficulty swallowing.
What is dyspnea?
Difficult breathing or shortness of breath.
What is atrophy?
Muscle waste away, decreasing in size and becoming weak.
What are anti-embolic stockings?
Aid in circulation and prevention of blood clots (thrombus, emboli).
What is posterior?
Dorsal; back of body or body part.
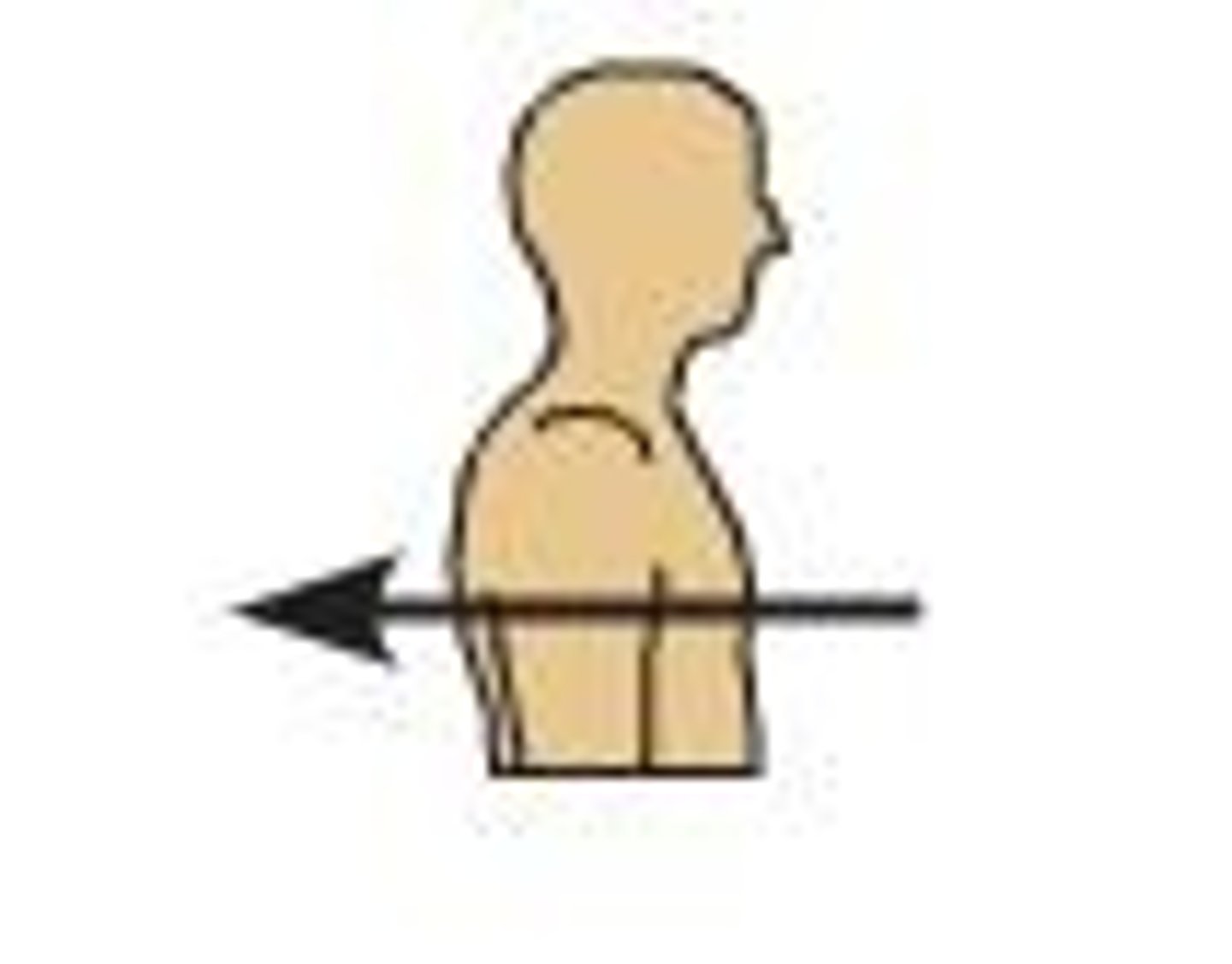
What is medial?
Toward the midline of the body.
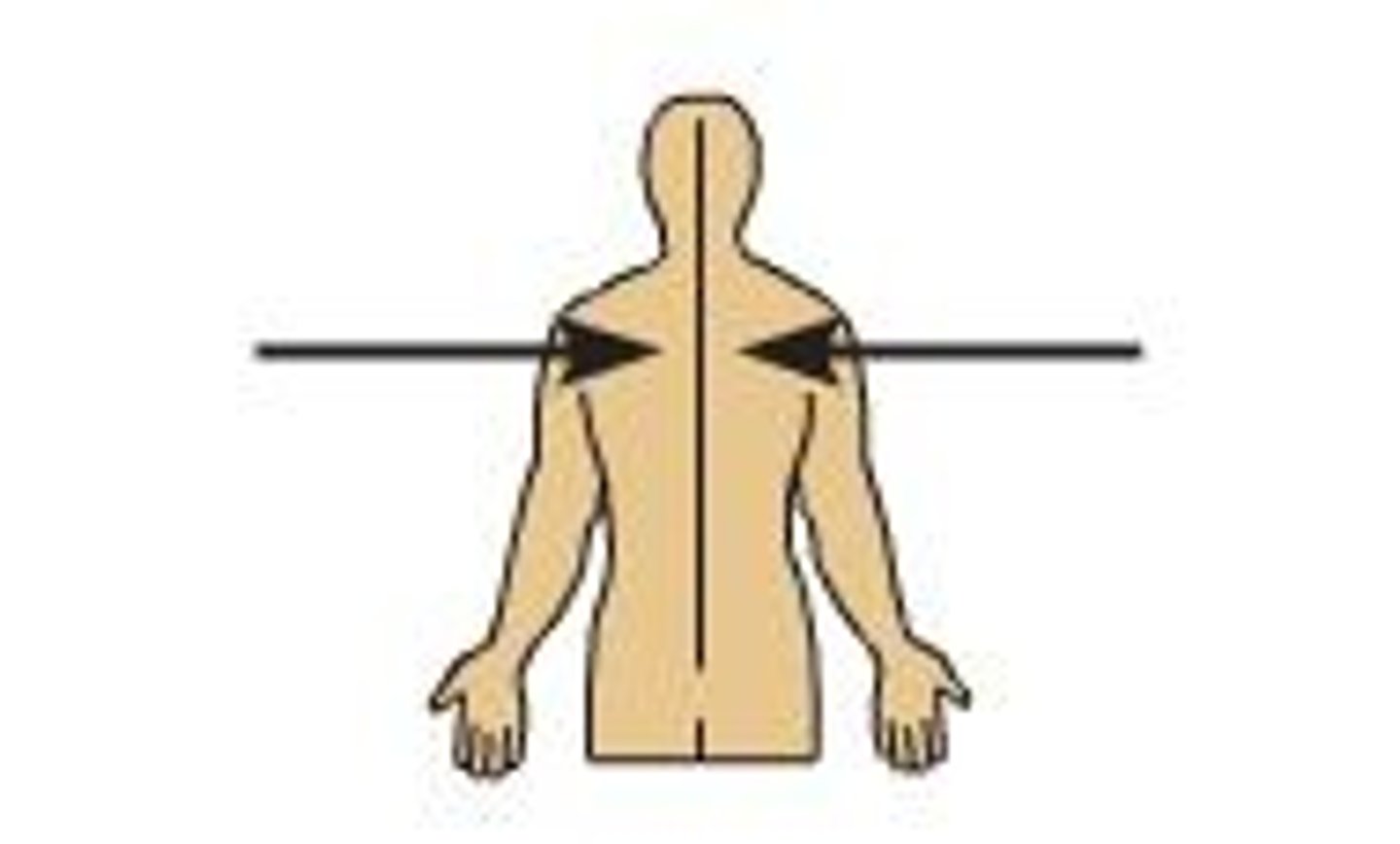
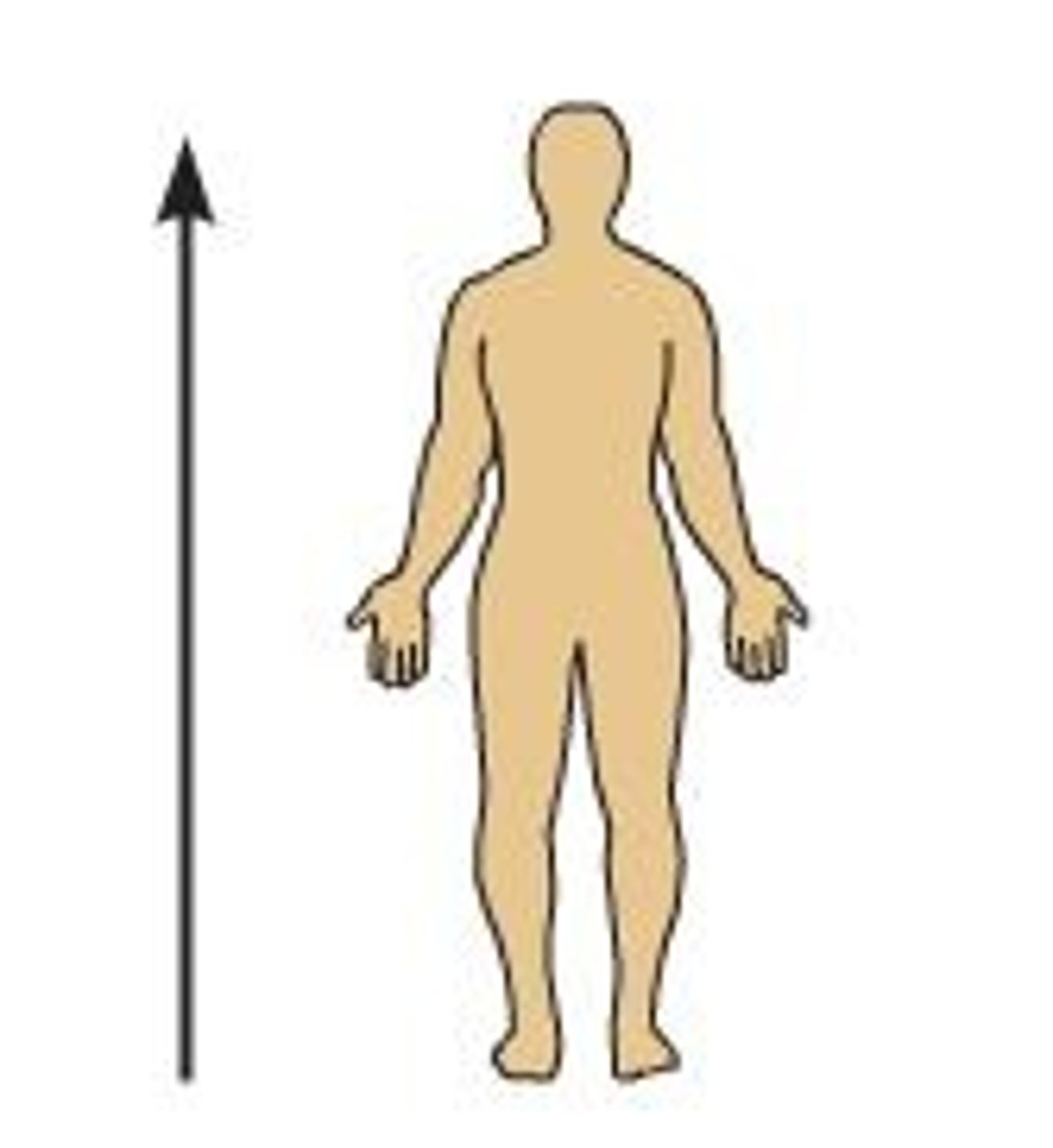
What is superior?
Toward the head or above.
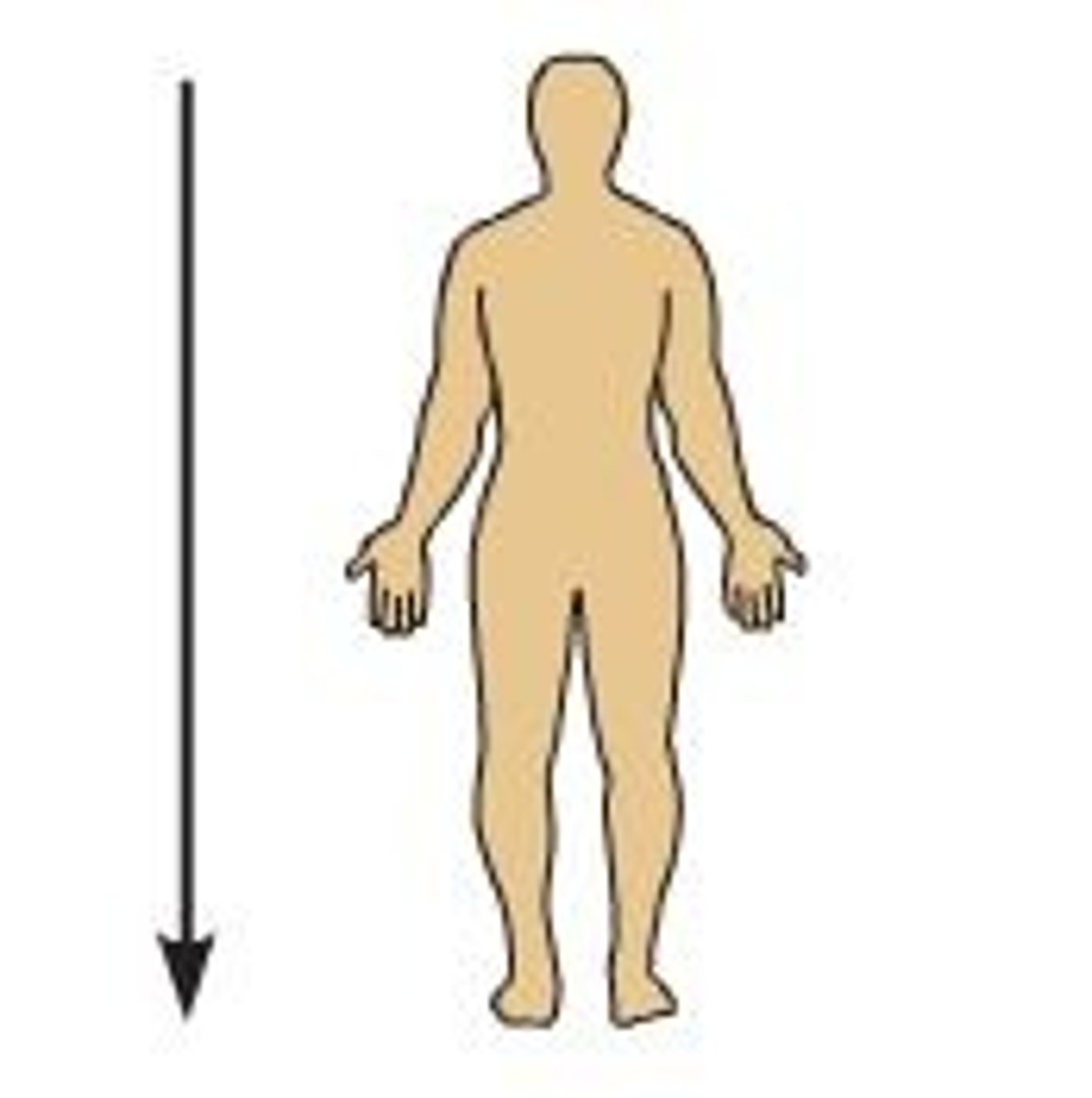
What is inferior?
Away from the head or below.
What is anterior?
Ventral; front of the body or body part.
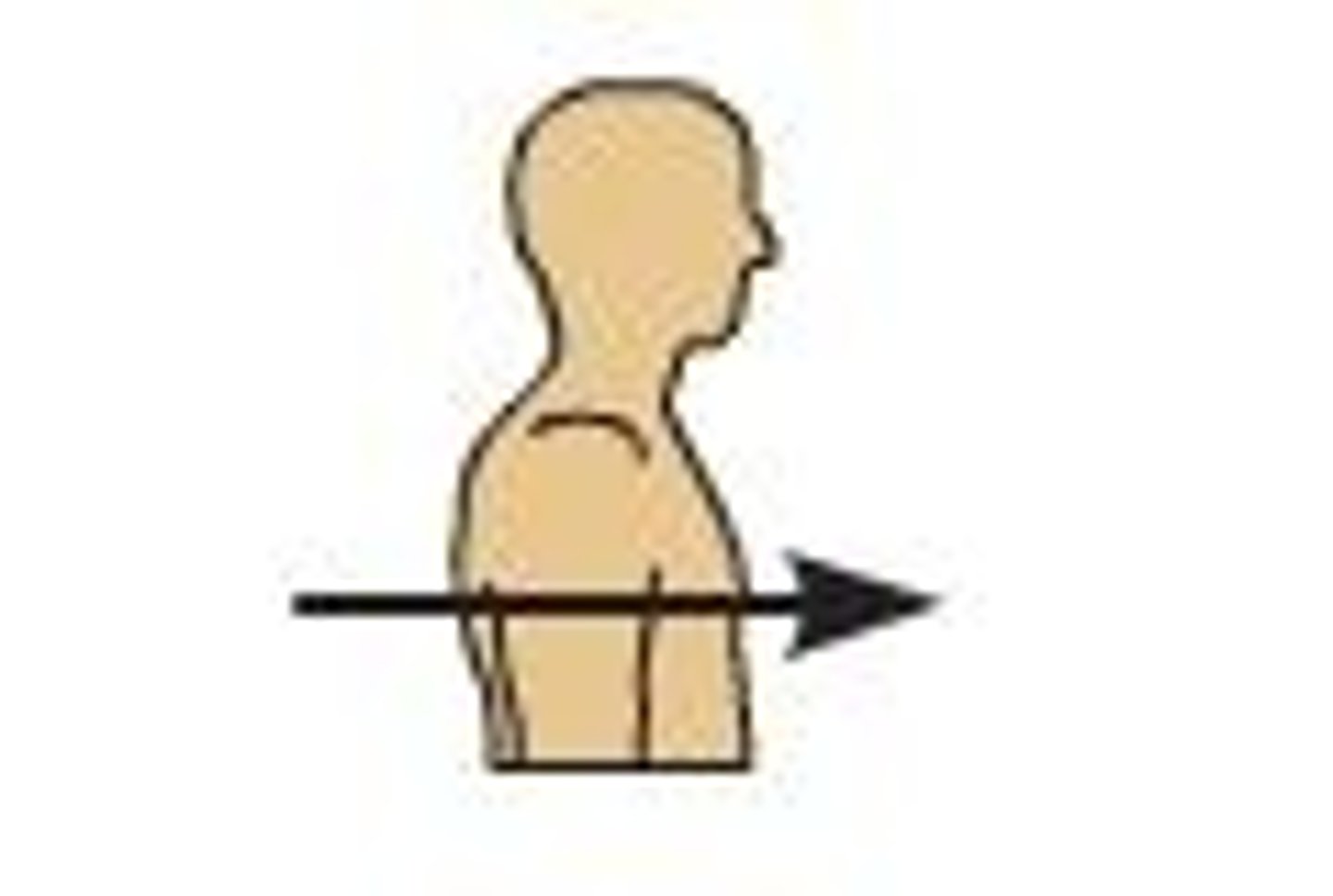
What is distal?
Farther away from the torso; fingers, toes.
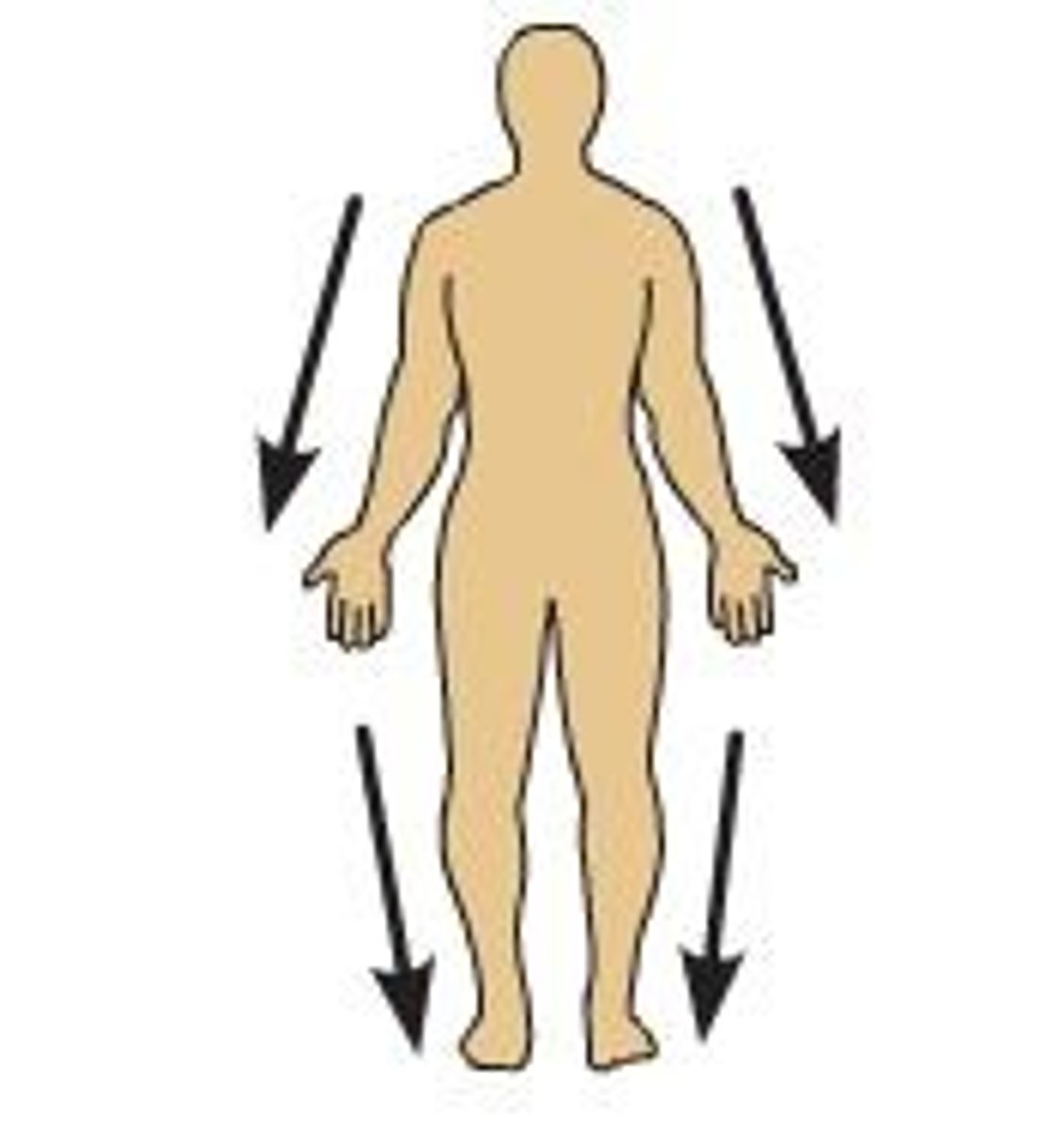
What is proximal?
Closer to the torso.
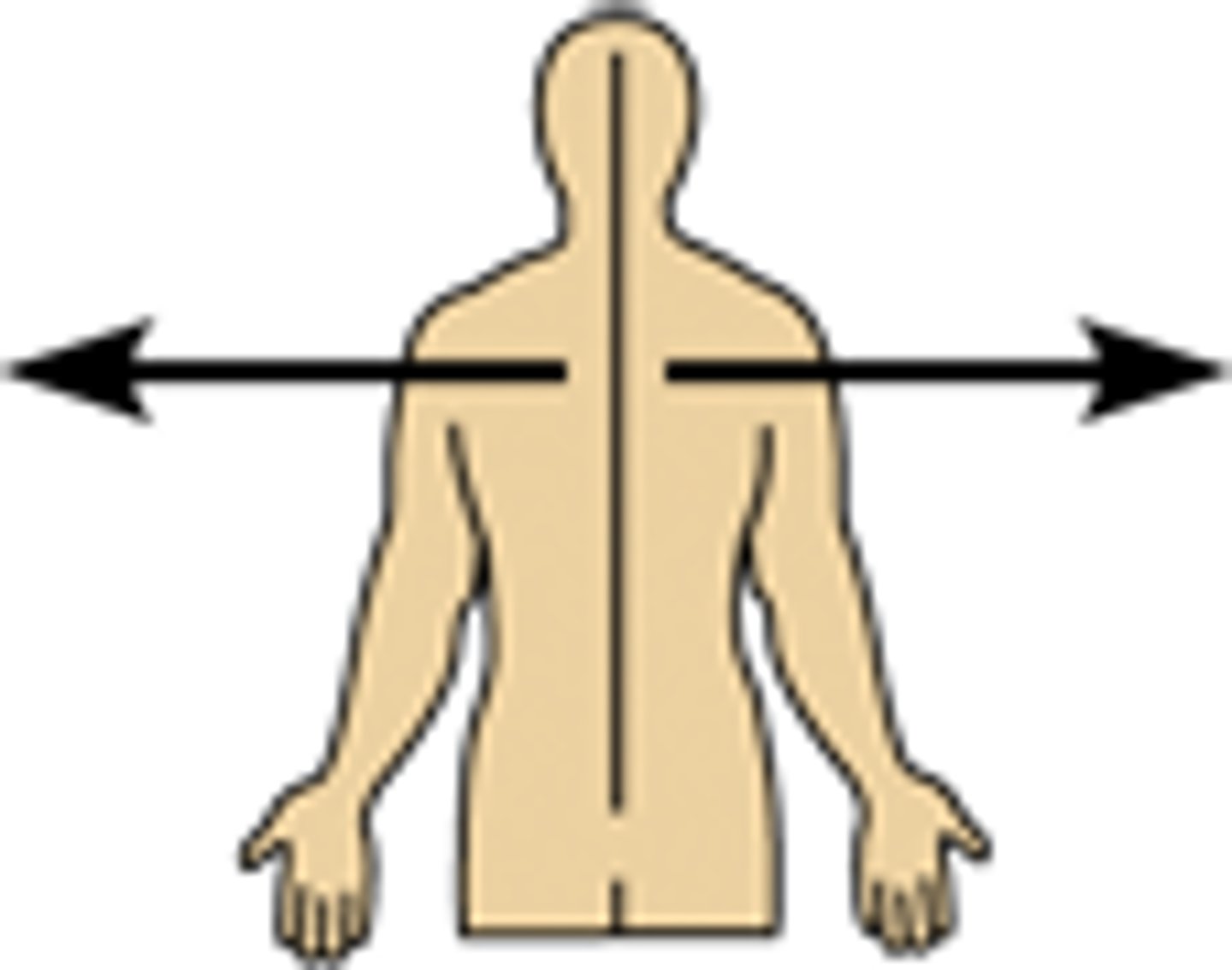
What is lateral?
To the side; either side.
confusion
the inability to think clearly, having trouble focusing and may be disoriented
cognition
the ability to think logically and clearly
cognition impairment
a disorder when a person is unable to think logically and clearly
What is delirium?
A severe state of confusion that occurs suddenly.
What is dementia?
A disease where a person has a serious loss of mental abilities, such as thinking, reasoning, remembering etc.
What is supine?
A patient laying flat on their back.
What is Fowlers?
A patient in a 45-60 degree sitting position.
What is lateral?
A patient lying on either side.
What is prone?
A patient lying flat on their stomach.
What is Sims?
A patient lying on their left side.
What is embolism?
An obstruction of a blood vessel usually by a blood clot.
What is pediculosis?
Infestation of lice.
What is perineum?
The genital and anal areas of patients.
What is dangle?
Allowing the patient to sit up on the side of the bed with legs hanging over.
What is aspiration?
The inhalation of food, fluid or foreign material into the lungs.
What are pressure injuries?
Injuries resulting from skin deterioration and shearing.
What is a stage 1 pressure injury?
Skin is intact but may be red. Redness is not relieved after repositioning patient.
What is a stage 2 pressure injury?
Partial skin loss, area may be pink, red and moist, and might look like a blister.
What is positioning?
Adjusting residents into positions that promote health and comfort.
What is shearing?
Rubbing or friction that results from the skin moving one way and the bone underneath remaining fixed or moving in opposite direction.
What is perseveration?
Repeating words, phrases, ques or actions.
What is pacing?
Walking back and forth in the same area.
What is wandering?
A resident who walks aimlessly around the facility.
What is sundowning?
A resident that gets agitated, restless or more confused in the late afternoon or evening time.
What is rummaging?
Going through drawers, closets, and personal items of items belonging to oneself or others.
What is hoarding?
Collecting and putting away items in a guarded way.
What is validating?
Giving value to or approving.
What is a rummaging drawer?
Putting safe items in a drawer or bin for resident to go through and use as a soothing technique.
What is Alzheimer's Disease?
A disease with no cure, caused by tangled nerve fibers and protein deposits.
What is dementia?
Serious loss of mental abilities caused by AD.
What are the mental abilities affected by dementia?
Thinking, learning, and reasoning.