Kingdom Monera
@@Bacteria@@ are the sole members of the Kingdom Monera.
- They are the %%most abundant microorganisms.%%
- Bacteria occur almost everywhere.
Hundreds of bacteria are present in a handful of soil.
- They also occur in extreme habitats such as hot springs, deserts, snow, and deep oceans where very few other life forms can survive.
Bacteria as a group show the %%most extensive metabolic diversity.%%
- Bacteria are grouped under four categories based on their shape:
- Coccus: spherical
- Bacillus: rod-shaped
- Vibrio: comma shaped
- Spirillum: spiral.
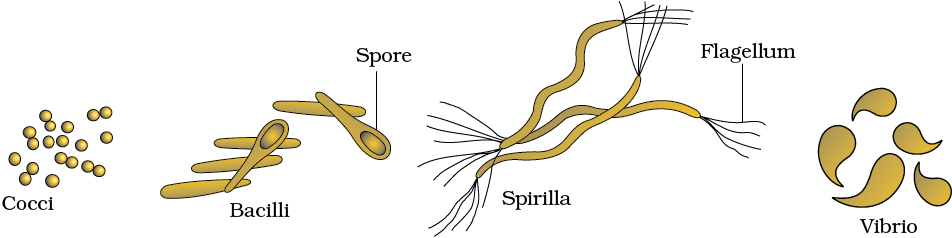
Some of the bacteria are:
- Autotrophic, i.e., they synthesize their own food from inorganic substrates. They may be photosynthetic autotrophic or chemosynthetic autotrophic.
- Heterotrophic, i.e., they depend on other organisms or on dead organic matter for food.
Archaebacteria:
- They live in some of the harshest habitats such as extreme salty areas (halophiles), hot springs (thermoacidophiles), and marshy areas (methanogens).
- They differ from other bacteria in having a different cell wall structure which helps them to survive in extreme conditions.
- Methanogens are present in the ^^gut of several ruminant animals^^ such as cows and buffaloes
- These are responsible for the ==production of methane== (biogas) from the dung of these animals.
Eubacteria:
- They are also referred to as %%‘true bacteria’.%%
- They are characterized by the presence of a rigid cell wall, and if motile, a flagellum.
Photosynthetic Autotrophs:
The @@cyanobacteria@@ (also referred to as blue-green algae) have chlorophyll similar to green plants and are @@photosynthetic autotrophs.@@
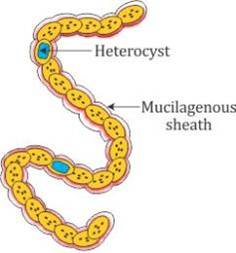
- The cyanobacteria are %%unicellular, colonial, or filamentous, and freshwater/marine or terrestrial algae.%%
- The colonies are generally surrounded by a @@gelatinous sheath@@@@.@@
- They often form a bloom in %%polluted water bodies%%%%.%%
- @@Some of these organisms can fix atmospheric nitrogen in specialized cells called heterocysts.@@
- Examples: Anabaena and Nostoc.
Chemosynthetic Autotrophs:
- These bacteria oxidize various inorganic substances such as nitrates, nitrites, and ammonia and use the released energy for their %%ATP production.%%
- They play a great role in ==recycling nutrients== like nitrogen, phosphorous, iron, and sulfur.
Heterotrophic Bacteria:
The majority of these are important decomposers.
They are helpful in making curd from milk, production of antibiotics, fixing nitrogen in legumes, etc.
Some are pathogens causing damage to human beings, crops, farm animals, and pets.
- Cholera, typhoid, tetanus, and citrus canker are well-known diseases caused by different bacteria.
Mycoplasm:
- These are organisms that completely %%lack a cell wall.%%
- They are the ==smallest living cells== known and ==can survive without oxygen (anaerobic).==
- Many mycoplasmas are pathogenic in animals and plants.
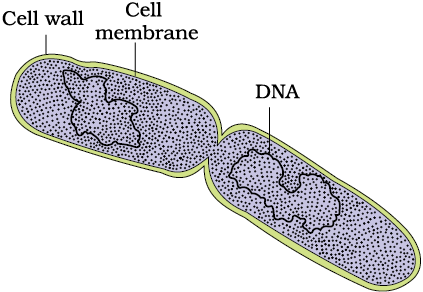
Reproduction:
- Bacteria reproduce mainly by fission.
- Sometimes, under @@unfavorable@@ conditions, they produce @@spores.@@
- They also reproduce by a sort of sexual reproduction by ^^adopting a primitive type of DNA transfer from one bacterium to the other.^^