Part 3: Care of Site Specific Side Effects: II. H&N
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
mnemonic for HN side effects
x-rays- xerostomia
treat- taste alterations
many- mucositis/ stomatitis
painful- pharyngitis/ esophagitis
tumors- trismus
even-eye effects
odd-otalgia
ones- other

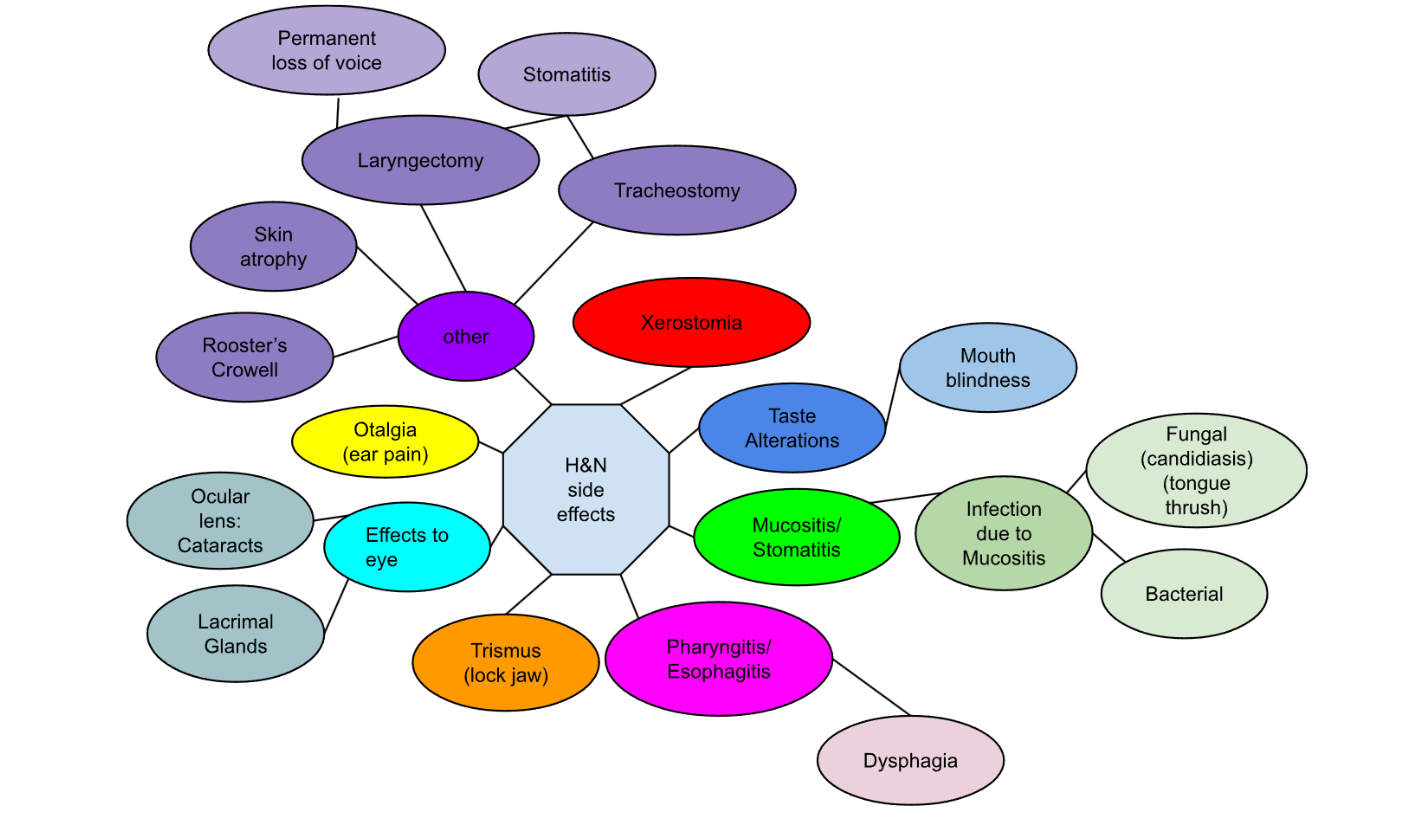
Side effects of H&N
term. xerostomia
dryness of the mucous membranes
What are the 3 sets of salivary glands?
parotids
sublingual
submandibular
When does xerostomia occur?
peaks at 2 weeks
Can linger for a LONG TIME
If xerostomia is temporary, how long may it take to go away?
months to years
Salivary function may not come back as good as it was prior to tx
Medical interventions for xerostomia
Artificial, Saliva Emulators
Salagen (injection) BEST [salava generator]
Artificial saliva
Ethiol (fyi: ethyl alcohol)
Hints to minimize xerostomia:
In general, what are you trying to do?
Stimulate whatever salivary function is left
Hints to minimize xerostomia:
3 things to do
6 things to avoid
Sugar Free Sour candy
humidifiers
force fluids (3L/day)
Avoid:
tobacco
alcohol
spices/salt
Citrus fruits (vitamin C)
Hard, course foods (pop corn, chips)
most mouthwashes
FYI: citrus fruits contraindicated cuz- In a dry mouth, the protective saliva layer is reduced or absent, so the mucosal tissues are more vulnerable. Course foods rasposa if no saliva
What type of mouthwashes can patients with xerostomia use
Alcohol-free mouth wash: Biotene (available OTC)

True or False: Xerostomia patients may require dental care/ Why or why not?
True. Because Saliva has an anti-bacteriostatic substance that helps prevent tooth decay
True or False: If the patient is experiencing xerostomia, they should seek dental care immediately even before consulting the radiation oncologist
False. The patient needs to consult the radiation oncologist before dental care begins
True or False: It is ok to treat patient with “suspect” teeth.
False, All suspect teeth should be removed prior to treatmentHow
How many days prior to tx should suspect teeth be removed ? Wny?
10-14 days
Cuz RTT inhibits healing process
Other general hints on dental care: (3)
establish a careful & extensive mouth-care routine
rinse with warm salt water
brush with soft bristled toothbrush after every meal
General Mouth Care instruction
Brushing teeth
Brush after each meal & at bed time w/ soft bristled toothbrush & non-abrasive toothpaste
Rinse mouth with ½ glass water + 1 tsp baking soda 4x/day
Massage gums after brushing for 1 min to stimulate blood flow
Floss regularly with direction from physician
Apply fluoride txs as prescribed by the dentist
Avoid most commercial mouthwashes
Avoid smoking/ alcohol
Apply lip & oral mucosa moisturizers
Examine mouth daily. Check for…
mouth soreness
bleeding gums
white patches or dots on tongue, mouth, lining of cheek
fever blisters/ cold sores
unable to wear dentures (pain)
Taste Alterations
Taste Alterations
What is the importance of saliva in taste.
No saliva causes mouth blindness: everything tastes the same
Causes of taste alterations (3)
destruction of taste buds
decreased saliva
CA can release substances resembling amino acids that stimulates bitter taste sensations
Food that generally tastes bad to cancer patients:
Good with protein in it, cuz it has amino acids
eggs
fish
poultry
pork
If patient complains that everything has a but of a metallic taste, one could suspect:
possible liver metastases
Interventions (what to do if foods don’t taste very good) (4)
avoid foods the patient doesn’t like
experiment with (moderate) different spices
-"package" the meal
plenty of liquids to assist in swallowing
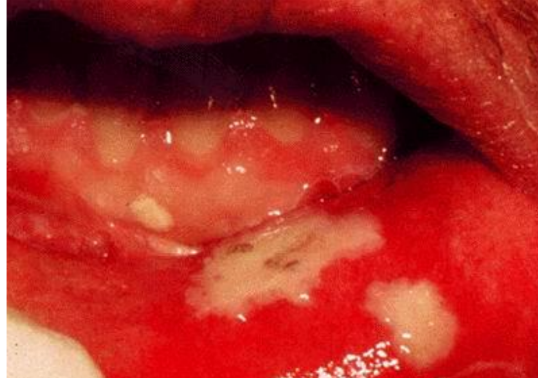
Mucositis/ Stomatitis
term. Mucositis
def. inflammation of the mucous membranes
term. Stomatitis
def. inflammation of the oral mucosa
(Mucositis/ Stomatitis) is associated with RTT, while (Mucositis/ Stomatitis) is associated with chemo
Mucositis
Stomatitis
Mucositis can happen at ___ Gy
30-40 Gy
Why does RTT cause mucositis?
the epithelial lining of the oral cavity has a rapid cell turnover, making the region highly vulnerable to the effects of RTT
How often is the epithelial lining of the oral cavity replaced?
Every 7 days
When can mucositis occur?
2 weeks into tx
ends 2 weeks after tx
Infection secondary to mucositis
2 types:
fungal
bacterial
f
fungal infection secondary to mucositis is also known as
candidiasis
tongue thrush
What causes fungal infections secondary to mucositis
An over-proliferation of the candida albicans microorganisms that naturally occur in the mouth
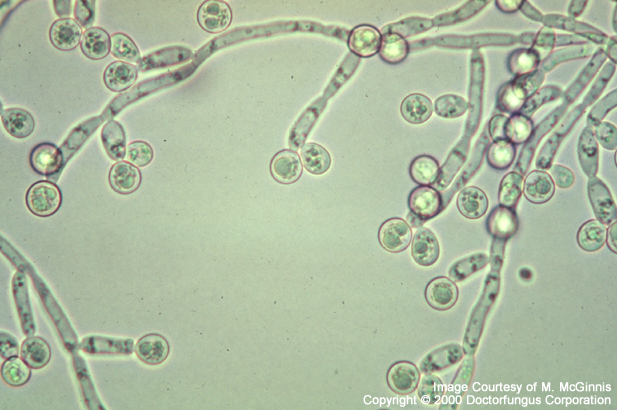
Appearance of fungal infections secondary to mucositis
white, powdery patches on the tongue / in mouth
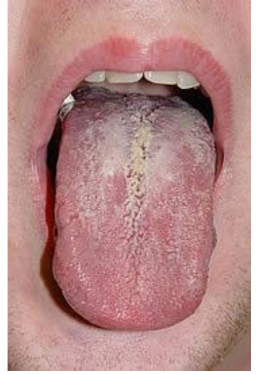
Treatment of fungal infections
diflucan -new and effective

Appearance of bacterial infections secondary to mucositis
(oozing) exudative- a pus-like serum
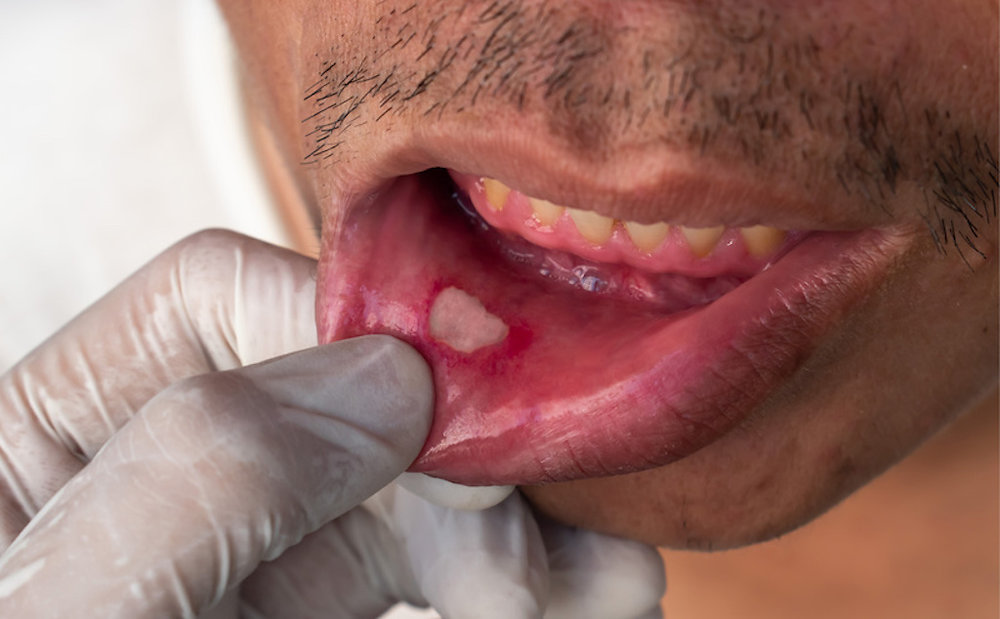
Treatment of bacterial infections secondary to mucositis
antibiotics
Possible side effect of treating bacterial infections secondary to mucositis with antibiotics
yeast infection
Suggestions for mucositis
Brushing teeth:
Brush with cotton-tip applicator (if toothbrush hurts)
rinse mouth regularly w/ hydrogen peroxide/ saline (or water) (mild mouthwashes can be added)
Avoid floss/ water-piks
Use petroleum jelly or lip balm to keep lips moist & prevent added oral discomfort
eating/ drinking
force fluids
Eat cold/ frozen foods
Avoid citrus fruits
Medical Interventions for mucositis
analgesics (pain relief)
The Mixture
Bromptons Cocktail
The Mixture aka
Miracle Mouthwash
Magic Mouthwash
The Mixture consists of:
3 Equal Parts:
Xylocaine Viscous
Benalyn or Benedryl
Antacid
How does The Mixture work
Relieves pain
Relieves inflammation
Promotes proper pH (to promote healing)
Promotes easier eating (swallowing)
PIPE
True or False: Bromptons Cocktail is available in the US
False. Only available in england
Brompton’s cocktail ingredients
cocaine/heroine
morphine
antiemetic (fyi: antinausea)
thorazine (tranq)
_____ is the most common affective response to cancer, followed by ____
anxiety
depression
FYI: affective = emotion
pharyngitis/esophagitis
4.pharyngitis/ esophagitisW
pharyngitis aka
sore throatW
What causes pharyngitis/ esophagitis
mucositis
drainage
dryness
When does pharyngitis/ esophagitis occur?
2 weeks into tx
fades 2 weeks after tx
term. dysphagia
def. difficulty swallowing
esophagitis shows up as
pain in the substernal area that is severe and constant
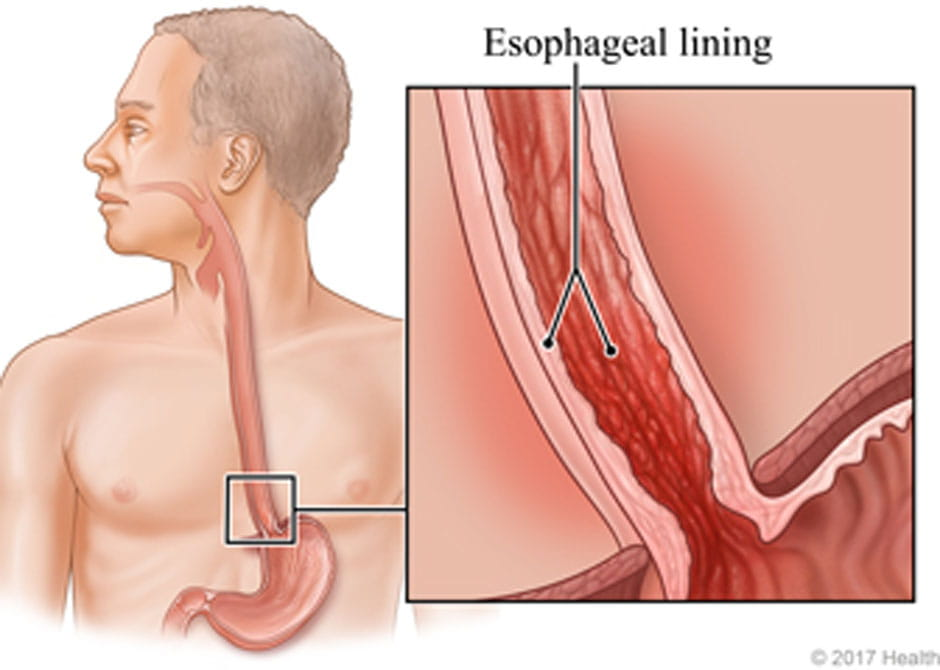
esophagitis closely mimics the symptoms of
myocardial infarction
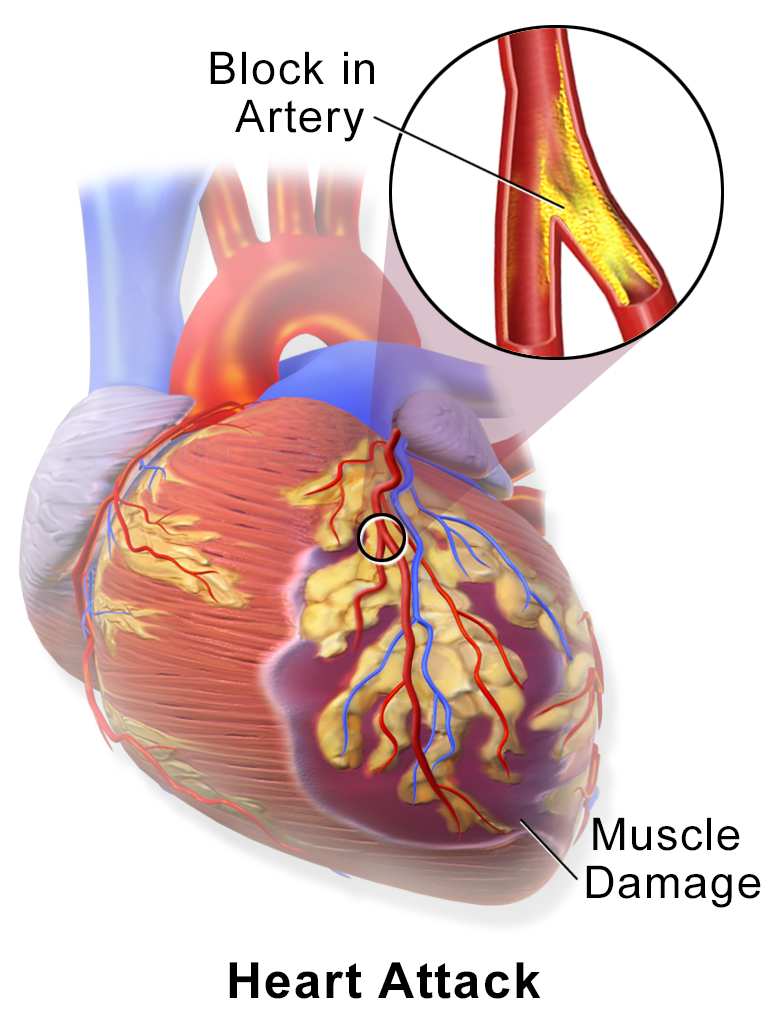
esophagitis can happen at ___ Gy
20 Gy
Interventions for esophagitis
Medical
The Mixture
Carafate
analgesics
Avoid hydrogen peroxide (may irritate mouth/ esophagus ulcers)
lifestyle
Nutritional counseling
Carafate aka
Sucralfate
What is Carafate?
A prescription for coating mucosa & relieve discomfort

Trismus aka
Lock jaw
Effects to the eye: 2 types
ocular lens:
lacrimal glands:
Ocular lens:
RTT can cause:
Tolerance dose
opacities (cataracts)
1000 cGy
Lacrimal glands:
aka
tolerance dose
tear ducts
30 Gy (3000cGy)
Otalgia aka
ear pain
Otalgia can happen if:
middle ear (Eustachian tube) is in the tx area
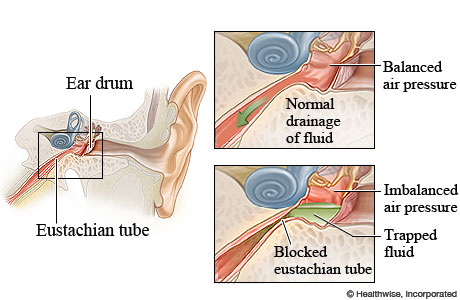
Intervention for otalgia
anesthetic ear drops
skin care for external ear
Other side effects to the H/N area include:
atrophy of the skin
Roosters Crowell
tracheostomy/ laryngectomy
term. Rooster’s Crowell
def. atrophy in adipose tissues (as a result of oblique incidence)
FYI: "When treating H&N with lateral fields that extend under the jaw and chin, due to the skin being thin in that area, it receives a higher dose, often leading to fibrosis and thickening resembling a rooster’s comb
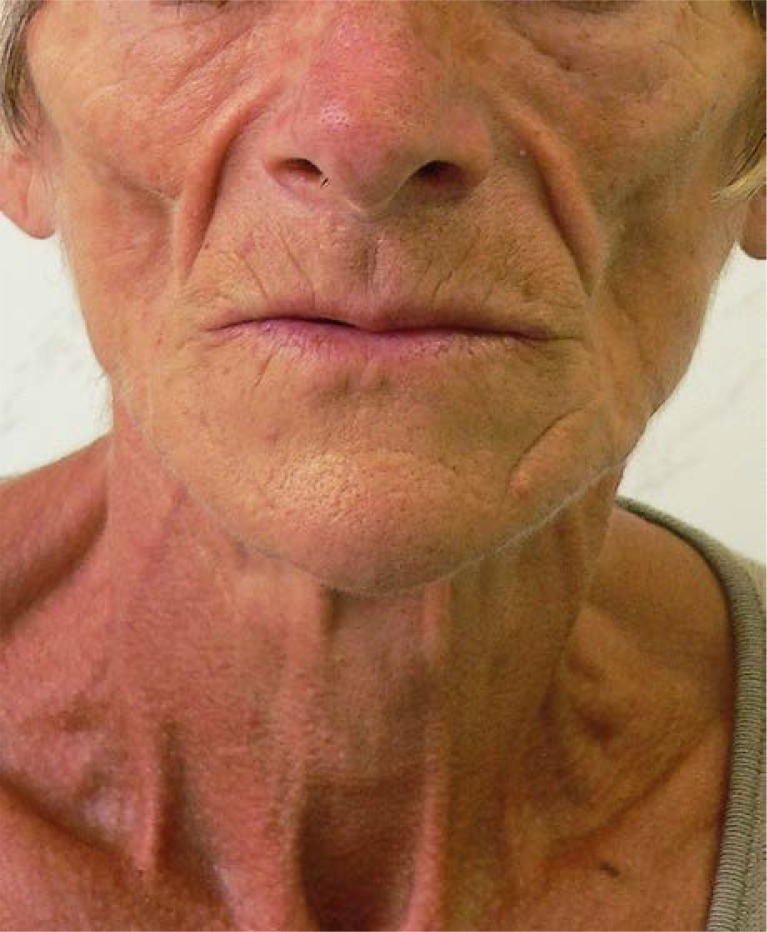

What’s this?
Tracheostomy/ laryngectomy patients may require saline suction
What side effect can happen to laryngectomy/ tracheotomy patients?
stomatitis during tx
in (tracheostomy/laryngectomy) vocal cords are still intact
tracheostomy
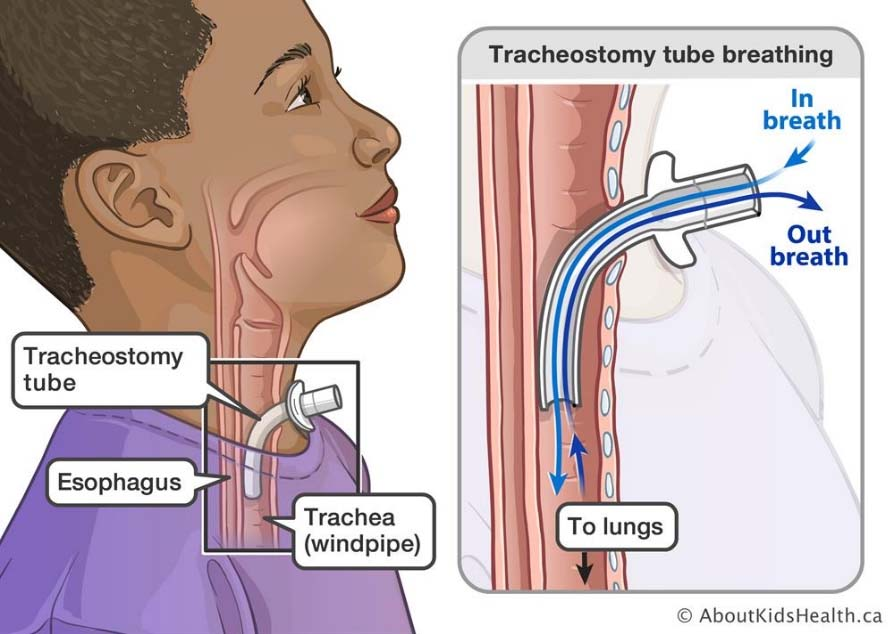
laryngectomy side effect
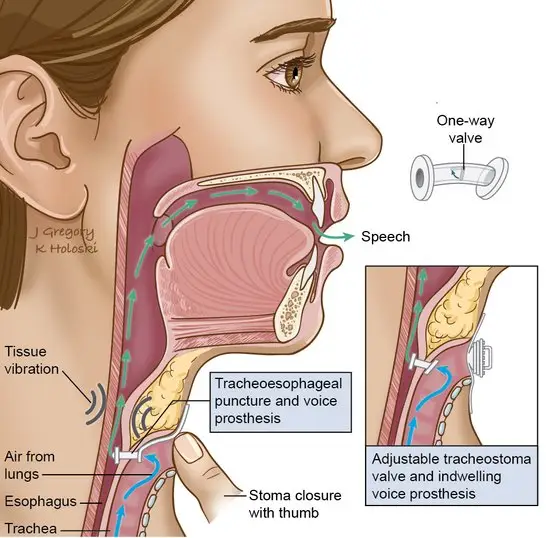
permanent loss of voice (larynx is removed)
4 options for speaking with laryngectomy patients
esophageal speech
transesophageal puncture (TEP)
reconstructive surgery (not super effective)
Artificial larynx (electrolarynx device)
fyi:
esophageal speech aka
burp talk
Transesophageal puncture (TEP)
connects trachea to esophagus with a plastic valve
(enhanced burp talk)
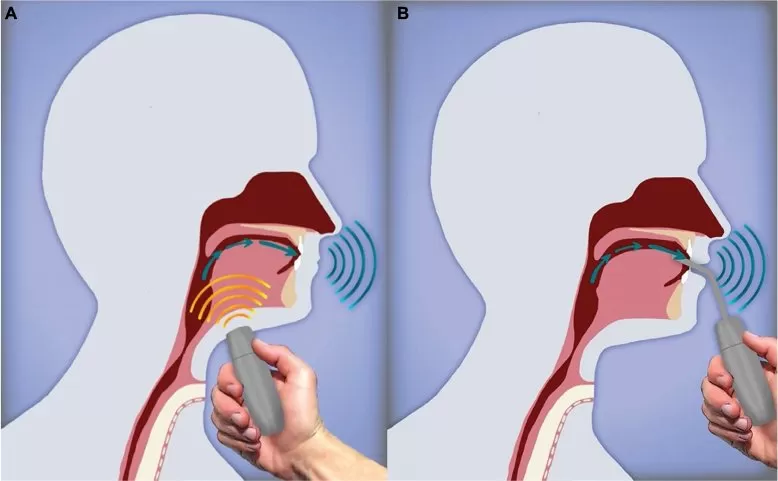
artificial larynx (electrolarynx device)
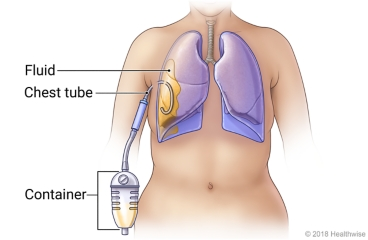
chest tube/ chest drain
a flexible tube that is inserted through the side of the chest into the pleural space
Used to remove air (pneumothorax) or fluid (pleural effusion, blood, chyle), or pus (empyema) from the interthoracic space
chest tube or chest drain:
Chest tube:
The free end of the tube is usually attached to:
an underwater seal, above the level of the chest
an underwater seal, below the level of the chest
an air filled bag, above the level of the chest
an air filled bag, below the level of the chest
2
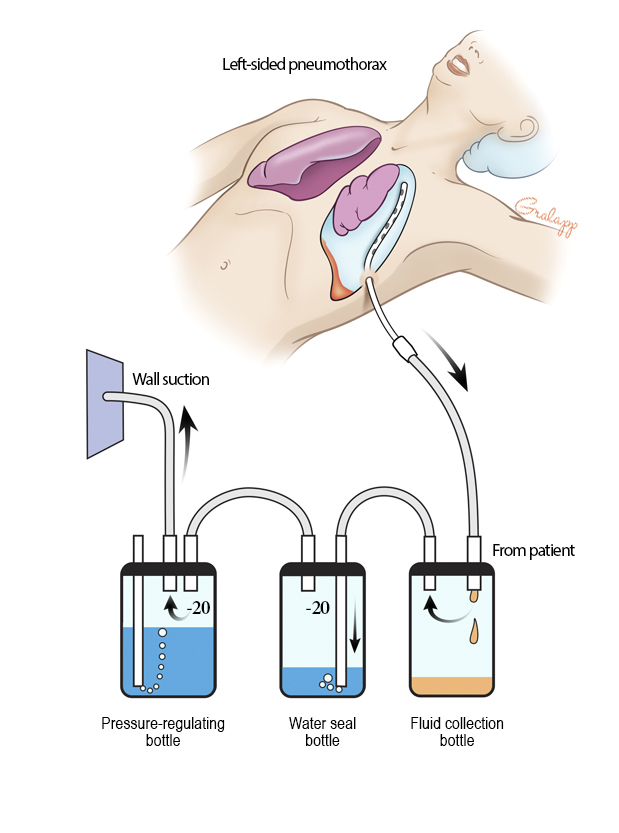
Chest tube:
The free end of the tube is usually attached to an underwater seal, below the level of the chest.
Why is it attached below the level of the chest? Select all that apply.
Allows air to escape from the pleural space
Allows pus to escape from the pleural space
Allows fluid to escape the pleural space
Prevents anything returning to the chest
1,3,4
Chest tubes are inserted under:
General anesthesia
local anesthesia
Analgesics
2
True or false: A small incision is made in the chest through the skin and muscle, and a tube is placed though this passage
True
True or false: if necessary paitens may be given additional analgesics for the procedure
True
True or False: To prevent the tube from falling, it is stapled in place
False, it is sutured in place
How long does the chest tube stay for?
as long as there is air or fluid to be removed
def. accumulation of AIR in the pleural space
term. pneumothorax
def. accumulation of FLUID in the pleural space
term. pleural effusion
Contraindications to chest tube placement include:
Chest pain
Refractory coagulopathy
Coughing
Wheezing
lack of cooperation by the patient
Diaphragmatic hernia
2,5,6
Major complications of chest tube
hemorrhage
fibrosis
necrosis
expansion pulmonary edema
blistering
infection
1, 4,6
Minor complications of chest tube
Depression
anxiety
SOB
Irritation
Dyspnea
cough
2,3,5,6